
LLMTSCS
Official code for article "LLMLight: Large Language Models as Traffic Signal Control Agents".
Stars: 173
LLMLight is a novel framework that employs Large Language Models (LLMs) as decision-making agents for Traffic Signal Control (TSC). The framework leverages the advanced generalization capabilities of LLMs to engage in a reasoning and decision-making process akin to human intuition for effective traffic control. LLMLight has been demonstrated to be remarkably effective, generalizable, and interpretable against various transportation-based and RL-based baselines on nine real-world and synthetic datasets.
README:
| 1 Introduction | 2 Requirements | 3 Usage | 4 Baselines | 5 LightGPT Training | 6 Code structure | 7 Datasets | 8 Citation | Website |
- [x] 🚀🔥 [2024.11] 🎯🎯📢📢 Exciting News! We are thrilled to announce that our 🌟LLMLight🌟 has been accepted by KDD'2025! 🎉🎉🎉 Thanks to all the team members 🤗
- [x] 🚀🔥 [2024.11] 🎯🎯📢📢 Exciting Update! We’re thrilled to announce that our LightGPT family has expanded with four new members now available on HuggingFace. These models include fine-tuned backbones based on Qwen2 and Llama3. Check them out!
Official code for article "LLMLight: Large Language Models as Traffic Signal Control Agents".
Traffic Signal Control (TSC) is a crucial component in urban traffic management, aiming to optimize road network efficiency and reduce congestion. Traditional methods in TSC, primarily based on transportation engineering and reinforcement learning (RL), often exhibit limitations in generalization across varied traffic scenarios and lack interpretability. This paper presents LLMLight, a novel framework employing Large Language Models (LLMs) as decision-making agents for TSC. Specifically, the framework begins by instructing the LLM with a knowledgeable prompt detailing real-time traffic conditions. Leveraging the advanced generalization capabilities of LLMs, LLMLight engages a reasoning and decision-making process akin to human intuition for effective traffic control. Moreover, we build LightGPT, a specialized backbone LLM tailored for TSC tasks. By learning nuanced traffic patterns and control strategies, LightGPT enhances the LLMLight framework cost-effectively. Extensive experiments on nine real-world and synthetic datasets showcase the remarkable effectiveness, generalization ability, and interpretability of LLMLight against nine transportation-based and RL-based baselines.
The code structure is based on Efficient_XLight.
https://github.com/usail-hkust/LLMTSCS/assets/62106026/90567f61-5d58-4dac-8c8e-836a421f3ff9
python>=3.9,tensorflow-cpu==2.8.0, cityflow, pandas==1.5.0, numpy==1.26.2, wandb, transformers==4.45.0, peft==0.7.1, accelerate==0.27.2, datasets==2.16.1, fire, vllm==0.6.2
cityflow needs a Linux environment, and we run the code on Ubuntu.
Parameters are well-prepared, and you can run the code directly.
- For example, to run
Advanced-MPLight:
python run_advanced_mplight.py --dataset hangzhou \
--traffic_file anon_4_4_hangzhou_real.json \
--proj_name TSCS- To run GPT-3.5/GPT-4 with LLMLight, you need to set your key in
./models/chatgpt.py:
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "YOUR_KEY_HERE"
}Then, run LLMLight by:
python run_chatgpt.py --prompt Commonsense \
--dataset hangzhou \
--traffic_file anon_4_4_hangzhou_real.json \
--gpt_version gpt-4 \
--proj_name TSCSYou can either choose Commonsense or Wait Time Forecast as the prompt argument.
- To run with open-sourced LLMs (or LightGPT) and LLMLight:
# with default methods of Transformers
python run_open_LLM.py --llm_model LLM_MODEL_NAME_ONLY_FOR_LOG \
--llm_path LLM_PATH \
--dataset hangzhou \
--traffic_file anon_4_4_hangzhou_real.json \
--proj_name TSCS
# or with VLLM (much faster but will cost more GPU memory)
python run_open_LLM_with_vllm.py --llm_model LLM_MODEL_NAME_ONLY_FOR_LOG \
--llm_path LLM_PATH \
--dataset hangzhou \
--traffic_file anon_4_4_hangzhou_real.json \
--proj_name TSCS-
Heuristic Methods:
- FixedTime, Maxpressure, EfficientMaxPressure
-
DNN-RL:
- PressLight, MPLight, CoLight, AttendLight, EfficientMPLight, EfficientPressLight, Efficient-Colight
-
Adv-DNN-RL:
- Advanced-MaxPressure, Advanced-MPLight, Advanced-Colight
-
LLMLight+LLM:
-
gpt-3.5-turbo-0613,gpt-4-0613,llama-2-13b-chat-hf,llama-2-70b-chat-hf
-
-
LLMLight+LightGPT:
- The model trained on Jinan 1 is available at https://huggingface.co/collections/usail-hkust/llmlight-lightgpt-673ac5a619cbbe309165b56d
python ./finetune/run_imitation_finetune.py --base_model MODEL_PATH \
--data_path DATA_PATH \
--output_dir OUTPUT_DIR
python ./finetune/merge_lora.py --adapter_model_name="OUTPUT_DIR" \
--base_model_name="MODEL_PATH" \
--output_name="MERGED_MODEL_PATH"We merge the adapter with the base model by running merge_lora.py.
- You first need to train
Advanced-CoLightby running:
python run_advanced_colight.py --dataset hangzhou \
--traffic_file anon_4_4_hangzhou_real.json \
--proj_name TSCSThe RL model weights will be automatically saved in a checkpoint folder in ./model. You need to copy it and put it under the ./model_weights/AdvancedColight/{traffic_file}/" folder.
- Then, collect the data by running:
python ./finetune/run_policy_refinement_data_collection.py --llm_model MODEL_NAME_ONLY_FOR_LOG \
--llm_path MODEL_PATH \
--dataset hangzhou \
--traffic_file anon_4_4_hangzhou_real.jsonThe fine-tuning data will be ready at ./data/cgpr/cgpr_{traffic_file}.json.
python ./finetune/run_policy_refinement.py --llm_model MODEL_NAME_ONLY_FOR_LOG \
--llm_path MODEL_PATH \
--llm_output_dir OUTPUT_DIR \
--dataset hangzhou \
--traffic_file anon_4_4_hangzhou_real.json \
--proj_name LightGPTFineTuning
python ./finetune/merge_lora.py --adapter_model_name="OUTPUT_DIR_{traffic_file}" \
--base_model_name="MODEL_PATH" \
--output_name="MERGED_MODEL_PATH"Similarly, we merge the adapter with the base model by running merge_lora.py.
-
models: contains all the models used in our article. -
utils: contains all the methods to simulate and train the models. -
frontend: contains visual replay files of different agents. -
errors: contains error logs of ChatGPT agents. -
{LLM_MODEL}_logs: contains dialog log files of a LLM. -
prompts: contains base prompts of ChatGPT agents. -
finetune: contains codes for LightGPT training.
| Road networks | Intersections | Road network arg | Traffic files |
| Jinan | 3 X 4 | jinan | anon_3_4_jinan_real |
|---|---|---|---|
| anon_3_4_jinan_real_2000 | |||
| anon_3_4_jinan_real_2500 | |||
| anon_3_4_jinan_synthetic_24000_60min | |||
| Hangzhou | 4 X 4 | hangzhou | anon_4_4_hangzhou_real |
| anon_4_4_hangzhou_real_5816 | |||
| anon_4_4_hangzhou_synthetic_24000_60min | |||
| New York | 28 X 7 | newyork_28x7 | anon_28_7_newyork_real_double |
| anon_28_7_newyork_real_triple |
@misc{lai2024llmlight,
title={LLMLight: Large Language Models as Traffic Signal Control Agents},
author={Siqi Lai and Zhao Xu and Weijia Zhang and Hao Liu and Hui Xiong},
year={2024},
eprint={2312.16044},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLMTSCS
Similar Open Source Tools

LLMTSCS
LLMLight is a novel framework that employs Large Language Models (LLMs) as decision-making agents for Traffic Signal Control (TSC). The framework leverages the advanced generalization capabilities of LLMs to engage in a reasoning and decision-making process akin to human intuition for effective traffic control. LLMLight has been demonstrated to be remarkably effective, generalizable, and interpretable against various transportation-based and RL-based baselines on nine real-world and synthetic datasets.

VITA
VITA is an open-source interactive omni multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) capable of processing video, image, text, and audio inputs simultaneously. It stands out with features like Omni Multimodal Understanding, Non-awakening Interaction, and Audio Interrupt Interaction. VITA can respond to user queries without a wake-up word, track and filter external queries in real-time, and handle various query inputs effectively. The model utilizes state tokens and a duplex scheme to enhance the multimodal interactive experience.
DeepResearch
Tongyi DeepResearch is an agentic large language model with 30.5 billion total parameters, designed for long-horizon, deep information-seeking tasks. It demonstrates state-of-the-art performance across various search benchmarks. The model features a fully automated synthetic data generation pipeline, large-scale continual pre-training on agentic data, end-to-end reinforcement learning, and compatibility with two inference paradigms. Users can download the model directly from HuggingFace or ModelScope. The repository also provides benchmark evaluation scripts and information on the Deep Research Agent Family.
quantalogic
QuantaLogic is a ReAct framework for building advanced AI agents that seamlessly integrates large language models with a robust tool system. It aims to bridge the gap between advanced AI models and practical implementation in business processes by enabling agents to understand, reason about, and execute complex tasks through natural language interaction. The framework includes features such as ReAct Framework, Universal LLM Support, Secure Tool System, Real-time Monitoring, Memory Management, and Enterprise Ready components.
evalchemy
Evalchemy is a unified and easy-to-use toolkit for evaluating language models, focusing on post-trained models. It integrates multiple existing benchmarks such as RepoBench, AlpacaEval, and ZeroEval. Key features include unified installation, parallel evaluation, simplified usage, and results management. Users can run various benchmarks with a consistent command-line interface and track results locally or integrate with a database for systematic tracking and leaderboard submission.
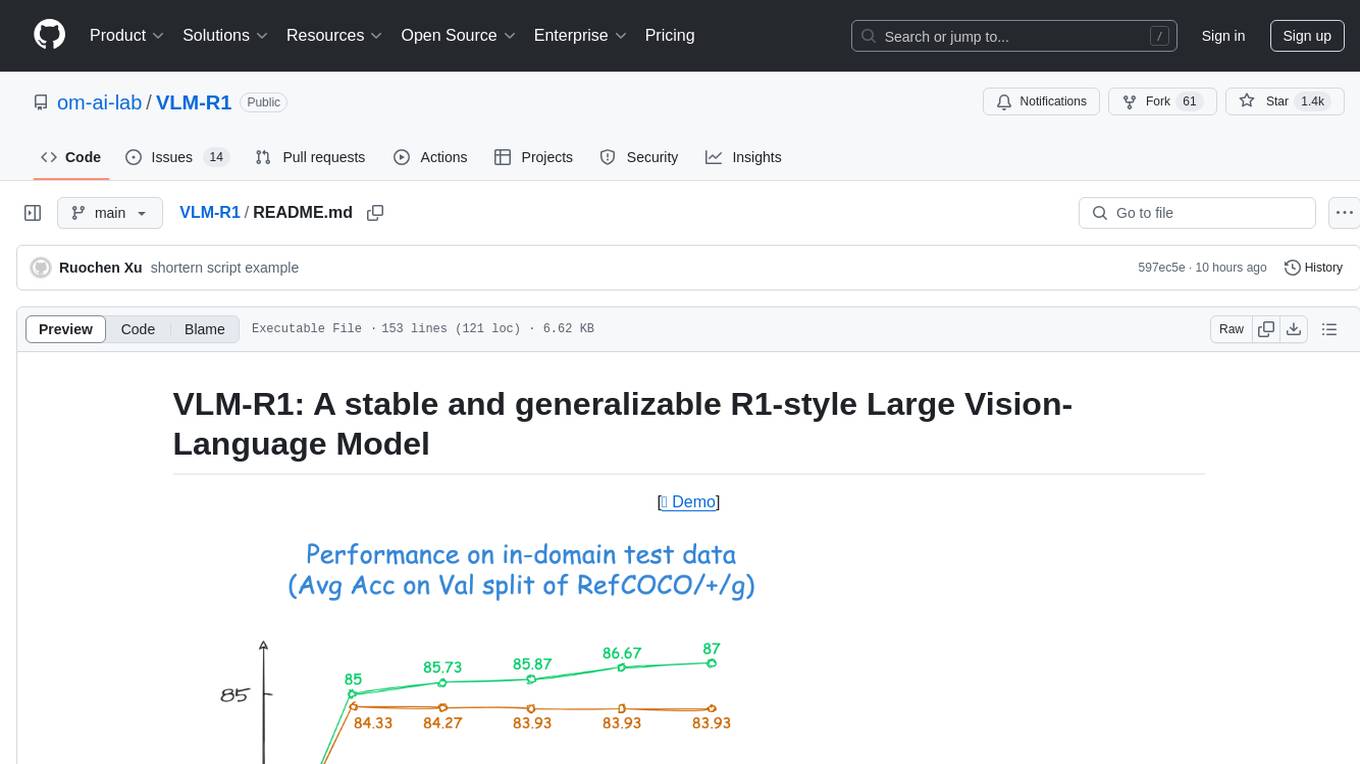
VLM-R1
VLM-R1 is a stable and generalizable R1-style Large Vision-Language Model proposed for Referring Expression Comprehension (REC) task. It compares R1 and SFT approaches, showing R1 model's steady improvement on out-of-domain test data. The project includes setup instructions, training steps for GRPO and SFT models, support for user data loading, and evaluation process. Acknowledgements to various open-source projects and resources are mentioned. The project aims to provide a reliable and versatile solution for vision-language tasks.
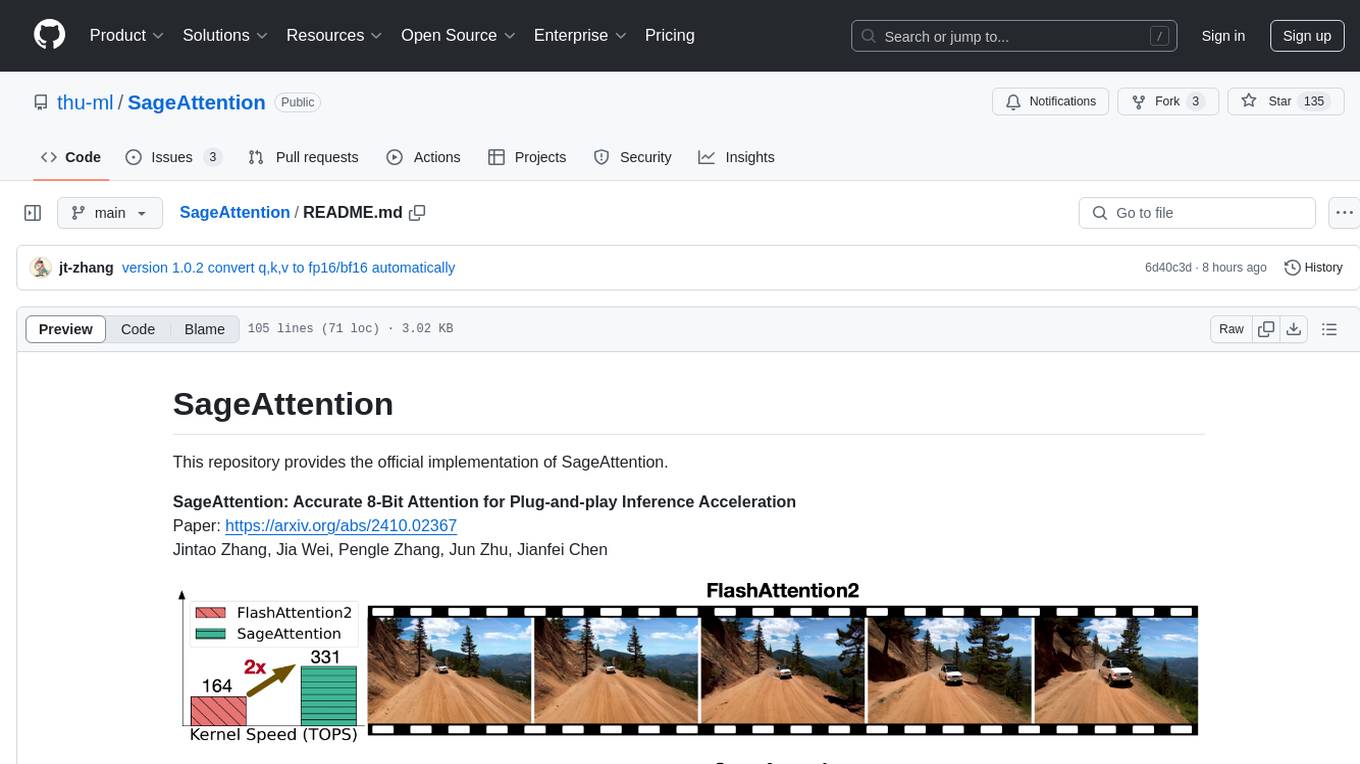
SageAttention
SageAttention is an official implementation of an accurate 8-bit attention mechanism for plug-and-play inference acceleration. It is optimized for RTX4090 and RTX3090 GPUs, providing performance improvements for specific GPU architectures. The tool offers a technique called 'smooth_k' to ensure accuracy in processing FP16/BF16 data. Users can easily replace 'scaled_dot_product_attention' with SageAttention for faster video processing.
candle-vllm
Candle-vllm is an efficient and easy-to-use platform designed for inference and serving local LLMs, featuring an OpenAI compatible API server. It offers a highly extensible trait-based system for rapid implementation of new module pipelines, streaming support in generation, efficient management of key-value cache with PagedAttention, and continuous batching. The tool supports chat serving for various models and provides a seamless experience for users to interact with LLMs through different interfaces.
npcpy
npcpy is a core library of the NPC Toolkit that enhances natural language processing pipelines and agent tooling. It provides a flexible framework for building applications and conducting research with LLMs. The tool supports various functionalities such as getting responses for agents, setting up agent teams, orchestrating jinx workflows, obtaining LLM responses, generating images, videos, audio, and more. It also includes a Flask server for deploying NPC teams, supports LiteLLM integration, and simplifies the development of NLP-based applications. The tool is versatile, supporting multiple models and providers, and offers a graphical user interface through NPC Studio and a command-line interface via NPC Shell.
RepairAgent
RepairAgent is an autonomous LLM-based agent for automated program repair targeting the Defects4J benchmark. It uses an LLM-driven loop to localize, analyze, and fix Java bugs. The tool requires Docker, VS Code with Dev Containers extension, OpenAI API key, disk space of ~40 GB, and internet access. Users can get started with RepairAgent using either VS Code Dev Container or Docker Image. Running RepairAgent involves checking out the buggy project version, autonomous bug analysis, fix candidate generation, and testing against the project's test suite. Users can configure hyperparameters for budget control, repetition handling, commands limit, and external fix strategy. The tool provides output structure, experiment overview, individual analysis scripts, and data on fixed bugs from the Defects4J dataset.
BrowserAI
BrowserAI is a production-ready tool that allows users to run AI models directly in the browser, offering simplicity, speed, privacy, and open-source capabilities. It provides WebGPU acceleration for fast inference, zero server costs, offline capability, and developer-friendly features. Perfect for web developers, companies seeking privacy-conscious AI solutions, researchers experimenting with browser-based AI, and hobbyists exploring AI without infrastructure overhead. The tool supports various AI tasks like text generation, speech recognition, and text-to-speech, with pre-configured popular models ready to use. It offers a simple SDK with multiple engine support and seamless switching between MLC and Transformers engines.
cellseg_models.pytorch
cellseg-models.pytorch is a Python library built upon PyTorch for 2D cell/nuclei instance segmentation models. It provides multi-task encoder-decoder architectures and post-processing methods for segmenting cell/nuclei instances. The library offers high-level API to define segmentation models, open-source datasets for training, flexibility to modify model components, sliding window inference, multi-GPU inference, benchmarking utilities, regularization techniques, and example notebooks for training and finetuning models with different backbones.
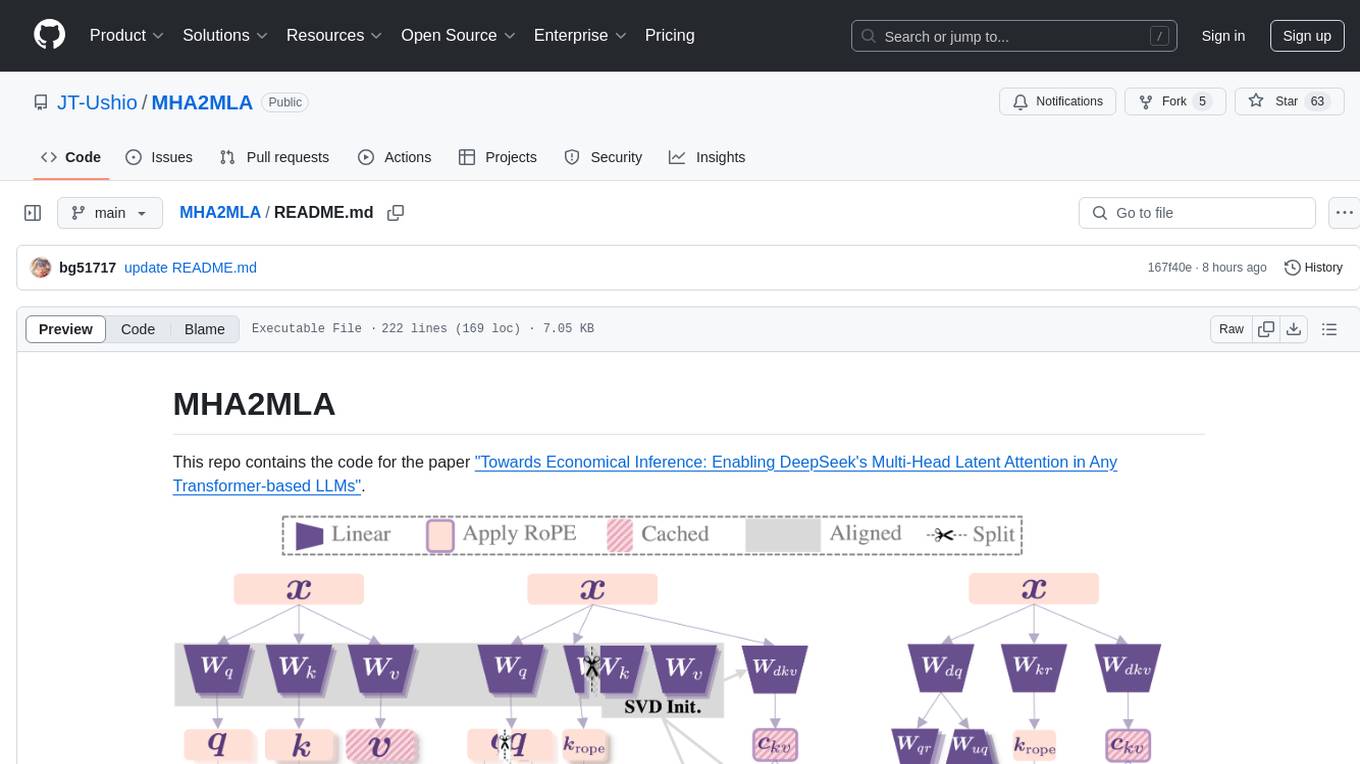
MHA2MLA
This repository contains the code for the paper 'Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs'. It provides tools for fine-tuning and evaluating Llama models, converting models between different frameworks, processing datasets, and performing specific model training tasks like Partial-RoPE Fine-Tuning and Multiple-Head Latent Attention Fine-Tuning. The repository also includes commands for model evaluation using Lighteval and LongBench, along with necessary environment setup instructions.
LightRAG
LightRAG is a repository hosting the code for LightRAG, a system that supports seamless integration of custom knowledge graphs, Oracle Database 23ai, Neo4J for storage, and multiple file types. It includes features like entity deletion, batch insert, incremental insert, and graph visualization. LightRAG provides an API server implementation for RESTful API access to RAG operations, allowing users to interact with it through HTTP requests. The repository also includes evaluation scripts, code for reproducing results, and a comprehensive code structure.
understand-r1-zero
The 'understand-r1-zero' repository focuses on understanding R1-Zero-like training from a critical perspective. It provides insights into base models and reinforcement learning components, highlighting findings and proposing solutions for biased optimization. The repository offers a minimalist recipe for R1-Zero training, detailing the RL-tuning process and achieving state-of-the-art performance with minimal compute resources. It includes codebase, models, and paper related to R1-Zero training implemented with the Oat framework, emphasizing research-friendly and efficient LLM RL techniques.
AnglE
AnglE is a library for training state-of-the-art BERT/LLM-based sentence embeddings with just a few lines of code. It also serves as a general sentence embedding inference framework, allowing for inferring a variety of transformer-based sentence embeddings. The library supports various loss functions such as AnglE loss, Contrastive loss, CoSENT loss, and Espresso loss. It provides backbones like BERT-based models, LLM-based models, and Bi-directional LLM-based models for training on single or multi-GPU setups. AnglE has achieved significant performance on various benchmarks and offers official pretrained models for both BERT-based and LLM-based models.
For similar tasks

LLMTSCS
LLMLight is a novel framework that employs Large Language Models (LLMs) as decision-making agents for Traffic Signal Control (TSC). The framework leverages the advanced generalization capabilities of LLMs to engage in a reasoning and decision-making process akin to human intuition for effective traffic control. LLMLight has been demonstrated to be remarkably effective, generalizable, and interpretable against various transportation-based and RL-based baselines on nine real-world and synthetic datasets.
llm-adaptive-attacks
This repository contains code and results for jailbreaking leading safety-aligned LLMs with simple adaptive attacks. We show that even the most recent safety-aligned LLMs are not robust to simple adaptive jailbreaking attacks. We demonstrate how to successfully leverage access to logprobs for jailbreaking: we initially design an adversarial prompt template (sometimes adapted to the target LLM), and then we apply random search on a suffix to maximize the target logprob (e.g., of the token ``Sure''), potentially with multiple restarts. In this way, we achieve nearly 100% attack success rate---according to GPT-4 as a judge---on GPT-3.5/4, Llama-2-Chat-7B/13B/70B, Gemma-7B, and R2D2 from HarmBench that was adversarially trained against the GCG attack. We also show how to jailbreak all Claude models---that do not expose logprobs---via either a transfer or prefilling attack with 100% success rate. In addition, we show how to use random search on a restricted set of tokens for finding trojan strings in poisoned models---a task that shares many similarities with jailbreaking---which is the algorithm that brought us the first place in the SaTML'24 Trojan Detection Competition. The common theme behind these attacks is that adaptivity is crucial: different models are vulnerable to different prompting templates (e.g., R2D2 is very sensitive to in-context learning prompts), some models have unique vulnerabilities based on their APIs (e.g., prefilling for Claude), and in some settings it is crucial to restrict the token search space based on prior knowledge (e.g., for trojan detection).
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.





