
hqq
Official implementation of Half-Quadratic Quantization (HQQ)
Stars: 879
HQQ is a fast and accurate model quantizer that skips the need for calibration data. It's super simple to implement (just a few lines of code for the optimizer). It can crunch through quantizing the Llama2-70B model in only 4 minutes! 🚀
README:
This repository contains the official implementation of Half-Quadratic Quantization (HQQ) presented in our articles:
HQQ is a fast and accurate model quantizer that skips the need for calibration data. Quantize the largest models, without calibration data, in just a few minutes at most 🚀.
FAQ
Why should I use HQQ instead of other quantization methods?- HQQ is very fast to quantize models.
- It supports 8,4,3,2,1 bits.
- You can use it on any model (LLMs, Vision, etc.).
- The dequantization step is a linear operation, this means that HQQ is compatbile with various optimized CUDA/Triton kernels.
- HQQ is compatible with peft training.
- We try to make HQQ fully compatible `torch.compile` for faster inference and training.
What is the quality of the quantized models?
We have detailed benchmarks on both language and vision models. Please refer to our blog posts: HQQ, HQQ+.
What is the speed of the quantized models?
4-bit models with axis=1 can use optimized inference fused kernels. Moreover, we focus on making hqq fully compatible with torch.compile which speeds-up both training and inference. For more details, please refer to the backend section below.
What quantization settings should I use?
You should start with nbits=4, group_size=64, axis=1. These settings offer a good balance between quality, vram usage and speed. If you want better results with the same vram usage, switch to axis=0 and use the ATEN backend, but this setting is not supported for fast inference.
What does the axis parameter mean?
The axis parameter is the axis along which grouping is performed. In general axis=0 gives better results than axis=1, especially at lower bits. However, the optimized inference runtime only supports axis=1 for the moment.
What is the difference between HQQ and HQQ+?
HQQ+ is HQQ with trainable low-rank adapters to improve the quantization quality at lower bits.
First, make sure you have a Pytorch 2 version that matches your CUDA version: https://pytorch.org/
You can install hqq via
#latest stable version
pip install hqq;
#Latest updates - recommended
pip install git+https://github.com/mobiusml/hqq.git;
#Disable building the CUDA kernels for the aten backend
DISABLE_CUDA=1 pip install ...
Alternatively, clone the repo and run pip install . from this current folder.
To perform quantization with HQQ, you simply need to replace the linear layers ( torch.nn.Linear) as follows:
from hqq.core.quantize import *
#Quantization settings
quant_config = BaseQuantizeConfig(nbits=4, group_size=64)
#Replace your linear layer
hqq_layer = HQQLinear(your_linear_layer, #torch.nn.Linear or None
quant_config=quant_config, #quantization configuration
compute_dtype=torch.float16, #compute dtype
device='cuda', #cuda device
initialize=True, #Use False to quantize later
del_orig=True #if True, delete the original layer
)
W_r = hqq_layer.dequantize() #dequantize()
W_q = hqq_layer.unpack(dtype=torch.uint8) #unpack
y = hqq_layer(x) #forward-passThe quantization parameters are set as follows:
-
nbits(int): supports 8, 4, 3, 2, 1 bits. -
group_size(int): no restrictions as long asweight.numel()is divisible by thegroup_size. -
view_as_float(bool): if True, the quantized parameter is viewed as float instead of an int type.
For usage with HF's transformers, see the example below from the documentation:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, HqqConfig
# All linear layers will use the same quantization config
quant_config = HqqConfig(nbits=4, group_size=64)
# Load and quantize
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_id,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
device_map="cuda",
quantization_config=quant_config
)You can save/load quantized models as regular transformers models via save_pretrained / from_pretrained.
You can also utilize the HQQ library to quantize transformers models:
#Load the model on CPU
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=compute_dtype)
#Quantize
from hqq.models.hf.base import AutoHQQHFModel
quant_config = BaseQuantizeConfig(nbits=4, group_size=64)
AutoHQQHFModel.quantize_model(model, quant_config=quant_config, compute_dtype=compute_dtype, device=device)You can save/load quantized models as follows:
from hqq.models.hf.base import AutoHQQHFModel
#Save: Make sure to save the model BEFORE any patching
AutoHQQHFModel.save_quantized(model, save_dir)
#Save as safetensors (to be load via transformers or vllm)
AutoHQQHFModel.save_to_safetensors(model, save_dir)
#Load
model = AutoHQQHFModel.from_quantized(save_dir)❗ Note that models saved via the hqq lib are not compatible with .from_pretrained()
The following native dequantization backends can be used by the HQQLinear module:
HQQLinear.set_backend(HQQBackend.PYTORCH) #Pytorch backend - Default
HQQLinear.set_backend(HQQBackend.PYTORCH_COMPILE) #Compiled Pytorch
HQQLinear.set_backend(HQQBackend.ATEN) #Aten/CUDA backend - only axis=0 supported❗ Note that HQQBackend.ATEN only supports axis=0.
We support external backends for faster inference with fused kernels. You can enable one of the backends after the model was quantized as follows:
from hqq.utils.patching import prepare_for_inference
#Pytorch backend that makes the model compatible with fullgraph torch.compile: works with any settings
#prepare_for_inference(model)
#Gemlite backend: nbits=4/2/1, compute_dtype=float16, axis=1
prepare_for_inference(model, backend="gemlite")
#Torchao's tiny_gemm backend (fast for batch-size<4): nbits=4, compute_dtype=bfloat16, axis=1
#prepare_for_inference(model, backend="torchao_int4") Note that these backends only work with axis=1. Additional restrictions apply regarding the group-size values depending on the backend. You should expect ~158 tokens/sec with a Llama3-8B 4-bit quantized model on a 4090 RTX.
When a quantization config is not supported by the specified inference backend, hqq will fallback to the native backend.
You can set up various quantization configurations for different layers by specifying the settings for each layer name:
# Each linear layer with the same tag will use a dedicated quantization config
q4_config = {'nbits':4, 'group_size':64}
q3_config = {'nbits':3, 'group_size':32}
quant_config = HqqConfig(dynamic_config={
'self_attn.q_proj':q4_config,
'self_attn.k_proj':q4_config,
'self_attn.v_proj':q4_config,
'self_attn.o_proj':q4_config,
'mlp.gate_proj':q3_config,
'mlp.up_proj' :q3_config,
'mlp.down_proj':q3_config,
})from hqq.core.quantize import *
q4_config = BaseQuantizeConfig(nbits=4, group_size=64)
q3_config = BaseQuantizeConfig(nbits=3, group_size=32)
quant_config = {'self_attn.q_proj':q4_config,
'self_attn.k_proj':q4_config,
'self_attn.v_proj':q4_config,
'self_attn.o_proj':q4_config,
'mlp.gate_proj':q3_config,
'mlp.up_proj' :q3_config,
'mlp.down_proj':q3_config,
}You can use HQQ in vllm. Make sure to install GemLite before using the backend.
#Or you can quantize on-the-fly
from hqq.utils.vllm import set_vllm_onthefly_hqq_quant
skip_modules = ['lm_head', 'visual', 'vision']
#Select one of the following modes:
#INT/FP format
set_vllm_onthefly_hqq_quant(weight_bits=8, group_size=None, quant_mode='int8_weightonly', skip_modules=skip_modules) #A16W8 - INT8 weight only
set_vllm_onthefly_hqq_quant(weight_bits=4, group_size=128, quant_mode='int4_weightonly', skip_modules=skip_modules) #A16W4 - HQQ weight only
set_vllm_onthefly_hqq_quant(weight_bits=8, quant_mode='int8_dynamic', skip_modules=skip_modules) #A8W8 - INT8 x INT8 dynamic
set_vllm_onthefly_hqq_quant(weight_bits=8, quant_mode='fp8_dynamic', skip_modules=skip_modules) #A8W8 - FP8 x FP8 dynamic
#MXFP format
set_vllm_onthefly_hqq_quant(weight_bits=8, group_size=None, quant_mode='mxfp8_dynamic', skip_modules=skip_modules) #A8W8 - MXFP8 x MXPF8 - post_scale=True
set_vllm_onthefly_hqq_quant(weight_bits=8, group_size=32, quant_mode='mxfp8_dynamic', skip_modules=skip_modules) #A8W8 - MXFP8 x MXPF8- post_scale=False
set_vllm_onthefly_hqq_quant(weight_bits=4, quant_mode='mxfp4_weightonly', skip_modules=skip_modules) #A16W4 - MXFP4 weight-only
set_vllm_onthefly_hqq_quant(weight_bits=4, quant_mode='mxfp8_dynamic', skip_modules=skip_modules) #A8W4 - MXFP8 x MXFP4 dynamic
set_vllm_onthefly_hqq_quant(weight_bits=4, quant_mode='mxfp4_dynamic', skip_modules=skip_modules) #A4W4 - MXPF4 x MXPF4 dynamic
set_vllm_onthefly_hqq_quant(weight_bits=4, quant_mode='nvfp4_dynamic', skip_modules=skip_modules) #A4W4 - NVFP4 x NVFP4 dynamic
llm = LLM(model="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct", max_model_len=4096, gpu_memory_utilization=0.80, dtype=torch.float16)Peft training is directly supported in the HuggingFace's peft library. If you still want to use hqq-lib's peft utilities, here's how:
#First, quantize/load a quantized HQQ model the
from hqq.core.peft import PeftUtils
base_lora_params = {'lora_type':'default', 'r':32, 'lora_alpha':64, 'dropout':0.05, 'train_dtype':torch.float32}
lora_params = {'self_attn.q_proj': base_lora_params,
'self_attn.k_proj': base_lora_params,
'self_attn.v_proj': base_lora_params,
'self_attn.o_proj': base_lora_params,
'mlp.gate_proj' : None,
'mlp.up_proj' : None,
'mlp.down_proj' : None}
#Add LoRA to linear/HQQ modules
PeftUtils.add_lora(model, lora_params)
#Optional: set your backend
HQQLinear.set_backend(HQQBackend.ATEN if axis==0 else HQQBackend.PYTORCH_COMPILE)
#Train ....
#Convert LoRA weights to the same model dtype for faster inference
model.eval()
PeftUtils.cast_lora_weights(model, dtype=compute_dtype)
#Save LoRA weights
PeftUtils.save_lora_weights(model, filename)
#Load LoRA weights: automatically calls add_lora
PeftUtils.load_lora_weights(model, filename)We provide a complete example to train a model with HQQ/LoRA that you can find in examples/hqq_plus.py.
If you want to use muti-gpu training via FSDP, check out this awesome repo by Answer.AI: https://github.com/AnswerDotAI/fsdp_qlora
We provide a variety of examples demonstrating model quantization across different backends within the examples directory.
@misc{badri2023hqq,
title = {Half-Quadratic Quantization of Large Machine Learning Models},
url = {https://mobiusml.github.io/hqq_blog/},
author = {Hicham Badri and Appu Shaji},
month = {November},
year = {2023}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for hqq
Similar Open Source Tools

hqq
HQQ is a fast and accurate model quantizer that skips the need for calibration data. It's super simple to implement (just a few lines of code for the optimizer). It can crunch through quantizing the Llama2-70B model in only 4 minutes! 🚀
llm-baselines
LLM-baselines is a modular codebase to experiment with transformers, inspired from NanoGPT. It provides a quick and easy way to train and evaluate transformer models on a variety of datasets. The codebase is well-documented and easy to use, making it a great resource for researchers and practitioners alike.

zeta
Zeta is a tool designed to build state-of-the-art AI models faster by providing modular, high-performance, and scalable building blocks. It addresses the common issues faced while working with neural nets, such as chaotic codebases, lack of modularity, and low performance modules. Zeta emphasizes usability, modularity, and performance, and is currently used in hundreds of models across various GitHub repositories. It enables users to prototype, train, optimize, and deploy the latest SOTA neural nets into production. The tool offers various modules like FlashAttention, SwiGLUStacked, RelativePositionBias, FeedForward, BitLinear, PalmE, Unet, VisionEmbeddings, niva, FusedDenseGELUDense, FusedDropoutLayerNorm, MambaBlock, Film, hyper_optimize, DPO, and ZetaCloud for different tasks in AI model development.
cursive-py
Cursive is a universal and intuitive framework for interacting with LLMs. It is extensible, allowing users to hook into any part of a completion life cycle. Users can easily describe functions that LLMs can use with any supported model. Cursive aims to bridge capabilities between different models, providing a single interface for users to choose any model. It comes with built-in token usage and costs calculations, automatic retry, and model expanding features. Users can define and describe functions, generate Pydantic BaseModels, hook into completion life cycle, create embeddings, and configure retry and model expanding behavior. Cursive supports various models from OpenAI, Anthropic, OpenRouter, Cohere, and Replicate, with options to pass API keys for authentication.
aicsimageio
AICSImageIO is a Python tool for Image Reading, Metadata Conversion, and Image Writing for Microscopy Images. It supports various file formats like OME-TIFF, TIFF, ND2, DV, CZI, LIF, PNG, GIF, and Bio-Formats. Users can read and write metadata and imaging data, work with different file systems like local paths, HTTP URLs, s3fs, and gcsfs. The tool provides functionalities for full image reading, delayed image reading, mosaic image reading, metadata reading, xarray coordinate plane attachment, cloud IO support, and saving to OME-TIFF. It also offers benchmarking and developer resources.

wllama
Wllama is a WebAssembly binding for llama.cpp, a high-performance and lightweight language model library. It enables you to run inference directly on the browser without the need for a backend or GPU. Wllama provides both high-level and low-level APIs, allowing you to perform various tasks such as completions, embeddings, tokenization, and more. It also supports model splitting, enabling you to load large models in parallel for faster download. With its Typescript support and pre-built npm package, Wllama is easy to integrate into your React Typescript projects.
zml
ZML is a high-performance AI inference stack built for production, using Zig language, MLIR, and Bazel. It allows users to create exciting AI projects, run pre-packaged models like MNIST, TinyLlama, OpenLLama, and Meta Llama, and compile models for accelerator runtimes. Users can also run tests, explore examples, and contribute to the project. ZML is licensed under the Apache 2.0 license.
ChatRex
ChatRex is a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) designed to seamlessly integrate fine-grained object perception and robust language understanding. By adopting a decoupled architecture with a retrieval-based approach for object detection and leveraging high-resolution visual inputs, ChatRex addresses key challenges in perception tasks. It is powered by the Rexverse-2M dataset with diverse image-region-text annotations. ChatRex can be applied to various scenarios requiring fine-grained perception, such as object detection, grounded conversation, grounded image captioning, and region understanding.

clarifai-python
The Clarifai Python SDK offers a comprehensive set of tools to integrate Clarifai's AI platform to leverage computer vision capabilities like classification , detection ,segementation and natural language capabilities like classification , summarisation , generation , Q&A ,etc into your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can leverage cutting-edge artificial intelligence to unlock valuable insights from visual and textual content.
react-native-fast-tflite
A high-performance TensorFlow Lite library for React Native that utilizes JSI for power, zero-copy ArrayBuffers for efficiency, and low-level C/C++ TensorFlow Lite core API for direct memory access. It supports swapping out TensorFlow Models at runtime and GPU-accelerated delegates like CoreML/Metal/OpenGL. Easy VisionCamera integration allows for seamless usage. Users can load TensorFlow Lite models, interpret input and output data, and utilize GPU Delegates for faster computation. The library is suitable for real-time object detection, image classification, and other machine learning tasks in React Native applications.
chatgpt
The ChatGPT R package provides a set of features to assist in R coding. It includes addins like Ask ChatGPT, Comment selected code, Complete selected code, Create unit tests, Create variable name, Document code, Explain selected code, Find issues in the selected code, Optimize selected code, and Refactor selected code. Users can interact with ChatGPT to get code suggestions, explanations, and optimizations. The package helps in improving coding efficiency and quality by providing AI-powered assistance within the RStudio environment.

syncode
SynCode is a novel framework for the grammar-guided generation of Large Language Models (LLMs) that ensures syntactically valid output based on a Context-Free Grammar (CFG). It supports various programming languages like Python, Go, SQL, Math, JSON, and more. Users can define custom grammars using EBNF syntax. SynCode offers fast generation, seamless integration with HuggingFace Language Models, and the ability to sample with different decoding strategies.
llm-chain
LLM Chain is a PHP library for building LLM-based features and applications. It provides abstractions for Language Models and Embeddings Models from platforms like OpenAI, Azure, Google, Replicate, and others. The core feature is to interact with language models via messages, supporting different message types and content. LLM Chain also supports tool calling, document embedding, vector stores, similarity search, structured output, response streaming, image processing, audio processing, embeddings, parallel platform calls, and input/output processing. Contributions are welcome, and the repository contains fixture licenses for testing multi-modal features.

syncode
SynCode is a novel framework for the grammar-guided generation of Large Language Models (LLMs) that ensures syntactically valid output with respect to defined Context-Free Grammar (CFG) rules. It supports general-purpose programming languages like Python, Go, SQL, JSON, and more, allowing users to define custom grammars using EBNF syntax. The tool compares favorably to other constrained decoders and offers features like fast grammar-guided generation, compatibility with HuggingFace Language Models, and the ability to work with various decoding strategies.
instructor
Instructor is a popular Python library for managing structured outputs from large language models (LLMs). It offers a user-friendly API for validation, retries, and streaming responses. With support for various LLM providers and multiple languages, Instructor simplifies working with LLM outputs. The library includes features like response models, retry management, validation, streaming support, and flexible backends. It also provides hooks for logging and monitoring LLM interactions, and supports integration with Anthropic, Cohere, Gemini, Litellm, and Google AI models. Instructor facilitates tasks such as extracting user data from natural language, creating fine-tuned models, managing uploaded files, and monitoring usage of OpenAI models.
KVCache-Factory
KVCache-Factory is a unified framework for KV Cache compression of diverse models. It supports multi-GPUs inference with big LLMs and various attention implementations. The tool enables KV cache compression without Flash Attention v2, multi-GPU inference, and specific models like Mistral. It also provides functions for KV cache budget allocation and batch inference. The visualization tools help in understanding the attention patterns of models.
For similar tasks
aimet
AIMET is a library that provides advanced model quantization and compression techniques for trained neural network models. It provides features that have been proven to improve run-time performance of deep learning neural network models with lower compute and memory requirements and minimal impact to task accuracy. AIMET is designed to work with PyTorch, TensorFlow and ONNX models. We also host the AIMET Model Zoo - a collection of popular neural network models optimized for 8-bit inference. We also provide recipes for users to quantize floating point models using AIMET.

hqq
HQQ is a fast and accurate model quantizer that skips the need for calibration data. It's super simple to implement (just a few lines of code for the optimizer). It can crunch through quantizing the Llama2-70B model in only 4 minutes! 🚀
llm-resource
llm-resource is a comprehensive collection of high-quality resources for Large Language Models (LLM). It covers various aspects of LLM including algorithms, training, fine-tuning, alignment, inference, data engineering, compression, evaluation, prompt engineering, AI frameworks, AI basics, AI infrastructure, AI compilers, LLM application development, LLM operations, AI systems, and practical implementations. The repository aims to gather and share valuable resources related to LLM for the community to benefit from.
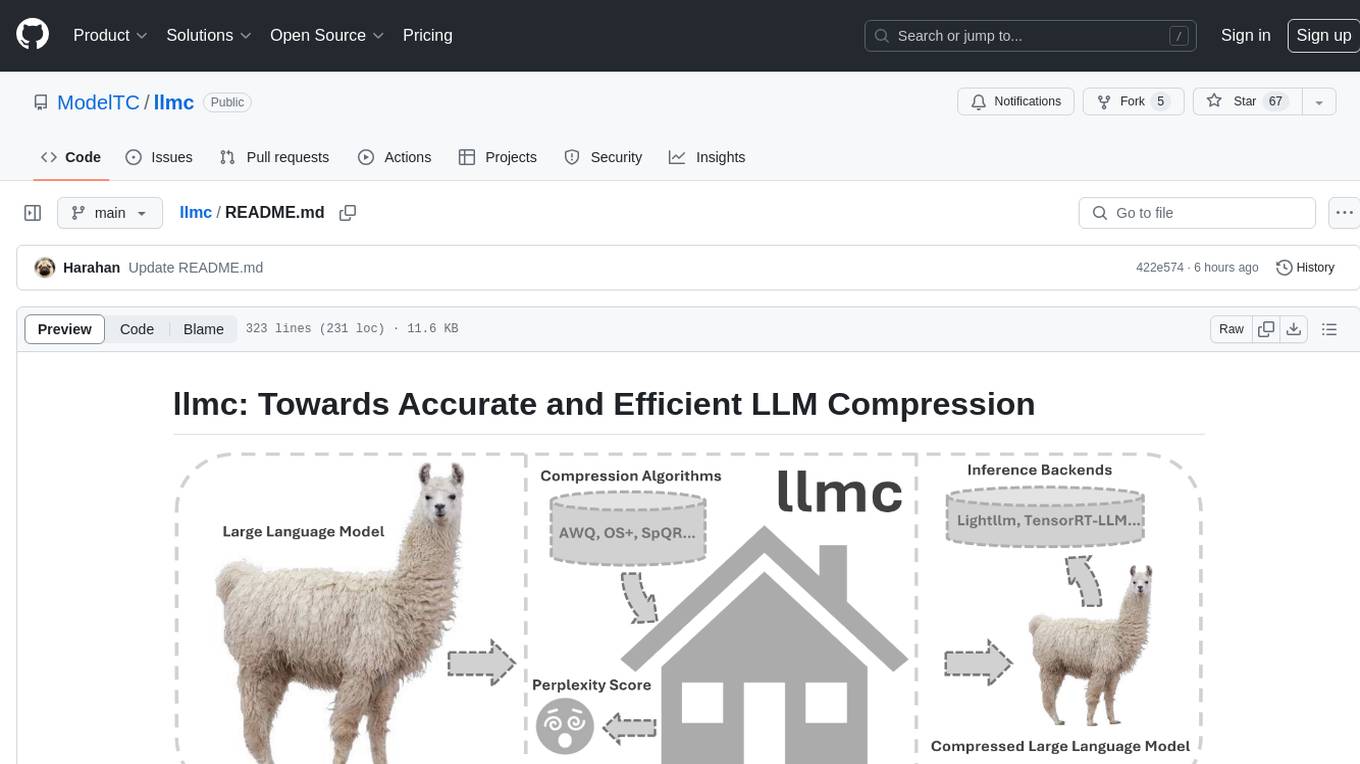
llmc
llmc is an off-the-shell tool designed for compressing LLM, leveraging state-of-the-art compression algorithms to enhance efficiency and reduce model size without compromising performance. It provides users with the ability to quantize LLMs, choose from various compression algorithms, export transformed models for further optimization, and directly infer compressed models with a shallow memory footprint. The tool supports a range of model types and quantization algorithms, with ongoing development to include pruning techniques. Users can design their configurations for quantization and evaluation, with documentation and examples planned for future updates. llmc is a valuable resource for researchers working on post-training quantization of large language models.
Awesome-Efficient-LLM
Awesome-Efficient-LLM is a curated list focusing on efficient large language models. It includes topics such as knowledge distillation, network pruning, quantization, inference acceleration, efficient MOE, efficient architecture of LLM, KV cache compression, text compression, low-rank decomposition, hardware/system, tuning, and survey. The repository provides a collection of papers and projects related to improving the efficiency of large language models through various techniques like sparsity, quantization, and compression.
TensorRT-Model-Optimizer
The NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer is a library designed to quantize and compress deep learning models for optimized inference on GPUs. It offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques including quantization and sparsity to reduce inference costs for generative AI models. Users can easily stack different optimization techniques to produce quantized checkpoints from torch or ONNX models. The quantized checkpoints are ready for deployment in inference frameworks like TensorRT-LLM or TensorRT, with planned integrations for NVIDIA NeMo and Megatron-LM. The tool also supports 8-bit quantization with Stable Diffusion for enterprise users on NVIDIA NIM. Model Optimizer is available for free on NVIDIA PyPI, and this repository serves as a platform for sharing examples, GPU-optimized recipes, and collecting community feedback.
Awesome_LLM_System-PaperList
Since the emergence of chatGPT in 2022, the acceleration of Large Language Model has become increasingly important. Here is a list of papers on LLMs inference and serving.
llm-compressor
llm-compressor is an easy-to-use library for optimizing models for deployment with vllm. It provides a comprehensive set of quantization algorithms, seamless integration with Hugging Face models and repositories, and supports mixed precision, activation quantization, and sparsity. Supported algorithms include PTQ, GPTQ, SmoothQuant, and SparseGPT. Installation can be done via git clone and local pip install. Compression can be easily applied by selecting an algorithm and calling the oneshot API. The library also offers end-to-end examples for model compression. Contributions to the code, examples, integrations, and documentation are appreciated.
For similar jobs

hqq
HQQ is a fast and accurate model quantizer that skips the need for calibration data. It's super simple to implement (just a few lines of code for the optimizer). It can crunch through quantizing the Llama2-70B model in only 4 minutes! 🚀
llm2vec
LLM2Vec is a simple recipe to convert decoder-only LLMs into text encoders. It consists of 3 simple steps: 1) enabling bidirectional attention, 2) training with masked next token prediction, and 3) unsupervised contrastive learning. The model can be further fine-tuned to achieve state-of-the-art performance.
open-parse
Open Parse is a Python library for visually discerning document layouts and chunking them effectively. It is designed to fill the gap in open-source libraries for handling complex documents. Unlike text splitting, which converts a file to raw text and slices it up, Open Parse visually analyzes documents for superior LLM input. It also supports basic markdown for parsing headings, bold, and italics, and has high-precision table support, extracting tables into clean Markdown formats with accuracy that surpasses traditional tools. Open Parse is extensible, allowing users to easily implement their own post-processing steps. It is also intuitive, with great editor support and completion everywhere, making it easy to use and learn.
RLHF-Reward-Modeling
This repository contains code for training reward models for Deep Reinforcement Learning-based Reward-modulated Hierarchical Fine-tuning (DRL-based RLHF), Iterative Selection Fine-tuning (Rejection sampling fine-tuning), and iterative Decision Policy Optimization (DPO). The reward models are trained using a Bradley-Terry model based on the Gemma and Mistral language models. The resulting reward models achieve state-of-the-art performance on the RewardBench leaderboard for reward models with base models of up to 13B parameters.
Efficient-LLMs-Survey
This repository provides a systematic and comprehensive review of efficient LLMs research. We organize the literature in a taxonomy consisting of three main categories, covering distinct yet interconnected efficient LLMs topics from **model-centric** , **data-centric** , and **framework-centric** perspective, respectively. We hope our survey and this GitHub repository can serve as valuable resources to help researchers and practitioners gain a systematic understanding of the research developments in efficient LLMs and inspire them to contribute to this important and exciting field.
AutoGPTQ
AutoGPTQ is an easy-to-use LLM quantization package with user-friendly APIs, based on GPTQ algorithm (weight-only quantization). It provides a simple and efficient way to quantize large language models (LLMs) to reduce their size and computational cost while maintaining their performance. AutoGPTQ supports a wide range of LLM models, including GPT-2, GPT-J, OPT, and BLOOM. It also supports various evaluation tasks, such as language modeling, sequence classification, and text summarization. With AutoGPTQ, users can easily quantize their LLM models and deploy them on resource-constrained devices, such as mobile phones and embedded systems.