
GPT4Point
[CVPR'24 Highlight] GPT4Point: A Unified Framework for Point-Language Understanding and Generation.
Stars: 253
GPT4Point is a unified framework for point-language understanding and generation. It aligns 3D point clouds with language, providing a comprehensive solution for tasks such as 3D captioning and controlled 3D generation. The project includes an automated point-language dataset annotation engine, a novel object-level point cloud benchmark, and a 3D multi-modality model. Users can train and evaluate models using the provided code and datasets, with a focus on improving models' understanding capabilities and facilitating the generation of 3D objects.
README:
🔥 2024/04/27: We have modified the point encoder section, and now evaluation is more functional, although the training section still needs modification.
🔥 2024/04/13: We release the GPT4Point v1.0, including training and 3D captioning evluation code.
🔥 2024/04/05: Our paper GPT4Point is selected as CVPR'24 Highlight 2.84% (324/11532) !
🔥 2024/02/27: Our paper GPT4Point is accepted by CVPR'24!
🔥 2024/01/19: We release the Objaverse-XL (Point Cloud Format) Download and Extraction way.
🔥 2023/12/05: The paper GPT4Point (arxiv) has been released, we unified the Point-language Understanding and Generation.
🔥 2023/08/13: Two-stage Pre-training code of PointBLIP has been released.
🔥 2023/08/13: Part of datasets used and result files has been uploaded.
This project presents GPT4Point ![]() , a 3D multi-modality model that aligns 3D point clouds with language. More details are shown in project page.
, a 3D multi-modality model that aligns 3D point clouds with language. More details are shown in project page.
-
Unified Framework for Point-language Understanding and Generation. We present the unified framework for point-language understanding and generation GPT4Point, including the 3D MLLM for point-text tasks and controlled 3D generation.
-
Automated Point-language Dataset Annotation Engine Pyramid-XL. We introduce the automated point-language dataset annotation engine Pyramid-XL based on Objaverse-XL, currently encompassing 1M pairs of varying levels of coarseness and can be extended cost-effectively.
-
Object-level Point Cloud Benchmark. Establishing a novel object-level point cloud benchmark with comprehensive evaluation metrics for 3D point cloud language tasks. This benchmark thoroughly assesses models' understanding capabilities and facilitates the evaluation of generated 3D objects.
-
v1.0 (2024/04/13). We release the training and evaluation (3D captioning) code.
Dataset and text annotation: Cap3D.
LLM Model: OPT 2.7b
- (Optional) Creating conda environment
conda create -n gpt4point python=3.8
conda activate gpt4point- install from PyPI
pip install salesforce-lavis- Or, for development, you may build from source
git clone https://github.com/salesforce/LAVIS.git
cd LAVIS
pip install -e .-
Annotations: All annotations will be downloaded automaticly through hugging_face.
-
Point Cloud: You can download the Cap3D point cloud dataset through the Google Drive Link. You should unzip these 10 tar.gz files and then put them together. and the all folder strucure is:
GPT4Point
├── data
│ ├── cap3d
│ │ ├── points
│ │ │ ├── Cap3D_pcs_8192_xyz_w_color
│ │ │ │ ├── <point cloud id>.pkl
│ │ │ │ ├── ...
│ │ │ │ ├── <point cloud id>.pkl
│ │ ├── annotations
│ │ │ ├── cap3d_caption_train.json
│ │ │ ├── cap3d_caption_val.json
│ │ │ ├── cap3d_real_and_chatgpt_caption_test.json
│ │ │ ├── cap3d_real_and_chatgpt_caption_test_gt.json (for evaluation)- For stage 1 training:
python -m torch.distributed.run --master_port=32339 --nproc_per_node=4 train.py --cfg-path lavis/projects/gpt4point/train/pretrain_stage1_cap3d.yaml- For stage 2 training:
python -m torch.distributed.run --master_port=32339 --nproc_per_node=4 train.py --cfg-path lavis/projects/gpt4point/train/pretrain_stage2_cap3d_opt2.7b.yamlpython -m torch.distributed.run --master_port=32239 --nproc_per_node=1 evaluate.py --cfg-path lavis/projects/gpt4point/eval/captioning3d_cap3d_opt2.7b_eval.yamlNote that you should cd in the Objaverse-xl_Download directory.
cd ./Objaverse-xl_DownloadThen please see the folder Objaverse-xl_Download for details.
Please see the Extract_Pointcloud for details.
Dataset and Data Engine
- [✔] Release the arxiv and the project page.
- [✔] Release the dataset (Objaverse-Xl) Download way.
- [✔] Release the dataset (Objaverse-Xl) rendering (points) way.
- [✔] Release pretrain training code and 3D captioning val code.
- [ ] Release dataset and data annotation engine (Pyramid-XL).
- [ ] Release more evaluation code.
- [ ] Release more trainingn code.
- [ ] Release more models.
If you find our work helpful, please cite:
@inproceedings{GPT4Point,
title={GPT4Point: A Unified Framework for Point-Language Understanding and Generation},
author={Zhangyang Qi and Ye Fang and Zeyi Sun and Xiaoyang Wu and Tong Wu and Jiaqi Wang and Dahua Lin and Hengshuang Zhao},
booktitle={CVPR},
year={2024},
}
This work is under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Together, Let's make LLM for 3D great!
- Point-Bind & Point-LLM: It aligns point clouds with Image-Bind to reason multi-modality input without 3D-instruction data training.
- 3D-LLM: employs 2D foundation models to encode multi-view images of 3D point clouds.
- PointLLM: employs 3D point clouds with LLaVA.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for GPT4Point
Similar Open Source Tools

GPT4Point
GPT4Point is a unified framework for point-language understanding and generation. It aligns 3D point clouds with language, providing a comprehensive solution for tasks such as 3D captioning and controlled 3D generation. The project includes an automated point-language dataset annotation engine, a novel object-level point cloud benchmark, and a 3D multi-modality model. Users can train and evaluate models using the provided code and datasets, with a focus on improving models' understanding capabilities and facilitating the generation of 3D objects.
LLMGA
LLMGA (Multimodal Large Language Model-based Generation Assistant) is a tool that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to assist users in image generation and editing. It provides detailed language generation prompts for precise control over Stable Diffusion (SD), resulting in more intricate and precise content in generated images. The tool curates a dataset for prompt refinement, similar image generation, inpainting & outpainting, and visual question answering. It offers a two-stage training scheme to optimize SD alignment and a reference-based restoration network to alleviate texture, brightness, and contrast disparities in image editing. LLMGA shows promising generative capabilities and enables wider applications in an interactive manner.
llmos
LLMos is an operating system designed for physical AI agents, providing a hybrid runtime environment where AI agents can perceive, reason, act on hardware, and evolve over time locally without cloud dependency. It allows natural language programming, dual-brain architecture for fast instinct and deep planner brains, markdown-as-code for defining agents and skills, and supports swarm intelligence and cognitive world models. The tool is built on a tech stack including Next.js, Electron, Python, and WebAssembly, and is structured around a dual-brain cognitive architecture, volume system, HAL for hardware abstraction, applet system for dynamic UI, and dreaming & evolution for robot improvement. The project is in Phase 1 (Foundation) and aims to move into Phase 2 (Dual-Brain & Local Intelligence), with contributions welcomed under the Apache 2.0 license by Evolving Agents Labs.
EnvScaler
EnvScaler is an automated, scalable framework that creates tool-interactive environments for training LLM agents. It consists of SkelBuilder for environment description mining and quality inspection, ScenGenerator for synthesizing multiple environment scenarios, and modules for supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning. The tool provides data, models, and evaluation guides for users to build, generate scenarios, collect training data, train models, and evaluate performance. Users can interact with environments, build environments from scratch, and improve LLMs' task-solving abilities in complex environments.
Linly-Talker
Linly-Talker is an innovative digital human conversation system that integrates the latest artificial intelligence technologies, including Large Language Models (LLM) 🤖, Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) 🎙️, Text-to-Speech (TTS) 🗣️, and voice cloning technology 🎤. This system offers an interactive web interface through the Gradio platform 🌐, allowing users to upload images 📷 and engage in personalized dialogues with AI 💬.
science-codeevolve
CodeEvolve is an open-source framework that combines large language models with evolutionary algorithms to discover and optimize high-performing code solutions. It democratizes algorithmic discovery by making LLM-driven evolutionary search transparent, reproducible, and accessible. CodeEvolve provides a modular foundation for automated code synthesis guided by quantifiable metrics, addressing meta-optimization tasks where complex optimization problems need to be solved. The framework features islands-based genetic algorithm, modular evolutionary operators, quality-diversity optimization, flexible LLM integration, and distributed islands for efficient exploration. Core components include CLI entry point, process runner, evolution engine, program database, exploration schedulers, evaluator, islands coordinator, LLM interface, prompt sampler, and utilities. CodeEvolve demonstrates superior performance on algorithm-discovery benchmarks and is suitable for mathematical discovery, algorithm design, scientific discovery, and software optimization. Reproducibility and determinism are emphasized, with seedable internal algorithmic decisions. Contributions from the community are welcome, focusing on new selection policies, LLM integrations, benchmark problems, documentation, performance optimizations, and bug fixes.
ai
Jetify's AI SDK for Go is a unified interface for interacting with multiple AI providers including OpenAI, Anthropic, and more. It addresses the challenges of fragmented ecosystems, vendor lock-in, poor Go developer experience, and complex multi-modal handling by providing a unified interface, Go-first design, production-ready features, multi-modal support, and extensible architecture. The SDK supports language models, embeddings, image generation, multi-provider support, multi-modal inputs, tool calling, and structured outputs.
FireRedTTS
FireRedTTS is a foundation text-to-speech framework designed for industry-level generative speech applications. It offers a rich-punctuation model with expanded punctuation coverage and enhanced audio production consistency. The tool provides pre-trained checkpoints, inference code, and an interactive demo space. Users can clone the repository, create a conda environment, download required model files, and utilize the tool for synthesizing speech in various languages. FireRedTTS aims to enhance stability and provide controllable human-like speech generation capabilities.
paelladoc
PAELLADOC is an intelligent documentation system that uses AI to analyze code repositories and generate comprehensive technical documentation. It offers a modular architecture with MECE principles, interactive documentation process, key features like Orchestrator and Commands, and a focus on context for successful AI programming. The tool aims to streamline documentation creation, code generation, and product management tasks for software development teams, providing a definitive standard for AI-assisted development documentation.
rllm
rLLM (relationLLM) is a Pytorch library for Relational Table Learning (RTL) with LLMs. It breaks down state-of-the-art GNNs, LLMs, and TNNs as standardized modules and facilitates novel model building in a 'combine, align, and co-train' way using these modules. The library is LLM-friendly, processes various graphs as multiple tables linked by foreign keys, introduces new relational table datasets, and is supported by students and teachers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Tsinghua University.
Trellis
Trellis is an all-in-one AI framework and toolkit designed for Claude Code, Cursor, and iFlow. It offers features such as auto-injection of required specs and workflows, auto-updated spec library, parallel sessions for running multiple agents simultaneously, team sync for sharing specs, and session persistence. Trellis helps users educate their AI, work on multiple features in parallel, define custom workflows, and provides a structured project environment with workflow guides, spec library, personal journal, task management, and utilities. The tool aims to enhance code review, introduce skill packs, integrate with broader tools, improve session continuity, and visualize progress for each agent.
RepoMaster
RepoMaster is an AI agent that leverages GitHub repositories to solve complex real-world tasks. It transforms how coding tasks are solved by automatically finding the right GitHub tools and making them work together seamlessly. Users can describe their tasks, and RepoMaster's AI analysis leads to auto discovery and smart execution, resulting in perfect outcomes. The tool provides a web interface for beginners and a command-line interface for advanced users, along with specialized agents for deep search, general assistance, and repository tasks.
seline
Seline is a local-first AI desktop application that integrates conversational AI, visual generation tools, vector search, and multi-channel connectivity. It allows users to connect WhatsApp, Telegram, or Slack to create always-on bots with full context and background task delivery. The application supports multi-channel connectivity, deep research mode, local web browsing with Puppeteer, local knowledge and privacy features, visual and creative tools, automation and agents, developer experience enhancements, and more. Seline is actively developed with a focus on improving user experience and functionality.
ComfyUI-Copilot
ComfyUI-Copilot is an intelligent assistant built on the Comfy-UI framework that simplifies and enhances the AI algorithm debugging and deployment process through natural language interactions. It offers intuitive node recommendations, workflow building aids, and model querying services to streamline development processes. With features like interactive Q&A bot, natural language node suggestions, smart workflow assistance, and model querying, ComfyUI-Copilot aims to lower the barriers to entry for beginners, boost development efficiency with AI-driven suggestions, and provide real-time assistance for developers.

MM-RLHF
MM-RLHF is a comprehensive project for aligning Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with human preferences. It includes a high-quality MLLM alignment dataset, a Critique-Based MLLM reward model, a novel alignment algorithm MM-DPO, and benchmarks for reward models and multimodal safety. The dataset covers image understanding, video understanding, and safety-related tasks with model-generated responses and human-annotated scores. The reward model generates critiques of candidate texts before assigning scores for enhanced interpretability. MM-DPO is an alignment algorithm that achieves performance gains with simple adjustments to the DPO framework. The project enables consistent performance improvements across 10 dimensions and 27 benchmarks for open-source MLLMs.
empirica
Empirica is an epistemic self-awareness framework for AI agents to understand their knowledge boundaries. It introduces epistemic vectors to measure knowledge state and uncertainty, enabling honest communication. The tool emerged from 600+ real working sessions across various AI systems, providing cognitive infrastructure for distinguishing between confident knowledge and guessing. Empirica's 13 foundational vectors cover engagement, domain knowledge depth, execution capability, information access, understanding clarity, coherence, signal-to-noise ratio, information richness, working state, progress rate, task completion level, work significance, and explicit doubt tracking. It is applicable across industries like software development, research, healthcare, legal, education, and finance, aiding in tasks such as code review, hypothesis testing, diagnostic confidence, case analysis, learning assessment, and risk assessment.
For similar tasks

GPT4Point
GPT4Point is a unified framework for point-language understanding and generation. It aligns 3D point clouds with language, providing a comprehensive solution for tasks such as 3D captioning and controlled 3D generation. The project includes an automated point-language dataset annotation engine, a novel object-level point cloud benchmark, and a 3D multi-modality model. Users can train and evaluate models using the provided code and datasets, with a focus on improving models' understanding capabilities and facilitating the generation of 3D objects.
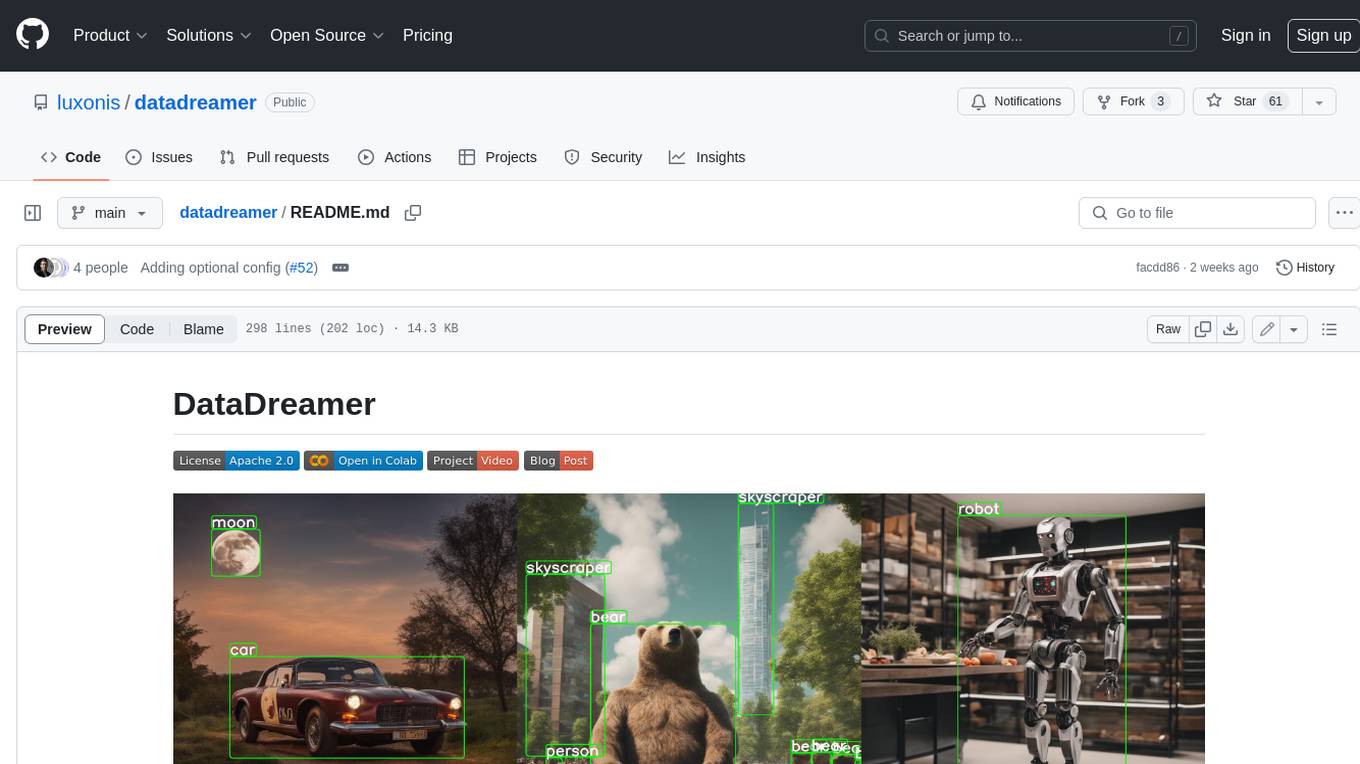
datadreamer
DataDreamer is an advanced toolkit designed to facilitate the development of edge AI models by enabling synthetic data generation, knowledge extraction from pre-trained models, and creation of efficient and potent models. It eliminates the need for extensive datasets by generating synthetic datasets, leverages latent knowledge from pre-trained models, and focuses on creating compact models suitable for integration into any device and performance for specialized tasks. The toolkit offers features like prompt generation, image generation, dataset annotation, and tools for training small-scale neural networks for edge deployment. It provides hardware requirements, usage instructions, available models, and limitations to consider while using the library.
hcaptcha-challenger
hCaptcha Challenger is a tool designed to gracefully face hCaptcha challenges using a multimodal large language model. It does not rely on Tampermonkey scripts or third-party anti-captcha services, instead implementing interfaces for 'AI vs AI' scenarios. The tool supports various challenge types such as image labeling, drag and drop, and advanced tasks like self-supervised challenges and Agentic Workflow. Users can access documentation in multiple languages and leverage resources for tasks like model training, dataset annotation, and model upgrading. The tool aims to enhance user experience in handling hCaptcha challenges with innovative AI capabilities.
byteir
The ByteIR Project is a ByteDance model compilation solution. ByteIR includes compiler, runtime, and frontends, and provides an end-to-end model compilation solution. Although all ByteIR components (compiler/runtime/frontends) are together to provide an end-to-end solution, and all under the same umbrella of this repository, each component technically can perform independently. The name, ByteIR, comes from a legacy purpose internally. The ByteIR project is NOT an IR spec definition project. Instead, in most scenarios, ByteIR directly uses several upstream MLIR dialects and Google Mhlo. Most of ByteIR compiler passes are compatible with the selected upstream MLIR dialects and Google Mhlo.
ScandEval
ScandEval is a framework for evaluating pretrained language models on mono- or multilingual language tasks. It provides a unified interface for benchmarking models on a variety of tasks, including sentiment analysis, question answering, and machine translation. ScandEval is designed to be easy to use and extensible, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners alike.
opencompass
OpenCompass is a one-stop platform for large model evaluation, aiming to provide a fair, open, and reproducible benchmark for large model evaluation. Its main features include: * Comprehensive support for models and datasets: Pre-support for 20+ HuggingFace and API models, a model evaluation scheme of 70+ datasets with about 400,000 questions, comprehensively evaluating the capabilities of the models in five dimensions. * Efficient distributed evaluation: One line command to implement task division and distributed evaluation, completing the full evaluation of billion-scale models in just a few hours. * Diversified evaluation paradigms: Support for zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought evaluations, combined with standard or dialogue-type prompt templates, to easily stimulate the maximum performance of various models. * Modular design with high extensibility: Want to add new models or datasets, customize an advanced task division strategy, or even support a new cluster management system? Everything about OpenCompass can be easily expanded! * Experiment management and reporting mechanism: Use config files to fully record each experiment, and support real-time reporting of results.
openvino.genai
The GenAI repository contains pipelines that implement image and text generation tasks. The implementation uses OpenVINO capabilities to optimize the pipelines. Each sample covers a family of models and suggests certain modifications to adapt the code to specific needs. It includes the following pipelines: 1. Benchmarking script for large language models 2. Text generation C++ samples that support most popular models like LLaMA 2 3. Stable Diffuison (with LoRA) C++ image generation pipeline 4. Latent Consistency Model (with LoRA) C++ image generation pipeline
octopus-v4
The Octopus-v4 project aims to build the world's largest graph of language models, integrating specialized models and training Octopus models to connect nodes efficiently. The project focuses on identifying, training, and connecting specialized models. The repository includes scripts for running the Octopus v4 model, methods for managing the graph, training code for specialized models, and inference code. Environment setup instructions are provided for Linux with NVIDIA GPU. The Octopus v4 model helps users find suitable models for tasks and reformats queries for effective processing. The project leverages Language Large Models for various domains and provides benchmark results. Users are encouraged to train and add specialized models following recommended procedures.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.



