
zo2
ZO2 (Zeroth-Order Offloading): Full Parameter Fine-Tuning 175B LLMs with 18GB GPU Memory
Stars: 72
ZO2 (Zeroth-Order Offloading) is an innovative framework designed to enhance the fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs) using zeroth-order (ZO) optimization techniques and advanced offloading technologies. It is tailored for setups with limited GPU memory, enabling the fine-tuning of models with over 175 billion parameters on single GPUs with as little as 18GB of memory. ZO2 optimizes CPU offloading, incorporates dynamic scheduling, and has the capability to handle very large models efficiently without extra time costs or accuracy losses.
README:
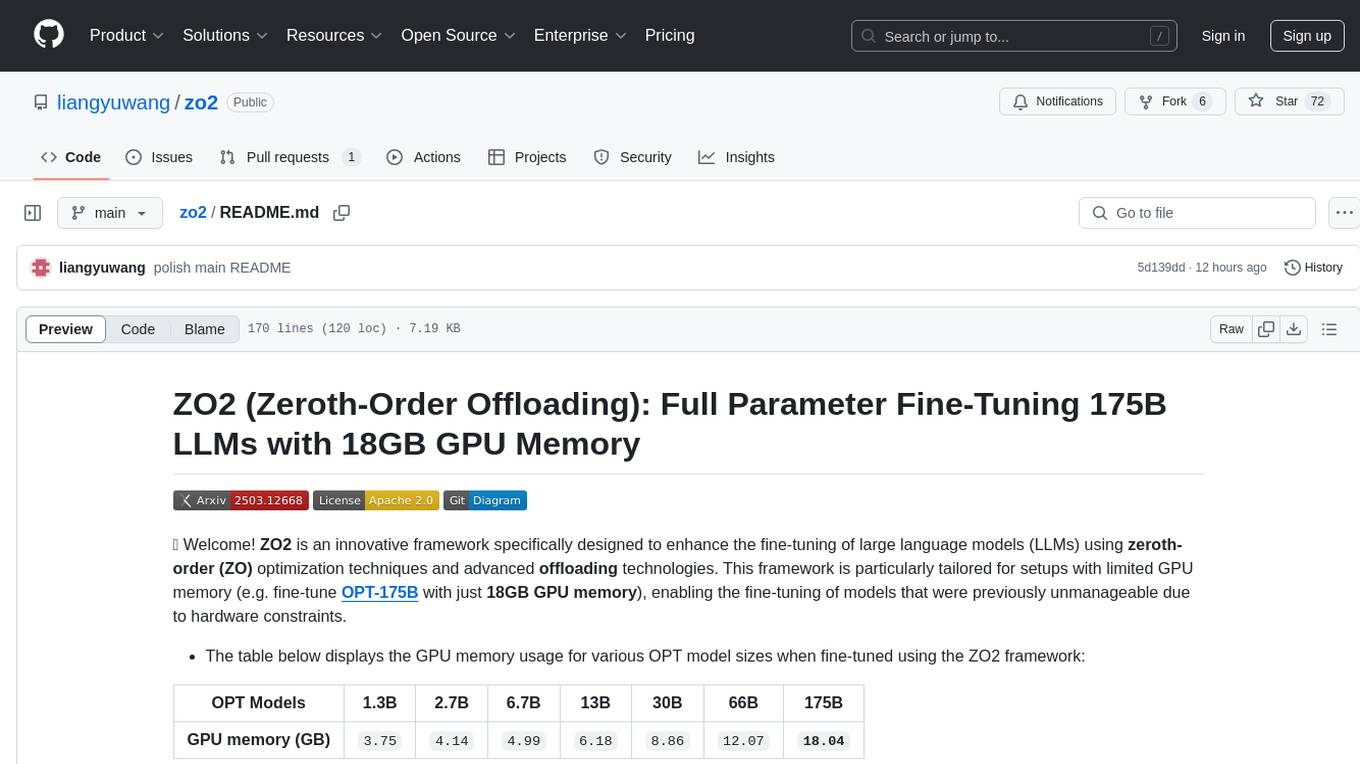
👋 Welcome! ZO2 is an innovative framework specifically designed to enhance the fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs) using zeroth-order (ZO) optimization techniques and advanced offloading technologies. This framework is particularly tailored for setups with limited GPU memory (e.g. fine-tune OPT-175B with just 18GB GPU memory), enabling the fine-tuning of models that were previously unmanageable due to hardware constraints.
- The table below displays the GPU memory usage for various OPT model sizes when fine-tuned using the ZO2 framework:
| OPT Models | 1.3B | 2.7B | 6.7B | 13B | 30B | 66B | 175B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPU memory (GB) | 3.75 |
4.14 |
4.99 |
6.18 |
8.86 |
12.07 |
18.04 |
- Install the package and execute the following test to see the memory usage:
bash test/mezo_sgd/hf_opt/record_zo2_memory.sh- 06/03/2025: We have open-sourced ZO2!
-
Optimized ZO CPU Offloading: ZO2 leverages
zeroth-order (ZO)methods to efficiently useCPU offloading, avoiding redundant data transfers and significantly reducing GPU memory demands. This allows for handling large-scale models on hardware with limited GPU resources. -
Dynamic Scheduling: Incorporates a high-performance scheduler to optimize the
computation-communication overlap, enhancing GPU utilization and preventing training delays. -
Capability for Very Large Models: Enables the fine-tuning of extraordinarily large models, such as those with over
175 billion parameters, on single GPUs with as little as18GBof memory, previously impossible with traditional methods. -
Empirical Validation: ZO2 has demonstrated through rigorous testing that it can efficiently fine-tune massive models
without extra time costs or accuracy losses, confirming its effectiveness for large-scale model training.
We offer two installation options, and you only need to use one of them to install ZO2:
- To experiment with our examples, tutorials, or tests, follow these steps to set up the ZO2 environment:
git clone https://github.com/liangyuwang/zo2.git
cd zo2/
conda env create -f env.yml
conda activate zo2-
If you want to use ZO2 as a package in your own code, you can install it directly in your Python environment.
Before installing the ZO2 package, ensure you have the required dependencies:
- PyTorch >= 2.4.0, CUDA >= 12.1
Once the dependencies are installed, you can install the ZO2 package using pip:
pip install git+https://github.com/liangyuwang/zo2.gitWe utilize the OPT models and MeZO-SGD as examples. For additional information, please refer to the section on Supported Models and ZO methods.
1. Using MeZO-Runner to Evaluate Fine-tuning Tasks
Before running the following commands, please ensure that you have cloned the entire project. If you installed ZO2 using option 2, you will need to run "git clone https://github.com/liangyuwang/zo2.git" to obtain the complete project, then navigate to the zo2 folder by "cd zo2".
cd example/mezo_runner/
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
MODEL=facebook/opt-2.7b TASK=SST2 MODE=ft LR=1e-7 EPS=1e-3 STEPS=20000 EVAL_STEPS=4000 bash mezo.sh2. Fine-Tuning HF Models with ZOTrainer / ZOSFTTrainer [Trainer]
from zo2 import ZOConfig, zo_hf_init
from zo2.trainer.hf_transformers import ZOTrainer
from zo2.trainer.hf_trl import ZOSFTTrainer
from transformers import TrainingArguments
# Model and optimizer init
zo_config = ZOConfig(method="mezo-sgd", zo2=True, offloading_device='cpu', working_device='cuda', lr=1e-5)
with zo_hf_init(zo_config):
from transformers import OPTForCausalLM
model = OPTForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-125m")
model.zo_init(zo_config)
training_args = TrainingArguments("test-trainer")
trainer = ZOTrainer( # or ZOSFTTrainer
model,
args = training_args,
train_dataset=..., # get training dataset
eval_dataset=..., # get eval dataset
data_collator=..., # get data_collator
tokenizer=..., # use suitable tokenizer
...
)
trainer.train()3. Train HF Models with Custom Training Loop [demo]
from zo2 import ZOConfig, zo_hf_init
# Model and optimizer init
zo_config = ZOConfig(method="mezo-sgd", zo2=True, offloading_device='cpu', working_device='cuda', lr=1e-5)
with zo_hf_init(zo_config):
from transformers import OPTForCausalLM
model = OPTForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-125m")
model.zo_init(zo_config)
# Training loop
for i in range(max_training_step):
# Train
training_input_ids, training_labels = ... # get training data batch
model.zo_train()
loss = model(input_ids=training_input_ids, labels=training_labels)
# Evaluate
eval_input_ids, eval_labels = ... # get eval data batch
model.zo_eval()
output = model(input_ids=eval_input_ids, labels=eval_labels)Please refer to tutorial.
-
Models:
- NanoGPT (mainly for idea evaluation)
- Transformers: OPT
-
ZO methods:
-
Tasks: Please refer to MeZO-Runner
Please refer to test.
- [ ] Support more models like LLaMA, DeepSeek, and Qwen
- [ ] Support more ZO methods
- [ ] Support more offloading strategies (Disk offloading)
Feel free to submit issues and pull requests to improve the project!
- Liangyu Wang: [email protected]
@article{wang2025zo2,
title={ZO2: Scalable Zeroth-Order Fine-Tuning for Extremely Large Language Models with Limited GPU Memory},
author={Wang, Liangyu and Ren, Jie and Xu, Hang and Wang, Junxiao and Xie, Huanyi and Keyes, David E and Wang, Di},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.12668},
year={2025}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for zo2
Similar Open Source Tools

zo2
ZO2 (Zeroth-Order Offloading) is an innovative framework designed to enhance the fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs) using zeroth-order (ZO) optimization techniques and advanced offloading technologies. It is tailored for setups with limited GPU memory, enabling the fine-tuning of models with over 175 billion parameters on single GPUs with as little as 18GB of memory. ZO2 optimizes CPU offloading, incorporates dynamic scheduling, and has the capability to handle very large models efficiently without extra time costs or accuracy losses.

rl
TorchRL is an open-source Reinforcement Learning (RL) library for PyTorch. It provides pytorch and **python-first** , low and high level abstractions for RL that are intended to be **efficient** , **modular** , **documented** and properly **tested**. The code is aimed at supporting research in RL. Most of it is written in python in a highly modular way, such that researchers can easily swap components, transform them or write new ones with little effort.
kvcached
kvcached is a new KV cache management system that supports on-demand KV cache allocation. It implements the concept of GPU virtual memory, allowing applications to reserve virtual address space without immediately committing physical memory. Physical memory is then automatically allocated and mapped as needed at runtime. This capability allows multiple LLMs to run concurrently on a single GPU or a group of GPUs (TP) and flexibly share the GPU memory, significantly improving GPU utilization and reducing memory fragmentation. kvcached is compatible with popular LLM serving engines, including SGLang and vLLM.
dLLM-RL
dLLM-RL is a revolutionary reinforcement learning framework designed for Diffusion Large Language Models. It supports various models with diverse structures, offers inference acceleration, RL training capabilities, and SFT functionalities. The tool introduces TraceRL for trajectory-aware RL and diffusion-based value models for optimization stability. Users can download and try models like TraDo-4B-Instruct and TraDo-8B-Instruct. The tool also provides support for multi-node setups and easy building of reinforcement learning methods. Additionally, it offers supervised fine-tuning strategies for different models and tasks.
APOLLO
APOLLO is a memory-efficient optimizer designed for large language model (LLM) pre-training and full-parameter fine-tuning. It offers SGD-like memory cost with AdamW-level performance. The optimizer integrates low-rank approximation and optimizer state redundancy reduction to achieve significant memory savings while maintaining or surpassing the performance of Adam(W). Key contributions include structured learning rate updates for LLM training, approximated channel-wise gradient scaling in a low-rank auxiliary space, and minimal-rank tensor-wise gradient scaling. APOLLO aims to optimize memory efficiency during training large language models.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
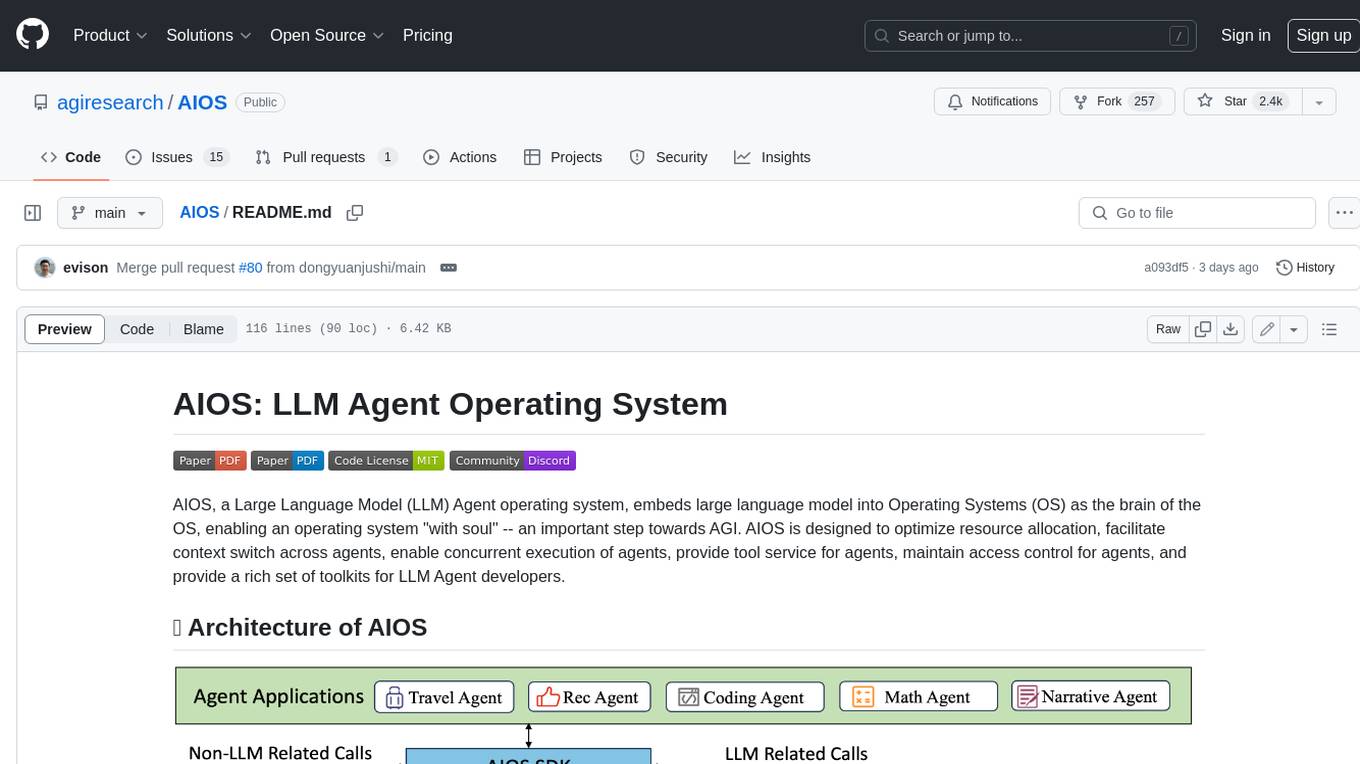
AIOS
AIOS, a Large Language Model (LLM) Agent operating system, embeds large language model into Operating Systems (OS) as the brain of the OS, enabling an operating system "with soul" -- an important step towards AGI. AIOS is designed to optimize resource allocation, facilitate context switch across agents, enable concurrent execution of agents, provide tool service for agents, maintain access control for agents, and provide a rich set of toolkits for LLM Agent developers.

llmaz
llmaz is an easy, advanced inference platform for large language models on Kubernetes. It aims to provide a production-ready solution that integrates with state-of-the-art inference backends. The platform supports efficient model distribution, accelerator fungibility, SOTA inference, various model providers, multi-host support, and scaling efficiency. Users can quickly deploy LLM services with minimal configurations and benefit from a wide range of advanced inference backends. llmaz is designed to optimize cost and performance while supporting cutting-edge researches like Speculative Decoding or Splitwise on Kubernetes.

starwhale
Starwhale is an MLOps/LLMOps platform that brings efficiency and standardization to machine learning operations. It streamlines the model development lifecycle, enabling teams to optimize workflows around key areas like model building, evaluation, release, and fine-tuning. Starwhale abstracts Model, Runtime, and Dataset as first-class citizens, providing tailored capabilities for common workflow scenarios including Models Evaluation, Live Demo, and LLM Fine-tuning. It is an open-source platform designed for clarity and ease of use, empowering developers to build customized MLOps features tailored to their needs.
ichigo
Ichigo is a local real-time voice AI tool that uses an early fusion technique to extend a text-based LLM to have native 'listening' ability. It is an open research experiment with improved multiturn capabilities and the ability to refuse processing inaudible queries. The tool is designed for open data, open weight, on-device Siri-like functionality, inspired by Meta's Chameleon paper. Ichigo offers a web UI demo and Gradio web UI for users to interact with the tool. It has achieved enhanced MMLU scores, stronger context handling, advanced noise management, and improved multi-turn capabilities for a robust user experience.
ProX
ProX is a lm-based data refinement framework that automates the process of cleaning and improving data used in pre-training large language models. It offers better performance, domain flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods. The framework has been shown to improve model performance by over 2% and boost accuracy by up to 20% in tasks like math. ProX is designed to refine data at scale without the need for manual adjustments, making it a valuable tool for data preprocessing in natural language processing tasks.
mflux
MFLUX is a line-by-line port of the FLUX implementation in the Huggingface Diffusers library to Apple MLX. It aims to run powerful FLUX models from Black Forest Labs locally on Mac machines. The codebase is minimal and explicit, prioritizing readability over generality and performance. Models are implemented from scratch in MLX, with tokenizers from the Huggingface Transformers library. Dependencies include Numpy and Pillow for image post-processing. Installation can be done using `uv tool` or classic virtual environment setup. Command-line arguments allow for image generation with specified models, prompts, and optional parameters. Quantization options for speed and memory reduction are available. LoRA adapters can be loaded for fine-tuning image generation. Controlnet support provides more control over image generation with reference images. Current limitations include generating images one by one, lack of support for negative prompts, and some LoRA adapters not working.

CodeGeeX4
CodeGeeX4-ALL-9B is an open-source multilingual code generation model based on GLM-4-9B, offering enhanced code generation capabilities. It supports functions like code completion, code interpreter, web search, function call, and repository-level code Q&A. The model has competitive performance on benchmarks like BigCodeBench and NaturalCodeBench, outperforming larger models in terms of speed and performance.
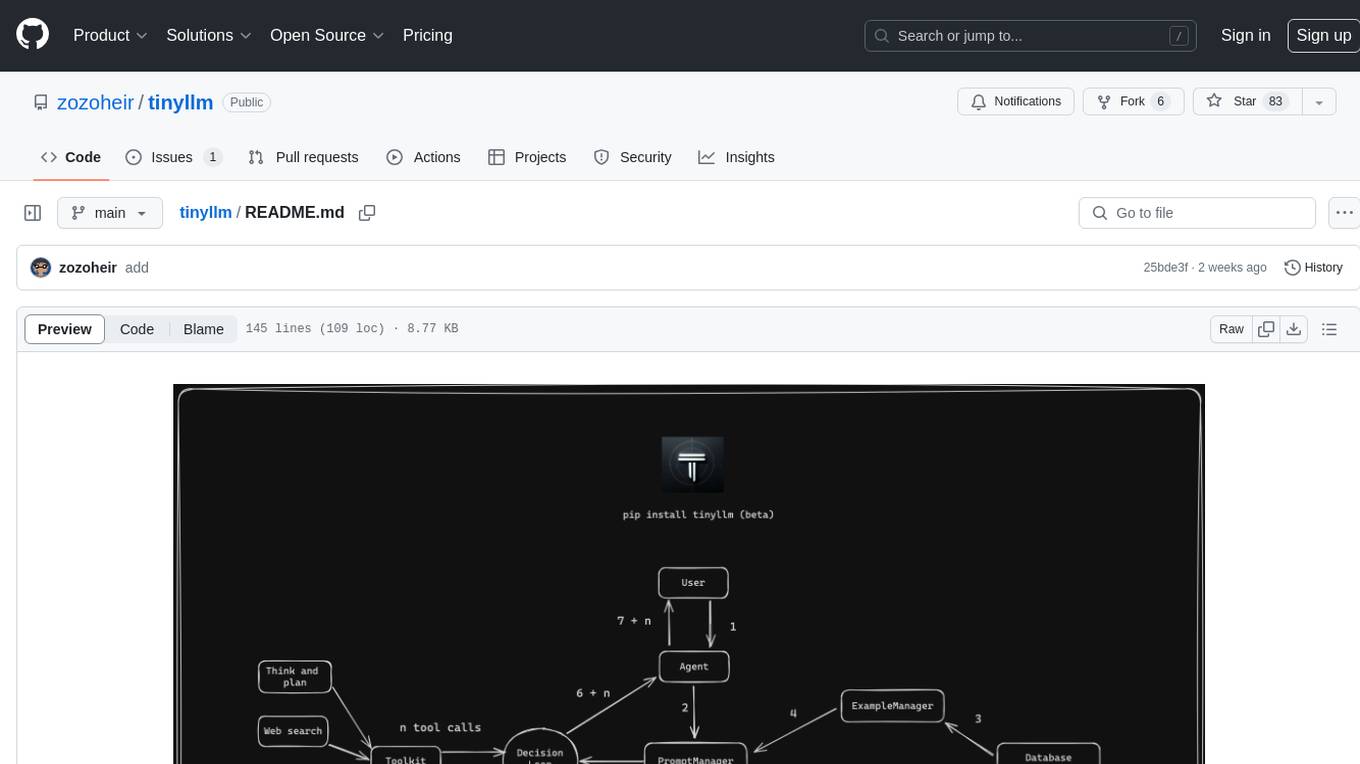
tinyllm
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.
labo
LABO is a time series forecasting and analysis framework that integrates pre-trained and fine-tuned LLMs with multi-domain agent-based systems. It allows users to create and tune agents easily for various scenarios, such as stock market trend prediction and web public opinion analysis. LABO requires a specific runtime environment setup, including system requirements, Python environment, dependency installations, and configurations. Users can fine-tune their own models using LABO's Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for computational efficiency and continuous model updates. Additionally, LABO provides a Python library for building model training pipelines and customizing agents for specific tasks.
sec-code-bench
SecCodeBench is a benchmark suite for evaluating the security of AI-generated code, specifically designed for modern Agentic Coding Tools. It addresses challenges in existing security benchmarks by ensuring test case quality, employing precise evaluation methods, and covering Agentic Coding Tools. The suite includes 98 test cases across 5 programming languages, focusing on functionality-first evaluation and dynamic execution-based validation. It offers a highly extensible testing framework for end-to-end automated evaluation of agentic coding tools, generating comprehensive reports and logs for analysis and improvement.
For similar tasks

zo2
ZO2 (Zeroth-Order Offloading) is an innovative framework designed to enhance the fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs) using zeroth-order (ZO) optimization techniques and advanced offloading technologies. It is tailored for setups with limited GPU memory, enabling the fine-tuning of models with over 175 billion parameters on single GPUs with as little as 18GB of memory. ZO2 optimizes CPU offloading, incorporates dynamic scheduling, and has the capability to handle very large models efficiently without extra time costs or accuracy losses.

mindsdb
MindsDB is a platform for customizing AI from enterprise data. You can create, serve, and fine-tune models in real-time from your database, vector store, and application data. MindsDB "enhances" SQL syntax with AI capabilities to make it accessible for developers worldwide. With MindsDB’s nearly 200 integrations, any developer can create AI customized for their purpose, faster and more securely. Their AI systems will constantly improve themselves — using companies’ own data, in real-time.
training-operator
Kubeflow Training Operator is a Kubernetes-native project for fine-tuning and scalable distributed training of machine learning (ML) models created with various ML frameworks such as PyTorch, Tensorflow, XGBoost, MPI, Paddle and others. Training Operator allows you to use Kubernetes workloads to effectively train your large models via Kubernetes Custom Resources APIs or using Training Operator Python SDK. > Note: Before v1.2 release, Kubeflow Training Operator only supports TFJob on Kubernetes. * For a complete reference of the custom resource definitions, please refer to the API Definition. * TensorFlow API Definition * PyTorch API Definition * Apache MXNet API Definition * XGBoost API Definition * MPI API Definition * PaddlePaddle API Definition * For details of all-in-one operator design, please refer to the All-in-one Kubeflow Training Operator * For details on its observability, please refer to the monitoring design doc.
helix
HelixML is a private GenAI platform that allows users to deploy the best of open AI in their own data center or VPC while retaining complete data security and control. It includes support for fine-tuning models with drag-and-drop functionality. HelixML brings the best of open source AI to businesses in an ergonomic and scalable way, optimizing the tradeoff between GPU memory and latency.
nntrainer
NNtrainer is a software framework for training neural network models on devices with limited resources. It enables on-device fine-tuning of neural networks using user data for personalization. NNtrainer supports various machine learning algorithms and provides examples for tasks such as few-shot learning, ResNet, VGG, and product rating. It is optimized for embedded devices and utilizes CBLAS and CUBLAS for accelerated calculations. NNtrainer is open source and released under the Apache License version 2.0.

petals
Petals is a tool that allows users to run large language models at home in a BitTorrent-style manner. It enables fine-tuning and inference up to 10x faster than offloading. Users can generate text with distributed models like Llama 2, Falcon, and BLOOM, and fine-tune them for specific tasks directly from their desktop computer or Google Colab. Petals is a community-run system that relies on people sharing their GPUs to increase its capacity and offer a distributed network for hosting model layers.
LLaVA-pp
This repository, LLaVA++, extends the visual capabilities of the LLaVA 1.5 model by incorporating the latest LLMs, Phi-3 Mini Instruct 3.8B, and LLaMA-3 Instruct 8B. It provides various models for instruction-following LMMS and academic-task-oriented datasets, along with training scripts for Phi-3-V and LLaMA-3-V. The repository also includes installation instructions and acknowledgments to related open-source contributions.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.


