
Scientific-LLM-Survey
Scientific Large Language Models: A Survey on Biological & Chemical Domains
Stars: 261
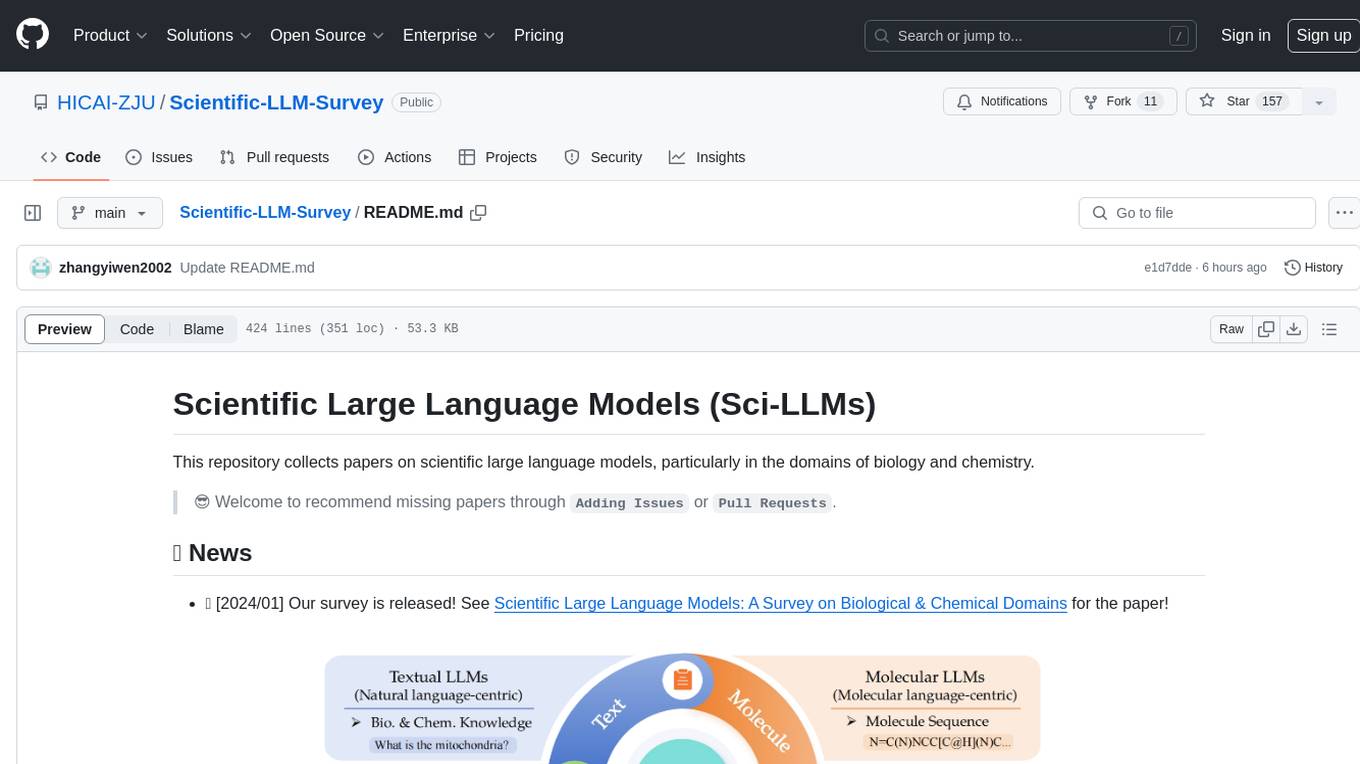
Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs) is a repository that collects papers on scientific large language models, focusing on biology and chemistry domains. It includes textual, molecular, protein, and genomic languages, as well as multimodal language. The repository covers various large language models for tasks such as molecule property prediction, interaction prediction, protein sequence representation, protein sequence generation/design, DNA-protein interaction prediction, and RNA prediction. It also provides datasets and benchmarks for evaluating these models. The repository aims to facilitate research and development in the field of scientific language modeling.
README:
This repository collects papers on scientific large language models, particularly in the domains of biology and chemistry.
😎 Welcome to recommend missing papers through
Adding IssuesorPull Requests.
-
💥 [2024/07] We have updated our survey paper by incorporating the latest related works. Please refer to the revised version on arXiv.
-
💥 [2024/01] Our survey paper 'Scientific Large Language Models: A Survey on Biological & Chemical Domains' has been released on arXiv.
 In this survey, we focus on scientific languages (i.e., textual, molecular, protein and genomic languages), as well as their combination (i.e., multimodal language).
In this survey, we focus on scientific languages (i.e., textual, molecular, protein and genomic languages), as well as their combination (i.e., multimodal language).
- Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs)
-
2019.04ClinicalBERT: Modeling Clinical Notes and Predicting Hospital Readmission, arXiv, Code -
2022.02GatorTron: A Large Clinical Language Model to Unlock Patient Information from Unstructured Electronic Health Records, arXiv, Model -
2022.12BioMedLM, .stanford.edu, huggingface -
2023.05A Study of Generative Large Language Model for Medical Research and Healthcare (GatorTronGPT), arXiv, Code -
2023.11MEDITRON-70B: Scaling Medical Pretraining for Large Language Models, arXiv, Code -
2024.03Small Language Models Learn Enhanced Reasoning Skills from Medical Textbooks (Meerkat), arXiv -
2023.06ClinicalGPT: Large Language Models Finetuned with Diverse Medical Data and Comprehensive Evaluation, arXiv -
2023.10Qilin-Med: Multi-stage Knowledge Injection Advanced Medical Large Language Model, arXiv, Code -
2023.03ChatDoctor: A Medical Chat Model Fine-Tuned on a Large Language Model Meta-AI (LLaMA) Using Medical Domain Knowledge, arXiv, Code -
2023.04HuaTuo: Tuning LLaMA Model with Chinese Medical Knowledge, arXiv, Code -
2023.05HuatuoGPT, towards Taming Language Model to Be a Doctor, arXiv, Code -
2023.04Baize: An Open-Source Chat Model with Parameter-Efficient Tuning on Self-Chat Data, arXiv, Code -
2023.08Zhongjing: Enhancing the Chinese Medical Capabilities of Large Language Model through Expert Feedback and Real-world Multi-turn Dialogue, arXiv, Code -
2023.04PMC-LLaMA: Towards Building Open-source Language Models for Medicine, arXiv, Code -
2023.09CPLLM: Clinical Prediction with Large Language Models, arXiv, Code -
2023.05Towards Expert-Level Medical Question Answering with Large Language Models(Med-PaLM 2), Google Research, arXiv -
2023.05Clinical Camel: An Open Expert-Level Medical Language Model with Dialogue-Based Knowledge Encoding, arXiv, Code -
2023.04DoctorGLM: Fine-tuning your Chinese Doctor is not a Herculean Task, arXiv, Code -
2023.10BianQue: Balancing the Questioning and Suggestion Ability of Health LLMs with Multi-turn Health Conversations Polished by ChatGPT, arXiv, Code -
2024.01Medical mT5: An Open-Source Multilingual Text-to-Text LLM for The Medical Domain, arXiv -
2024.02Me LLaMA: Foundation Large Language Models for Medical Applications, arXiv, Code -
2024.02BiMediX: Bilingual Medical Mixture of Experts LLM, arXiv, Code, Hugging Face
-
2019.04BioELMo: Probing Biomedical Embeddings from Language Models, arXiv, Code -
2019.05BioBERT: a pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining, arXiv, Code -
2019.07Transfer Learning in Biomedical Natural Language Processing: An Evaluation of BERT and ELMo on Ten Benchmarking Datasets, arXiv, Code -
2020.10BioMegatron: Larger Biomedical Domain Language Model, arXiv, Code -
2020.10Domain-Specific Language Model Pretraining for Biomedical Natural Language Processing, arXiv, Hugging Face -
2021.06BioM-Transformers: Building Large Biomedical Language Models with BERT, ALBERT and ELECTRA, ACL Anthology, Code -
2022.03LinkBERT: Pretraining Language Models with Document Links, arXiv, Code -
2023.03BioGPT: Generative Pre-trained Transformer for Biomedical Text Generation and Mining, arXiv, Code -
2023.08BioMedGPT: Open Multimodal Generative Pre-trained Transformer for BioMedicine, arXiv, Code -
2023.09BioinspiredLLM: Conversational Large Language Model for the Mechanics of Biological and Bio-Inspired Materials, arXiv -
2024.02BioMistral: BioMistral: A Collection of Open-Source Pretrained Large Language Models for Medical Domains, arXiv, Code
-
2021.06Automated Chemical Reaction Extraction from Scientific Literature. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, Code -
2021.09MatSciBERT: A materials domain language model for text mining and information extraction, npj Computational Materials, Code -
2022.09A general-purpose material property data extraction pipeline from large polymer corpora using natural language processing, npj Computational Materials, Hugging Face -
2024.01ChemDFM: Dialogue Foundation Model for Chemistry, arXiv, Model -
2024.02ChemLLM: A Chemical Large Language Model, arXiv, Model -
2024.02LlaSMol: Advancing Large Language Models for Chemistry with a Large-Scale, Comprehensive, High-Quality Instruction Tuning Dataset, arXiv, Page, Model, Dataset -
2024.02PharmaGPT: Domain-Specific Large Language Models for Bio-Pharmaceutical and Chemistry, arXiv
-
2019.09SciBERT: A Pretrained Language Model for Scientific Text, arXiv, Code -
2023.05The Diminishing Returns of Masked Language Models to Science, arXiv, Hugging Face -
2023.08DARWIN Series: Domain Specific Large Language Models for Natural Science, arXiv, Code -
2024.01SciGLM: Training Scientific Language Models with Self-Reflective Instruction Annotation and Tuning, arXiv, GitHub -
2024.03Uni-SMART: Universal Science Multimodal Analysis and Research Transformer, arXiv -
2024.05INDUS: Effective and Efficient Language Models for Scientific Applications,arXiv
-
The MIMIC dataset,
2016.05. mimic-code, Data Descriptor: MIMIC-III, a freely accessible critical care database, Scientific Data -
eICU-CRD.
2019.04. The eICU Collaborative Research Database, a freely available multi-center database for critical care research, Scientific Data -
cMedQA2,
2018.11. Multi-Scale Attentive Interaction Networks for Chinese Medical Question Answer Selection, IEEE Access - MedDialog-Chinese. MedDialog: Large-scale Medical Dialogue Datasets, EMNLP 2020
-
ChiMed.
2023.10. Qilin-Med: Multi-stage Knowledge Injection Advanced Medical Large Language Model, arXiv -
HealthCareMagic-100k,
2023.03. ChatDoctor: A Medical Chat Model Fine-Tuned on a Large Language Model Meta-AI (LLaMA) Using Medical Domain Knowledge, arXiv -
MedQuAD,
2019.01. A Question-Entailment Approach to Question Answering, arXiv -
MultiMedQA,
2023.07. Large language models encode clinical knowledge, Nature -
Open-I,
2015.07. Preparing a collection of radiology examinations for distribution and retrieval, JAMIA -
Psych8k,
2024.03. ChatCounselor: A Large Language Models for Mental Health Support, arXiv -
CMD. dataset,
2019.09. DoctorGLM: Fine-tuning your Chinese Doctor is not a Herculean Task, arXiv -
BianQueCorpus,
2023.10. BianQue: Balancing the Questioning and Suggestion Ability of Health LLMs with Multi-turn Health Conversations Polished by ChatGPT, arXiv -
MedQA-USMLE,
2021.04. What Disease does this Patient Have? A Large-scale Open Domain Question Answering Dataset from Medical Exams, arXiv -
MedMCQA,
2022.03. MedMCQA : A Large-scale Multi-Subject Multi-Choice Dataset for Medical domain Question Answering, arXiv -
JAMA Clinical Challenge dataset,
2024.05. Benchmarking Large Language Models on Answering and Explaining Challenging Medical Questions, arXiv -
CMtMedQA,
2023.08. Zhongjing: Enhancing the Chinese Medical Capabilities of Large Language Model through Expert Feedback and Real-world Multi-turn Dialogue, arXiv -
huatuo-26M,
2023.05. Huatuo-26M, a Large-scale Chinese Medical QA Dataset, arXiv -
MMLU,
2020.09. Measuring Massive Multitask Language Understanding, arXiv -
C-Eval,
2023.05. C-Eval: A Multi-Level Multi-Discipline Chinese Evaluation Suite for Foundation Models, arXiv -
AGIEval
2023.05. AGIEval: A Human-Centric Benchmark for Evaluating Foundation Models, arXiv - ScienceQA, 2022.09. Learn to Explain: Multimodal Reasoning via Thought Chains for Science Question Answering, arXiv
-
Xiezhi,
2023.06. Xiezhi: An Ever-Updating Benchmark for Holistic Domain Knowledge Evaluation, arXiv -
SciEval,
2023.08. SciEval: A Multi-Level Large Language Model Evaluation Benchmark for Scientific Research, arXiv -
Bioinfo-Bench,
2023.10. A Simple Benchmark Framework for LLM Bioinformatics Skills Evaluation, bioRxiv -
BLURB,
2020.07. Domain-Specific Language Model Pretraining for Biomedical Natural Language Processing, arXiv -
ARC,
2018.03. Think you have Solved Question Answering? Try ARC, the AI2 Reasoning Challenge, arXiv -
SciQ,
2017.07. Crowdsourcing Multiple Choice Science Questions, arXiv
-
2019.09SMILES-BERT: Large Scale Unsupervised Pre-Training for Molecular Property Prediction, ACM-BCB, Code -
2019.11SMILES Transformer: Pre-trained Molecular Fingerprint for Low Data Drug Discovery, arXiv, Code -
2020.02Molecule attention transformer, arXiv, Code -
2020.10ChemBERTa: Large-Scale Self-Supervised Pretraining for Molecular Property Prediction, arXiv, Code -
2020.10Self-Supervised Graph Transformer on Large-Scale Molecular Data, arXiv, Code -
2020.11Language models in molecular discovery, NeurIPS, Code -
2021.05MG-BERT: leveraging unsupervised atomic representation learning for molecular property prediction, Briefings in Bioinformatics, Code -
2021.06Algebraic graph-assisted bidirectional transformers for molecular property prediction, Nature Communications, Code -
2021.09Mol-BERT: An Effective Molecular Representation with BERT for Molecular Property Prediction, Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, Code -
2021.10Relative molecule self-attention transformer, Journal of Cheminformatics, Code -
2022.08KPGT: Knowledge-Guided Pre-training of Graph Transformer for Molecular Property Prediction, Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Code -
2022.09ChemBERTa-2: Towards Chemical Foundation Models, arXiv, Code -
2022.01Chemformer: a pre-trained transformer for computational chemistry, Mach. Learn.: Sci. Technol., Code -
2022.10Large-Scale Distributed Training of Transformers for Chemical Fingerprinting, JCIM, Code -
2022.11BARTSmiles: Generative Masked Language Models for Molecular Representations, arXiv, Code -
2022.12Large-Scale Chemical Language Representations Capture Molecular Structure and Properties, arXiv, Code -
2022.12Pushing the Boundaries of Molecular Property Prediction for Drug Discovery with Multitask Learning BERT Enhanced by SMILES Enumeration, Research, Code -
2023.01MolRoPE-BERT: An enhanced molecular representation with Rotary Position Embedding for molecular property prediction, Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling -
2023.01Molformer: Motif-based Transformer on 3D Heterogeneous Molecular Graphs, arXiv, Code -
2023.02UNI-MOL: A UNIVERSAL 3D MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION LEARNING FRAMEWORK, NeurIPS, Code -
2023.05SELFORMER: MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION LEARNING VIA SELFIES LANGUAGE MODELS, arXiv, Code -
2023.07Molecular Descriptors Property Prediction Using Transformer-Based Approach, IJMS -
2023.10GTMGC: USING GRAPH TRANSFORMER TO PREDICT MOLECULE’S GROUND-STATE CONFORMATION, ICLR
-
2020.12X-MOL: large-scale pre-training for molecular understanding and diverse molecular analysis, bioRxiv, Code
-
2021.05MolGPT: Molecular Generation Using a Transformer-Decoder Model, JCIM, Code -
2021.07Transmol: repurposing a language model for molecular generation, RSC Advances, Code -
2021.09GENERATIVE PRE-TRAINING FROM MOLECULES, ChemRxiv, Code -
2021.12Generative Chemical Transformer: Neural Machine Learning of Molecular Geometric Structures from Chemical Language via Attention, JCIM, Code -
2022.10A Pre-trained Conditional Transformer for Target-specific De Novo Molecular Generation, arXiv -
2023.05iupacGPT: IUPAC-based large-scale molecular pre-trained model for property prediction and molecule generation, ChemRxiv, Code -
2023.05cMolGPT: A Conditional Generative Pre-Trained Transformer for Target-Specific De Novo Molecular Generation, Molecules, Code -
2023.05Molecule generation using transformers and policy gradient reinforcement learning, Scientific Reports, Code -
2023.10DOMAIN-AGNOSTIC MOLECULAR GENERATION WITH SELF-FEEDBACK, arXiv, Code
-
2019.08Molecular Transformer: A Model for Uncertainty-Calibrated Chemical Reaction Prediction, ACS Cent. Sci., Code -
2019.08Molecular Transformer unifies reaction prediction and retrosynthesis across pharma chemical space, Chemical Communications -
2019.09A Transformer Model for Retrosynthesis, ICANN, Code -
2019.12Predicting Retrosynthetic Reaction using Self-Corrected Transformer Neural Networks, arXiv, Code -
2020.11State-of-the-art augmented NLP transformer models for direct and single-step retrosynthesis, Nature Communications, Code -
2021.01Valid, Plausible, and Diverse Retrosynthesis Using Tied Two-Way Transformers with Latent Variables, JCIM, Code -
2021.01Prediction of chemical reaction yields using deep learning, Mach. Learn.: Sci. Technol., Code -
2021.03Predicting Chemical Reaction Outcomes: A Grammar Ontology-based Transformer Framework, AIChE Journal -
2021.10Molecular Graph Enhanced Transformer for Retrosynthesis Prediction, Neurocomputing, Code -
2021.10PERMUTATION INVARIANT GRAPH-TO-SEQUENCE MODEL FOR TEMPLATE-FREE RETROSYNTHESIS AND REACTION PREDICTION, arXiv, Code -
2022.03Retrosynthetic reaction pathway prediction through neural machine translation of atomic environments, Nature Communications, Code -
2023.02Enhancing diversity in language based models for single-step retrosynthesis, Digital Discovery, Code -
2023.07Unbiasing Retrosynthesis Language Models with Disconnection Prompts, ACS Cent. Sci., Code
-
ZINC 15,
2015.10ZINC 15 – Ligand Discovery for Everyone, JCIM -
ZINC 20,
2020.12ZINC20—A Free Ultralarge-Scale Chemical Database for Ligand Discovery, JCIM -
ZINC-250k,
2012.07ZINC − A Free Database of Commercially Available Compounds for Virtual Screening, JCIM -
PubChem,
2023.01PubChem 2023 update, Nucleic Acids Research -
USPTO, USPTO MIT, USPTO-15K, USPTO-full,
2012.10Extraction of chemical structures and reactions from the literature, University of Cambridge -
PCQM4Mv2,
2021.10OGB-LSC: A Large-Scale Challenge for Machine Learning on Graphs, arXiv -
PCQM4M-LSC,
2021.06First Place Solution of KDD Cup 2021 & OGB Large-Scale Challenge Graph Prediction Track, arXiv -
GEOM,
2022.04GEOM, energy-annotated molecular conformations for property prediction and molecular generation, Nature -
ToyMix, LargeMix, UltraLarge,
2023.10Towards Foundational Models for Molecular Learning on Large-Scale Multi-Task Datasets, arXiv -
ChEMBL,
2023.05The ChEMBL Database in 2023: a drug discovery platform spanning multiple bioactivity data types and time periods, Nucleic Acids Research -
DrugBank 5.0,
2017.11DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018, Nucleic Acids Research -
GDB-17,
2012.10Enumeration of 166 Billion Organic Small Molecules in the Chemical Universe Database GDB-17, JCIM -
ExCAPE-DB,
2017.03ExCAPE-DB: an integrated large scale dataset facilitating Big Data analysis in chemogenomics, Journal of Cheminformatics -
MoleculeNet,
2017.10MoleculeNet: a benchmark for molecular machine learning, Chemical Science -
MARCEL,
2023.09Learning Over Molecular Conformer Ensembles: Datasets and Benchmarks, arXiv -
GuacaMol,
2019.03GuacaMol: Benchmarking Models for de Novo Molecular Design, JCIM -
MOSES,
2020.12Molecular Sets (MOSES): A Benchmarking Platform for Molecular Generation Models, Frontiers in Pharmacology -
ADMETlab 2.0,
2021.04ADMETlab 2.0: an integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMET properties, Nucleic Acids Research -
SPECTRA,
2024.02Evaluating generalizability of artificial intelligence models for molecular datasets, bioRxiv -
Molecule3D,
2021.09Molecule3D: A Benchmark for Predicting 3D Geometries from Molecular Graphs, arXiv
-
2020.02Biological Structure and Function Emerge from Scaling Unsupervised Learning to 250 Million Protein Sequences, PNAS, Code -
2021.02MSA transformer, PMLR, Code -
2021.02Multi-scale representation learning on proteins, Neurips -
2021.02Language models enable zero-shot prediction of the effects of mutations on protein function, Neurips, Code -
2021.07ProtTrans: Toward Understanding the Language of Life Through Self-Supervised Learning, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Code -
2021.07Pre-training Co-evolutionary Protein Representation via A Pairwise Masked Language Model, CoRR -
2021.09Toward more general embeddings for protein design: Harnessing joint representations of sequence and structure, bioRxiv -
2022.02ProteinBERT: a universal deep-learning model of protein sequence and function, bioRxiv, Code -
2022.04Lm-gvp: an extensible sequence and structure informed deep learning framework for protein property prediction, bioRxiv, Code -
2022.05Retrieved Sequence Augmentation for Protein Representation Learning, bioRxiv, Code -
2022.06OntoProtein: Protein Pretraining With Gene Ontology Embedding, arXiv, Code -
2022.07Language models of protein sequences at the scale of evolution enable accurate structure prediction, bioRxiv, Code -
2023.02Multi-level Protein Structure Pre-training via Prompt Learning, ICLR, Code -
2023.02Protein Representation Learning via Knowledge Enhanced Primary Structure Modeling, arXiv, Code -
2023.10Deciphering the protein landscape with ProtFlash, a lightweight language model, bioRxiv, Code -
2023.10Enhancing protein language models with structure-based encoder and pre-training, arXiv, Code -
2023.10Saprot: Protein language modeling with structure-aware vocabulary, bioRxiv, Code -
2023.12ProteinNPT: Improving Protein Property Prediction and Design with Non-Parametric Transformers, bioRxiv -
2024.02Codon language embeddings provide strong signals for use in protein engineering, Nature Machine Intelligence, Code -
2024.04Pre-training Sequence, Structure, and Surface Features for Comprehensive Protein Representation Learning, ICLR -
2024.06ESM All-Atom: Multi-scale Protein Language Model for Unified Molecular Modeling, bioRxiv -
2024.06Knowledge-aware Reinforced Language Models for Protein Directed Evolution, ICML -
2024.06Simulating 500 million years of evolution with a language model, bioRxiv, Code
-
2020.03ProGen: Language Modeling for Protein Generation, arXiv, Code -
2021.01A deep unsupervised language model for protein design, bioRxiv, Code -
2021.01Fold2seq: A joint sequence (1d)-fold (3d) embedding-based generative model for protein design, PMLR, Code -
2022.01ZymCTRL: a conditional language model for the controllable generation of artificial enzymes, NeurIPS, Code -
2022.04Few Shot Protein Generation, arXiv -
2022.05RITA: a Study on Scaling Up Generative Protein Sequence Models, arXiv -
2022.12Generative language modeling for antibody design, arXiv, Code -
2023.02Structure-informed Language Models Are Protein Designers, bioRxiv -
2023.02Generative power of a protein language model trained on multiple sequence alignments, Elife, Code -
2023.02Protein sequence design in a latent space via model-based reinforcement learning, ICLR -
2023.06Enhancing the Protein Tertiary Structure Prediction by Multiple Sequence Alignment Generation, arXiv, Code -
2023.07ProstT5: Bilingual Language Model for Protein Sequence and Structure, bioRxiv, Code -
2023.07xTrimoPGLM: unified 100B-scale pre-trained transformer for deciphering the language of protein, bioRxiv -
2023.08Efficient and accurate sequence generation with small-scale protein language models, bioRxiv -
2023.10Generative Antibody Design for Complementary Chain Pairing Sequences through Encoder-Decoder Language Model, NeurIPS -
2023.10ProGen2: exploring the boundaries of protein language models, Cell, Code -
2023.10ProteinRL: Reinforcement learning with generative protein language models for property-directed sequence design, NeurIPS -
2023.11PoET: A generative model of protein families as sequences-of-sequences, arXiv -
2024.03Protein Discovery with Discrete Walk-Jump Sampling, arxiv.
-
UniRef100, 90, 50,
2007.03UniRef: comprehensive and non-redundant UniProt reference clusters, Bioinformatics -
UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot,
2016.01UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot, the manually annotated section of the UniProt KnowledgeBase: how to use the entry view, Springer Plant Bioinformatics -
UniProtKB/TrEMBL,
1999.03EDITtoTrEMBL: a distributed approach to high-quality automated protein sequence annotation, Bioinformatics -
UniParc,
2022.11UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023, Bioinformatics -
Pfam,
1999.03Pfam: clans, web tools and services, Nucleic Acids Research -
BFD,
2018.06Clustering huge protein sequence sets in linear time, Nature Communications -
PDB,
2018.10Protein Data Bank: the single global archive for 3D macromolecular structure data, Nucleic Acids Research -
AlphaFoldDB,
2021.11AlphaFold Protein Structure Database: massively expanding the structural coverage of protein-sequence space with high-accuracy models, Nucleic Acids Research -
CASP,
2021.09Critical assessment of methods of protein structure prediction (CASP)—Round XIV, PROTEINS -
EC,
2008.09ExplorEnz: the primary source of the IUBMB enzyme list, Nucleic Acids Research -
GO,
2000.05Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology, Nature Genetics -
CATH,
1997.08CATH--a hierarchic classification of protein domain structures, NIH -
HIPPIE,
2012.02HIPPIE: Integrating protein interaction networks with experiment based quality scores, PLoS ONE -
SCOP,
2000.01SCOP: a structural classification of proteins database, Nucleic Acids Research -
ProteinGym,
2023.09Proteingym: Large-scale benchmarks for protein fitness prediction and design, NeurIPS -
FLIP,
2022.01FLIP: Benchmark tasks in fitness landscape inference for proteins, bioRxiv -
PEER,
2022.09Peer: a comprehensive and multi-task benchmark for protein sequence understanding, NeurIPS -
TAPE,
2019.09Evaluating Protein Transfer Learning with TAPE, NeurIPS
-
2021.02DNABERT: pre-trained Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers model for DNA-language in genome Bioinformatics -
2022.08MoDNA: motif-oriented pre-training for DNA language model ACM-BCB -
2023.01Species-aware DNA language modeling bioRxiv -
2023.01The Nucleotide Transformer: Building and Evaluating Robust Foundation Models for Human Genomics bioRxiv -
2023.06HyenaDNA: Long-Range Genomic Sequence Modeling at Single Nucleotide Resolution arXiv -
2023.06DNABERT-2: Efficient Foundation Model and Benchmark For Multi-Species Genome arXiv -
2023.06GENA-LM: A Family of Open-Source Foundational Models for Long DNA Sequences bioRxiv -
2023.06Geneformer: Transfer learning enables predictions in network biology bioRxiv -
2023.07EpiGePT: a Pretrained Transformer model for epigenomics bioRxiv -
2023.08Understanding the Natural Language of DNA using Encoder-Decoder Foundation Models with Byte-level Precision bioRxiv -
2023.08DNAGPT: A Generalized Pre-trained Tool for Versatile DNA Sequence Analysis Tasks bioRxiv -
2024.02Evo: Sequence modeling and design from molecular to genome scale with Evo Nature -
2024.02GenomicLLM: Exploring Genomic Large Language Models: Bridging the Gap between Natural Language and Gene Sequences BioRxiv
-
2021.10Effective gene expression prediction from sequence by integrating long-range interactions Nature Methods -
2022.08iEnhancer-BERT: A Novel Transfer Learning Architecture Based on DNA-Language Model for Identifying Enhancers and Their Strength ICIC 2022 -
2022.10iDNA-ABF: multi-scale deep biological language learning model for the interpretable prediction of DNA methylations Genome Biology -
2022.12iEnhancer-ELM: improve enhancer identification by extracting position-related multiscale contextual information based on enhancer language models arXiv -
2023.03miProBERT: identification of microRNA promoters based on the pre-trained model BERT Briefings in Bioinformatics -
2023.07PLPMpro: Enhancing promoter sequence prediction with prompt-learning based pre-trained language model Computers in Biology and Medicine -
2024.02FGBERT: Function-Driven Pre-trained Gene Language Model for Metagenomics ArXiv
-
2022.08DNA language models are powerful predictors of genome-wide variant effects bioRxiv -
2022.10GenSLMs: Genome-scale language models reveal SARS-CoV-2 evolutionary dynamics bioRxiv -
2023.10GPN-MSA: an alignment-based DNA language model for genome-wide variant effect prediction bioRxiv -
2024.12Bio-xLSTM: Generative modeling, representation and in-context learning of biological and chemical sequences ArXiv
-
2023.05Improving language model of human genome for DNA–protein binding prediction based on task-specific pre-training Interdisciplinary Sciences: Computational Life Sciences -
2024.04gLM: Genomic language model predicts protein co-regulation and function BioRxiv
-
2023.02Self-supervised learning on millions of pre-mRNA sequences improves sequence-based RNA splicing prediction bioRxiv -
2023.03Multiple sequence-alignment-based RNA language model and its application to structural inference bioRxiv -
2023.06Prediction of Multiple Types of RNA Modifications via Biological Language Model IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics -
2023.07Uni-RNA: Universal Pre-trained Models Revolutionize RNA Research bioRxiv -
2024.02RiNALMo: General-Purpose RNA Language Models Can Generalize Well on Structure Prediction Tasks ArXiv -
2024.05RNAErnie: Multi-purpose RNA language modelling with motif-aware pretraining and type-guided fine-tuning Nature Machine Intelligence
-
MGC,
1999.10The Mammalian Gene Collection Science -
GRCh38,
2013.12Improvements and impacts of GRCh38 human reference on high throughput sequencing data analysis Genomics -
690 ChIP-seq,
2016.06Convolutional neural network architectures for predicting DNA–protein binding -
DeepSEA,
2017.04Predicting effects of noncoding variants with deep learning–based sequence model Nature Methods -
1000 Genomes Project,
2017.10A global reference for human genetic variation Nature -
EPDnew,
2019.11EPD and EPDnew, high-quality promoter resources in the next-generation sequencing era Nucleic Acids Research -
Panglao Dataset,
2020.03PanglaoDB: a web server for exploration of mouse and human single-cell RNA sequencing data Database -
ExPecto,
2020.12Sequence-based prediction of variants’ effects Nature Methods -
UCSC Genome Database,
2022.11The UCSC Genome Browser Database Nucleic Acids Research -
BV-BRC,
2023.01Introducing the Bacterial and Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center (BV-BRC): a resource combining PATRIC, IRD and ViPR Nucleic Acids Research -
Ensembl,
2023.02The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): improved gene annotation and new tools Nucleic Acids Research -
RNAcmap,
2023.07RNAcmap: a fully automatic pipeline for predicting contact maps of RNAs by evolutionary coupling analysis -
ENCODE,
2023.09An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome Nature -
NCBI Genome Database,
2023.10 -
TAIR,
2023.12The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): improved gene annotation and new tools Nucleic Acids Research -
VGDB,
2023.12Viral Genome DataBase: storing and analyzing genes and proteins from complete viral genomes Bioinformatics -
CAGI5,
2023.07CAGI5: Objective performance assessments of predictions based on the Evolutionary Action equation Human Mutation -
Protein–RNA Interaction Prediction,
2023.08A systematic benchmark of machine learning methods for protein–RNA interaction prediction -
The Nucleaotide Transformer Benchmark,
2023.09The Nucleotide Transformer: Building and Evaluating Robust Foundation Models for Human Genomics -
GenBench
2024.06GenBench: A Benchmarking Suite for Systematic Evaluation of Genomic Foundation Models ArXiv - BEACON BEACON: Benchmark for Comprehensive RNA Tasks and Language Models ArXiv
-
2021.11Text2Mol: Cross-Modal Molecule Retrieval with Natural Language Queries, EMNLP, Code -
2022.02KV-PLM: A deep-learning system bridging molecule structure and biomedical text with comprehension comparable to human professionals, Nature, Code -
2022.09MoMu: A Molecular Multimodal Foundation Model Associating Molecule Graphs with Natural Language, arXiv, Code -
2022.11MolT5: Translation between Molecules and Natural Language, arXiv, Code -
2023.05Text+Chem T5: Unifying Molecular and Textual Representations via Multi-task Language Modelling, arXiv, Code -
2023.05DrugChat: Towards Enabling ChatGPT-Like Capabilities on Drug Molecule Graphs, techRxiv, Code -
2023.06Enhancing Activity Prediction Models in Drug Discovery with the Ability to Understand Human Language, arXiv, Code -
2023.06GIMLET: A Unified Graph-Text Model for Instruction-Based Molecule Zero-Shot Learning, bioRxiv, Code -
2023.06MolReGPT: Empowering Molecule Discovery for Molecule-Caption Translation with Large Language Models: A ChatGPT Perspective, arXiv, Code -
2023.06ChatMol: Interactive Molecular Discovery with Natural Language, arXiv, Code -
2023.07MolXPT: Wrapping Molecules with Text for Generative Pre-training, ACL -
2023.07MolFM: A Multimodal Molecular Foundation Model, arXiv, Code -
2023.08GIT-Mol: A Multi-modal Large Language Model for Molecular Science with Graph, Image, and Text, arXiv -
2023.10GPT-MolBERTa: GPT Molecular Features Language Model for molecular property prediction, arXiv, Code -
2023.12MoleculeSTM: Multi-modal Molecule Structure-text Model for Text-based Retrieval and Editing, arXiv, Code -
2024.04Atomas: Hierarchical Alignment on Molecule-Text for Unified Molecule Understanding and Generation, arXiv, Code -
2024.05DrugLLM: Open Large Language Model for Few-shot Molecule Generation, arXiv -
2024.063D-MolT5: Towards Unified 3D Molecule-Text Modeling with 3D Molecular Tokenization, arXiv -
2024.06MolecularGPT: Open Large Language Model (LLM) for Few-Shot Molecular Property Prediction, arXiv, Code -
2024.10Chemical Language Model Linker: blending text and molecules with modular adapters, arXiv, Code -
2024.11MolReFlect: Towards In-Context Fine-grained Alignments between Molecules and Texts, arXiv
-
2022.04ProTranslator: zero-shot protein function prediction using textual description, arXiv, Code -
2023.02ProteinDT: A Text-guided Protein Design Framework, arXiv -
2023.07ProtST: Multi-Modality Learning of Protein Sequences and Biomedical Texts, arXiv, Code -
2023.07Prot2Text: Multimodal Protein's Function Generation with GNNs and Transformers, arXiv -
2023.10InstructProtein: Aligning Human and Protein Language via Knowledge Instruction, arXiv -
2024.02ProtLLM: An Interleaved Protein-Language LLM with Protein-as-Word Pre-Training, arXiv, Code -
2024.02ProtChatGPT: Towards Understanding Proteins with Large Language Models, arXiv -
2024.02ProLLaMA: A Protein Large Language Model for Multi-Task Protein Language Processing, arXiv, Code -
2024.04Functional Protein Design with Local Domain Alignment, arXiv -
2024.05ProtT3: Protein-to-Text Generation for Text-based Protein Understanding, arXiv, Code -
2024.05ProteinCLIP: enhancing protein language models with natural language, bioArXiv, Code -
2024.07ProLLM: Protein Chain-of-Thoughts Enhanced LLM for Protein-Protein Interaction Prediction, bioArXiv, Code -
2024.08ProteinGPT: Multimodal LLM for Protein Property Prediction and Structure Understanding, arXiv -
2024.10ProteinAligner: A Multi-modal Pretraining Framework for Protein Foundation Models, bioArXiv, Code -
2024.10Structure-Enhanced Protein Instruction Tuning: Towards General-Purpose Protein Understanding, arXiv -
2024.10TourSynbio: A Multi-Modal Large Model and Agent Framework to Bridge Text and Protein Sequences for Protein Engineering, IEEE 2024, Code -
2024.12ProtDAT: A Unified Framework for Protein Sequence Design from Any Protein Text Description, arXiv, Code
-
2022.09ChemBERTaLM: Exploiting pretrained biochemical language models for targeted drug design, Bioinformatics, Code -
2023.03Deep generative model for drug design from protein target sequence, Journal of Cheminformatics , Code -
2023.06DrugGPT: A GPT-based Strategy for Designing Potential Ligands Targeting Specific Proteins, bioRxiv, Code -
2023.10DrugCLIP: Contrastive Protein-Molecule Representation Learning for Virtual Screening, arXiv -
2024.10scChat: A Large Language Model-Powered Co-Pilot for Contextualized Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Analysis, bioArXiv, Code -
2024.10BioLLMNet: Enhancing RNA-Interaction Prediction with a Specialized Cross-LLM Transformation Network, bioArXiv
-
2023.09Cell2Sentence: Teaching Large Language Models the Language of Biology, bioRxiv, Code -
2023.10CELLPLM: PRE-TRAINING OF CELL LANGUAGE MODEL BEYOND SINGLE CELLS, ICLR, Code -
2023.10GenePT: A Simple But Effective Foundation Model for Genes and Cells Built From ChatGPT, bioRxiv, Code -
2024.02ChatCell: Facilitating Single-Cell Analysis with Natural Language, arXiv, Code -
2024.03Assessing GPT-4 for cell type annotation in single-cell RNA-seq analysis, Nature Methods, Code -
2024.03Joint Embedding of Transcriptomes and Text Enables Interactive Single-Cell RNA-seq Data Exploration via Natural Language, ICLR, Code -
2024.06LangCell: Language-Cell Pre-training for Cell Identity Understanding, arXiv, Code -
2024.11RNA-GPT: Multimodal Generative System for RNA Sequence Understanding, NeurIPS 2024 -
2024.11BioLLM: A Standardized Framework for Integrating and Benchmarking Single-Cell Foundation Models, bioArxiv, Code
-
2022.11Galactica: A Large Language Model for Science, arXiv, Code -
2023.02BioTranslator: Multilingual translation for zero-shot biomedical classification using BioTranslator, Nature, Code -
2023.05ChatDrug: ChatGPT-powered Conversational Drug Editing Using Retrieval and Domain Feedback, arXiv, Code -
2023.08BioMedGPT:A Pre-trained Language Model for Biomedical Text Mining, arXiv, Code -
2023.08DARWIN Series: Domain Specific Large Language Models for Natural Science, arXiv, Code -
2023.10BioT5: Enriching Cross-modal Integration in Biology with Chemical Knowledge and Natural Language Associations, arXiv, Code -
2023.11Mol-Instructions: A Large-Scale Biomolecular Instruction Dataset for Large Language Models, arXiv, Code -
2024.01BioBridge: Bridging Biomedical Foundation Models via Knowledge Graphs, arXiv, Code -
2024.02LlaSMol: Advancing Large Language Models for Chemistry with a Large-Scale, Comprehensive, High-Quality Instruction Tuning Dataset, arXiv, Page, Model, Dataset -
2024.02Sequence modeling and design from molecular to genome scale with Evo, bioRxiv, Code -
2024.02BioT5+: Towards Generalized Biological Understanding with IUPAC Integration and Multi-task Tuning, arXiv, Code -
2024.04MolBind: Multimodal Alignment of Language, Molecules, and Proteins, arXiv, Code -
2024.06Uni-SMART: Universal Science Multimodal Analysis and Research Transformer, arXiv -
2024.07SciMind: A Multimodal Mixture-of-Experts Model for Advancing Pharmaceutical Sciences, ACL Workshop -
2024.10BSM: Small but Powerful Biological Sequence Model for Genes and Proteins, arXiv -
2024.10MAMMAL -- Molecular Aligned Multi-Modal Architecture and Language, arXiv, Code
-
ChEBI-20,
2021.11Text2mol: Cross-modal molecule retrieval with natural language queries, EMNLP2021 -
PCdes,
2022.02A deep-learning system bridging molecule structure and biomedical text with comprehension comparable to human professionals, Nature -
MoMu,
2022.09A Molecular Multimodal Foundation Model Associating Molecule Graphs with Natural Language, arXiv -
PubChemSTM,
2022.12. Multi-modal Molecule Structure-text Model for Text-based Retrieval and Editing, arXiv -
ChEBL-dia,
2023.06ChatMol: Interactive Molecular Discovery with Natural Language, arXiv -
PubChemQA,
2023.08BioMedGPT:A Pre-trained Language Model for Biomedical Text Mining, arXiv -
MoleculeQA,
2024.03MoleculeQA: A Dataset to Evaluate Factual Accuracy in Molecular Comprehension, arXiv -
MolCap-Arena,
2024.11MolCap-Arena: A Comprehensive Captioning Benchmark on Language-Enhanced Molecular Property Prediction, arXiv -
TOMG-Bench,
2024.12TOMG-Bench: Evaluating LLMs on Text-based Open Molecule Generation, arXiv
- SwissProtCLAP,
2023.02ProteinDT: A Text-guided Protein Design Framework, arXiv -
ProtDescribe,
2023.07ProtST: Multi-Modality Learning of Protein Sequences and Biomedical Texts, arXiv - Prot2Text,
2023.07Prot2Text: Multimodal Protein's Function Generation with GNNs and Transformers, arXiv -
UniProtQA,
2023.08BioMedGPT:A Pre-trained Language Model for Biomedical Text Mining, arXiv - InstructProtein,
2023.10InstructProtein: Aligning Human and Protein Language via Knowledge Instruction, arXiv -
ProteinLMDataset,ProteinLMBench,
2024.06A Fine-tuning Dataset and Benchmark for Large Language Models for Protein Understanding, arXiv -
OPI,
2024.11OPI: An Open Instruction Dataset for Adapting Large Language Models to Protein-Related Tasks, Neurips 2024
-
DUD-E,
2012.06Directory of Useful Decoys, Enhanced (DUD-E): Better Ligands and Decoys for Better Benchmarking, Journal of Medicinal Chemistry -
BioLiP,
2012.10BioLiP: a semi-manually curated database for biologically relevant ligand–protein interactions, Nucleic Acids Research -
BindingDB,
2016.01BindingDB in 2015: A public database for medicinal chemistry, computational chemistry and systems pharmacology, Nucleic Acids Research
-
GEO,
2016The gene expression omnibus database, Methods Mol Biol -
The Human Cell Atlas,
2017.12The Human Cell Atlas, eLife -
ARCHS4,
2018.04Massive mining of publicly available RNA-seq data from human and mouse, Nat Commun -
NCBI,
2020.10Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information, Nucleic Acids Res -
SRT,
2021.11High-Plex Multiomic Analysis in FFPE Tissue at Single-Cellular and Subcellular Resolution by Spatial Molecular Imaging, bioRxiv -
cellxgene,
2021.04cellxgene: a performant, scalable exploration platform for high dimensional sparse matrices, arXiv -
CellTypist,
2022.05Cross-tissue immune cell analysis reveals tissue-specific features in humans, arXiv - scLibrary,
2024.06LangCell: Language-Cell Pre-training for Cell Identity Understanding, arXiv
- Galactica,
2022.11Galactica: A Large Language Model for Science, arXiv -
Scientific Knowledge Dataset,
2023.08DARWIN Series: Domain Specific Large Language Models for Natural Science, arXiv -
Mol-Instructions,
2023.10Mol-Instructions: A Large-Scale Biomolecular Instruction Dataset for Large Language Models, arXiv -
SMolInstruct,
2024.02LlaSMol: Advancing Large Language Models for Chemistry with a Large-Scale, arXiv -
MolBind-M4,
2024.04MolBind: Multimodal Alignment of Language, Molecules, and Proteins, arXiv
If you find this repository useful, please cite our paper:
@misc{zhang2024scientific,
title={Scientific Large Language Models: A Survey on Biological & Chemical Domains},
author={Qiang Zhang and Keyan Ding and Tianwen Lyv and Xinda Wang and Qingyu Yin and Yiwen Zhang and Jing Yu and Yuhao Wang and Xiaotong Li and Zhuoyi Xiang and Xiang Zhuang and Zeyuan Wang and Ming Qin and Mengyao Zhang and Jinlu Zhang and Jiyu Cui and Renjun Xu and Hongyang Chen and Xiaohui Fan and Huabin Xing and Huajun Chen},
year={2024},
eprint={2401.14656},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}
- Keyan Ding @dingkeyan93
- Jing Yu @jiing17
- Tianwen Lyu @smiling-k
- Yiwen Zhang @zhangyiwen2002
- Xinda Wang @Wwwduojin
- Qingyu Yin @MikaStars39
- Xinda Wang [email protected]
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Scientific-LLM-Survey
Similar Open Source Tools

Scientific-LLM-Survey
Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs) is a repository that collects papers on scientific large language models, focusing on biology and chemistry domains. It includes textual, molecular, protein, and genomic languages, as well as multimodal language. The repository covers various large language models for tasks such as molecule property prediction, interaction prediction, protein sequence representation, protein sequence generation/design, DNA-protein interaction prediction, and RNA prediction. It also provides datasets and benchmarks for evaluating these models. The repository aims to facilitate research and development in the field of scientific language modeling.

interpreto
Interpreto is an interpretability toolkit for large language models (LLMs) that provides a modular framework encompassing attribution methods, concept-based methods, and evaluation metrics. It includes various inference-based and gradient-based attribution methods for both classification and generation tasks. The toolkit also offers concept-based explanations to provide high-level interpretations of latent model representations through steps like concept discovery, interpretation, and concept-to-output attribution. Interpreto aims to enhance model interpretability and facilitate understanding of model decisions and outputs.
ProLLM
ProLLM is a framework that leverages Large Language Models to interpret and analyze protein sequences and interactions through natural language processing. It introduces the Protein Chain of Thought (ProCoT) method to transform complex protein interaction data into intuitive prompts, enhancing predictive accuracy by incorporating protein-specific embeddings and fine-tuning on domain-specific datasets.
LLM-as-HH
LLM-as-HH is a codebase that accompanies the paper ReEvo: Large Language Models as Hyper-Heuristics with Reflective Evolution. It introduces Language Hyper-Heuristics (LHHs) that leverage LLMs for heuristic generation with minimal manual intervention and open-ended heuristic spaces. Reflective Evolution (ReEvo) is presented as a searching framework that emulates the reflective design approach of human experts while surpassing human capabilities with scalable LLM inference, Internet-scale domain knowledge, and powerful evolutionary search. The tool can improve various algorithms on problems like Traveling Salesman Problem, Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem, Orienteering Problem, Multiple Knapsack Problems, Bin Packing Problem, and Decap Placement Problem in both black-box and white-box settings.
interpret
InterpretML is an open-source package that incorporates state-of-the-art machine learning interpretability techniques under one roof. With this package, you can train interpretable glassbox models and explain blackbox systems. InterpretML helps you understand your model's global behavior, or understand the reasons behind individual predictions. Interpretability is essential for: - Model debugging - Why did my model make this mistake? - Feature Engineering - How can I improve my model? - Detecting fairness issues - Does my model discriminate? - Human-AI cooperation - How can I understand and trust the model's decisions? - Regulatory compliance - Does my model satisfy legal requirements? - High-risk applications - Healthcare, finance, judicial, ...
MathCoder
MathCoder is a repository focused on enhancing mathematical reasoning by fine-tuning open-source language models to use code for modeling and deriving math equations. It introduces MathCodeInstruct dataset with solutions interleaving natural language, code, and execution results. The repository provides MathCoder models capable of generating code-based solutions for challenging math problems, achieving state-of-the-art scores on MATH and GSM8K datasets. It offers tools for model deployment, inference, and evaluation, along with a citation for referencing the work.
InstructGraph
InstructGraph is a framework designed to enhance large language models (LLMs) for graph-centric tasks by utilizing graph instruction tuning and preference alignment. The tool collects and decomposes 29 standard graph datasets into four groups, enabling LLMs to better understand and generate graph data. It introduces a structured format verbalizer to transform graph data into a code-like format, facilitating code understanding and generation. Additionally, it addresses hallucination problems in graph reasoning and generation through direct preference optimization (DPO). The tool aims to bridge the gap between textual LLMs and graph data, offering a comprehensive solution for graph-related tasks.
Adaptive-MT-LLM-Fine-tuning
The repository Adaptive-MT-LLM-Fine-tuning contains code and data for the paper 'Fine-tuning Large Language Models for Adaptive Machine Translation'. It focuses on enhancing Mistral 7B, a large language model, for real-time adaptive machine translation in the medical domain. The fine-tuning process involves using zero-shot and one-shot translation prompts to improve terminology and style adherence. The repository includes training and test data, data processing code, fuzzy match retrieval techniques, fine-tuning methods, conversion to CTranslate2 format, tokenizers, translation codes, and evaluation metrics.
TxAgent
TxAgent is an AI agent designed for precision therapeutics, leveraging multi-step reasoning and real-time biomedical knowledge retrieval across a toolbox of 211 tools. It evaluates drug interactions, contraindications, and tailors treatment strategies to individual patient characteristics. TxAgent outperforms leading models across various drug reasoning tasks and personalized treatment scenarios, ensuring treatment recommendations align with clinical guidelines and real-world evidence.
KG-LLM-Papers
KG-LLM-Papers is a repository that collects papers integrating knowledge graphs (KGs) and large language models (LLMs). It serves as a comprehensive resource for research on the role of KGs in the era of LLMs, covering surveys, methods, and resources related to this integration.
stochastic-rs
stochastic-rs is a high-performance Rust library for simulating and analyzing stochastic processes. It is designed for applications in quantitative finance, AI training, and statistical modeling, providing efficient tools to generate synthetic data and analyze complex stochastic systems. The library is actively developed and welcomes contributions such as bug reports, feature suggestions, and documentation improvements. It is licensed under the MIT License.
FATE-LLM
FATE-LLM is a framework supporting federated learning for large and small language models. It promotes training efficiency of federated LLMs using Parameter-Efficient methods, protects the IP of LLMs using FedIPR, and ensures data privacy during training and inference through privacy-preserving mechanisms.
Genesis
Genesis is a physics platform designed for general purpose Robotics/Embodied AI/Physical AI applications. It includes a universal physics engine, a lightweight, ultra-fast, pythonic, and user-friendly robotics simulation platform, a powerful and fast photo-realistic rendering system, and a generative data engine that transforms user-prompted natural language description into various modalities of data. It aims to lower the barrier to using physics simulations, unify state-of-the-art physics solvers, and minimize human effort in collecting and generating data for robotics and other domains.
pywhy-llm
PyWhy-LLM is an innovative library that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) into the causal analysis process, empowering users with knowledge previously only available through domain experts. It seamlessly augments existing causal inference processes by suggesting potential confounders, relationships between variables, backdoor sets, front door sets, IV sets, estimands, critiques of DAGs, latent confounders, and negative controls. By leveraging LLMs and formalizing human-LLM collaboration, PyWhy-LLM aims to enhance causal analysis accessibility and insight.
MMC
This repository, MMC, focuses on advancing multimodal chart understanding through large-scale instruction tuning. It introduces a dataset supporting various tasks and chart types, a benchmark for evaluating reasoning capabilities over charts, and an assistant achieving state-of-the-art performance on chart QA benchmarks. The repository provides data for chart-text alignment, benchmarking, and instruction tuning, along with existing datasets used in experiments. Additionally, it offers a Gradio demo for the MMCA model.
AwesomeResponsibleAI
Awesome Responsible AI is a curated list of academic research, books, code of ethics, courses, data sets, frameworks, institutes, newsletters, principles, podcasts, reports, tools, regulations, and standards related to Responsible, Trustworthy, and Human-Centered AI. It covers various concepts such as Responsible AI, Trustworthy AI, Human-Centered AI, Responsible AI frameworks, AI Governance, and more. The repository provides a comprehensive collection of resources for individuals interested in ethical, transparent, and accountable AI development and deployment.
For similar tasks

Scientific-LLM-Survey
Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs) is a repository that collects papers on scientific large language models, focusing on biology and chemistry domains. It includes textual, molecular, protein, and genomic languages, as well as multimodal language. The repository covers various large language models for tasks such as molecule property prediction, interaction prediction, protein sequence representation, protein sequence generation/design, DNA-protein interaction prediction, and RNA prediction. It also provides datasets and benchmarks for evaluating these models. The repository aims to facilitate research and development in the field of scientific language modeling.
matchem-llm
A public repository collecting links to state-of-the-art training sets, QA, benchmarks and other evaluations for various ML and LLM applications in materials science and chemistry. It includes datasets related to chemistry, materials, multimodal data, and knowledge graphs in the field. The repository aims to provide resources for training and evaluating machine learning models in the materials science and chemistry domains.
For similar jobs

NoLabs
NoLabs is an open-source biolab that provides easy access to state-of-the-art models for bio research. It supports various tasks, including drug discovery, protein analysis, and small molecule design. NoLabs aims to accelerate bio research by making inference models accessible to everyone.
OpenCRISPR
OpenCRISPR is a set of free and open gene editing systems designed by Profluent Bio. The OpenCRISPR-1 protein maintains the prototypical architecture of a Type II Cas9 nuclease but is hundreds of mutations away from SpCas9 or any other known natural CRISPR-associated protein. You can view OpenCRISPR-1 as a drop-in replacement for many protocols that need a cas9-like protein with an NGG PAM and you can even use it with canonical SpCas9 gRNAs. OpenCRISPR-1 can be fused in a deactivated or nickase format for next generation gene editing techniques like base, prime, or epigenome editing.
ersilia
The Ersilia Model Hub is a unified platform of pre-trained AI/ML models dedicated to infectious and neglected disease research. It offers an open-source, low-code solution that provides seamless access to AI/ML models for drug discovery. Models housed in the hub come from two sources: published models from literature (with due third-party acknowledgment) and custom models developed by the Ersilia team or contributors.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.
bia-bob
BIA `bob` is a Jupyter-based assistant for interacting with data using large language models to generate Python code. It can utilize OpenAI's chatGPT, Google's Gemini, Helmholtz' blablador, and Ollama. Users need respective accounts to access these services. Bob can assist in code generation, bug fixing, code documentation, GPU-acceleration, and offers a no-code custom Jupyter Kernel. It provides example notebooks for various tasks like bio-image analysis, model selection, and bug fixing. Installation is recommended via conda/mamba environment. Custom endpoints like blablador and ollama can be used. Google Cloud AI API integration is also supported. The tool is extensible for Python libraries to enhance Bob's functionality.

Scientific-LLM-Survey
Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs) is a repository that collects papers on scientific large language models, focusing on biology and chemistry domains. It includes textual, molecular, protein, and genomic languages, as well as multimodal language. The repository covers various large language models for tasks such as molecule property prediction, interaction prediction, protein sequence representation, protein sequence generation/design, DNA-protein interaction prediction, and RNA prediction. It also provides datasets and benchmarks for evaluating these models. The repository aims to facilitate research and development in the field of scientific language modeling.
polaris
Polaris establishes a novel, industry‑certified standard to foster the development of impactful methods in AI-based drug discovery. This library is a Python client to interact with the Polaris Hub. It allows you to download Polaris datasets and benchmarks, evaluate a custom method against a Polaris benchmark, and create and upload new datasets and benchmarks.
awesome-AI4MolConformation-MD
The 'awesome-AI4MolConformation-MD' repository focuses on protein conformations and molecular dynamics using generative artificial intelligence and deep learning. It provides resources, reviews, datasets, packages, and tools related to AI-driven molecular dynamics simulations. The repository covers a wide range of topics such as neural networks potentials, force fields, AI engines/frameworks, trajectory analysis, visualization tools, and various AI-based models for protein conformational sampling. It serves as a comprehensive guide for researchers and practitioners interested in leveraging AI for studying molecular structures and dynamics.