
ersilia
The Ersilia Model Hub, a repository of AI/ML models for infectious and neglected disease research.
Stars: 249
The Ersilia Model Hub is a unified platform of pre-trained AI/ML models dedicated to infectious and neglected disease research. It offers an open-source, low-code solution that provides seamless access to AI/ML models for drug discovery. Models housed in the hub come from two sources: published models from literature (with due third-party acknowledgment) and custom models developed by the Ersilia team or contributors.
README:
The Ersilia Model Hub is a unified platform of pre-trained AI/ML models for 🦠 infectious and neglected disease research. Our mission is to offer an open-source, 🛠 low-code solution that provides seamless access to AI/ML models for 💊 drug discovery. Models housed in our hub come from two sources:
- Published models from literature (with due third-party acknowledgement)
- Custom models developed by the Ersilia team or our valued contributors
You can read more about the project in the Ersilia Book and browse available models in the Ersilia Model Hub.
Please check the package requirements in the Installation Guide. The following steps are a quick start guide to using Ersilia.
First, create a conda environment and activate it:
conda create -n ersilia python=3.10
conda activate ersiliaThen, clone this repository and install with pip:
git clone https://github.com/ersilia-os/ersilia.git
cd ersilia
pip install -e .Alternatively, you can directly install from PyPi:
pip install ersiliaOnce the Ersilia package is installed, you can use the CLI to run predictions. First, select a model from the Ersilia Model Hub and fetch it:
ersilia fetch eos4e40Note that you can use the model identifier (eos4e40) or its human-readable slug (antibiotic-activity).
Now you can serve the model:
ersilia serve eos4e40To view some information of the model, type the following:
ersilia infoThe simplest way to run a model is by passing a CSV file as input. If you don't have one, you can generate it easily. In this case, we take 5 molecules as an example:
ersilia example -n 5 -f my_input.csvNow you can run the model:
ersilia run -i my_input.csv -o my_output.csvTo stop the service, you can simply close the model:
ersilia closeFinally, if you don't want to use the model anymore, delete it as follows:
ersilia delete eos4e40Please see the Ersilia Book for more examples and detailed explanations.
For Python versions 3.12, Ersilia explicitly installs the setuptools library during installation. This is due to a compatibility issue in Python 3.12, which is described in python/cpython#95299.
Note: If you are using Python 3.12, you don’t need to take any manual action. The Ersilia CLI automatically handles this by installing setuptools as part of the setup process.
The Ersilia Model Hub is a Free, Open Source Software and we highly value new contributors. There are several ways in which you can contribute to the project:
- A good place to start is checking open issues
- If you have identified a bug in the code, please open a new issue using the bug template
- Share any feedback with the community using GitHub Discussions for the project
- Check our Contributing Guide for more details
The Ersilia Open Source Initiative adheres to the Contributor Covenant code of conduct.
To maintain consistency and code quality, we follow certain coding and linting standards. Please adhere to these guidelines when contributing:
We use pre-commit and ruff to automate code quality checks. Ensure you install and set up pre-commit and ruff before committing any changes:
- Install pre-commit:
pip install pre-commit - Set up pre-commit hooks in your local repository by running:
pre-commit install
- When you commit it automatically fix the issues but will fail for critical error such as missing docstring on a public class and public methods.
- Run
ruffto check for linting errors:ruff check . - Automatically fix linting issues (where possible):
ruff check . --fix
We adhere to the NumPy-style docstring format. Please document all public methods and functions using this style.
Consistent documentation ensures the code is easy to understand and maintain.
Thank you for your contributions and for helping make the Ersilia Model Hub a better project!
If you want to incorporate a new model in the platform, open a new issue using the model request template or contact us using the following form.
After submitting your model request via an issue (suggested), an Ersilia maintainer will review your request. If they approve your request, a new model respository will be created for you to fork and use! There is a demo repository explaining the steps one-by-one.
This repository is open-sourced under the GPL-3 License. Please cite us if you use it!
Please note that Ersilia distinguises between software contributors and software authors. The Ersilia Model Hub Authorship guidelines can be found in the Authorship file and current authors can be found in the Citation file. We acknowledge past authors of the software below:
- Carolina Caballero
The Ersilia Model Hub is used in a number of scientific projects. Read more about how we are implementing it in:
- Turon, Hlozek et al, Nat Commun, 2023
- Van Heerden et al, ACS Omega, 2023
- Offensperger et al, Science, 2024
- Turon et al, ACS Med Chem Lett, 2024
The Ersilia Open Source Initiative is a Non Profit Organization with the mission is to equip labs, universities and clinics in LMIC with AI/ML tools for infectious disease research. Help us achieve our mission!
The Ersilia Model Hub is the flagship product of Ersilia. It has been funded thanks to a combination of funding sources. Full disclosure can be found in our website. Highlighted supporters include the Mozilla Builders Accelerator, Fast Forward, Splunk Pledge and the AI2050 Program by Schmidt Sciences.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ersilia
Similar Open Source Tools

ersilia
The Ersilia Model Hub is a unified platform of pre-trained AI/ML models dedicated to infectious and neglected disease research. It offers an open-source, low-code solution that provides seamless access to AI/ML models for drug discovery. Models housed in the hub come from two sources: published models from literature (with due third-party acknowledgment) and custom models developed by the Ersilia team or contributors.
hi-ml
The Microsoft Health Intelligence Machine Learning Toolbox is a repository that provides low-level and high-level building blocks for Machine Learning / AI researchers and practitioners. It simplifies and streamlines work on deep learning models for healthcare and life sciences by offering tested components such as data loaders, pre-processing tools, deep learning models, and cloud integration utilities. The repository includes two Python packages, 'hi-ml-azure' for helper functions in AzureML, 'hi-ml' for ML components, and 'hi-ml-cpath' for models and workflows related to histopathology images.
atomic_agents
Atomic Agents is a modular and extensible framework designed for creating powerful applications. It follows the principles of Atomic Design, emphasizing small and single-purpose components. Leveraging Pydantic for data validation and serialization, the framework offers a set of tools and agents that can be combined to build AI applications. It depends on the Instructor package and supports various APIs like OpenAI, Cohere, Anthropic, and Gemini. Atomic Agents is suitable for developers looking to create AI agents with a focus on modularity and flexibility.
lumigator
Lumigator is an open-source platform developed by Mozilla.ai to help users select the most suitable language model for their specific needs. It supports the evaluation of summarization tasks using sequence-to-sequence models such as BART and BERT, as well as causal models like GPT and Mistral. The platform aims to make model selection transparent, efficient, and empowering by providing a framework for comparing LLMs using task-specific metrics to evaluate how well a model fits a project's needs. Lumigator is in the early stages of development and plans to expand support to additional machine learning tasks and use cases in the future.
aiid
The Artificial Intelligence Incident Database (AIID) is a collection of incidents involving the development and use of artificial intelligence (AI). The database is designed to help researchers, policymakers, and the public understand the potential risks and benefits of AI, and to inform the development of policies and practices to mitigate the risks and promote the benefits of AI. The AIID is a collaborative project involving researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, the University of Washington, and the University of Toronto.
comfyui_LLM_party
COMFYUI LLM PARTY is a node library designed for LLM workflow development in ComfyUI, an extremely minimalist UI interface primarily used for AI drawing and SD model-based workflows. The project aims to provide a complete set of nodes for constructing LLM workflows, enabling users to easily integrate them into existing SD workflows. It features various functionalities such as API integration, local large model integration, RAG support, code interpreters, online queries, conditional statements, looping links for large models, persona mask attachment, and tool invocations for weather lookup, time lookup, knowledge base, code execution, web search, and single-page search. Users can rapidly develop web applications using API + Streamlit and utilize LLM as a tool node. Additionally, the project includes an omnipotent interpreter node that allows the large model to perform any task, with recommendations to use the 'show_text' node for display output.
ezkl
EZKL is a library and command-line tool for doing inference for deep learning models and other computational graphs in a zk-snark (ZKML). It enables the following workflow: 1. Define a computational graph, for instance a neural network (but really any arbitrary set of operations), as you would normally in pytorch or tensorflow. 2. Export the final graph of operations as an .onnx file and some sample inputs to a .json file. 3. Point ezkl to the .onnx and .json files to generate a ZK-SNARK circuit with which you can prove statements such as: > "I ran this publicly available neural network on some private data and it produced this output" > "I ran my private neural network on some public data and it produced this output" > "I correctly ran this publicly available neural network on some public data and it produced this output" In the backend we use the collaboratively-developed Halo2 as a proof system. The generated proofs can then be verified with much less computational resources, including on-chain (with the Ethereum Virtual Machine), in a browser, or on a device.
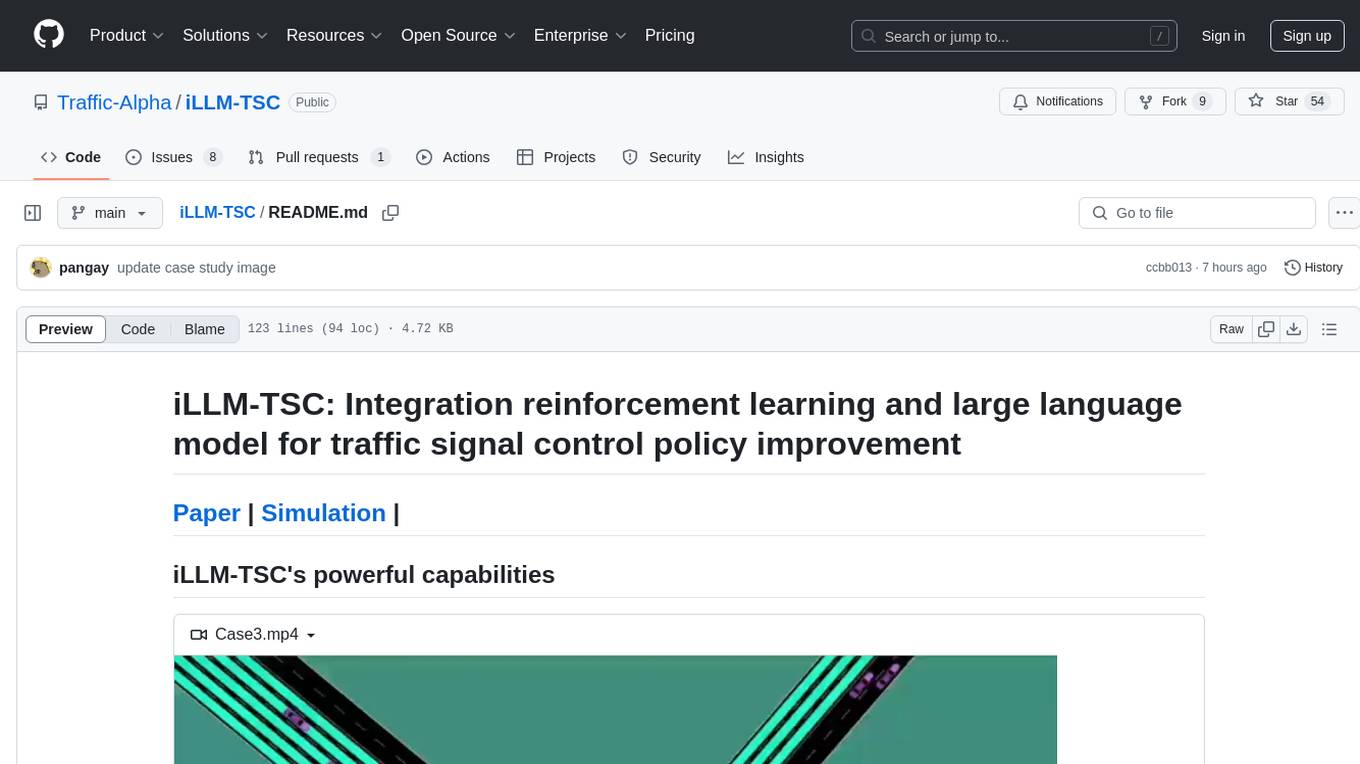
iLLM-TSC
iLLM-TSC is a framework that integrates reinforcement learning and large language models for traffic signal control policy improvement. It refines RL decisions based on real-world contexts and provides reasonable actions when RL agents make erroneous decisions. The framework includes cases where the large language model provides explanations and recommendations for RL agent actions, such as prioritizing emergency vehicles at intersections. Users can install and run the framework locally to train RL models and evaluate the combined RL+LLM approach.
ModernBERT
ModernBERT is a repository focused on modernizing BERT through architecture changes and scaling. It introduces FlexBERT, a modular approach to encoder building blocks, and heavily relies on .yaml configuration files to build models. The codebase builds upon MosaicBERT and incorporates Flash Attention 2. The repository is used for pre-training and GLUE evaluations, with a focus on reproducibility and documentation. It provides a collaboration between Answer.AI, LightOn, and friends.
hackingBuddyGPT
hackingBuddyGPT is a framework for testing LLM-based agents for security testing. It aims to create common ground truth by creating common security testbeds and benchmarks, evaluating multiple LLMs and techniques against those, and publishing prototypes and findings as open-source/open-access reports. The initial focus is on evaluating the efficiency of LLMs for Linux privilege escalation attacks, but the framework is being expanded to evaluate the use of LLMs for web penetration-testing and web API testing. hackingBuddyGPT is released as open-source to level the playing field for blue teams against APTs that have access to more sophisticated resources.
AppAgent
AppAgent is a novel LLM-based multimodal agent framework designed to operate smartphone applications. Our framework enables the agent to operate smartphone applications through a simplified action space, mimicking human-like interactions such as tapping and swiping. This novel approach bypasses the need for system back-end access, thereby broadening its applicability across diverse apps. Central to our agent's functionality is its innovative learning method. The agent learns to navigate and use new apps either through autonomous exploration or by observing human demonstrations. This process generates a knowledge base that the agent refers to for executing complex tasks across different applications.

HackBot
HackBot is an AI-powered cybersecurity chatbot designed to provide accurate answers to cybersecurity-related queries, conduct code analysis, and scan analysis. It utilizes the Meta-LLama2 AI model through the 'LlamaCpp' library to respond coherently. The chatbot offers features like local AI/Runpod deployment support, cybersecurity chat assistance, interactive interface, clear output presentation, static code analysis, and vulnerability analysis. Users can interact with HackBot through a command-line interface and utilize it for various cybersecurity tasks.
EdgeChains
EdgeChains is an open-source chain-of-thought engineering framework tailored for Large Language Models (LLMs)- like OpenAI GPT, LLama2, Falcon, etc. - With a focus on enterprise-grade deployability and scalability. EdgeChains is specifically designed to **orchestrate** such applications. At EdgeChains, we take a unique approach to Generative AI - we think Generative AI is a deployment and configuration management challenge rather than a UI and library design pattern challenge. We build on top of a tech that has solved this problem in a different domain - Kubernetes Config Management - and bring that to Generative AI. Edgechains is built on top of jsonnet, originally built by Google based on their experience managing a vast amount of configuration code in the Borg infrastructure.
second-brain-agent
The Second Brain AI Agent Project is a tool designed to empower personal knowledge management by automatically indexing markdown files and links, providing a smart search engine powered by OpenAI, integrating seamlessly with different note-taking methods, and enhancing productivity by accessing information efficiently. The system is built on LangChain framework and ChromaDB vector store, utilizing a pipeline to process markdown files and extract text and links for indexing. It employs a Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) process to provide context for asking questions to the large language model. The tool is beneficial for professionals, students, researchers, and creatives looking to streamline workflows, improve study sessions, delve deep into research, and organize thoughts and ideas effortlessly.
BentoDiffusion
BentoDiffusion is a BentoML example project that demonstrates how to serve and deploy diffusion models in the Stable Diffusion (SD) family. These models are specialized in generating and manipulating images based on text prompts. The project provides a guide on using SDXL Turbo as an example, along with instructions on prerequisites, installing dependencies, running the BentoML service, and deploying to BentoCloud. Users can interact with the deployed service using Swagger UI or other methods. Additionally, the project offers the option to choose from various diffusion models available in the repository for deployment.

GlaDOS
This project aims to create a real-life version of GLaDOS, an aware, interactive, and embodied AI entity. It involves training a voice generator, developing a 'Personality Core,' implementing a memory system, providing vision capabilities, creating 3D-printable parts, and designing an animatronics system. The software architecture focuses on low-latency voice interactions, utilizing a circular buffer for data recording, text streaming for quick transcription, and a text-to-speech system. The project also emphasizes minimal dependencies for running on constrained hardware. The hardware system includes servo- and stepper-motors, 3D-printable parts for GLaDOS's body, animations for expression, and a vision system for tracking and interaction. Installation instructions cover setting up the TTS engine, required Python packages, compiling llama.cpp, installing an inference backend, and voice recognition setup. GLaDOS can be run using 'python glados.py' and tested using 'demo.ipynb'.
For similar tasks

ersilia
The Ersilia Model Hub is a unified platform of pre-trained AI/ML models dedicated to infectious and neglected disease research. It offers an open-source, low-code solution that provides seamless access to AI/ML models for drug discovery. Models housed in the hub come from two sources: published models from literature (with due third-party acknowledgment) and custom models developed by the Ersilia team or contributors.
For similar jobs

NoLabs
NoLabs is an open-source biolab that provides easy access to state-of-the-art models for bio research. It supports various tasks, including drug discovery, protein analysis, and small molecule design. NoLabs aims to accelerate bio research by making inference models accessible to everyone.
OpenCRISPR
OpenCRISPR is a set of free and open gene editing systems designed by Profluent Bio. The OpenCRISPR-1 protein maintains the prototypical architecture of a Type II Cas9 nuclease but is hundreds of mutations away from SpCas9 or any other known natural CRISPR-associated protein. You can view OpenCRISPR-1 as a drop-in replacement for many protocols that need a cas9-like protein with an NGG PAM and you can even use it with canonical SpCas9 gRNAs. OpenCRISPR-1 can be fused in a deactivated or nickase format for next generation gene editing techniques like base, prime, or epigenome editing.

ersilia
The Ersilia Model Hub is a unified platform of pre-trained AI/ML models dedicated to infectious and neglected disease research. It offers an open-source, low-code solution that provides seamless access to AI/ML models for drug discovery. Models housed in the hub come from two sources: published models from literature (with due third-party acknowledgment) and custom models developed by the Ersilia team or contributors.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.
bia-bob
BIA `bob` is a Jupyter-based assistant for interacting with data using large language models to generate Python code. It can utilize OpenAI's chatGPT, Google's Gemini, Helmholtz' blablador, and Ollama. Users need respective accounts to access these services. Bob can assist in code generation, bug fixing, code documentation, GPU-acceleration, and offers a no-code custom Jupyter Kernel. It provides example notebooks for various tasks like bio-image analysis, model selection, and bug fixing. Installation is recommended via conda/mamba environment. Custom endpoints like blablador and ollama can be used. Google Cloud AI API integration is also supported. The tool is extensible for Python libraries to enhance Bob's functionality.
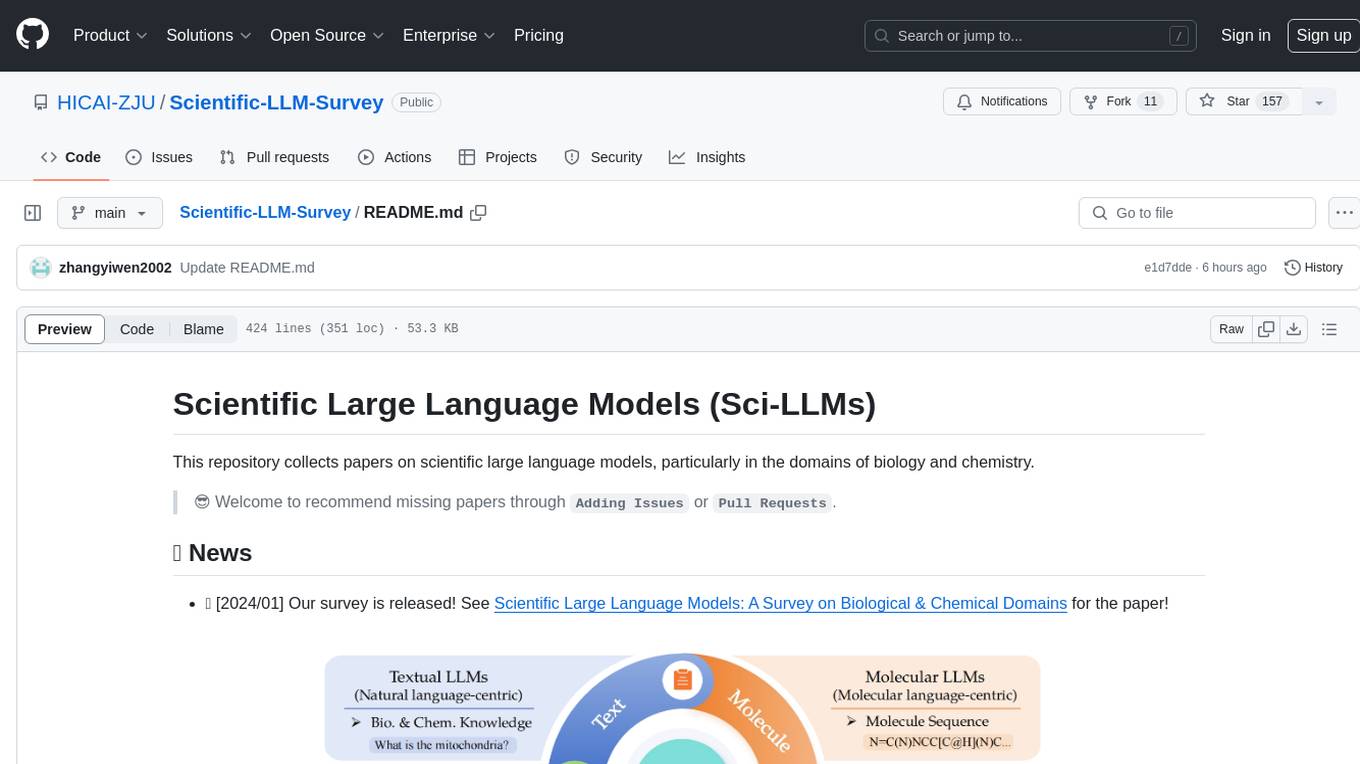
Scientific-LLM-Survey
Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs) is a repository that collects papers on scientific large language models, focusing on biology and chemistry domains. It includes textual, molecular, protein, and genomic languages, as well as multimodal language. The repository covers various large language models for tasks such as molecule property prediction, interaction prediction, protein sequence representation, protein sequence generation/design, DNA-protein interaction prediction, and RNA prediction. It also provides datasets and benchmarks for evaluating these models. The repository aims to facilitate research and development in the field of scientific language modeling.
polaris
Polaris establishes a novel, industry‑certified standard to foster the development of impactful methods in AI-based drug discovery. This library is a Python client to interact with the Polaris Hub. It allows you to download Polaris datasets and benchmarks, evaluate a custom method against a Polaris benchmark, and create and upload new datasets and benchmarks.
awesome-AI4MolConformation-MD
The 'awesome-AI4MolConformation-MD' repository focuses on protein conformations and molecular dynamics using generative artificial intelligence and deep learning. It provides resources, reviews, datasets, packages, and tools related to AI-driven molecular dynamics simulations. The repository covers a wide range of topics such as neural networks potentials, force fields, AI engines/frameworks, trajectory analysis, visualization tools, and various AI-based models for protein conformational sampling. It serves as a comprehensive guide for researchers and practitioners interested in leveraging AI for studying molecular structures and dynamics.







