
LL3DA
[CVPR 2024] "LL3DA: Visual Interactive Instruction Tuning for Omni-3D Understanding, Reasoning, and Planning"; an interactive Large Language 3D Assistant.
Stars: 207
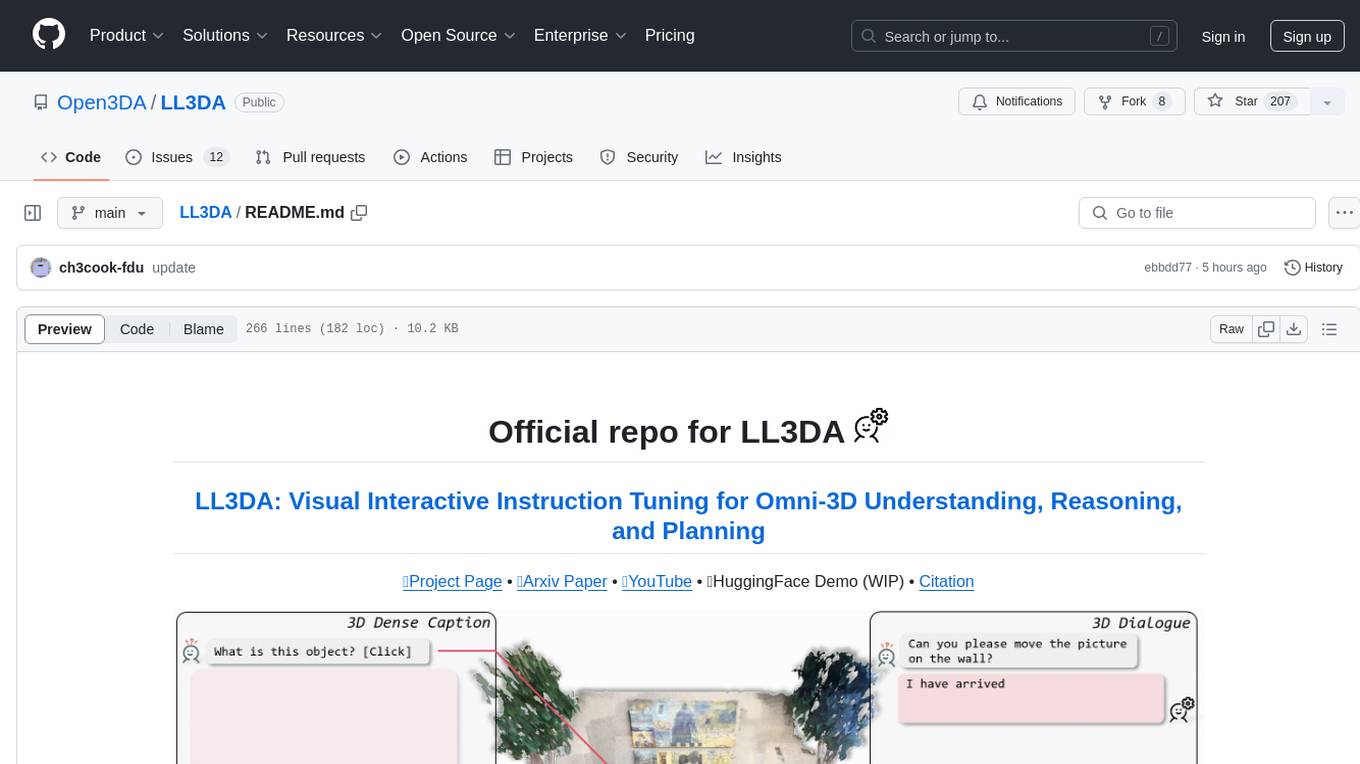
LL3DA is a Large Language 3D Assistant that responds to both visual and textual interactions within complex 3D environments. It aims to help Large Multimodal Models (LMM) comprehend, reason, and plan in diverse 3D scenes by directly taking point cloud input and responding to textual instructions and visual prompts. LL3DA achieves remarkable results in 3D Dense Captioning and 3D Question Answering, surpassing various 3D vision-language models. The code is fully released, allowing users to train customized models and work with pre-trained weights. The tool supports training with different LLM backends and provides scripts for tuning and evaluating models on various tasks.
README:
💻Project Page • 📄Arxiv Paper • 🎞YouTube • 🤗HuggingFace Demo (WIP) • Citation
LL3DA is a Large Language 3D Assistant that could respond to both visual and textual interactions within complex 3D environments.
Recent advances in Large Multimodal Models (LMM) have made it possible for various applications in human-machine interactions. However, developing LMMs that can comprehend, reason, and plan in complex and diverse 3D environments remains a challenging topic, especially considering the demand for understanding permutation-invariant point cloud 3D representations of the 3D scene. Existing works seek help from multi-view images, and project 2D features to 3D space as 3D scene representations. This, however, leads to huge computational overhead and performance degradation. In this paper, we present LL3DA, a Large Language 3D Assistant that takes point cloud as direct input and respond to both textual-instructions and visual-prompts. This help LMMs better comprehend human interactions and further help to remove the ambiguities in cluttered 3D scenes. Experiments show that LL3DA achieves remarkable results, and surpasses various 3D vision-language models on both 3D Dense Captioning and 3D Question Answering.
- 2024-03-04. 💥 The code is fully released! Now you can train your customized models!
- 2024-02-27. 🎉 LL3DA is accepted by CVPR 2024! See you in Seattle!
- 2023-11-30. 📣 Upload paper and init project
TODO:
- [x] Upload our paper to arXiv and build project pages.
- [x] Pray for acceptance.
- [x] Upload all the code and training scripts.
- [x] Release pre-trained weights. (see checkpoint)
- [ ] Add local demo interface.
- [ ] Train on larger 3D VL benchmarks and scale up models.
Environment Setup
Step 1. Build Dependencies. Our code is tested with CUDA 11.6 and Python 3.8.16. To run the codes, you should first install the following packages:
h5py
scipy
cython
plyfile
'trimesh>=2.35.39,<2.35.40'
'networkx>=2.2,<2.3'
'torch=1.13.1+cu116'
'transformers>=4.37.0'
After that, build the pointnet2 and accelerated giou from source:
cd third_party/pointnet2
python setup.py install
cd utils
python cython_compile.py build_ext --inplace
Step 2. Download pre-trained embeddings. Download the pre-processed BERT embedding weights from huggingface and store them under the ./bert-base-embedding folder. The weights are the same from the official BERT model, we just modified the names of certain parameters.
Data Preparation
Our repo requires the 3D data from ScanNet, the natural language annotations, and the pre-trained LLM weights.
Step 1. Download and Prepare the ScanNet 3D Data.
Updates 2024-07-01: You can download the pre-processed data from here.
- Follow the instructions here and download the ScanNetV2 dataset.
- Change the
SCANNET_DIRto the scans folder indata/scannet/batch_load_scannet_data.py, and run the following commands.
cd data/scannet/
python batch_load_scannet_data.py
Step 2. Prepare Language Annotations
To train the model, you are required to prepare language annotations from ScanRefer, Nr3D, ScanQA, and the ScanNet part of 3D-LLM.
-
ScanRefer. Follow the commands here to download theScanReferdataset. -
Nr3D. Follow the commands here to download theNr3Ddataset, and pre-process it. -
ScanQA. Follow the commands here to download theScanQAdataset. -
3D-LLM. The data are located at here. We have also shared our pre-processing scripts here.
We will update the latest released data (V3) from 3D-LLM.
Finally, organize the files into the following folders:
./data/
ScanRefer/
ScanRefer_filtered_train.json
ScanRefer_filtered_train.txt
ScanRefer_filtered_val.json
ScanRefer_filtered_val.txt
Nr3D/
nr3d_train.json
nr3d_train.txt
nr3d_val.json
nr3d_val.txt
ScanQA/
ScanQA_v1.0_test_w_obj.json
ScanQA_v1.0_test_wo_obj.json
ScanQA_v1.0_train.json
ScanQA_v1.0_val.json
3D_LLM/
3d_llm_embodied_dialogue_filtered_train.json
3d_llm_embodied_dialogue_filtered_val.json
3d_llm_embodied_planning_filtered_train.json
3d_llm_embodied_planning_filtered_val.json
3d_llm_scene_description_train.json
3d_llm_scene_description_val.json
Step 3. [Optional] Download Pre-trained LLM weights. If your server has no trouble auto-downloading weights from huggingface🤗, feel free to skip this step.
Download files from the opt-1.3b checkpoint (or any other decoder-only LLM) at huggingface, and store them under the ./facebook/opt-1.3b directory. Make sure the required files are downloaded:
./facebook/opt-1.3b/
config.json
merges.txt
pytorch_model.bin
special_tokens_map.json
tokenizer_config.json
vocab.json
Updates 2024-07-01: The released version is slightly different from our paper implementation. In our released version, we standardized the data format and dropped duplicated text annotations. To reproduce our reported results, please use the scripts provided in scripts-v0 to produce the generalist weights.
bash scripts-v0/opt-1.3b/train.generalist.sh
Our code should support any decoder-only LLMs (facebook/opt-1.3b, gpt2-xl, meta-llama/Llama-2-7b or even the LATEST Qwen/Qwen1.5-1.8B and Qwen/Qwen1.5-4B). Check out the following table for recommended LLMs in different scales! By default, the models are trained with eight GPUs.
| <1B | 1B-4B | ~7B |
|---|---|---|
gpt2(124m) |
TinyLlama-1.1B(1.1b) |
facebook/opt-6.7b(6.7b) |
facebook/opt-125m(125m) |
facebook/opt-1.3b(1.3b) |
meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf(6.7b) |
gpt2-medium(355m) |
gpt2-xl(1.6b) |
Qwen/Qwen1.5-7B(7.7b) |
Qwen/Qwen1.5-0.5B(620m) |
Qwen/Qwen1.5-1.8B(1.8b) |
- |
gpt2-large(774m) |
facebook/opt-2.7b(2.7b) |
- |
| - |
microsoft/phi-2(2.8b) |
- |
| - |
Qwen/Qwen1.5-4B(3.9b) |
- |
We provide training scripts in the scripts folder with different LLM backends. Feel free to modify the hyper parameters in those commands.
For other LLM backends, please modify the commands manually by changing --vocab to other LLMs.
Training
To train the model as a 3D generalist: (We have also uploaded the pre-trained weights to huggingface.)
bash scripts/opt-1.3b/train.generalist.sh
After the model is trained, you can tune the model on ScanQA for 3D Question Answering:
bash scripts/opt-1.3b/tuning.scanqa.sh
And, on ScanRefer / Nr3D for 3D Dense Captioning:
bash scripts/opt-1.3b/tuning.scanrefer.sh
bash scripts/opt-1.3b/tuning.nr3d.sh
You can also tune the model to predict bounding boxes for open vocabulary object detection!
bash scripts/opt-1.3b/tuning.ovdet.sh
Evaluation
To evaluate the model as a 3D generalist:
bash scripts/opt-1.3b/eval.generalist.sh
On ScanQA for 3D Question Answering:
bash scripts/opt-1.3b/eval.scanqa.sh
And, on ScanRefer / Nr3D for 3D Dense Captioning:
bash scripts/opt-1.3b/eval.scanrefer.sh
bash scripts/opt-1.3b/eval.nr3d.sh
If you find our code or paper helpful, please consider starring ⭐ us and citing:
@misc{chen2023ll3da,
title={LL3DA: Visual Interactive Instruction Tuning for Omni-3D Understanding, Reasoning, and Planning},
author={Sijin Chen and Xin Chen and Chi Zhang and Mingsheng Li and Gang Yu and Hao Fei and Hongyuan Zhu and Jiayuan Fan and Tao Chen},
year={2023},
eprint={2311.18651},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
Thanks to Vote2Cap-DETR, 3D-LLM, Scan2Cap, and 3DETR. We borrow some of their codes and data.
This code is distributed under an MIT LICENSE. If there are any problem regarding our paper and code, feel free to open an issue!
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LL3DA
Similar Open Source Tools

LL3DA
LL3DA is a Large Language 3D Assistant that responds to both visual and textual interactions within complex 3D environments. It aims to help Large Multimodal Models (LMM) comprehend, reason, and plan in diverse 3D scenes by directly taking point cloud input and responding to textual instructions and visual prompts. LL3DA achieves remarkable results in 3D Dense Captioning and 3D Question Answering, surpassing various 3D vision-language models. The code is fully released, allowing users to train customized models and work with pre-trained weights. The tool supports training with different LLM backends and provides scripts for tuning and evaluating models on various tasks.
langroid
Langroid is a Python framework that makes it easy to build LLM-powered applications. It uses a multi-agent paradigm inspired by the Actor Framework, where you set up Agents, equip them with optional components (LLM, vector-store and tools/functions), assign them tasks, and have them collaboratively solve a problem by exchanging messages. Langroid is a fresh take on LLM app-development, where considerable thought has gone into simplifying the developer experience; it does not use Langchain.
VLM-R1
VLM-R1 is a stable and generalizable R1-style Large Vision-Language Model proposed for Referring Expression Comprehension (REC) task. It compares R1 and SFT approaches, showing R1 model's steady improvement on out-of-domain test data. The project includes setup instructions, training steps for GRPO and SFT models, support for user data loading, and evaluation process. Acknowledgements to various open-source projects and resources are mentioned. The project aims to provide a reliable and versatile solution for vision-language tasks.

VITA
VITA is an open-source interactive omni multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) capable of processing video, image, text, and audio inputs simultaneously. It stands out with features like Omni Multimodal Understanding, Non-awakening Interaction, and Audio Interrupt Interaction. VITA can respond to user queries without a wake-up word, track and filter external queries in real-time, and handle various query inputs effectively. The model utilizes state tokens and a duplex scheme to enhance the multimodal interactive experience.

HuixiangDou
HuixiangDou is a **group chat** assistant based on LLM (Large Language Model). Advantages: 1. Design a two-stage pipeline of rejection and response to cope with group chat scenario, answer user questions without message flooding, see arxiv2401.08772 2. Low cost, requiring only 1.5GB memory and no need for training 3. Offers a complete suite of Web, Android, and pipeline source code, which is industrial-grade and commercially viable Check out the scenes in which HuixiangDou are running and join WeChat Group to try AI assistant inside. If this helps you, please give it a star ⭐
curator
Bespoke Curator is an open-source tool for data curation and structured data extraction. It provides a Python library for generating synthetic data at scale, with features like programmability, performance optimization, caching, and integration with HuggingFace Datasets. The tool includes a Curator Viewer for dataset visualization and offers a rich set of functionalities for creating and refining data generation strategies.
TheoremExplainAgent
TheoremExplainAgent is an AI system that generates long-form Manim videos to visually explain theorems, proving its deep understanding while uncovering reasoning flaws that text alone often hides. The codebase for the paper 'TheoremExplainAgent: Towards Multimodal Explanations for LLM Theorem Understanding' is available in this repository. It provides a tool for creating multimodal explanations for theorem understanding using AI technology.
ALMA
ALMA (Advanced Language Model-based Translator) is a many-to-many LLM-based translation model that utilizes a two-step fine-tuning process on monolingual and parallel data to achieve strong translation performance. ALMA-R builds upon ALMA models with LoRA fine-tuning and Contrastive Preference Optimization (CPO) for even better performance, surpassing GPT-4 and WMT winners. The repository provides ALMA and ALMA-R models, datasets, environment setup, evaluation scripts, training guides, and data information for users to leverage these models for translation tasks.
LLMTSCS
LLMLight is a novel framework that employs Large Language Models (LLMs) as decision-making agents for Traffic Signal Control (TSC). The framework leverages the advanced generalization capabilities of LLMs to engage in a reasoning and decision-making process akin to human intuition for effective traffic control. LLMLight has been demonstrated to be remarkably effective, generalizable, and interpretable against various transportation-based and RL-based baselines on nine real-world and synthetic datasets.
mLoRA
mLoRA (Multi-LoRA Fine-Tune) is an open-source framework for efficient fine-tuning of multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) using LoRA and its variants. It allows concurrent fine-tuning of multiple LoRA adapters with a shared base model, efficient pipeline parallelism algorithm, support for various LoRA variant algorithms, and reinforcement learning preference alignment algorithms. mLoRA helps save computational and memory resources when training multiple adapters simultaneously, achieving high performance on consumer hardware.
DeepResearch
Tongyi DeepResearch is an agentic large language model with 30.5 billion total parameters, designed for long-horizon, deep information-seeking tasks. It demonstrates state-of-the-art performance across various search benchmarks. The model features a fully automated synthetic data generation pipeline, large-scale continual pre-training on agentic data, end-to-end reinforcement learning, and compatibility with two inference paradigms. Users can download the model directly from HuggingFace or ModelScope. The repository also provides benchmark evaluation scripts and information on the Deep Research Agent Family.
ichigo
Ichigo is a local real-time voice AI tool that uses an early fusion technique to extend a text-based LLM to have native 'listening' ability. It is an open research experiment with improved multiturn capabilities and the ability to refuse processing inaudible queries. The tool is designed for open data, open weight, on-device Siri-like functionality, inspired by Meta's Chameleon paper. Ichigo offers a web UI demo and Gradio web UI for users to interact with the tool. It has achieved enhanced MMLU scores, stronger context handling, advanced noise management, and improved multi-turn capabilities for a robust user experience.

Qwen
Qwen is a series of large language models developed by Alibaba DAMO Academy. It outperforms the baseline models of similar model sizes on a series of benchmark datasets, e.g., MMLU, C-Eval, GSM8K, MATH, HumanEval, MBPP, BBH, etc., which evaluate the models’ capabilities on natural language understanding, mathematic problem solving, coding, etc. Qwen models outperform the baseline models of similar model sizes on a series of benchmark datasets, e.g., MMLU, C-Eval, GSM8K, MATH, HumanEval, MBPP, BBH, etc., which evaluate the models’ capabilities on natural language understanding, mathematic problem solving, coding, etc. Qwen-72B achieves better performance than LLaMA2-70B on all tasks and outperforms GPT-3.5 on 7 out of 10 tasks.
llm-leaderboard
Nejumi Leaderboard 3 is a comprehensive evaluation platform for large language models, assessing general language capabilities and alignment aspects. The evaluation framework includes metrics for language processing, translation, summarization, information extraction, reasoning, mathematical reasoning, entity extraction, knowledge/question answering, English, semantic analysis, syntactic analysis, alignment, ethics/moral, toxicity, bias, truthfulness, and robustness. The repository provides an implementation guide for environment setup, dataset preparation, configuration, model configurations, and chat template creation. Users can run evaluation processes using specified configuration files and log results to the Weights & Biases project.

xFasterTransformer
xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for Large Language Models (LLMs) on the X86 platform, providing high performance and scalability for inference on mainstream LLM models. It offers C++ and Python APIs for easy integration, along with example codes and benchmark scripts. Users can prepare models in a different format, convert them, and use the APIs for tasks like encoding input prompts, generating token ids, and serving inference requests. The tool supports various data types and models, and can run in single or multi-rank modes using MPI. A web demo based on Gradio is available for popular LLM models like ChatGLM and Llama2. Benchmark scripts help evaluate model inference performance quickly, and MLServer enables serving with REST and gRPC interfaces.
zml
ZML is a high-performance AI inference stack built for production, using Zig language, MLIR, and Bazel. It allows users to create exciting AI projects, run pre-packaged models like MNIST, TinyLlama, OpenLLama, and Meta Llama, and compile models for accelerator runtimes. Users can also run tests, explore examples, and contribute to the project. ZML is licensed under the Apache 2.0 license.
For similar tasks

LL3DA
LL3DA is a Large Language 3D Assistant that responds to both visual and textual interactions within complex 3D environments. It aims to help Large Multimodal Models (LMM) comprehend, reason, and plan in diverse 3D scenes by directly taking point cloud input and responding to textual instructions and visual prompts. LL3DA achieves remarkable results in 3D Dense Captioning and 3D Question Answering, surpassing various 3D vision-language models. The code is fully released, allowing users to train customized models and work with pre-trained weights. The tool supports training with different LLM backends and provides scripts for tuning and evaluating models on various tasks.
Co-LLM-Agents
This repository contains code for building cooperative embodied agents modularly with large language models. The agents are trained to perform tasks in two different environments: ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport (TDW-MAT) and Communicative Watch-And-Help (C-WAH). TDW-MAT is a multi-agent environment where agents must transport objects to a goal position using containers. C-WAH is an extension of the Watch-And-Help challenge, which enables agents to send messages to each other. The code in this repository can be used to train agents to perform tasks in both of these environments.
GPT4Point
GPT4Point is a unified framework for point-language understanding and generation. It aligns 3D point clouds with language, providing a comprehensive solution for tasks such as 3D captioning and controlled 3D generation. The project includes an automated point-language dataset annotation engine, a novel object-level point cloud benchmark, and a 3D multi-modality model. Users can train and evaluate models using the provided code and datasets, with a focus on improving models' understanding capabilities and facilitating the generation of 3D objects.

asreview
The ASReview project implements active learning for systematic reviews, utilizing AI-aided pipelines to assist in finding relevant texts for search tasks. It accelerates the screening of textual data with minimal human input, saving time and increasing output quality. The software offers three modes: Oracle for interactive screening, Exploration for teaching purposes, and Simulation for evaluating active learning models. ASReview LAB is designed to support decision-making in any discipline or industry by improving efficiency and transparency in screening large amounts of textual data.
Groma
Groma is a grounded multimodal assistant that excels in region understanding and visual grounding. It can process user-defined region inputs and generate contextually grounded long-form responses. The tool presents a unique paradigm for multimodal large language models, focusing on visual tokenization for localization. Groma achieves state-of-the-art performance in referring expression comprehension benchmarks. The tool provides pretrained model weights and instructions for data preparation, training, inference, and evaluation. Users can customize training by starting from intermediate checkpoints. Groma is designed to handle tasks related to detection pretraining, alignment pretraining, instruction finetuning, instruction following, and more.
amber-train
Amber is the first model in the LLM360 family, an initiative for comprehensive and fully open-sourced LLMs. It is a 7B English language model with the LLaMA architecture. The model type is a language model with the same architecture as LLaMA-7B. It is licensed under Apache 2.0. The resources available include training code, data preparation, metrics, and fully processed Amber pretraining data. The model has been trained on various datasets like Arxiv, Book, C4, Refined-Web, StarCoder, StackExchange, and Wikipedia. The hyperparameters include a total of 6.7B parameters, hidden size of 4096, intermediate size of 11008, 32 attention heads, 32 hidden layers, RMSNorm ε of 1e^-6, max sequence length of 2048, and a vocabulary size of 32000.
kan-gpt
The KAN-GPT repository is a PyTorch implementation of Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPTs) using Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) for language modeling. It provides a model for generating text based on prompts, with a focus on improving performance compared to traditional MLP-GPT models. The repository includes scripts for training the model, downloading datasets, and evaluating model performance. Development tasks include integrating with other libraries, testing, and documentation.
LLM-SFT
LLM-SFT is a Chinese large model fine-tuning tool that supports models such as ChatGLM, LlaMA, Bloom, Baichuan-7B, and frameworks like LoRA, QLoRA, DeepSpeed, UI, and TensorboardX. It facilitates tasks like fine-tuning, inference, evaluation, and API integration. The tool provides pre-trained weights for various models and datasets for Chinese language processing. It requires specific versions of libraries like transformers and torch for different functionalities.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

