
AIMNet2
None
Stars: 58
AIMNet2 Calculator is a package that integrates the AIMNet2 neural network potential into simulation workflows, providing fast and reliable energy, force, and property calculations for molecules with diverse elements. It excels at modeling various systems, offers flexible interfaces for popular simulation packages, and supports long-range interactions using DSF or Ewald summation Coulomb models. The tool is designed for accurate and versatile molecular simulations, suitable for large molecules and periodic calculations.
README:
__ Update 6/10/24 __ We release new code, suaitable for large molecules and perioric calculations. Old code available in the old branch. Models were re-compiled and are not compatible with the new code.
This package integrates the powerful AIMNet2 neural network potential into your simulation workflows. AIMNet2 provides fast and reliable energy, force, and property calculations for molecules containing a diverse range of elements.
- Accurate and Versatile: AIMNet2 excels at modeling neutral, charged, organic, and elemental-organic systems.
- Flexible Interfaces: Use AIMNet2 through convenient calculators for popular simulation packages like ASE and PySisyphus.
- Flexible Long-Range Interactions: Optionally employ the Dumped-Shifted Force (DSF) or Ewald summation Coulomb models for accurate calculations in large or periodic systems.
While package is in alpha stage and repository is private, please install into your conda envoronment manually with
# install requirements
conda install -y pytorch pytorch-cuda=12.1 -c pytorch -c nvidia
conda install -y -c pyg pytorch-cluster
conda install -y -c conda-forge openbabel ase
## pysis requirements
conda install -y -c conda-forge autograd dask distributed h5py fabric jinja2 joblib matplotlib numpy natsort psutil pyyaml rmsd scipy sympy scikit-learn
# now should not do any pip installs
pip install git+https://github.com/eljost/pysisyphus.git
# finally, this repo
git clone [email protected]:zubatyuk/aimnet2calc.git
cd aimnet2calc
python setup.py install
from aimnet2calc import AIMNet2ASE
calc = AIMNet2ASE('aimnet2')
To specify total molecular charge and spin multiplicity, use optional charge and mult keyword arguments, or set_charge and set_mult methods:
calc = AIMNet2ASE('aimnet2', charge=1)
atoms1.calc = calc
# calculations on atoms1 will be done with charge 1
....
atoms2.calc = calc
calc.set_charge(-2)
# calculations on atoms1 will be done with charge -2
PySisyphus [https://pysisyphus.readthedocs.io]
from aimnet2calc import AIMNet2PySis
calc = AIMNet2PySis('aimnet2')
This produces standard PySisyphus calculator.
Instead of Pysis command line utility, use aimnet2pysis. This registeres AIMNet2 calculator with PySisyphus.
Example calc section for PySisyphus YAML files:
calc:
type: aimnet # use AIMNet2 calculator
model: aimnet2_b973c # use aimnet2_b973c_0.jpt model
from aimnet2calc import AIMNet2Calculator
calc = AIMNet2Calculator('aimnet2')
will load default AIMNet2 model aimnet2_wb97m_0.jpt as defined at aimnet2calc/models.py . If file does not exist on the machine, it will be downloaded from aimnet-model-zoo repository.
calc = AIMNet2Calculator('/path/to_a/model.jpt')
will load model from the file.
The calculator accepts a dictionary containig lists, numpy arrays, torch tensors, or anything that could be accepted by torch.as_tensor.
The input could be for a single molecule (dict keys and shapes):
coord: (B, N, 3) # atomic coordinates in Angstrom
numbers (B, N) # atomic numbers
charge (B,) # molecular charge
mult (B,) # spin multiplicity, optional
or for a concatenation of molecules:
coord: (N, 3) # atomic coordinates in Angstrom
numbers (N,) # atomic numbers
charge (B,) # molecular charge
mult (B,) # spin multiplicity, optional
mol_idx (N,) # molecule index for each atom, should contain integers in increasing order, with (B-1) is the maximum number.
where B is the number of molecules, N is number of atoms.
results = calc(data, forces=False, stress=False, hessian=False)
results would be a dictionary of PyTorch tensors containing energy, charges, and possibly forces, stress and hessian if requested.
By default, Coulomb energy is calculated in O(N^2) manner, e.g. pair interaction between every pair of atoms in system. For very large or periodic systems, O(N) Dumped-Shifted Force Coulomb model could be employed doi: 10.1063/1.2206581. With AIMNet2Calculator interface, switch between standard and DSF Coulomb implementations im AIMNet2 models:
# switch to O(N)
calc.set_lrcoulomb_method('dsf', cutoff=15.0, dsf_alpha=0.2)
# switch to O(N^2), not suitable for PBC
calc.set_lrcoulomb_method('simple')
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AIMNet2
Similar Open Source Tools

AIMNet2
AIMNet2 Calculator is a package that integrates the AIMNet2 neural network potential into simulation workflows, providing fast and reliable energy, force, and property calculations for molecules with diverse elements. It excels at modeling various systems, offers flexible interfaces for popular simulation packages, and supports long-range interactions using DSF or Ewald summation Coulomb models. The tool is designed for accurate and versatile molecular simulations, suitable for large molecules and periodic calculations.
aigverse
aigverse is a Python infrastructure framework that bridges the gap between logic synthesis and AI/ML applications. It allows efficient representation and manipulation of logic circuits, making it easier to integrate logic synthesis and optimization tasks into machine learning pipelines. Built upon EPFL Logic Synthesis Libraries, particularly mockturtle, aigverse provides a high-level Python interface to state-of-the-art algorithms for And-Inverter Graph (AIG) manipulation and logic synthesis, widely used in formal verification, hardware design, and optimization tasks.
mirage
Mirage Persistent Kernel (MPK) is a compiler and runtime system that automatically transforms LLM inference into a single megakernel—a fused GPU kernel that performs all necessary computation and communication within a single kernel launch. This end-to-end GPU fusion approach reduces LLM inference latency by 1.2× to 6.7×, all while requiring minimal developer effort.
hqq
HQQ is a fast and accurate model quantizer that skips the need for calibration data. It's super simple to implement (just a few lines of code for the optimizer). It can crunch through quantizing the Llama2-70B model in only 4 minutes! 🚀

sieves
sieves is a library for zero- and few-shot NLP tasks with structured generation, enabling rapid prototyping of NLP applications without the need for training. It simplifies NLP prototyping by bundling capabilities into a single library, providing zero- and few-shot model support, a unified interface for structured generation, built-in tasks for common NLP operations, easy extendability, document-based pipeline architecture, caching to prevent redundant model calls, and more. The tool draws inspiration from spaCy and spacy-llm, offering features like immediate inference, observable pipelines, integrated tools for document parsing and text chunking, ready-to-use tasks such as classification, summarization, translation, and more, persistence for saving and loading pipelines, distillation for specialized model creation, and caching to optimize performance.
PDEBench
PDEBench provides a diverse and comprehensive set of benchmarks for scientific machine learning, including challenging and realistic physical problems. The repository consists of code for generating datasets, uploading and downloading datasets, training and evaluating machine learning models as baselines. It features a wide range of PDEs, realistic and difficult problems, ready-to-use datasets with various conditions and parameters. PDEBench aims for extensibility and invites participation from the SciML community to improve and extend the benchmark.
probsem
ProbSem is a repository that provides a framework to leverage large language models (LLMs) for assigning context-conditional probability distributions over queried strings. It supports OpenAI engines and HuggingFace CausalLM models, and is flexible for research applications in linguistics, cognitive science, program synthesis, and NLP. Users can define prompts, contexts, and queries to derive probability distributions over possible completions, enabling tasks like cloze completion, multiple-choice QA, semantic parsing, and code completion. The repository offers CLI and API interfaces for evaluation, with options to customize models, normalize scores, and adjust temperature for probability distributions.
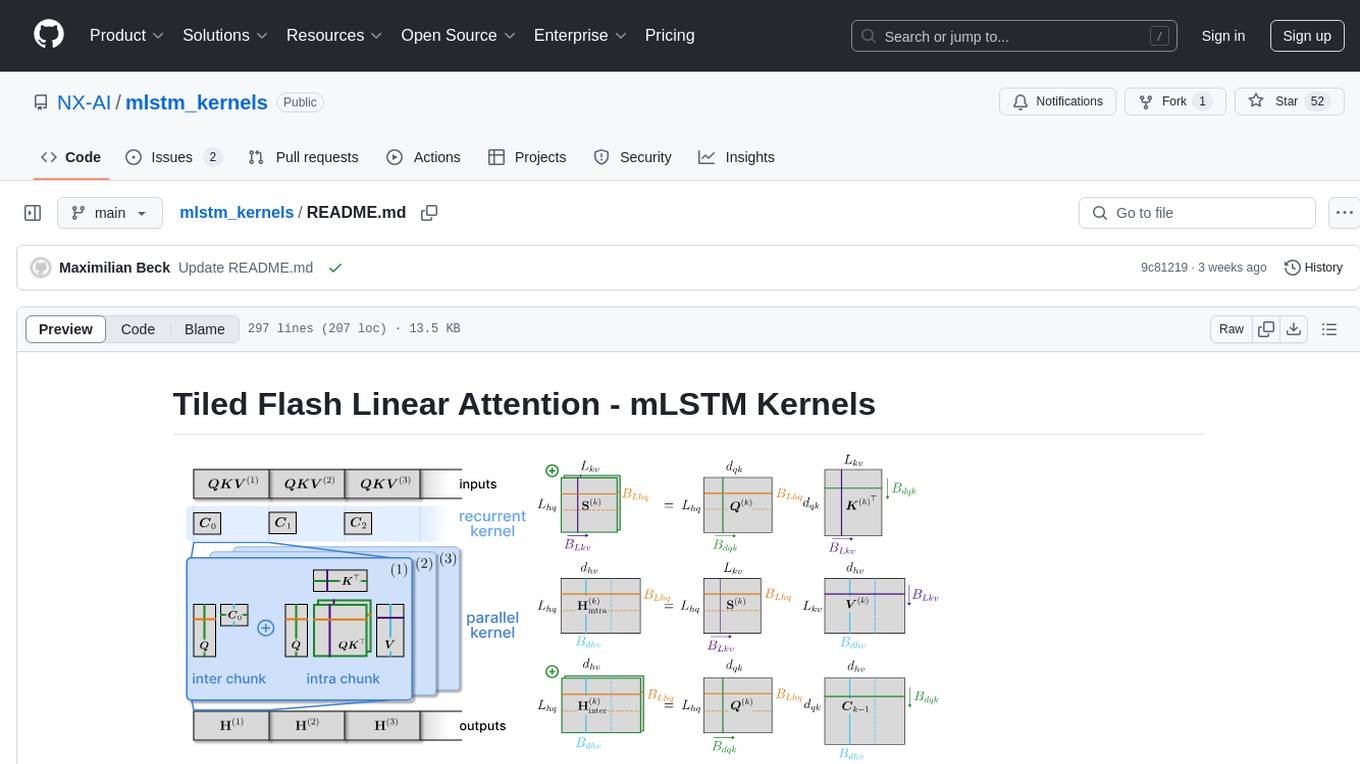
mlstm_kernels
This repository provides fast and efficient mLSTM training and inference Triton kernels built on Tiled Flash Linear Attention (TFLA). It includes implementations in JAX, PyTorch, and Triton, with chunkwise, parallel, and recurrent kernels for mLSTM. The repository also contains a benchmark library for runtime benchmarks and full mLSTM Huggingface models.
mergekit
Mergekit is a toolkit for merging pre-trained language models. It uses an out-of-core approach to perform unreasonably elaborate merges in resource-constrained situations. Merges can be run entirely on CPU or accelerated with as little as 8 GB of VRAM. Many merging algorithms are supported, with more coming as they catch my attention.
topicGPT
TopicGPT is a repository containing scripts and prompts for the paper 'TopicGPT: Topic Modeling by Prompting Large Language Models' (NAACL'24). The 'topicgpt_python' package offers functions to generate high-level and specific topics, refine topics, assign topics to input text, and correct generated topics. It supports various APIs like OpenAI, VertexAI, Azure, Gemini, and vLLM for inference. Users can prepare data in JSONL format, run the pipeline using provided scripts, and evaluate topic alignment with ground-truth labels.
verifiers
Verifiers is a library of modular components for creating RL environments and training LLM agents. It includes an async GRPO implementation built around the `transformers` Trainer, is supported by `prime-rl` for large-scale FSDP training, and can easily be integrated into any RL framework which exposes an OpenAI-compatible inference client. The library provides tools for creating and evaluating RL environments, training LLM agents, and leveraging OpenAI-compatible models for various tasks. Verifiers aims to be a reliable toolkit for building on top of, minimizing fork proliferation in the RL infrastructure ecosystem.
ice-score
ICE-Score is a tool designed to instruct large language models to evaluate code. It provides a minimum viable product (MVP) for evaluating generated code snippets using inputs such as problem, output, task, aspect, and model. Users can also evaluate with reference code and enable zero-shot chain-of-thought evaluation. The tool is built on codegen-metrics and code-bert-score repositories and includes datasets like CoNaLa and HumanEval. ICE-Score has been accepted to EACL 2024.
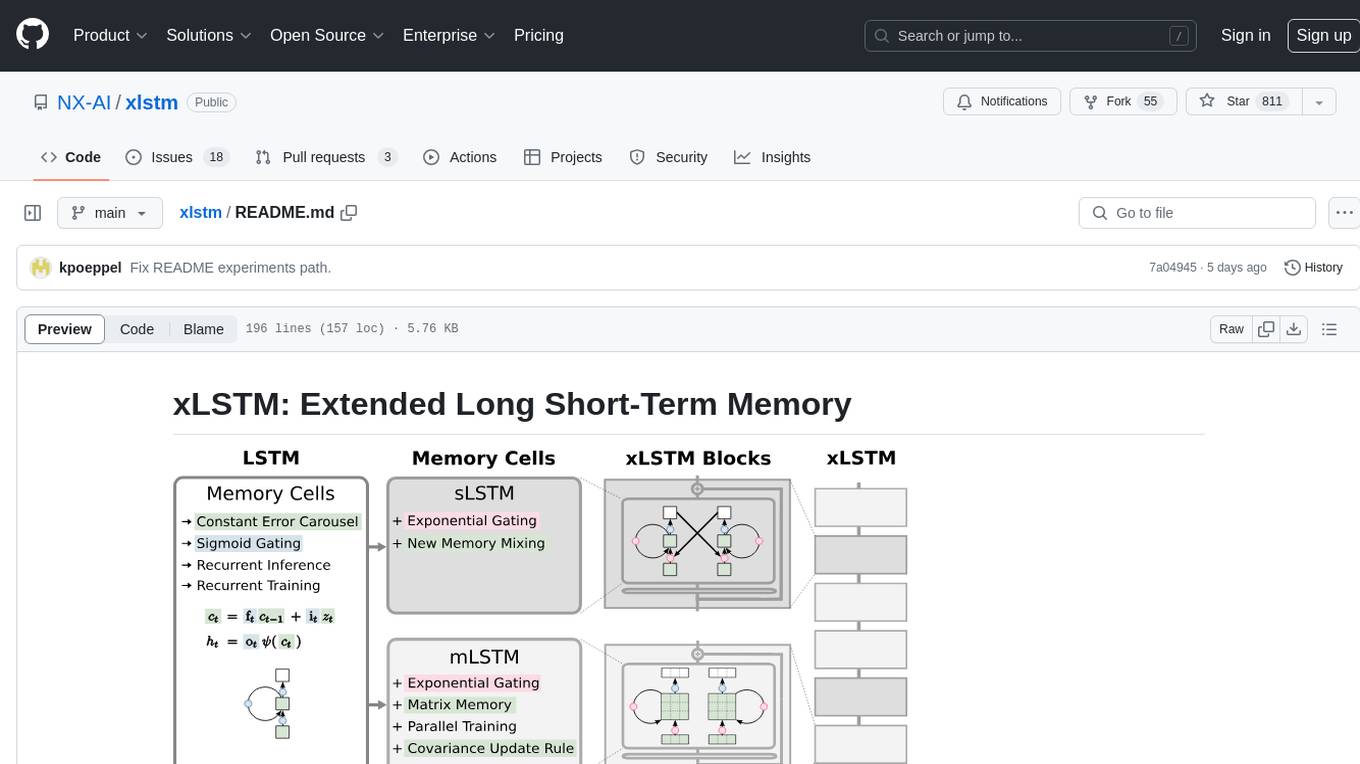
xlstm
xLSTM is a new Recurrent Neural Network architecture based on ideas of the original LSTM. Through Exponential Gating with appropriate normalization and stabilization techniques and a new Matrix Memory it overcomes the limitations of the original LSTM and shows promising performance on Language Modeling when compared to Transformers or State Space Models. The package is based on PyTorch and was tested for versions >=1.8. For the CUDA version of xLSTM, you need Compute Capability >= 8.0. The xLSTM tool provides two main components: xLSTMBlockStack for non-language applications or integrating in other architectures, and xLSTMLMModel for language modeling or other token-based applications.
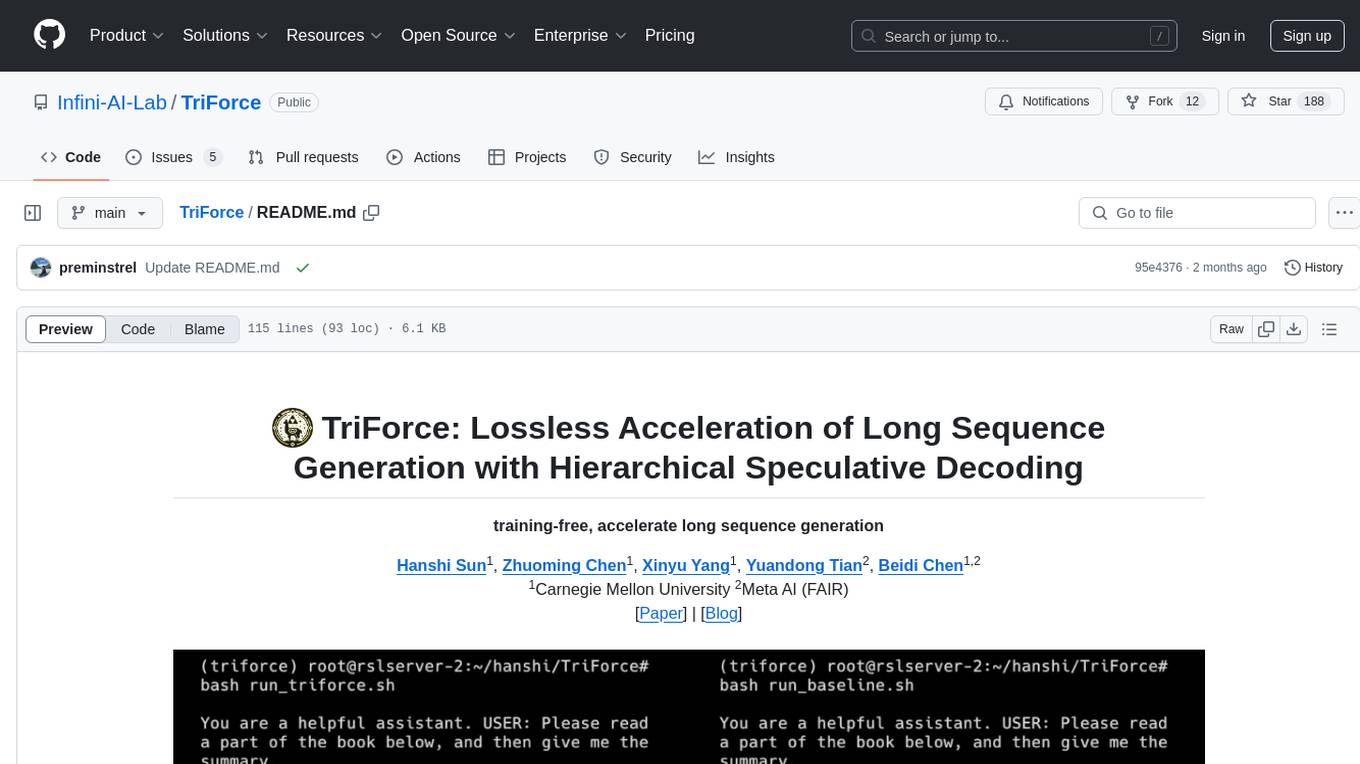
TriForce
TriForce is a training-free tool designed to accelerate long sequence generation. It supports long-context Llama models and offers both on-chip and offloading capabilities. Users can achieve a 2.2x speedup on a single A100 GPU. TriForce also provides options for offloading with tensor parallelism or without it, catering to different hardware configurations. The tool includes a baseline for comparison and is optimized for performance on RTX 4090 GPUs. Users can cite the associated paper if they find TriForce useful for their projects.
neural-speed
Neural Speed is an innovative library designed to support the efficient inference of large language models (LLMs) on Intel platforms through the state-of-the-art (SOTA) low-bit quantization powered by Intel Neural Compressor. The work is inspired by llama.cpp and further optimized for Intel platforms with our innovations in NeurIPS' 2023
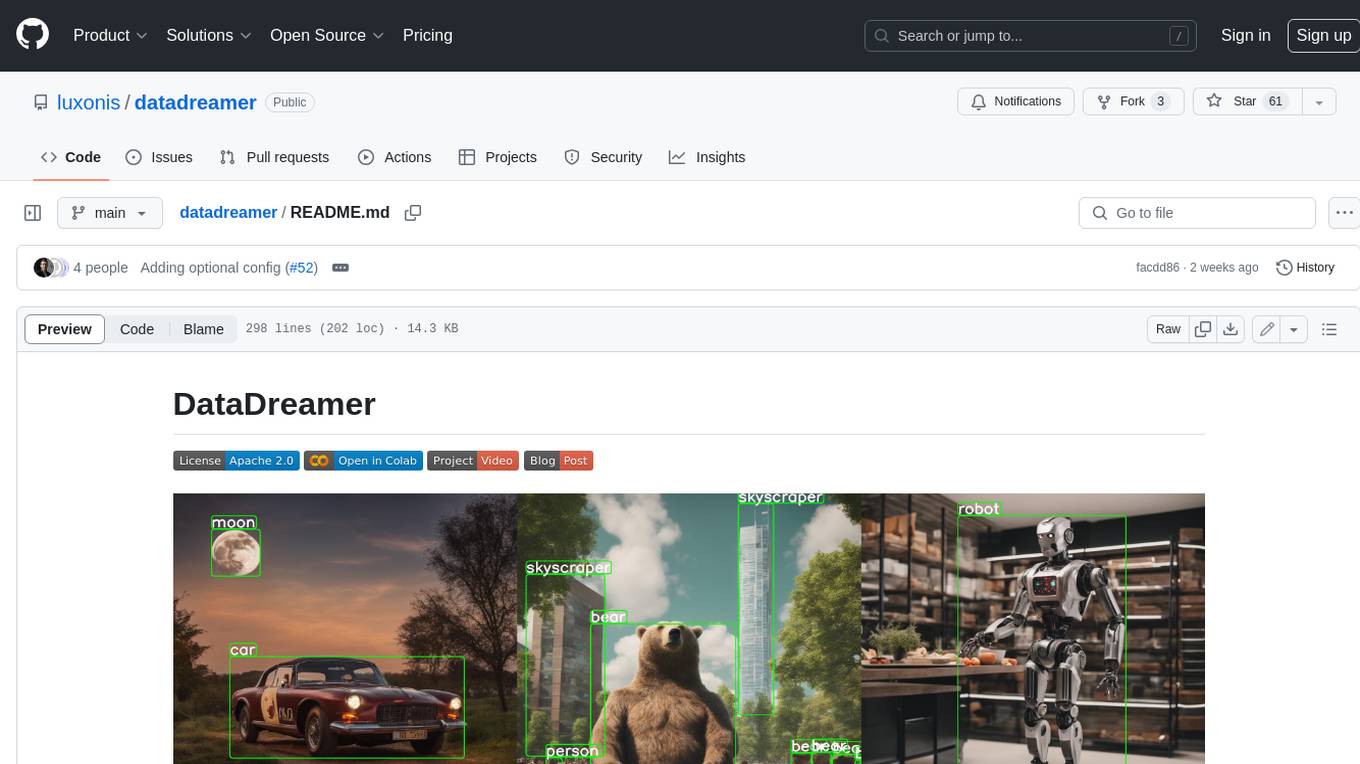
datadreamer
DataDreamer is an advanced toolkit designed to facilitate the development of edge AI models by enabling synthetic data generation, knowledge extraction from pre-trained models, and creation of efficient and potent models. It eliminates the need for extensive datasets by generating synthetic datasets, leverages latent knowledge from pre-trained models, and focuses on creating compact models suitable for integration into any device and performance for specialized tasks. The toolkit offers features like prompt generation, image generation, dataset annotation, and tools for training small-scale neural networks for edge deployment. It provides hardware requirements, usage instructions, available models, and limitations to consider while using the library.
For similar tasks

AIMNet2
AIMNet2 Calculator is a package that integrates the AIMNet2 neural network potential into simulation workflows, providing fast and reliable energy, force, and property calculations for molecules with diverse elements. It excels at modeling various systems, offers flexible interfaces for popular simulation packages, and supports long-range interactions using DSF or Ewald summation Coulomb models. The tool is designed for accurate and versatile molecular simulations, suitable for large molecules and periodic calculations.
trubrics-python
Trubrics is a Python client for event tracking and analyzing LLM interactions. It offers fast and non-blocking queuing system with automatic flushing to Trubrics API. Users can track events and LLM interactions, adjust logging verbosity, and configure flush intervals and batch sizes. The tool simplifies tracking user interactions and analyzing data for LLM applications.
dyad
Dyad is a lightweight Python library for analyzing dyadic data, which involves pairs of individuals and their interactions. It provides functions for computing various network metrics, visualizing network structures, and conducting statistical analyses on dyadic data. Dyad is designed to be user-friendly and efficient, making it suitable for researchers and practitioners working with relational data in fields such as social network analysis, communication studies, and psychology.
md-agent
MD-Agent is a LLM-agent based toolset for Molecular Dynamics. It uses Langchain and a collection of tools to set up and execute molecular dynamics simulations, particularly in OpenMM. The tool assists in environment setup, installation, and usage by providing detailed steps. It also requires API keys for certain functionalities, such as OpenAI and paper-qa for literature searches. Contributions to the project are welcome, with a detailed Contributor's Guide available for interested individuals.
For similar jobs

md-agent
MD-Agent is a LLM-agent based toolset for Molecular Dynamics. It uses Langchain and a collection of tools to set up and execute molecular dynamics simulations, particularly in OpenMM. The tool assists in environment setup, installation, and usage by providing detailed steps. It also requires API keys for certain functionalities, such as OpenAI and paper-qa for literature searches. Contributions to the project are welcome, with a detailed Contributor's Guide available for interested individuals.

AIMNet2
AIMNet2 Calculator is a package that integrates the AIMNet2 neural network potential into simulation workflows, providing fast and reliable energy, force, and property calculations for molecules with diverse elements. It excels at modeling various systems, offers flexible interfaces for popular simulation packages, and supports long-range interactions using DSF or Ewald summation Coulomb models. The tool is designed for accurate and versatile molecular simulations, suitable for large molecules and periodic calculations.

chem-bench
ChemBench is a project aimed at expanding chemistry benchmark tasks in a BIG-bench compatible way, providing a pipeline to benchmark frontier and open models. It allows users to run benchmarking tasks on models with existing presets, offering predefined parameters and processing steps. The library facilitates benchmarking models on the entire suite, addressing challenges such as prompt structure, parsing, and scoring methods. Users can contribute to the project by following the developer notes.
matsciml
The Open MatSci ML Toolkit is a flexible framework for machine learning in materials science. It provides a unified interface to a variety of materials science datasets, as well as a set of tools for data preprocessing, model training, and evaluation. The toolkit is designed to be easy to use for both beginners and experienced researchers, and it can be used to train models for a wide range of tasks, including property prediction, materials discovery, and materials design.

NoLabs
NoLabs is an open-source biolab that provides easy access to state-of-the-art models for bio research. It supports various tasks, including drug discovery, protein analysis, and small molecule design. NoLabs aims to accelerate bio research by making inference models accessible to everyone.
AlphaFold3
AlphaFold3 is an implementation of the Alpha Fold 3 model in PyTorch for accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions. It includes modules for genetic diffusion and full model examples for forward pass computations. The tool allows users to generate random pair and single representations, operate on atomic coordinates, and perform structure predictions based on input tensors. The implementation also provides functionalities for training and evaluating the model.
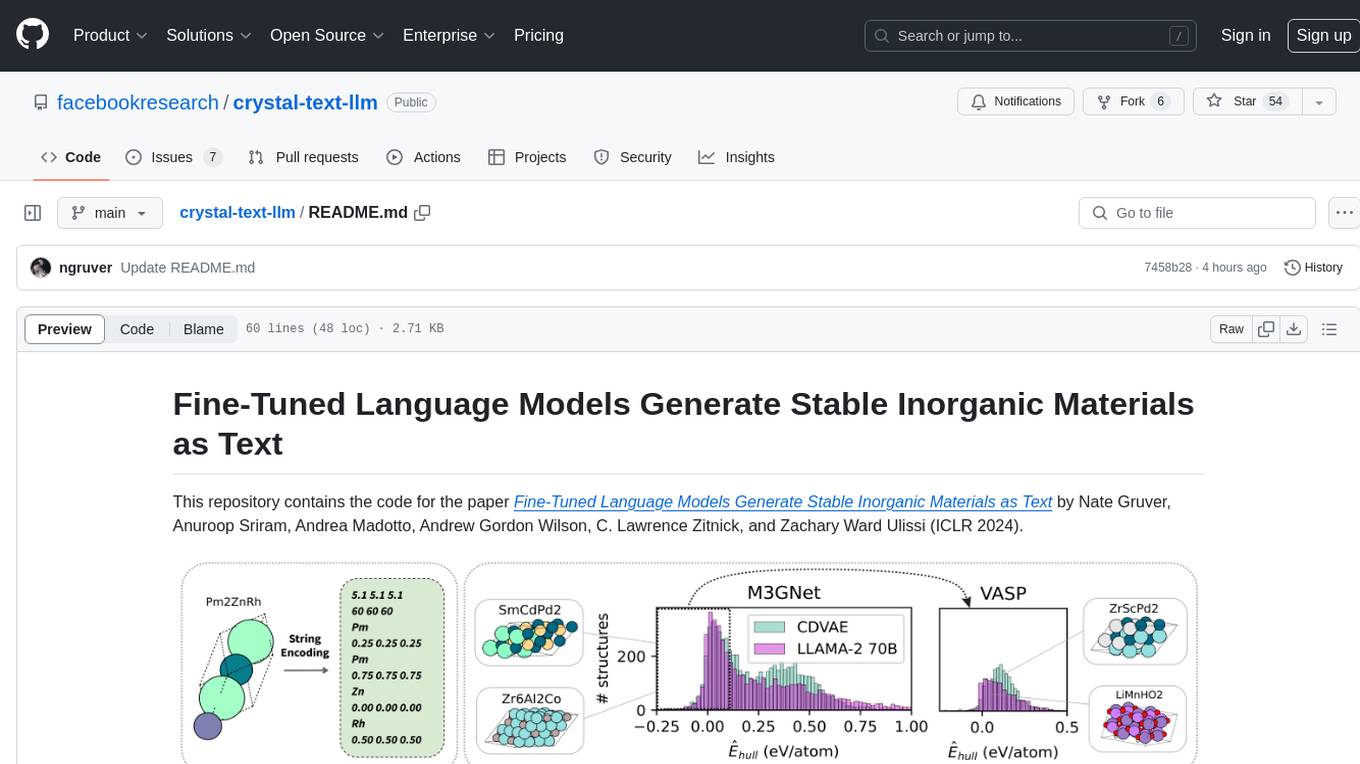
crystal-text-llm
This repository contains the code for the paper Fine-Tuned Language Models Generate Stable Inorganic Materials as Text. It demonstrates how finetuned LLMs can be used to generate stable materials, match or exceed the performance of domain specific models, mutate existing materials, and sample crystal structures conditioned on text descriptions. The method is distinct from CrystaLLM, which trains language models from scratch on CIF-formatted crystals.
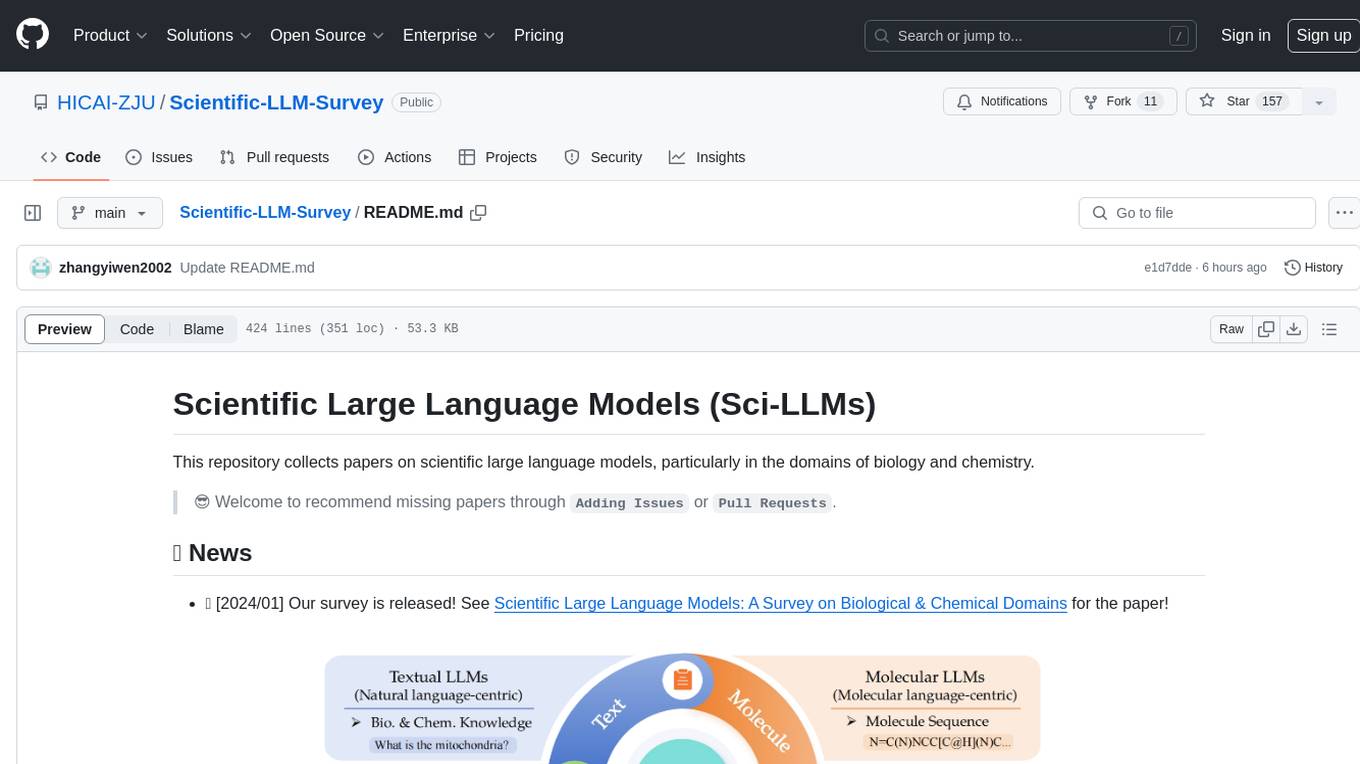
Scientific-LLM-Survey
Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs) is a repository that collects papers on scientific large language models, focusing on biology and chemistry domains. It includes textual, molecular, protein, and genomic languages, as well as multimodal language. The repository covers various large language models for tasks such as molecule property prediction, interaction prediction, protein sequence representation, protein sequence generation/design, DNA-protein interaction prediction, and RNA prediction. It also provides datasets and benchmarks for evaluating these models. The repository aims to facilitate research and development in the field of scientific language modeling.