
twitter-automation-ai
Advanced Python-based Twitter (X.com) automation framework using Selenium and LLMs (OpenAI, Gemini) for multi-account scraping, posting, engagement, and content analysis. Modular and configurable.
Stars: 56
Advanced Twitter Automation AI is a modular Python-based framework for automating Twitter at scale. It supports multiple accounts, robust Selenium automation with optional undetected Chrome + stealth, per-account proxies and rotation, structured LLM generation/analysis, community posting, and per-account metrics/logs. The tool allows seamless management and automation of multiple Twitter accounts, content scraping, publishing, LLM integration for generating and analyzing tweet content, engagement automation, configurable automation, browser automation using Selenium, modular design for easy extension, comprehensive logging, community posting, stealth mode for reduced fingerprinting, per-account proxies, LLM structured prompts, and per-account JSON summaries and event logs for observability.
README:
Advanced Twitter Automation AI is a modular Python-based framework for automating X (Twitter) at scale. It supports multiple accounts, robust Selenium automation (with optional undetected Chrome + stealth), per‑account proxies and rotation, structured LLM generation/analysis (OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Gemini), community posting, and per‑account metrics/logs.
- Advanced Twitter Automation AI
- Multi-Account Management: Seamlessly manage and automate actions for multiple Twitter accounts.
-
Content Scraping:
- Scrape tweets based on keywords, user profiles, and news/research sites.
- Extract tweet content, user information, and engagement metrics.
-
Content Publishing:
- Post new tweets, including text and media.
- Reply to tweets based on various triggers.
- Repost (retweet) content from competitor profiles or based on engagement metrics.
-
LLM Integration:
- Utilize OpenAI (GPT models) and Google Gemini for:
- Generating tweet content and replies.
- Analyzing tweet threads and sentiment.
- Summarizing articles for posting.
- Flexible LLM preference settings at global and per-account levels.
- Utilize OpenAI (GPT models) and Google Gemini for:
-
Engagement Automation:
- Engage with tweets through likes, replies, and reposts.
- Analyze competitor activity and engage strategically.
-
Configurable Automation:
- Fine-grained control over automation parameters via JSON configuration files.
- Per-account overrides for keywords, target profiles, LLM settings, and action behaviors.
- Browser Automation: Uses Selenium for interacting with Twitter, handling dynamic content and complex UI elements.
- Modular Design: Easily extendable with new features and functionalities.
- Logging: Comprehensive logging for monitoring and debugging.
- Community Posting: Switch audience and post into configured communities (by ID or name).
- Stealth Mode (Chrome): Optional undetected-chromedriver + selenium-stealth to reduce fingerprinting.
- Proxies: Per-account proxies, named proxy pools, and rotation strategies (hash/round-robin) with env interpolation.
- LLM Structured Prompts: Strict JSON prompting with few-shots, system prompts, and robust extraction.
- Metrics: Per-account JSON summaries and JSONL event logs for observability.
- Programming Language: Python 3.9+
- Browser Automation: Selenium, WebDriver Manager
- HTTP Requests: Requests
- Data Validation: Pydantic
- LLM Integration: Langchain (for Google GenAI), OpenAI SDK
- Stealth: undetected-chromedriver, selenium-stealth (optional)
- Configuration: JSON, python-dotenv
- Web Interaction: Fake Headers (for mimicking browser headers)
The project is organized as follows:
twitter-automation-ai/
├── config/
│ ├── accounts.json # Configuration for multiple Twitter accounts
│ └── settings.json # Global settings (API keys, automation parameters)
├── src/
│ ├── core/ # Core modules (browser, LLM, config)
│ │ ├── browser_manager.py
│ │ ├── config_loader.py
│ │ └── llm_service.py
│ ├── features/ # Modules for Twitter features (scraper, publisher, etc.)
│ │ ├── scraper.py
│ │ ├── publisher.py
│ │ └── engagement.py
│ ├── utils/ # Utility modules (logger, file handler, etc.)
│ │ ├── logger.py
│ │ ├── file_handler.py
│ │ ├── progress.py
│ │ └── scroller.py
│ ├── data_models.py # Pydantic models for data structures
│ ├── main.py # Main orchestrator script
│ └── __init__.py
├── .env # Environment variables (optional, for API keys)
├── requirements.txt # Python dependencies
├── .gitignore # Specifies intentionally untracked files
├── LICENSE # Project license
├── CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md # Contributor Code of Conduct
├── CONTRIBUTING.md # Guidelines for contributing
└── README.md # This file
- Python 3.9 or higher.
- A modern web browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox) compatible with Selenium.
Follow these steps to set up and run the project:
Quick-start templates are available in presets/.
- Settings presets:
presets/settings/*.json(defaults, Chrome undetected, proxies hash/round-robin) - Accounts presets:
presets/accounts/*.json(growth, brand_safe, replies_first, engagement_light, community_posting) - How to apply:
- cp
presets/settings/beginner-chrome-undetected.jsonconfig/settings.json - cp
presets/accounts/growth.jsonconfig/accounts.json - Edit placeholders for API keys, cookie paths, and community IDs.
- See
presets/README.mdanddata/README.md(dummy cookies/proxies).
- cp
git clone https://github.com/ihuzaifashoukat/twitter-automation-ai
cd twitter-automation-aiIt's highly recommended to use a virtual environment:
python -m venv venv
# On Windows
venv\Scripts\activate
# On macOS/Linux
source venv/bin/activateInstall the required Python packages:
pip install -r requirements.txtThis file manages individual Twitter account configurations. It should be an array of account objects.
-
Key Fields per Account:
-
account_id: A unique identifier for the account. -
is_active: Boolean, set totrueto enable automation for this account. -
cookie_file_path: Path to a JSON file containing cookies for the account (e.g.,config/my_account_cookies.json). -
cookies: Alternatively, an array of cookie objects can be provided directly. -
proxy(optional): Per-account proxy URL. Examples:http://user:pass@host:port,socks5://host:port. -
post_to_community(optional): Whentrue, switch the audience to a community before posting. -
community_id(optional): Community ID used to select the audience (preferred). -
community_name(optional): Fallback visible name in the audience picker if ID selection fails. -
Overrides: You can specify per-account overrides for various settings like
target_keywords_override,competitor_profiles_override,llm_settings_override, andaction_config_override. If an override is not present, the global defaults fromconfig/settings.jsonwill be used.
-
-
Example
config/accounts.jsonentry:// Minimal example: ONLY add the community fields you need; keep your existing structure as-is. // Below shows adding community + (optional) proxy to one of your existing account objects: { "account_id": "your_existing_account_id", "is_active": true, "cookie_file_path": "config/your_existing_cookie_file.json", // ... all your existing fields remain unchanged ... "proxy": "http://127.0.0.1:8888", // optional "post_to_community": true, // optional "community_id": "1737236915810627584", // preferred when known "community_name": "One Piece" // fallback by visible name }
(Refer to the example in the original README section for a more detailed structure if needed, or adapt based on current
data_models.py.) -
Obtaining Cookies: Use browser developer tools (e.g., "EditThisCookie" extension) to export cookies for
x.comafter logging in. Save them as a JSON array of cookie objects if usingcookie_file_path. -
Per-Account Proxy: If set, the proxy overrides the global
browser_settings.proxyfor that account. Chrome uses--proxy-server; Firefox is configured via profile preferences (proxy auth prompts are not handled automatically). -
Community Posting: When
post_to_communityis true, the publisher clicks the "Choose audience" button in the composer and selects your community usingcommunity_id(preferred) orcommunity_nameas a fallback, then posts. -
Important: We do not require changing your existing
accounts.jsonstructure. Simply add the optional fields (post_to_community,community_id,community_name, and/orproxy) to the appropriate account objects. -
For rewrite-based posting to communities or personal profiles, ensure each account has competitor sources configured via
competitor_profiles(orcompetitor_profiles_overridein your current structure). The scraper uses these as input for rewriting and posting.
This file contains global configurations for the application.
-
Key Sections:
-
api_keys: Store API keys for LLM services (e.g.,openai_api_key,gemini_api_key). -
twitter_automation:-
action_config: Default behaviors for automation actions (e.g.,max_posts_per_run,min_likes_for_repost). -
response_interval_seconds: Default delay between actions. -
media_directory: Path to store downloaded media. -
analysis_config: Enable/disable relevance filters per pipeline and thresholds.
-
enable_relevance_filter.competitor_reposts(bool),thresholds.competitor_reposts_min(0–1) -
enable_relevance_filter.likes(bool),thresholds.likes_min(0–1)
-
engagement_decision: Ifenabled: true, automatically chooses between repost/retweet/quote/like based on relevance and sentiment.
-
use_sentiment: include sentiment in decision -
thresholds.quote_min|retweet_min|repost_min: relevance cutoffs (0–1)
-
-
logging: Configuration for the logger.
-
-
browser_settings: Settings for Selenium WebDriver (e.g.,headlessmode).-
type:chromeorfirefox. For best anti-detection, use Chrome withuse_undetected_chromedriver. -
use_undetected_chromedriver(Chrome only): Whentrue, usesundetected-chromedriverfor stealthier automation. -
enable_stealth(Chrome only): Whentrueandselenium-stealthis installed, applies additional anti-detection tweaks. -
user_agent_generation:randomorcustomwithcustom_user_agentstring. -
proxy: Global proxy (can be overridden per account). -
driver_options: Extra Chrome/Firefox CLI options. -
page_load_timeout_seconds,script_timeout_seconds,window_size.
-
LLM prompt engineering
- LLM prompts now use stronger, schema-first instructions for structured JSON with optional few-shot examples and hard character limits.
-
LLMService.generate_textaccepts an optionalsystem_promptandmessagesfor OpenAI/Azure; Gemini concatenates system+user. -
LLMService.generate_structuredaddsfew_shots,system_prompt, andhard_character_limitto guide safer, parsable outputs.-
proxy_pools: Named pools for per-account proxies. Use"pool:<name>"in accountproxyto select from a pool. -
proxy_pool_strategy:hash(stable per-account) orround_robin(rotates across runs/accounts). -
proxy_pool_state_file: Persist file for round-robin counters (defaultdata/proxy_pools_state.json).
-
-
Important Note: Content source lists like
target_keywords,competitor_profiles, etc., are primarily managed per-account inconfig/accounts.json. The globalaction_configinsettings.jsondefines default how actions run, which can be overridden per account.
For sensitive data like API keys, you can use a .env file in the project root. python-dotenv is included in requirements.txt to load these variables.
- Create a
.envfile:The application is designed to prioritize environment variables for API keys if available.OPENAI_API_KEY="your_openai_api_key" GEMINI_API_KEY="your_gemini_api_key" # Add other sensitive variables as needed
Execute the main orchestrator script from the project root:
python src/main.pyThe orchestrator will iterate through active accounts in config/accounts.json and perform actions based on their respective configurations and global settings.
To post into a community instead of your public timeline, set the following on the account object in config/accounts.json:
post_to_community: true- Provide at least one of:
-
community_id: preferred (appears in URLs like/i/communities/<id>) -
community_name: fallback by the visible label in the audience picker
-
How selection works:
- The app opens the “Choose audience” control, locates the audience menu container (dialog or
data-testid="HoverCard"), and attempts to click your community. - It scrolls the virtualized list to reveal off-screen items and uses JS-click fallbacks to avoid overlay interception.
- After selection, it posts using the chosen audience.
If it fails to select your community:
- Verify the account has joined the community and it appears under “My Communities”.
- Provide a DOM snapshot from the audience menu in a GitHub issue so selectors can be tuned.
Controls live under twitter_automation.action_config (globally) and per-account action_config_override:
- Replies:
enable_keyword_replies,max_replies_per_keyword_run, optional recencyreply_only_to_recent_tweets_hours. - Likes:
enable_liking_tweets,max_likes_per_run,like_tweets_from_keywords(defaults to accounttarget_keywordswhen omitted). - Retweets (new):
enable_keyword_retweets,max_retweets_per_keyword_run.
Relevance filters (optional):
-
enable_relevance_filter_keyword_replies,relevance_threshold_keyword_replies -
enable_relevance_filter_likes,relevance_threshold_likes
-
ElementClickInterceptedException or “not clickable”:
- The app automatically scrolls into view, waits for the composer mask to disappear, and uses JS-click or Ctrl+Enter fallbacks.
- If it persists, consider adding small delays or switching to Chrome (
browser_settings.type: "chrome").
-
Community not selected:
- Ensure
post_to_community: trueand setcommunity_id(best) orcommunity_name. - The audience list is virtualized; the app scrolls within the menu to reveal items. If your UI differs, open an issue with a DOM snippet.
- Ensure
-
WebDriver downloads blocked or offline:
- The app prefers local drivers (
chromedriver,geckodriver) if found in PATH or viachrome_driver_path/gecko_driver_path. Install via your OS package manager or ensure they’re in PATH.
- The app prefers local drivers (
-
Gemini errors (429/500):
- Use
gemini-1.5-flash-latest, reduce calls, or configure OpenAI/Azure.
- Use
- Structured analysis and generation use strict schema-first prompts with robust JSON extraction. OpenAI JSON mode is attempted when available.
- Internally supports system prompts and few-shot examples for more controllable outputs.
- Content generation for posts composes final text (with optional hashtags) within 280 chars.
- Chrome: set
browser_settings.typeto"chrome"and enableuse_undetected_chromedriver. Optionalenable_stealthapplies extra anti-detection tweaks. - Firefox: standard Selenium with proxy prefs; auth prompts are not auto-handled.
- Headless: Chrome uses
--headless=newfor better parity. User-Agent randomized by default.
- Per-account
proxyoverrides global. Use"pool:<name>"to select frombrowser_settings.proxy_pools. - Rotation strategies:
hash(stable per-account) orround_robin(usesdata/proxy_pools_state.json). - Env interpolation:
${ENV_VAR}inside proxy strings is expanded at runtime.
- Point
cookie_file_pathto a JSON array of cookies forx.com. The app navigates tobrowser_settings.cookie_domain_urlbefore injecting cookies. - Example file:
data/cookies/dummy_cookies_example.json.
- Summary per account:
data/metrics/<account_id>.json(counters for posts, replies, retweets, quote_tweets, likes, errors; last run timestamps) - Structured events per account:
logs/accounts/<account_id>.jsonl(JSON lines of each action attempt with metadata)
See docs/CONFIG_REFERENCE.md for a concise schema of config/settings.json and config/accounts.json, including per-account action_config_override fields and decision thresholds.
-
Logging: Detailed logs are output to the console. Configuration is in
config/settings.jsonand managed bysrc/utils/logger.py. -
Selenium Selectors: Twitter's (X.com) UI is subject to change. XPath and CSS selectors in
src/features/scraper.pyandsrc/features/publisher.pymay require updates if the site structure changes. - Error Handling: The project includes basic error handling. Enhancements with more specific exception management and retry mechanisms are potential areas for improvement.
-
Extensibility: To add new features:
- Define necessary data structures in
src/data_models.py. - Create new feature modules within the
src/features/directory. - Integrate the new module into the
TwitterOrchestratorinsrc/main.py.
- Define necessary data structures in
Contributions are welcome! Please read our CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines on how to contribute, report bugs, or suggest enhancements.
To ensure a welcoming and inclusive environment, this project adheres to a Code of Conduct. Please review and follow it in all your interactions with the project.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
- GUI or web interface for managing accounts, settings, and monitoring.
- Advanced error handling, including robust retry logic for network issues or UI changes.
- Integration with proxy services for enhanced multi-account management and anonymity.
- More detailed per-account activity logging and analytics.
- Improved AI-driven content analysis and decision-making.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for twitter-automation-ai
Similar Open Source Tools

twitter-automation-ai
Advanced Twitter Automation AI is a modular Python-based framework for automating Twitter at scale. It supports multiple accounts, robust Selenium automation with optional undetected Chrome + stealth, per-account proxies and rotation, structured LLM generation/analysis, community posting, and per-account metrics/logs. The tool allows seamless management and automation of multiple Twitter accounts, content scraping, publishing, LLM integration for generating and analyzing tweet content, engagement automation, configurable automation, browser automation using Selenium, modular design for easy extension, comprehensive logging, community posting, stealth mode for reduced fingerprinting, per-account proxies, LLM structured prompts, and per-account JSON summaries and event logs for observability.
graphiti
Graphiti is a framework for building and querying temporally-aware knowledge graphs, tailored for AI agents in dynamic environments. It continuously integrates user interactions, structured and unstructured data, and external information into a coherent, queryable graph. The framework supports incremental data updates, efficient retrieval, and precise historical queries without complete graph recomputation, making it suitable for developing interactive, context-aware AI applications.
forge
Forge is a powerful open-source tool for building modern web applications. It provides a simple and intuitive interface for developers to quickly scaffold and deploy projects. With Forge, you can easily create custom components, manage dependencies, and streamline your development workflow. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer, Forge offers a flexible and efficient solution for your web development needs.
pentagi
PentAGI is an innovative tool for automated security testing that leverages cutting-edge artificial intelligence technologies. It is designed for information security professionals, researchers, and enthusiasts who need a powerful and flexible solution for conducting penetration tests. The tool provides secure and isolated operations in a sandboxed Docker environment, fully autonomous AI-powered agent for penetration testing steps, a suite of 20+ professional security tools, smart memory system for storing research results, web intelligence for gathering information, integration with external search systems, team delegation system, comprehensive monitoring and reporting, modern interface, API integration, persistent storage, scalable architecture, self-hosted solution, flexible authentication, and quick deployment through Docker Compose.
Groqqle
Groqqle 2.1 is a revolutionary, free AI web search and API that instantly returns ORIGINAL content derived from source articles, websites, videos, and even foreign language sources, for ANY target market of ANY reading comprehension level! It combines the power of large language models with advanced web and news search capabilities, offering a user-friendly web interface, a robust API, and now a powerful Groqqle_web_tool for seamless integration into your projects. Developers can instantly incorporate Groqqle into their applications, providing a powerful tool for content generation, research, and analysis across various domains and languages.

golf
Golf is a simple command-line tool for calculating the distance between two geographic coordinates. It uses the Haversine formula to accurately determine the distance between two points on the Earth's surface. This tool is useful for developers working on location-based applications or projects that require distance calculations. With Golf, users can easily input latitude and longitude coordinates and get the precise distance in kilometers or miles. The tool is lightweight, easy to use, and can be integrated into various programming workflows.
TermNet
TermNet is an AI-powered terminal assistant that connects a Large Language Model (LLM) with shell command execution, browser search, and dynamically loaded tools. It streams responses in real-time, executes tools one at a time, and maintains conversational memory across steps. The project features terminal integration for safe shell command execution, dynamic tool loading without code changes, browser automation powered by Playwright, WebSocket architecture for real-time communication, a memory system to track planning and actions, streaming LLM output integration, a safety layer to block dangerous commands, dual interface options, a notification system, and scratchpad memory for persistent note-taking. The architecture includes a multi-server setup with servers for WebSocket, browser automation, notifications, and web UI. The project structure consists of core backend files, various tools like web browsing and notification management, and servers for browser automation and notifications. Installation requires Python 3.9+, Ollama, and Chromium, with setup steps provided in the README. The tool can be used via the launcher for managing components or directly by starting individual servers. Additional tools can be added by registering them in `toolregistry.json` and implementing them in Python modules. Safety notes highlight the blocking of dangerous commands, allowed risky commands with warnings, and the importance of monitoring tool execution and setting appropriate timeouts.
code2prompt
Code2Prompt is a powerful command-line tool that generates comprehensive prompts from codebases, designed to streamline interactions between developers and Large Language Models (LLMs) for code analysis, documentation, and improvement tasks. It bridges the gap between codebases and LLMs by converting projects into AI-friendly prompts, enabling users to leverage AI for various software development tasks. The tool offers features like holistic codebase representation, intelligent source tree generation, customizable prompt templates, smart token management, Gitignore integration, flexible file handling, clipboard-ready output, multiple output options, and enhanced code readability.
text-extract-api
The text-extract-api is a powerful tool that allows users to convert images, PDFs, or Office documents to Markdown text or JSON structured documents with high accuracy. It is built using FastAPI and utilizes Celery for asynchronous task processing, with Redis for caching OCR results. The tool provides features such as PDF/Office to Markdown and JSON conversion, improving OCR results with LLama, removing Personally Identifiable Information from documents, distributed queue processing, caching using Redis, switchable storage strategies, and a CLI tool for task management. Users can run the tool locally or on cloud services, with support for GPU processing. The tool also offers an online demo for testing purposes.
uLoopMCP
uLoopMCP is a Unity integration tool designed to let AI drive your Unity project forward with minimal human intervention. It provides a 'self-hosted development loop' where an AI can compile, run tests, inspect logs, and fix issues using tools like compile, run-tests, get-logs, and clear-console. It also allows AI to operate the Unity Editor itself—creating objects, calling menu items, inspecting scenes, and refining UI layouts from screenshots via tools like execute-dynamic-code, execute-menu-item, and capture-window. The tool enables AI-driven development loops to run autonomously inside existing Unity projects.
rag-gpt
RAG-GPT is a tool that allows users to quickly launch an intelligent customer service system with Flask, LLM, and RAG. It includes frontend, backend, and admin console components. The tool supports cloud-based and local LLMs, offers quick setup for conversational service robots, integrates diverse knowledge bases, provides flexible configuration options, and features an attractive user interface.
openai-chat-api-workflow
**OpenAI Chat API Workflow for Alfred** An Alfred 5 Workflow for using OpenAI Chat API to interact with GPT-3.5/GPT-4 🤖💬 It also allows image generation 🖼️, image understanding 👀, speech-to-text conversion 🎤, and text-to-speech synthesis 🔈 **Features:** * Execute all features using Alfred UI, selected text, or a dedicated web UI * Web UI is constructed by the workflow and runs locally on your Mac 💻 * API call is made directly between the workflow and OpenAI, ensuring your chat messages are not shared online with anyone other than OpenAI 🔒 * OpenAI does not use the data from the API Platform for training 🚫 * Export chat data to a simple JSON format external file 📄 * Continue the chat by importing the exported data later 🔄
Unity-MCP
Unity-MCP is an AI helper designed for game developers using Unity. It facilitates a wide range of tasks in Unity Editor and running games on any platform by connecting to AI via TCP connection. The tool allows users to chat with AI like with a human, supports local and remote usage, and offers various default AI tools. Users can provide detailed information for classes, fields, properties, and methods using the 'Description' attribute in C# code. Unity-MCP enables instant C# code compilation and execution, provides access to assets and C# scripts, and offers tools for proper issue understanding and project data manipulation. It also allows users to find and call methods in the codebase, work with Unity API, and access human-readable descriptions of code elements.
agents-starter
A starter template for building AI-powered chat agents using Cloudflare's Agent platform, powered by agents-sdk. It provides a foundation for creating interactive chat experiences with AI, complete with a modern UI and tool integration capabilities. Features include interactive chat interface with AI, built-in tool system with human-in-the-loop confirmation, advanced task scheduling, dark/light theme support, real-time streaming responses, state management, and chat history. Prerequisites include a Cloudflare account and OpenAI API key. The project structure includes components for chat UI implementation, chat agent logic, tool definitions, and helper functions. Customization guide covers adding new tools, modifying the UI, and example use cases for customer support, development assistant, data analysis assistant, personal productivity assistant, and scheduling assistant.

shellChatGPT
ShellChatGPT is a shell wrapper for OpenAI's ChatGPT, DALL-E, Whisper, and TTS, featuring integration with LocalAI, Ollama, Gemini, Mistral, Groq, and GitHub Models. It provides text and chat completions, vision, reasoning, and audio models, voice-in and voice-out chatting mode, text editor interface, markdown rendering support, session management, instruction prompt manager, integration with various service providers, command line completion, file picker dialogs, color scheme personalization, stdin and text file input support, and compatibility with Linux, FreeBSD, MacOS, and Termux for a responsive experience.
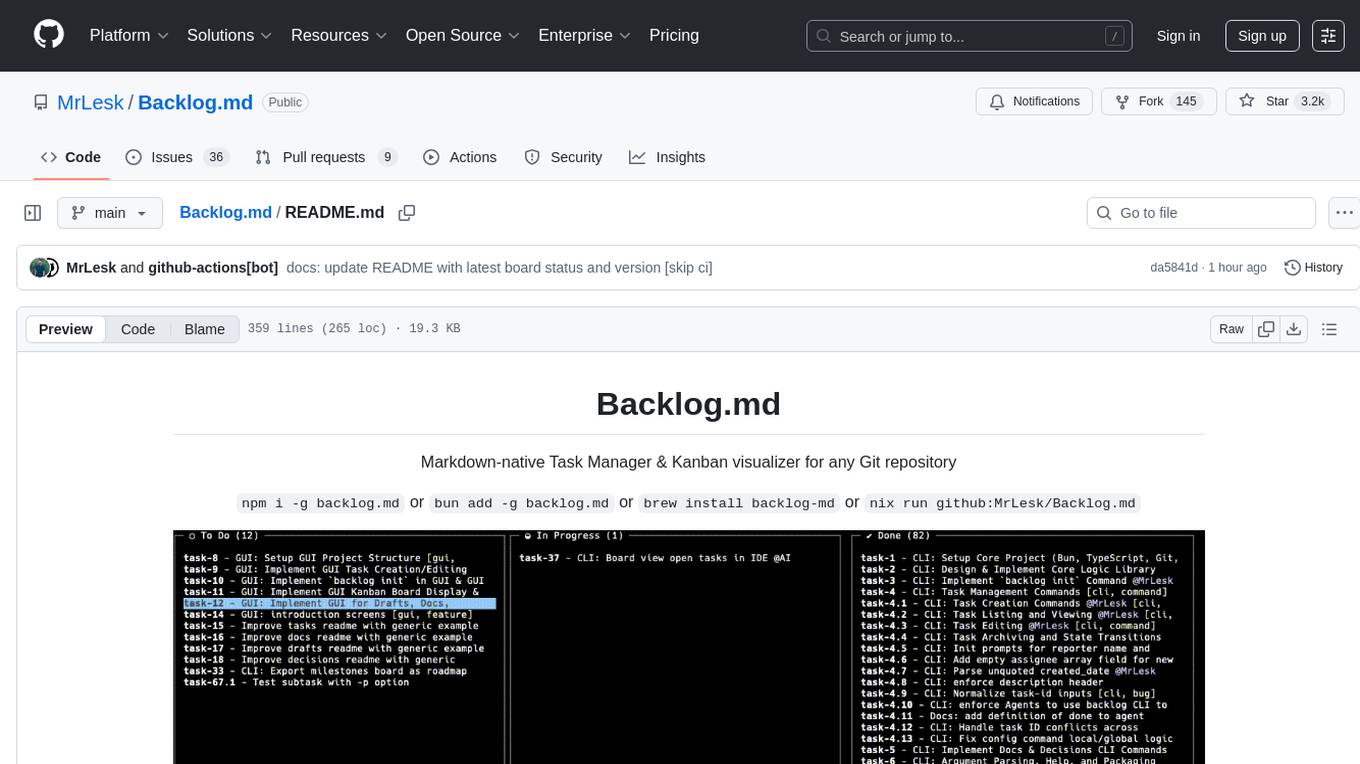
Backlog.md
Backlog.md is a Markdown-native Task Manager & Kanban visualizer for any Git repository. It turns any folder with a Git repo into a self-contained project board powered by plain Markdown files and a zero-config CLI. Features include managing tasks as plain .md files, private & offline usage, instant terminal Kanban visualization, board export, modern web interface, AI-ready CLI, rich query commands, cross-platform support, and MIT-licensed open-source. Users can create tasks, view board, assign tasks to AI, manage documentation, make decisions, and configure settings easily.
For similar tasks

twitter-automation-ai
Advanced Twitter Automation AI is a modular Python-based framework for automating Twitter at scale. It supports multiple accounts, robust Selenium automation with optional undetected Chrome + stealth, per-account proxies and rotation, structured LLM generation/analysis, community posting, and per-account metrics/logs. The tool allows seamless management and automation of multiple Twitter accounts, content scraping, publishing, LLM integration for generating and analyzing tweet content, engagement automation, configurable automation, browser automation using Selenium, modular design for easy extension, comprehensive logging, community posting, stealth mode for reduced fingerprinting, per-account proxies, LLM structured prompts, and per-account JSON summaries and event logs for observability.
THE-SANDBOX-AutoClicker
The Sandbox AutoClicker is a bot designed for the crypto game The Sandbox, allowing users to automate various processes within the game. The tool offers features such as auto tuning, multi-account auto clicker, multi-threading, a convenient menu, and free proxies. It provides full optimization through a simple menu and is guaranteed to be safe for Windows systems, supporting versions 7/8/8.1/10/11 (x32/64).
kirara-ai
Kirara AI is a chatbot that supports mainstream large language models and chat platforms. It provides features such as image sending, keyword-triggered replies, multi-account support, personality settings, and support for various chat platforms like QQ, Telegram, Discord, and WeChat. The tool also supports HTTP server for Web API, popular large models like OpenAI and DeepSeek, plugin mechanism, conditional triggers, admin commands, drawing models, voice replies, multi-turn conversations, cross-platform message sending, custom workflows, web management interface, and built-in Frpc intranet penetration.
oba-live-tool
The oba live tool is a small tool for Douyin small shops and Kuaishou Baiying live broadcasts. It features multiple account management, intelligent message assistant, automatic product explanation, AI automatic reply, and AI intelligent assistant. The tool requires Windows 10 or above, Chrome or Edge browser, and a valid account for Douyin small shops or Kuaishou Baiying. Users can download the tool from the Releases page, connect to the control panel, set API keys for AI functions, and configure auto-reply prompts. The tool is licensed under the MIT license.
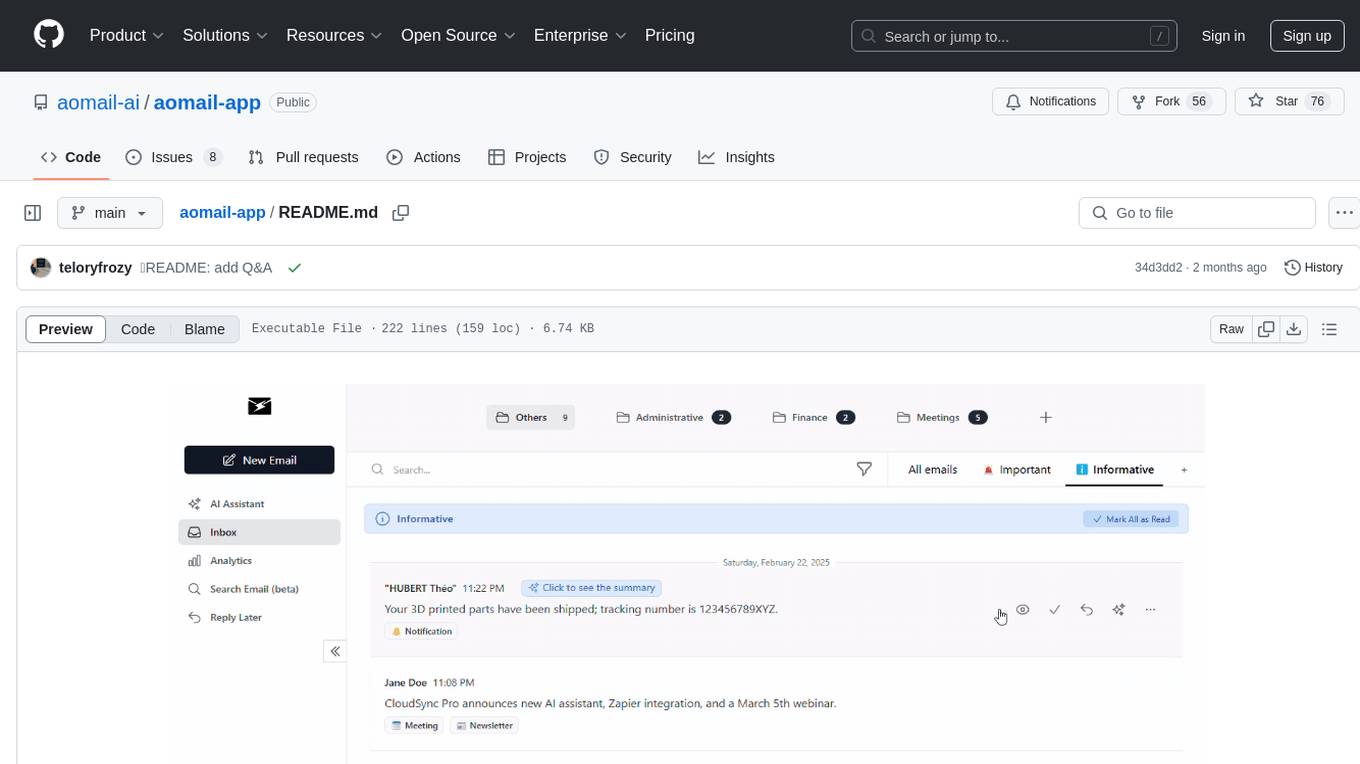
aomail-app
Aomail is an intelligent, open-source email management platform with AI capabilities. It offers email provider integration, AI-powered tools for smart categorization and assistance, analytics and management features. Users can self-host for complete control. Coming soon features include AI custom rules, platform integration with Discord & Slack, and support for various AI providers. The tool is designed to revolutionize email management by providing advanced AI features and analytics.
claude-craft
Claude Craft is a comprehensive framework for AI-assisted development with Claude Code, providing standardized rules, agents, and commands across multiple technology stacks. It includes autonomous sprint capabilities, documentation accuracy improvements, CI hardening, and test coverage enhancements. With support for 10 technology stacks, 5 languages, 40 AI agents, 157 slash commands, and various project management features like BMAD v6 framework, Ralph Wiggum loop execution, skills, templates, checklists, and hooks system, Claude Craft offers a robust solution for project development and management. The tool also supports workflow methodology, development tracks, document generation, BMAD v6 project management, quality gates, batch processing, backlog migration, and Claude Code hooks integration.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.





