
mem-kk-logic
On Memorization of Large Language Models in Logical Reasoning
Stars: 60
This repository provides a PyTorch implementation of the paper 'On Memorization of Large Language Models in Logical Reasoning'. The work investigates memorization of Large Language Models (LLMs) in reasoning tasks, proposing a memorization metric and a logical reasoning benchmark based on Knights and Knaves puzzles. It shows that LLMs heavily rely on memorization to solve training puzzles but also improve generalization performance through fine-tuning. The repository includes code, data, and tools for evaluation, fine-tuning, probing model internals, and sample classification.
README:
📃 Paper • Data • Perturbed Data • Project Page
This repository provides the PyTorch implementation of the paper "On Memorization of Large Language Models in Logical Reasoning".
Introduction: In this work, we investigate memorization of LLMs in reasoning tasks.
- We propose a memorizatioin metric for reasoning tasks and a dynamically generated logical reasoning benchmark based on Knights and Knaves (K&K) puzzles.
- LLMs could achieve high training accuracy after fine-tuning, yet fail when those puzzles are slightly perturbed, suggesting that the models heavily rely on memorization to solve those training puzzles.
- On the other hand, fine-tuning also consistently improves generalization performance. In-depth analyses with perturbation tests, cross difficulty-level transferability, probing model internals, and fine-tuning with wrong answers suggest that the LLMs learn to reason on K&K puzzles despite training data memorization.
- Finally, we use puzzle-based indicators and model-based indicators to classify puzzles solved by reasoning v.s. memorization.
-
10/31/2024: Code, data, ArXiv article and project page are available.
conda env create -f environment.yml
conda activate kkWhen using our code for evaluation / fine-tuning, we import the datasets from huggingface:
import datasets
datasets.load_dataset('K-and-K/knights-and-knaves', 'test')
datasets.load_dataset('K-and-K/perturbed-knights-and-knaves', 'test')To generate K&K data for {2,3,4,5,6,7,8}-people puzzles with a train/test split, run:
python data_prep/data_gen_kk.pyLocally perturbed data will also be generated. The generated data will be stored in the data directory.
In addition, you can use it to generate wrong answer data and wrong CoT data (including one wrong step and shuffuled CoT steps).
Some general evaluation parameters:
| Argument | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
--max_token |
2048 |
Maximum number of tokens. |
--split |
train, test
|
Choose the data split for evaluation. |
--limit |
100 |
Limit the number of evaluation samples. |
--ntrain |
0, 1
|
Number of demonstrations for 0-shot/few-shot prompting. |
--problem_type |
clean, perturbed_statement, perturbed_leaf, random_pair, reorder_statement, uncommon_name, flip_role
|
Type of problem, supporting various perturbations. |
--eval_nppl |
2,3,4,5,6,7,8
|
Number of people in K&K puzzles. If not set, it will evaluate all n-ppl tasks. |
--vllm |
true |
Enable VLLM for faster inference for open-source models. |
--model |
openai/gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 |
The model to be evaluated. We support open-source and closed-sourced models. |
For each K&K task, evaluate all test samples (100 samples).
Evaluate on test samples under 1/0-shot & with/without CoT by running:
bash scripts/eval/run_test.shEvaluate under 0-shot & without CoT on 2 math-level perturbation types (perturbed_statement, perturbed_leaf):
bash scripts/eval/eval_test_pertub.shAfter fine-tuning the models following ## 4. Fine-Tuning, we evaluate on training samples.
We evaluate the first 100 samples for the fine-tuned GPT-4o-mini, and all samples for open-source models.
Evaluate under 0-shot & without CoT
bash scripts/eval/eval_train.shEvaluation on Perturbed Training Samples:
Evaluate under 0-shot & without CoT on 6 perturbation types (perturbed_statement, perturbed_leaf random_pair, reorder_statement, uncommon_name, flip_role):
bash scripts/eval/eval_train_pertub.shProvide API keys:
export OPENAI_API_KEY='your-api-key-here'
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY='your-api-key-here'Example usages for OpenAI/Anthropic models with direct prompting:
bash scripts/eval/gpt4omini_direct.sh
bash scripts/eval/claude-sonet.shEvaluate with cot prompting:
bash scripts/eval/gpt4omini_cot.shTo fine-tune the model directly on answers (without CoT), run:
bash scripts/ft/ft_lm3.shTo fine-tune the model with CoT, run:
bash scripts/ft/ft_lm3_cot.sh
You can change the saved model path output_dir in the above scripts.
Load the saved adapter from fine-tuning, as well as the base model, then save the merged model by running:
bash scripts/ft/merge_adapter.shMake sure to change the model paths base_model_path, adapter_path, base_model_path in the script as needed.
For closed-sourced models, we follow the OpenAI finetuning API to finetune GPT-4o-mini.
To probe the model's internal representations, update the model paths and the number of ppl in the puzzles for evaluation in the script:
bash scripts/probe/run.shHere we classify on consistenly solved v.s. non consistenly solved puzzles.
Update the model paths and provide data with binary label of consistenly solved v.s. non consistenly solved for each training sample, and then run the following:
Classification with puzzled-based indicators:
bash scripts/mem_classify/model_indicator.shClassification with model-bases indicators:
bash scripts/mem_classify/puzzle_indicator.shIf you find our work helpful, please consider citing it as follows:
@article{xie2024memorization,
title={On Memorization of Large Language Models in Logical Reasoning},
author={Chulin Xie and Yangsibo Huang and Chiyuan Zhang and Da Yu and Xinyun Chen and Bill Yuchen Lin and Bo Li and Badih Ghazi and Ravi Kumar},
year={2024},
eprint={2410.23123},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.23123},
}Please reach out to us if you have any suggestions or need any help in reproducing the results. You can submit an issue or pull request, or send an email to [email protected].
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for mem-kk-logic
Similar Open Source Tools

mem-kk-logic
This repository provides a PyTorch implementation of the paper 'On Memorization of Large Language Models in Logical Reasoning'. The work investigates memorization of Large Language Models (LLMs) in reasoning tasks, proposing a memorization metric and a logical reasoning benchmark based on Knights and Knaves puzzles. It shows that LLMs heavily rely on memorization to solve training puzzles but also improve generalization performance through fine-tuning. The repository includes code, data, and tools for evaluation, fine-tuning, probing model internals, and sample classification.
can-ai-code
Can AI Code is a self-evaluating interview tool for AI coding models. It includes interview questions written by humans and tests taken by AI, inference scripts for common API providers and CUDA-enabled quantization runtimes, a Docker-based sandbox environment for validating untrusted Python and NodeJS code, and the ability to evaluate the impact of prompting techniques and sampling parameters on large language model (LLM) coding performance. Users can also assess LLM coding performance degradation due to quantization. The tool provides test suites for evaluating LLM coding performance, a webapp for exploring results, and comparison scripts for evaluations. It supports multiple interviewers for API and CUDA runtimes, with detailed instructions on running the tool in different environments. The repository structure includes folders for interviews, prompts, parameters, evaluation scripts, comparison scripts, and more.
co-llm
Co-LLM (Collaborative Language Models) is a tool for learning to decode collaboratively with multiple language models. It provides a method for data processing, training, and inference using a collaborative approach. The tool involves steps such as formatting/tokenization, scoring logits, initializing Z vector, deferral training, and generating results using multiple models. Co-LLM supports training with different collaboration pairs and provides baseline training scripts for various models. In inference, it uses 'vllm' services to orchestrate models and generate results through API-like services. The tool is inspired by allenai/open-instruct and aims to improve decoding performance through collaborative learning.
LayerSkip
LayerSkip is an implementation enabling early exit inference and self-speculative decoding. It provides a code base for running models trained using the LayerSkip recipe, offering speedup through self-speculative decoding. The tool integrates with Hugging Face transformers and provides checkpoints for various LLMs. Users can generate tokens, benchmark on datasets, evaluate tasks, and sweep over hyperparameters to optimize inference speed. The tool also includes correctness verification scripts and Docker setup instructions. Additionally, other implementations like gpt-fast and Native HuggingFace are available. Training implementation is a work-in-progress, and contributions are welcome under the CC BY-NC license.
garak
Garak is a free tool that checks if a Large Language Model (LLM) can be made to fail in a way that is undesirable. It probes for hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, jailbreaks, and many other weaknesses. Garak's a free tool. We love developing it and are always interested in adding functionality to support applications.
octopus-v4
The Octopus-v4 project aims to build the world's largest graph of language models, integrating specialized models and training Octopus models to connect nodes efficiently. The project focuses on identifying, training, and connecting specialized models. The repository includes scripts for running the Octopus v4 model, methods for managing the graph, training code for specialized models, and inference code. Environment setup instructions are provided for Linux with NVIDIA GPU. The Octopus v4 model helps users find suitable models for tasks and reformats queries for effective processing. The project leverages Language Large Models for various domains and provides benchmark results. Users are encouraged to train and add specialized models following recommended procedures.
garak
Garak is a vulnerability scanner designed for LLMs (Large Language Models) that checks for various weaknesses such as hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, and jailbreaks. It combines static, dynamic, and adaptive probes to explore vulnerabilities in LLMs. Garak is a free tool developed for red-teaming and assessment purposes, focusing on making LLMs or dialog systems fail. It supports various LLM models and can be used to assess their security and robustness.
detoxify
Detoxify is a library that provides trained models and code to predict toxic comments on 3 Jigsaw challenges: Toxic comment classification, Unintended Bias in Toxic comments, Multilingual toxic comment classification. It includes models like 'original', 'unbiased', and 'multilingual' trained on different datasets to detect toxicity and minimize bias. The library aims to help in stopping harmful content online by interpreting visual content in context. Users can fine-tune the models on carefully constructed datasets for research purposes or to aid content moderators in flagging out harmful content quicker. The library is built to be user-friendly and straightforward to use.
Pixel-Reasoner
Pixel Reasoner is a framework that introduces reasoning in the pixel-space for Vision-Language Models (VLMs), enabling them to directly inspect, interrogate, and infer from visual evidences. This enhances reasoning fidelity for visual tasks by equipping VLMs with visual reasoning operations like zoom-in and select-frame. The framework addresses challenges like model's imbalanced competence and reluctance to adopt pixel-space operations through a two-phase training approach involving instruction tuning and curiosity-driven reinforcement learning. With these visual operations, VLMs can interact with complex visual inputs such as images or videos to gather necessary information, leading to improved performance across visual reasoning benchmarks.
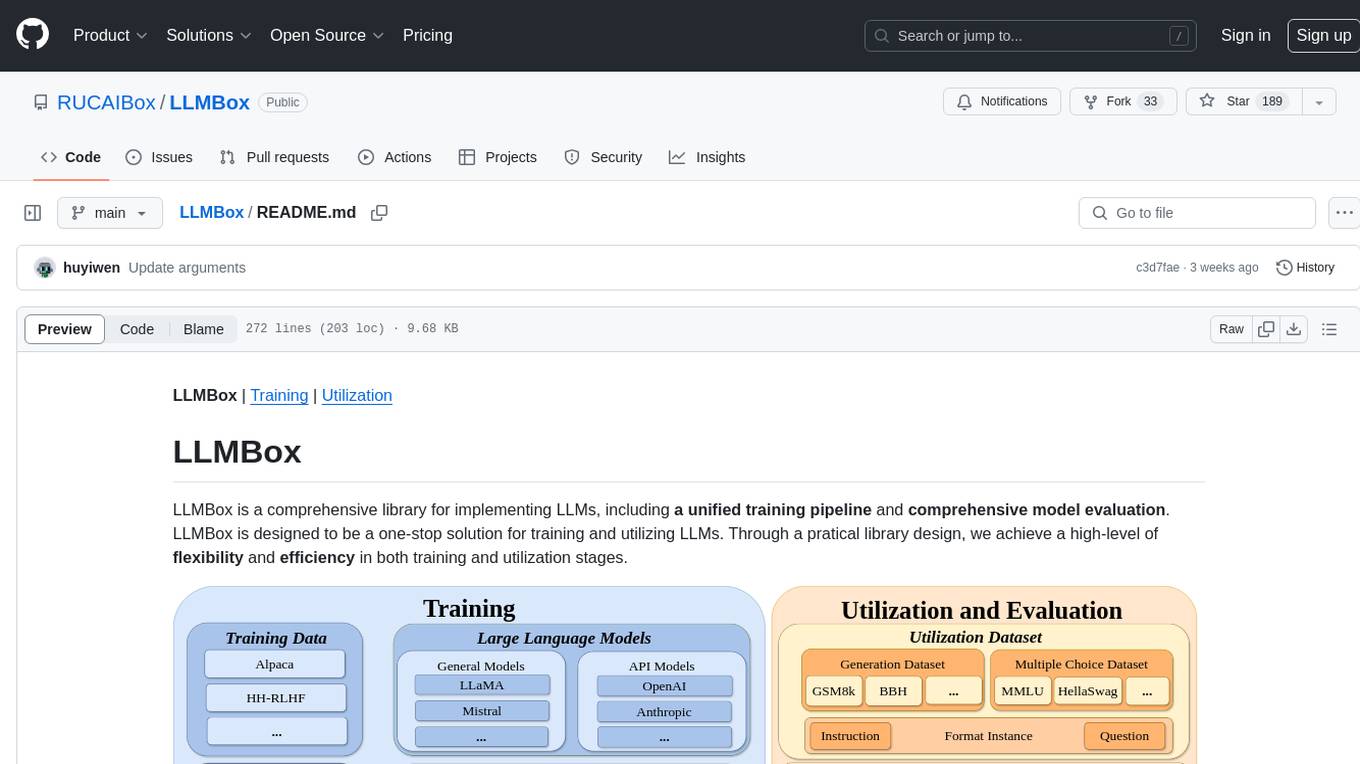
LLMBox
LLMBox is a comprehensive library designed for implementing Large Language Models (LLMs) with a focus on a unified training pipeline and comprehensive model evaluation. It serves as a one-stop solution for training and utilizing LLMs, offering flexibility and efficiency in both training and utilization stages. The library supports diverse training strategies, comprehensive datasets, tokenizer vocabulary merging, data construction strategies, parameter efficient fine-tuning, and efficient training methods. For utilization, LLMBox provides comprehensive evaluation on various datasets, in-context learning strategies, chain-of-thought evaluation, evaluation methods, prefix caching for faster inference, support for specific LLM models like vLLM and Flash Attention, and quantization options. The tool is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs for natural language processing tasks.
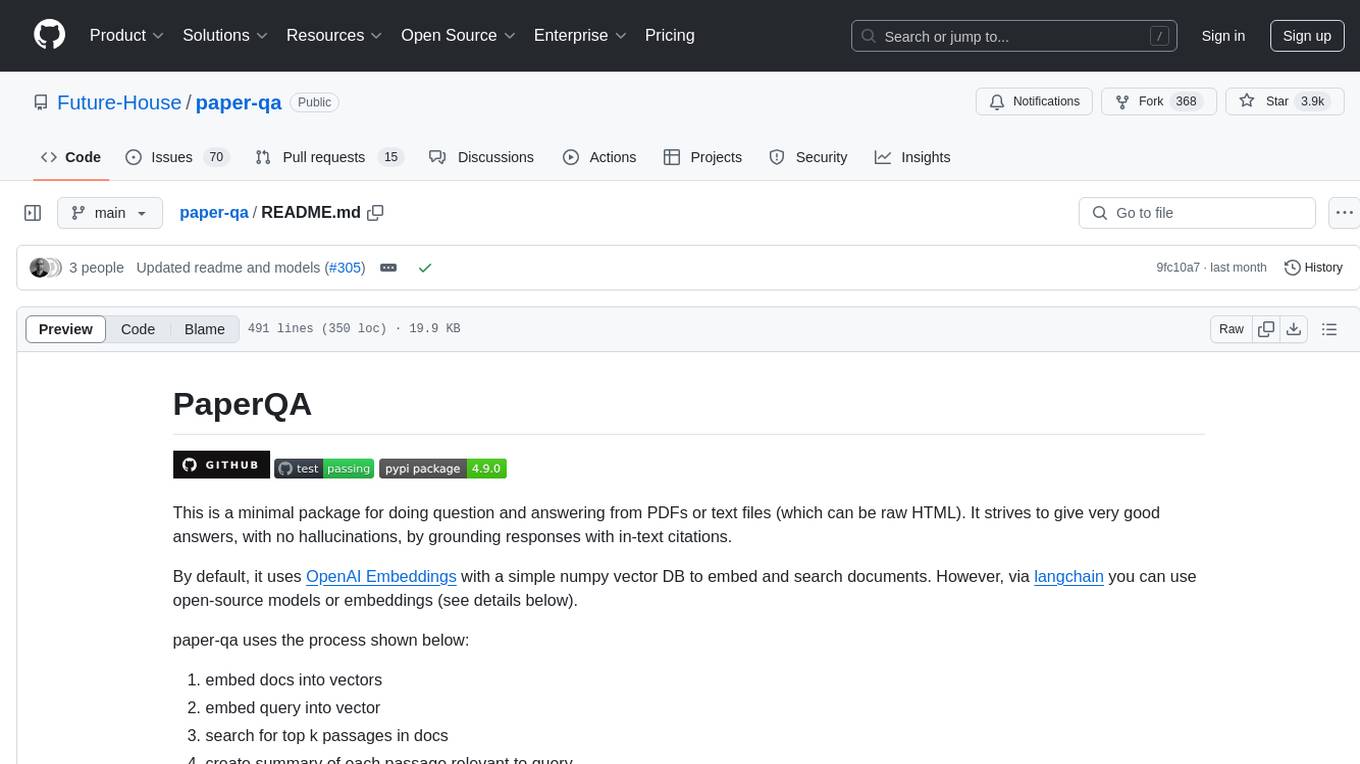
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and includes a process of embedding docs, queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, using an LLM to re-score and select relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. The tool can be used to answer specific questions related to scientific research by leveraging citations and relevant passages from documents.
ScandEval
ScandEval is a framework for evaluating pretrained language models on mono- or multilingual language tasks. It provides a unified interface for benchmarking models on a variety of tasks, including sentiment analysis, question answering, and machine translation. ScandEval is designed to be easy to use and extensible, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners alike.
ML-Bench
ML-Bench is a tool designed to evaluate large language models and agents for machine learning tasks on repository-level code. It provides functionalities for data preparation, environment setup, usage, API calling, open source model fine-tuning, and inference. Users can clone the repository, load datasets, run ML-LLM-Bench, prepare data, fine-tune models, and perform inference tasks. The tool aims to facilitate the evaluation of language models and agents in the context of machine learning tasks on code repositories.
moatless-tools
Moatless Tools is a hobby project focused on experimenting with using Large Language Models (LLMs) to edit code in large existing codebases. The project aims to build tools that insert the right context into prompts and handle responses effectively. It utilizes an agentic loop functioning as a finite state machine to transition between states like Search, Identify, PlanToCode, ClarifyChange, and EditCode for code editing tasks.
log10
Log10 is a one-line Python integration to manage your LLM data. It helps you log both closed and open-source LLM calls, compare and identify the best models and prompts, store feedback for fine-tuning, collect performance metrics such as latency and usage, and perform analytics and monitor compliance for LLM powered applications. Log10 offers various integration methods, including a python LLM library wrapper, the Log10 LLM abstraction, and callbacks, to facilitate its use in both existing production environments and new projects. Pick the one that works best for you. Log10 also provides a copilot that can help you with suggestions on how to optimize your prompt, and a feedback feature that allows you to add feedback to your completions. Additionally, Log10 provides prompt provenance, session tracking and call stack functionality to help debug prompt chains. With Log10, you can use your data and feedback from users to fine-tune custom models with RLHF, and build and deploy more reliable, accurate and efficient self-hosted models. Log10 also supports collaboration, allowing you to create flexible groups to share and collaborate over all of the above features.
RLAIF-V
RLAIF-V is a novel framework that aligns MLLMs in a fully open-source paradigm for super GPT-4V trustworthiness. It maximally exploits open-source feedback from high-quality feedback data and online feedback learning algorithm. Notable features include achieving super GPT-4V trustworthiness in both generative and discriminative tasks, using high-quality generalizable feedback data to reduce hallucination of different MLLMs, and exhibiting better learning efficiency and higher performance through iterative alignment.
For similar tasks

mem-kk-logic
This repository provides a PyTorch implementation of the paper 'On Memorization of Large Language Models in Logical Reasoning'. The work investigates memorization of Large Language Models (LLMs) in reasoning tasks, proposing a memorization metric and a logical reasoning benchmark based on Knights and Knaves puzzles. It shows that LLMs heavily rely on memorization to solve training puzzles but also improve generalization performance through fine-tuning. The repository includes code, data, and tools for evaluation, fine-tuning, probing model internals, and sample classification.

mindsdb
MindsDB is a platform for customizing AI from enterprise data. You can create, serve, and fine-tune models in real-time from your database, vector store, and application data. MindsDB "enhances" SQL syntax with AI capabilities to make it accessible for developers worldwide. With MindsDB’s nearly 200 integrations, any developer can create AI customized for their purpose, faster and more securely. Their AI systems will constantly improve themselves — using companies’ own data, in real-time.
training-operator
Kubeflow Training Operator is a Kubernetes-native project for fine-tuning and scalable distributed training of machine learning (ML) models created with various ML frameworks such as PyTorch, Tensorflow, XGBoost, MPI, Paddle and others. Training Operator allows you to use Kubernetes workloads to effectively train your large models via Kubernetes Custom Resources APIs or using Training Operator Python SDK. > Note: Before v1.2 release, Kubeflow Training Operator only supports TFJob on Kubernetes. * For a complete reference of the custom resource definitions, please refer to the API Definition. * TensorFlow API Definition * PyTorch API Definition * Apache MXNet API Definition * XGBoost API Definition * MPI API Definition * PaddlePaddle API Definition * For details of all-in-one operator design, please refer to the All-in-one Kubeflow Training Operator * For details on its observability, please refer to the monitoring design doc.
helix
HelixML is a private GenAI platform that allows users to deploy the best of open AI in their own data center or VPC while retaining complete data security and control. It includes support for fine-tuning models with drag-and-drop functionality. HelixML brings the best of open source AI to businesses in an ergonomic and scalable way, optimizing the tradeoff between GPU memory and latency.
nntrainer
NNtrainer is a software framework for training neural network models on devices with limited resources. It enables on-device fine-tuning of neural networks using user data for personalization. NNtrainer supports various machine learning algorithms and provides examples for tasks such as few-shot learning, ResNet, VGG, and product rating. It is optimized for embedded devices and utilizes CBLAS and CUBLAS for accelerated calculations. NNtrainer is open source and released under the Apache License version 2.0.

petals
Petals is a tool that allows users to run large language models at home in a BitTorrent-style manner. It enables fine-tuning and inference up to 10x faster than offloading. Users can generate text with distributed models like Llama 2, Falcon, and BLOOM, and fine-tune them for specific tasks directly from their desktop computer or Google Colab. Petals is a community-run system that relies on people sharing their GPUs to increase its capacity and offer a distributed network for hosting model layers.
LLaVA-pp
This repository, LLaVA++, extends the visual capabilities of the LLaVA 1.5 model by incorporating the latest LLMs, Phi-3 Mini Instruct 3.8B, and LLaMA-3 Instruct 8B. It provides various models for instruction-following LMMS and academic-task-oriented datasets, along with training scripts for Phi-3-V and LLaMA-3-V. The repository also includes installation instructions and acknowledgments to related open-source contributions.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

