
LLM-as-HH
Large Language Models as Hyper-Heuristics for Combinatorial Optimization (CO)
Stars: 78
LLM-as-HH is a codebase that accompanies the paper ReEvo: Large Language Models as Hyper-Heuristics with Reflective Evolution. It introduces Language Hyper-Heuristics (LHHs) that leverage LLMs for heuristic generation with minimal manual intervention and open-ended heuristic spaces. Reflective Evolution (ReEvo) is presented as a searching framework that emulates the reflective design approach of human experts while surpassing human capabilities with scalable LLM inference, Internet-scale domain knowledge, and powerful evolutionary search. The tool can improve various algorithms on problems like Traveling Salesman Problem, Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem, Orienteering Problem, Multiple Knapsack Problems, Bin Packing Problem, and Decap Placement Problem in both black-box and white-box settings.
README:
🥳 Welcome! This is a codebase that accompanies the paper Large Language Models as Hyper-Heuristics for Combinatorial Optimization.
Give ReEvo 5 minutes, and get a state-of-the-art algorithm in return!
- 1. News 📰
- 2. Introduction 🚀
- 3. Exciting Highlights 🌟
- 4. Usage 🔑
- 4.1. Dependency
- 4.2. To run ReEvo
- 4.3. Available problems
- 4.4. Simple steps to apply ReEvo to your problem
- 4.5. Use Alternative LLMs
- 5. Citation 🤩
- 6. Acknowledgments 🫡
- 2024.05: We release a new paper version.
- 2024.04: Novel use cases for Neural Combinatorial Optimization (NCO) and Electronic Design Automation (EDA).
- 2024.02: We are excited to release ReEvo! 🚀
We introduce Language Hyper-Heuristics (LHHs), an emerging variant of Hyper-Heuristics (HHs) that leverages LLMs for heuristic generation, featuring minimal manual intervention and open-ended heuristic spaces.
To empower LHHs, we present Reflective Evolution (ReEvo), a generic searching framework that emulates the reflective design approach of human experts while much surpassing human capabilities with its scalable LLM inference, Internet-scale domain knowledge, and powerful evolutionary search.
We can improve the following types of algorithms:
- Neural Combinatorial Optimization (NCO)
- Genetic Algorithm (GA)
- Ant Colony Optimization (ACO)
- Guided Local Search (GLS)
- Constructive Heuristics
on the following problems:
- Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
- Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem (CVRP)
- Orienteering Problem (OP)
- Multiple Knapsack Problems (MKP)
- Bin Packing Problem (BPP)
- Decap Placement Problem (DPP)
with both black-box and white-box settings.
- Set your LLM API key (OpenAI API, ZhiPu API, Llama API) here or as an environment variable.
- Running logs and intermediate results are saved in
./outputs/main/by default. - Datasets are generated on the fly.
- Some test notebooks are provided in
./problems/*/test.ipynb.
- Python >= 3.11
- openai >= 1.0.0
- hydra-core
- scipy
You may install the dependencies above via pip install -r requirements.txt.
Problem-specific dependencies:
-
tsp_aco(_black_box): pytorch, scikit-learn -
cvrp_aco(_black_box)/mkp_aco(_black_box)/op_aco(_black_box)/NCO: pytorch -
tsp_gls: numba==0.58
# e.g., for tsp_aco
python main.py problem=tsp_acoCheck out ./cfg/ for more options.
- Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP):
tsp_aco,tsp_aco_black_box,tsp_constructive,tsp_gls,tsp_pomo,tsp_lehd - Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem (CVRP):
cvrp_aco,cvrp_aco_black_box,cvrp_pomo,cvrp_lehd - Bin Packing Problem (BPP):
bpp_offline_aco,bpp_offline_aco_black_box,bpp_online - Multiple Knapsack Problems (MKP):
mkp_aco,mkp_aco_black_box - Orienteering Problem (OP):
op_aco,op_aco_black_box - Decap Placement Problem (DPP):
dpp_ga
- Define your problem in
./cfg/problem/. - Generate problem instances and implement the evaluation pipeline in
./problems/. - Add function_description, function_signature, and seed_function in
./prompts/.
Use the cli parameter llm_client to designate an LLM API provider, and llm_client.model to determine the model to use. For example,
$ export LLAMA_API_KEY=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
$ python main.py llm_client=llama_api llm_client.model=gemma2-9bSupported LLM API providers and models including (to be noted that only chat models are supported):
- OpenAI: gpt-3.5-turbo (default), gpt-4o, gpt-4o-mini, gpt-4-turbo, etc.
- Zhipu AI: GLM-3-Turbo, GLM-4-Air, GLM-4-0520, etc. (full list)
- DeepSeek: deepseek-chat
- Llama API: llama3.1-8b/70b/405b, gemma2-9b/27b, Qwen2-72B, etc. (full list)
- And more providers supported via LiteLLM.
If you encounter any difficulty using our code, please do not hesitate to submit an issue or directly contact us! If you find our work helpful (or if you are so kind as to offer us some encouragement), please consider giving us a star, and citing our paper.
@article{ye2024large,
title={Large Language Models as Hyper-Heuristics for Combinatorial Optimization},
author={Haoran Ye and Jiarui Wang and Zhiguang Cao and Federico Berto and Chuanbo Hua and Haeyeon Kim and Jinkyoo Park and Guojie Song},
year={2024},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.01145},
note={\url{https://github.com/ai4co/LLM-as-HH}}
}We are very grateful to Yuan Jiang, Yining Ma, Yifan Yang, and AI4CO community for valuable discussions and feedback.
Also, our work is built upon the following projects, among others:
- DeepACO: Neural-enhanced Ant Systems for Combinatorial Optimization
- Eureka: Human-Level Reward Design via Coding Large Language Models
- Algorithm Evolution Using Large Language Model
- Mathematical discoveries from program search with large language models
- An Example of Evolutionary Computation + Large Language Model Beating Human: Design of Efficient Guided Local Search
- DevFormer: A Symmetric Transformer for Context-Aware Device Placement
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLM-as-HH
Similar Open Source Tools

LLM-as-HH
LLM-as-HH is a codebase that accompanies the paper ReEvo: Large Language Models as Hyper-Heuristics with Reflective Evolution. It introduces Language Hyper-Heuristics (LHHs) that leverage LLMs for heuristic generation with minimal manual intervention and open-ended heuristic spaces. Reflective Evolution (ReEvo) is presented as a searching framework that emulates the reflective design approach of human experts while surpassing human capabilities with scalable LLM inference, Internet-scale domain knowledge, and powerful evolutionary search. The tool can improve various algorithms on problems like Traveling Salesman Problem, Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem, Orienteering Problem, Multiple Knapsack Problems, Bin Packing Problem, and Decap Placement Problem in both black-box and white-box settings.
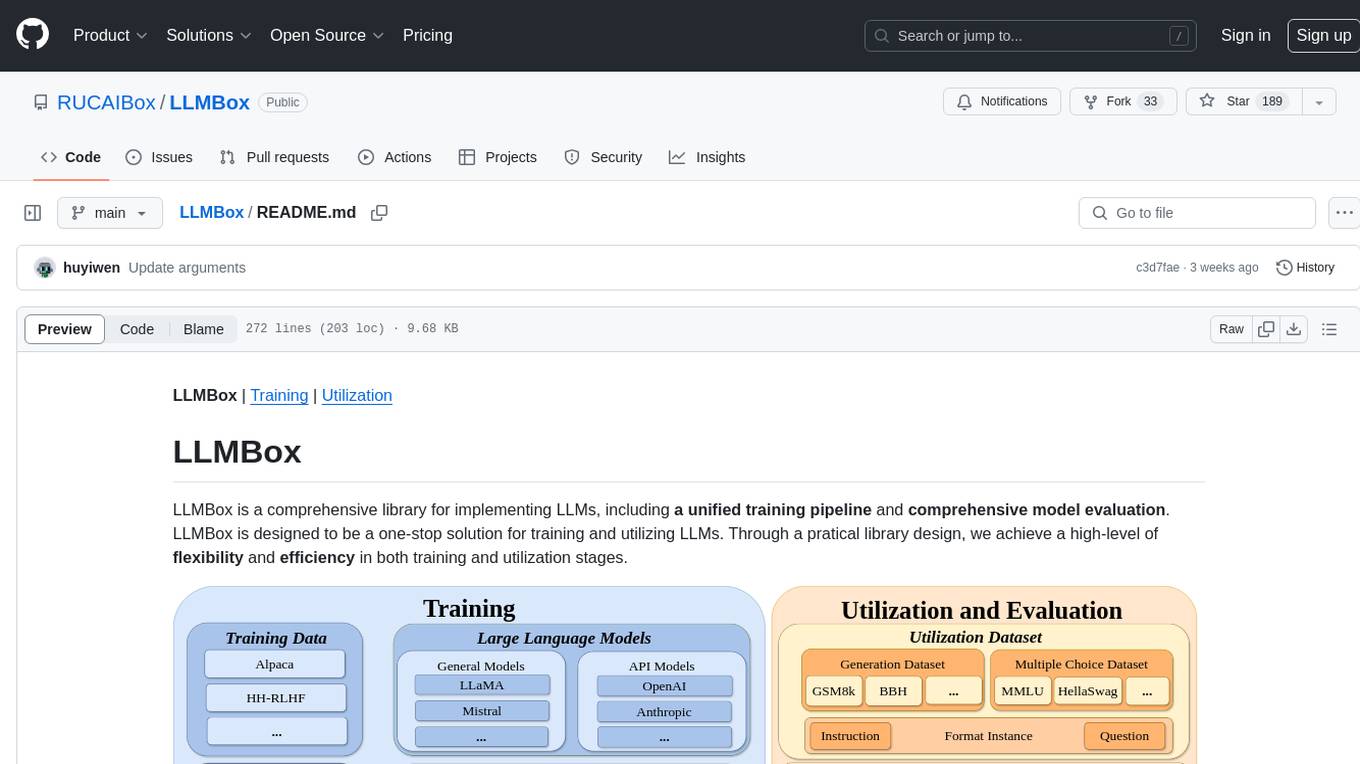
LLMBox
LLMBox is a comprehensive library designed for implementing Large Language Models (LLMs) with a focus on a unified training pipeline and comprehensive model evaluation. It serves as a one-stop solution for training and utilizing LLMs, offering flexibility and efficiency in both training and utilization stages. The library supports diverse training strategies, comprehensive datasets, tokenizer vocabulary merging, data construction strategies, parameter efficient fine-tuning, and efficient training methods. For utilization, LLMBox provides comprehensive evaluation on various datasets, in-context learning strategies, chain-of-thought evaluation, evaluation methods, prefix caching for faster inference, support for specific LLM models like vLLM and Flash Attention, and quantization options. The tool is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs for natural language processing tasks.

sieves
sieves is a library for zero- and few-shot NLP tasks with structured generation, enabling rapid prototyping of NLP applications without the need for training. It simplifies NLP prototyping by bundling capabilities into a single library, providing zero- and few-shot model support, a unified interface for structured generation, built-in tasks for common NLP operations, easy extendability, document-based pipeline architecture, caching to prevent redundant model calls, and more. The tool draws inspiration from spaCy and spacy-llm, offering features like immediate inference, observable pipelines, integrated tools for document parsing and text chunking, ready-to-use tasks such as classification, summarization, translation, and more, persistence for saving and loading pipelines, distillation for specialized model creation, and caching to optimize performance.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
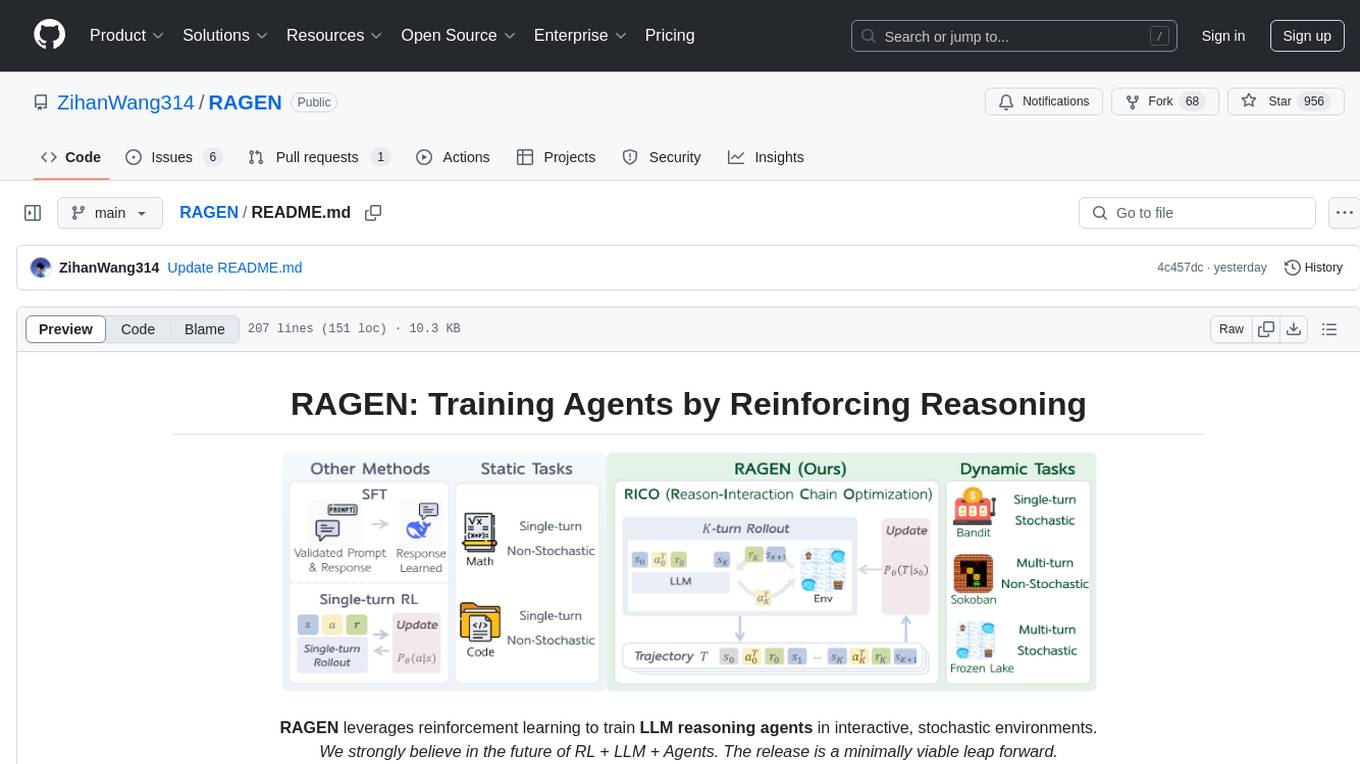
RAGEN
RAGEN is a reinforcement learning framework designed to train reasoning-capable large language model (LLM) agents in interactive, stochastic environments. It addresses challenges such as multi-turn interactions and stochastic environments through a Markov Decision Process (MDP) formulation, Reason-Interaction Chain Optimization (RICO) algorithm, and progressive reward normalization strategies. The framework enables LLMs to reason and interact with the environment, optimizing entire trajectories for long-horizon reasoning while maintaining computational efficiency.
llmxcpg
LLMxCPG is a framework for vulnerability detection using Code Property Graphs (CPG) and Large Language Models (LLM). It involves a two-phase process: Slice Construction where an LLM generates queries for a CPG to extract a code slice, and Vulnerability Detection where another LLM classifies the code slice as vulnerable or safe. The repository includes implementations of baseline models, information on datasets, scripts for running models, prompt templates, query generation examples, and configurations for fine-tuning models.
VeritasGraph
VeritasGraph is an enterprise-grade graph RAG framework designed for secure, on-premise AI applications. It leverages a knowledge graph to perform complex, multi-hop reasoning, providing transparent, auditable reasoning paths with full source attribution. The framework excels at answering complex questions that traditional vector search engines struggle with, ensuring trust and reliability in enterprise AI. VeritasGraph offers full control over data and AI models, verifiable attribution for every claim, advanced graph reasoning capabilities, and open-source deployment with sovereignty and customization.
MathCoder
MathCoder is a repository focused on enhancing mathematical reasoning by fine-tuning open-source language models to use code for modeling and deriving math equations. It introduces MathCodeInstruct dataset with solutions interleaving natural language, code, and execution results. The repository provides MathCoder models capable of generating code-based solutions for challenging math problems, achieving state-of-the-art scores on MATH and GSM8K datasets. It offers tools for model deployment, inference, and evaluation, along with a citation for referencing the work.

rl
TorchRL is an open-source Reinforcement Learning (RL) library for PyTorch. It provides pytorch and **python-first** , low and high level abstractions for RL that are intended to be **efficient** , **modular** , **documented** and properly **tested**. The code is aimed at supporting research in RL. Most of it is written in python in a highly modular way, such that researchers can easily swap components, transform them or write new ones with little effort.
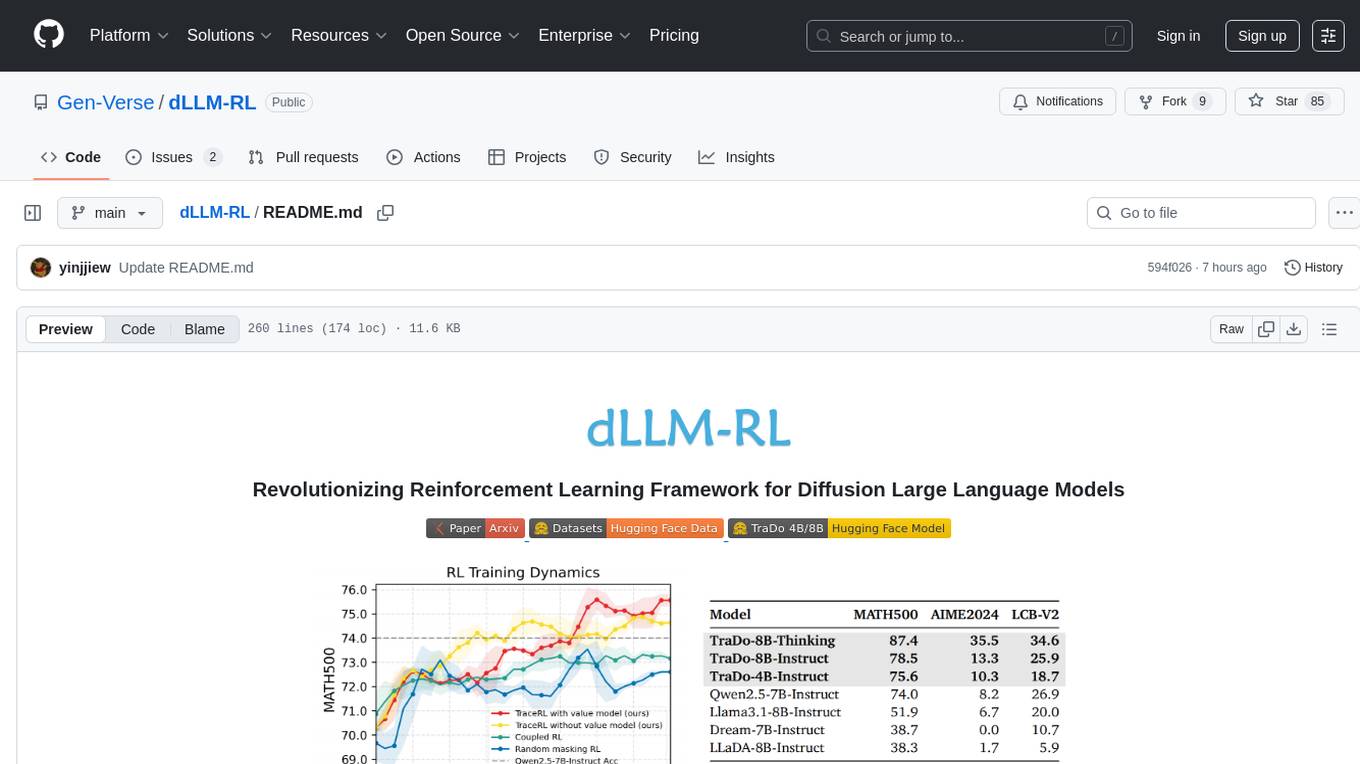
dLLM-RL
dLLM-RL is a revolutionary reinforcement learning framework designed for Diffusion Large Language Models. It supports various models with diverse structures, offers inference acceleration, RL training capabilities, and SFT functionalities. The tool introduces TraceRL for trajectory-aware RL and diffusion-based value models for optimization stability. Users can download and try models like TraDo-4B-Instruct and TraDo-8B-Instruct. The tool also provides support for multi-node setups and easy building of reinforcement learning methods. Additionally, it offers supervised fine-tuning strategies for different models and tasks.
architext
Architext is a Python library designed for Large Language Model (LLM) applications, focusing on Context Engineering. It provides tools to construct and reorganize input context for LLMs dynamically. The library aims to elevate context construction from ad-hoc to systematic engineering, enabling precise manipulation of context content for AI Agents.

embodied-agents
Embodied Agents is a toolkit for integrating large multi-modal models into existing robot stacks with just a few lines of code. It provides consistency, reliability, scalability, and is configurable to any observation and action space. The toolkit is designed to reduce complexities involved in setting up inference endpoints, converting between different model formats, and collecting/storing datasets. It aims to facilitate data collection and sharing among roboticists by providing Python-first abstractions that are modular, extensible, and applicable to a wide range of tasks. The toolkit supports asynchronous and remote thread-safe agent execution for maximal responsiveness and scalability, and is compatible with various APIs like HuggingFace Spaces, Datasets, Gymnasium Spaces, Ollama, and OpenAI. It also offers automatic dataset recording and optional uploads to the HuggingFace hub.
lionagi
LionAGI is a powerful intelligent workflow automation framework that introduces advanced ML models into any existing workflows and data infrastructure. It can interact with almost any model, run interactions in parallel for most models, produce structured pydantic outputs with flexible usage, automate workflow via graph based agents, use advanced prompting techniques, and more. LionAGI aims to provide a centralized agent-managed framework for "ML-powered tools coordination" and to dramatically lower the barrier of entries for creating use-case/domain specific tools. It is designed to be asynchronous only and requires Python 3.10 or higher.
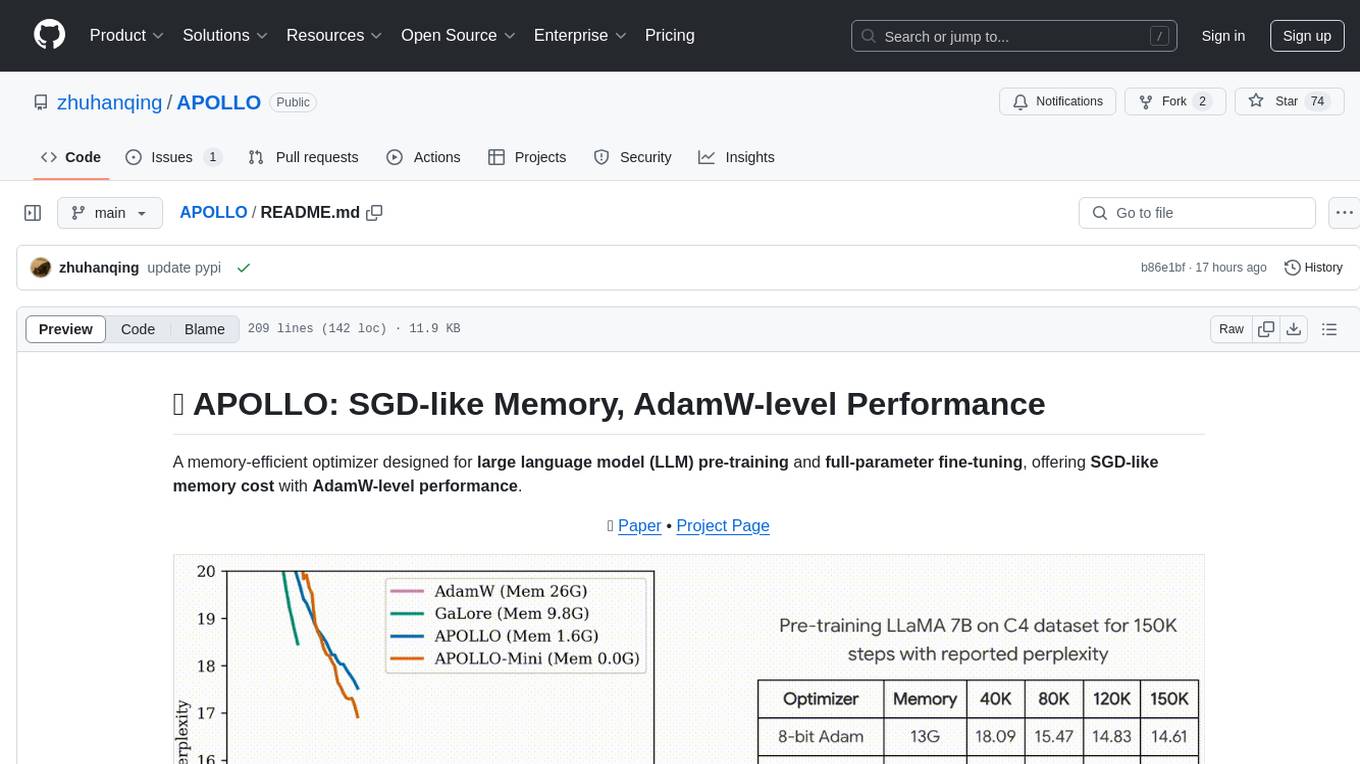
APOLLO
APOLLO is a memory-efficient optimizer designed for large language model (LLM) pre-training and full-parameter fine-tuning. It offers SGD-like memory cost with AdamW-level performance. The optimizer integrates low-rank approximation and optimizer state redundancy reduction to achieve significant memory savings while maintaining or surpassing the performance of Adam(W). Key contributions include structured learning rate updates for LLM training, approximated channel-wise gradient scaling in a low-rank auxiliary space, and minimal-rank tensor-wise gradient scaling. APOLLO aims to optimize memory efficiency during training large language models.
distilabel
Distilabel is a framework for synthetic data and AI feedback for AI engineers that require high-quality outputs, full data ownership, and overall efficiency. It helps you synthesize data and provide AI feedback to improve the quality of your AI models. With Distilabel, you can: * **Synthesize data:** Generate synthetic data to train your AI models. This can help you to overcome the challenges of data scarcity and bias. * **Provide AI feedback:** Get feedback from AI models on your data. This can help you to identify errors and improve the quality of your data. * **Improve your AI output quality:** By using Distilabel to synthesize data and provide AI feedback, you can improve the quality of your AI models and get better results.
For similar tasks

LLM-as-HH
LLM-as-HH is a codebase that accompanies the paper ReEvo: Large Language Models as Hyper-Heuristics with Reflective Evolution. It introduces Language Hyper-Heuristics (LHHs) that leverage LLMs for heuristic generation with minimal manual intervention and open-ended heuristic spaces. Reflective Evolution (ReEvo) is presented as a searching framework that emulates the reflective design approach of human experts while surpassing human capabilities with scalable LLM inference, Internet-scale domain knowledge, and powerful evolutionary search. The tool can improve various algorithms on problems like Traveling Salesman Problem, Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem, Orienteering Problem, Multiple Knapsack Problems, Bin Packing Problem, and Decap Placement Problem in both black-box and white-box settings.
open-ai
Open AI is a powerful tool for artificial intelligence research and development. It provides a wide range of machine learning models and algorithms, making it easier for developers to create innovative AI applications. With Open AI, users can explore cutting-edge technologies such as natural language processing, computer vision, and reinforcement learning. The platform offers a user-friendly interface and comprehensive documentation to support users in building and deploying AI solutions. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced AI practitioner, Open AI offers the tools and resources you need to accelerate your AI projects and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence.

universal
The Universal Numbers Library is a header-only C++ template library designed for universal number arithmetic, offering alternatives to native integer and floating-point for mixed-precision algorithm development and optimization. It tailors arithmetic types to the application's precision and dynamic range, enabling improved application performance and energy efficiency. The library provides fast implementations of special IEEE-754 formats like quarter precision, half-precision, and quad precision, as well as vendor-specific extensions. It supports static and elastic integers, decimals, fixed-points, rationals, linear floats, tapered floats, logarithmic, interval, and adaptive-precision integers, rationals, and floats. The library is suitable for AI, DSP, HPC, and HFT algorithms.
how-to-optim-algorithm-in-cuda
This repository documents how to optimize common algorithms based on CUDA. It includes subdirectories with code implementations for specific optimizations. The optimizations cover topics such as compiling PyTorch from source, NVIDIA's reduce optimization, OneFlow's elementwise template, fast atomic add for half data types, upsample nearest2d optimization in OneFlow, optimized indexing in PyTorch, OneFlow's softmax kernel, linear attention optimization, and more. The repository also includes learning resources related to deep learning frameworks, compilers, and optimization techniques.
data-scientist-roadmap2024
The Data Scientist Roadmap2024 provides a comprehensive guide to mastering essential tools for data science success. It includes programming languages, machine learning libraries, cloud platforms, and concepts categorized by difficulty. The roadmap covers a wide range of topics from programming languages to machine learning techniques, data visualization tools, and DevOps/MLOps tools. It also includes web development frameworks and specific concepts like supervised and unsupervised learning, NLP, deep learning, reinforcement learning, and statistics. Additionally, it delves into DevOps tools like Airflow and MLFlow, data visualization tools like Tableau and Matplotlib, and other topics such as ETL processes, optimization algorithms, and financial modeling.
ML-AI-2-LT
ML-AI-2-LT is a repository that serves as a glossary for machine learning and deep learning concepts. It contains translations and explanations of various terms related to artificial intelligence, including definitions and notes. Users can contribute by filling issues for unclear concepts or by submitting pull requests with suggestions or additions. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive resource for understanding key terminology in the field of AI and machine learning.
sciml.ai
SciML.ai is an open source software organization dedicated to unifying packages for scientific machine learning. It focuses on developing modular scientific simulation support software, including differential equation solvers, inverse problems methodologies, and automated model discovery. The organization aims to provide a diverse set of tools with a common interface, creating a modular, easily-extendable, and highly performant ecosystem for scientific simulations. The website serves as a platform to showcase SciML organization's packages and share news within the ecosystem. Pull requests are encouraged for contributions.
PHS-AI
PHS-AI is a project that provides functionality as is, without any warranties or commitments. Users are advised to exercise caution when using the code and conduct thorough testing before deploying in a production environment. The author assumes no responsibility for any losses or damages incurred through the use of this code. Feedback and contributions to improve the project are always welcome.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
