
mLoRA
An Efficient "Factory" to Build Multiple LoRA Adapters
Stars: 262
mLoRA (Multi-LoRA Fine-Tune) is an open-source framework for efficient fine-tuning of multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) using LoRA and its variants. It allows concurrent fine-tuning of multiple LoRA adapters with a shared base model, efficient pipeline parallelism algorithm, support for various LoRA variant algorithms, and reinforcement learning preference alignment algorithms. mLoRA helps save computational and memory resources when training multiple adapters simultaneously, achieving high performance on consumer hardware.
README:
mLoRA
An Efficient "Factory" to Build Multiple LoRA Adapters
mLoRA (a.k.a Multi-LoRA Fine-Tune) is an open-source framework designed for efficient fine-tuning of multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) using LoRA and its variants. Key features of mLoRA include:
-
Concurrent fine-tuning of multiple LoRA adapters.
-
Shared base model among multiple LoRA adapters.
-
Efficient pipeline parallelism algorithm.
-
Support for multiple LoRA variant algorithms and various base models.
-
Support for multiple reinforcement learning preference alignment algorithms.
The end-to-end architecture of the mLoRA is shown in the figure:
Firstly, you should clone this repository and install dependencies (or use our image):
# Clone Repository
git clone https://github.com/TUDB-Labs/mLoRA
cd mLoRA
# Install requirements need the Python >= 3.12
pip install .The mlora_train.py code is a starting point for batch fine-tuning LoRA adapters.
python mlora_train.py \
--base_model TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v0.4 \
--config demo/lora/lora_case_1.yamlYou can check the adapters' configuration in demo folder, there are some configuration regarding the use of different LoRA variants and reinforcement learning preference alignment algorithms.
For further detailed usage information, please use --help option:
python mlora_train.py --helpSimilar to Quickstart, the command to start in a two-node environment is as follows:
NOTE1: Use environment variables MASTER_ADDR/MASTER_PORT to set the master node.
NOTE2: Set balance, indicating the number of decoder layers allocated to each rank.
# in the first node
export MASTER_ADDR=master.svc.cluster.local
export MASTER_PORT=12355
python mlora_pp_train.py \
--base_model TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v0.4 \
--config demo/lora/lora_case_1.yaml \
--pipeline \
--device "cuda:0" \
--rank 0 \
--balance 12 13 \
--no-recompute \
--precision fp32
# in the second node
export MASTER_ADDR=master.svc.cluster.local
export MASTER_PORT=12355
python mlora_pp_train.py \
--base_model TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v0.4 \
--config demo/lora/lora_case_1.yaml \
--pipeline \
--device "cuda:1" \
--rank 1 \
--balance 12 13 \
--no-recompute \
--precision fp32mLoRA offers an official Docker image for quick start and development, The image is available on Dockerhub Packages registry.
First, you should pull the latest image (the image also use for development):
docker pull yezhengmaolove/mlora:latestDeploy and enter a container to run mLoRA:
docker run -itd --runtime nvidia --gpus all \
-v ~/your_dataset_dir:/dataset \
-v ~/your_model_dir:/model \
-p <host_port>:22 \
--name mlora \
yezhengmaolove/mlora:latest
# when the container started, use the ssh to login
# the default password is mlora@123
ssh root@localhost -p <host_port>
# pull the latest code and run the mlora
cd /mLoRA
git pull
python mlora_train.py \
--base_model TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v0.4 \
--config demo/lora/lora_case_1.yamlWe can deploy mLoAR as a service to continuously receive user requests and perform fine-tuning task.
First, you should pull the latest image (use same image for deploy):
docker pull yezhengmaolove/mlora:latestDeploy our mLoRA server:
docker run -itd --runtime nvidia --gpus all \
-v ~/your_dataset_cache_dir:/cache \
-v ~/your_model_dir:/model \
-p <host_port>:8000 \
--name mlora_server \
-e "BASE_MODEL=TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v0.4" \
-e "STORAGE_DIR=/cache" \
yezhengmaolove/mlora:latest /bin/bash /opt/deploy.shOnce the service is deployed, install and use mlora_cli.py to interact with the server.
# install the client tools
pip install mlora-cli
# use the mlora cli tool to connect to mlora server
mlora_cli
(mLoRA) set port <host_port>
(mLoRA) set host http://<host_ip>
# and enjoy it!!Step-by-step
docker pull yezhengmaolove/mlora:latest
pip install mlora-cli# first, we create a cache dir in host for cache some file
mkdir ~/cache
# second, we manually download the model weights from Hugging Face.
mkdir ~/model && cd ~/model
git clone https://huggingface.co/TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0
# we map port 8000 used by the mlora server to port 1288 on the host machine.
# the BASE_MODEL environment variable indicates the path of the base model used by mlora.
# the STORAGE_DIR environment variable indicates the path where datasets and lora adapters are stored.
# we use the script /opt/deploy.sh in container to start the server.
docker run -itd --runtime nvidia --gpus all \
-v ~/cache:/cache \
-v ~/model:/model \
-p 1288:8000 \
--name mlora_server \
-e "BASE_MODEL=/model/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0" \
-e "STORAGE_DIR=/cache" \
yezhengmaolove/mlora:latest /bin/bash /opt/deploy.shwe use mlora_cli link to the server http://127.0.0.1:1288 (must use the http protocal)
(mLoRA) set port 1288
(mLoRA) set host http://127.0.0.1we use the Stanford Alpaca dataset as a demo, the data just like below:
[{"instruction": "", "input": "", "output": }, {...}](mLoRA) file upload
? file type: train data
? name: alpaca
? file path: /home/yezhengmao/alpaca-lora/alpaca_data.jsonthe template in a yaml file, and write by templating language Jinja2, see the demo/prompt.yaml file
the data file you upload can be considered as array data, with the elements in the array being of dictionary type. we consider each element as a data point in the template.
(mLoRA) file upload
? file type: prompt template
? name: simple_prompt
? file path: /home/yezhengmao/mLoRA/demo/prompt.yamlwe create a dataset, the dataset consists of data, a template, and the corresponding prompter.
we can use dataset showcase command to check the if the prompts are generated correctly.
(mLoRA) dataset create
? name: alpaca_dataset
? train data file: alpaca
? prompt template file: simple_prompt
? prompter: instruction
? data preprocessing: default
(mLoRA) dataset showcase
? dataset name: alpaca_datasetnow we can use adapter create command to create a adapter for train.
Finally, we can submit the task to train our adapter using the defined dataset.
NOTE: you can continuously submit or terminal training tasks.
use the adapter ls or task ls to check the tasks' status
Using mLoRA can save significant computational and memory resources when training multiple adapters simultaneously.
We fine-tuned multiple LoRA adapters using four A6000 graphics cards with fp32 precision and without using checkpointing and any quantization techniques:
| Model | mLoRA (tokens/s) | PEFT-LoRA with FSDP (tokens/s) | PEFT-LoRA with TP (tokens/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| llama-2-7b (32fp) | 2364 | 1750 | 1500 |
| llama-2-13b (32fp) | 1280 | OOM | 875 |
| Model | |
|---|---|
| ✓ | LLaMA |
| Variant | |
|---|---|
| ✓ | QLoRA,NIPS,2023 |
| ✓ | LoRA+,ICML,2024 |
| ✓ | VeRA,ICLR,2024 |
| ✓ | DoRA,ICML,2024 |
| Variant | |
|---|---|
| ✓ | DPO,NeurIPS,2024 |
| ✓ | CPO,ICML,2024 |
| ✓ | CIT,arXiv,2024 |
- Help Document[TODO]
- Design Document
- How to develop a new adapter
We welcome contributions to improve this repository! Please review the contribution guidelines before submitting pull requests or issues.
Fork the repository. Create a new branch for your feature or fix. Submit a pull request with a detailed explanation of your changes.
You can use the pre-commit to check your code.
# Install requirements
pip install .[ci_test]
ln -s ../../.github/workflows/pre-commit .git/hooks/pre-commitOr just call the script to check your code
.github/workflows/pre-commitPlease cite the repo if you use the code in this repo.
@misc{m-LoRA,
author = {Zhengmao, Ye\textsuperscript{*} and Dengchun, Li\textsuperscript{*} and Jingqi, Tian and Tingfeng, Lan and Yanbo, Liang and Yexi, Jiang and Jie, Zuo and Hui, Lu and Lei, Duan and Mingjie, Tang},
title = {m-LoRA: Efficient LLM Model Fine-tune and Inference via Multi-Lora Optimization},
year = {2023},
publisher = {GitHub},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/TUDB-Labs/mLoRA}},
note={\textsuperscript{*}: these authors contributed equally to this work.}
}Copyright © 2024 All Rights Reserved.
This project is licensed under the Apache 2.0 License.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for mLoRA
Similar Open Source Tools

mLoRA
mLoRA (Multi-LoRA Fine-Tune) is an open-source framework for efficient fine-tuning of multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) using LoRA and its variants. It allows concurrent fine-tuning of multiple LoRA adapters with a shared base model, efficient pipeline parallelism algorithm, support for various LoRA variant algorithms, and reinforcement learning preference alignment algorithms. mLoRA helps save computational and memory resources when training multiple adapters simultaneously, achieving high performance on consumer hardware.

ragflow
RAGFlow is an open-source Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) engine that combines deep document understanding with Large Language Models (LLMs) to provide accurate question-answering capabilities. It offers a streamlined RAG workflow for businesses of all sizes, enabling them to extract knowledge from unstructured data in various formats, including Word documents, slides, Excel files, images, and more. RAGFlow's key features include deep document understanding, template-based chunking, grounded citations with reduced hallucinations, compatibility with heterogeneous data sources, and an automated and effortless RAG workflow. It supports multiple recall paired with fused re-ranking, configurable LLMs and embedding models, and intuitive APIs for seamless integration with business applications.

xFasterTransformer
xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for Large Language Models (LLMs) on the X86 platform, providing high performance and scalability for inference on mainstream LLM models. It offers C++ and Python APIs for easy integration, along with example codes and benchmark scripts. Users can prepare models in a different format, convert them, and use the APIs for tasks like encoding input prompts, generating token ids, and serving inference requests. The tool supports various data types and models, and can run in single or multi-rank modes using MPI. A web demo based on Gradio is available for popular LLM models like ChatGLM and Llama2. Benchmark scripts help evaluate model inference performance quickly, and MLServer enables serving with REST and gRPC interfaces.
r2ai
r2ai is a tool designed to run a language model locally without internet access. It can be used to entertain users or assist in answering questions related to radare2 or reverse engineering. The tool allows users to prompt the language model, index large codebases, slurp file contents, embed the output of an r2 command, define different system-level assistant roles, set environment variables, and more. It is accessible as an r2lang-python plugin and can be scripted from various languages. Users can use different models, adjust query templates dynamically, load multiple models, and make them communicate with each other.
swe-rl
SWE-RL is the official codebase for the paper 'SWE-RL: Advancing LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning on Open Software Evolution'. It is the first approach to scale reinforcement learning based LLM reasoning for real-world software engineering, leveraging open-source software evolution data and rule-based rewards. The code provides prompt templates and the implementation of the reward function based on sequence similarity. Agentless Mini, a part of SWE-RL, builds on top of Agentless with improvements like fast async inference, code refactoring for scalability, and support for using multiple reproduction tests for reranking. The tool can be used for localization, repair, and reproduction test generation in software engineering tasks.

skyvern
Skyvern automates browser-based workflows using LLMs and computer vision. It provides a simple API endpoint to fully automate manual workflows, replacing brittle or unreliable automation solutions. Traditional approaches to browser automations required writing custom scripts for websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions which would break whenever the website layouts changed. Instead of only relying on code-defined XPath interactions, Skyvern adds computer vision and LLMs to the mix to parse items in the viewport in real-time, create a plan for interaction and interact with them. This approach gives us a few advantages: 1. Skyvern can operate on websites it’s never seen before, as it’s able to map visual elements to actions necessary to complete a workflow, without any customized code 2. Skyvern is resistant to website layout changes, as there are no pre-determined XPaths or other selectors our system is looking for while trying to navigate 3. Skyvern leverages LLMs to reason through interactions to ensure we can cover complex situations. Examples include: 1. If you wanted to get an auto insurance quote from Geico, the answer to a common question “Were you eligible to drive at 18?” could be inferred from the driver receiving their license at age 16 2. If you were doing competitor analysis, it’s understanding that an Arnold Palmer 22 oz can at 7/11 is almost definitely the same product as a 23 oz can at Gopuff (even though the sizes are slightly different, which could be a rounding error!) Want to see examples of Skyvern in action? Jump to #real-world-examples-of- skyvern

raglite
RAGLite is a Python toolkit for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with PostgreSQL or SQLite. It offers configurable options for choosing LLM providers, database types, and rerankers. The toolkit is fast and permissive, utilizing lightweight dependencies and hardware acceleration. RAGLite provides features like PDF to Markdown conversion, multi-vector chunk embedding, optimal semantic chunking, hybrid search capabilities, adaptive retrieval, and improved output quality. It is extensible with a built-in Model Context Protocol server, customizable ChatGPT-like frontend, document conversion to Markdown, and evaluation tools. Users can configure RAGLite for various tasks like configuring, inserting documents, running RAG pipelines, computing query adapters, evaluating performance, running MCP servers, and serving frontends.
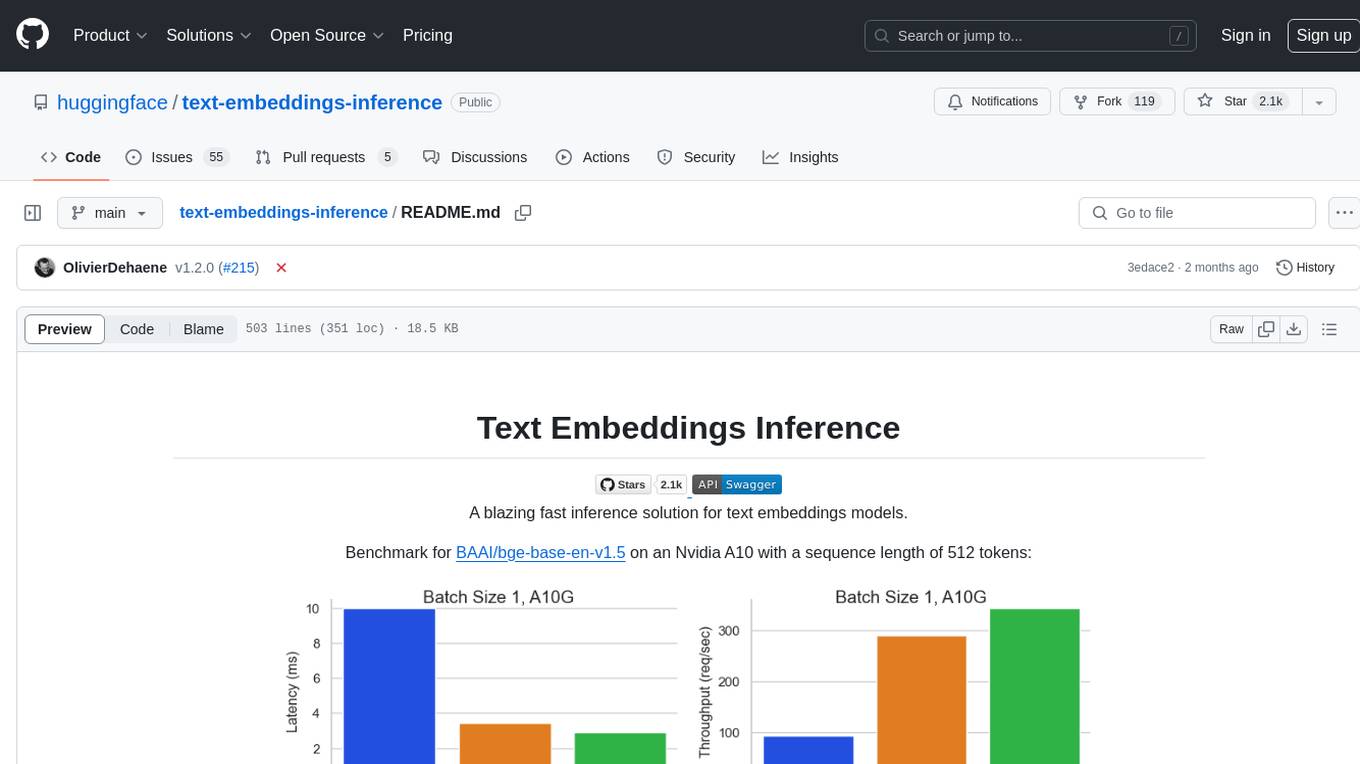
text-embeddings-inference
Text Embeddings Inference (TEI) is a toolkit for deploying and serving open source text embeddings and sequence classification models. TEI enables high-performance extraction for popular models like FlagEmbedding, Ember, GTE, and E5. It implements features such as no model graph compilation step, Metal support for local execution on Macs, small docker images with fast boot times, token-based dynamic batching, optimized transformers code for inference using Flash Attention, Candle, and cuBLASLt, Safetensors weight loading, and production-ready features like distributed tracing with Open Telemetry and Prometheus metrics.
MockingBird
MockingBird is a toolbox designed for Mandarin speech synthesis using PyTorch. It supports multiple datasets such as aidatatang_200zh, magicdata, aishell3, and data_aishell. The toolbox can run on Windows, Linux, and M1 MacOS, providing easy and effective speech synthesis with pretrained encoder/vocoder models. It is webserver ready for remote calling. Users can train their own models or use existing ones for the encoder, synthesizer, and vocoder. The toolbox offers a demo video and detailed setup instructions for installation and model training.
metis
Metis is an open-source, AI-driven tool for deep security code review, created by Arm's Product Security Team. It helps engineers detect subtle vulnerabilities, improve secure coding practices, and reduce review fatigue. Metis uses LLMs for semantic understanding and reasoning, RAG for context-aware reviews, and supports multiple languages and vector store backends. It provides a plugin-friendly and extensible architecture, named after the Greek goddess of wisdom, Metis. The tool is designed for large, complex, or legacy codebases where traditional tooling falls short.
gollama
Gollama is a delightful tool that brings Ollama, your offline conversational AI companion, directly into your terminal. It provides a fun and interactive way to generate responses from various models without needing internet connectivity. Whether you're brainstorming ideas, exploring creative writing, or just looking for inspiration, Gollama is here to assist you. The tool offers an interactive interface, customizable prompts, multiple models selection, and visual feedback to enhance user experience. It can be installed via different methods like downloading the latest release, using Go, running with Docker, or building from source. Users can interact with Gollama through various options like specifying a custom base URL, prompt, model, and enabling raw output mode. The tool supports different modes like interactive, piped, CLI with image, and TUI with image. Gollama relies on third-party packages like bubbletea, glamour, huh, and lipgloss. The roadmap includes implementing piped mode, support for extracting codeblocks, copying responses/codeblocks to clipboard, GitHub Actions for automated releases, and downloading models directly from Ollama using the rest API. Contributions are welcome, and the project is licensed under the MIT License.

langserve
LangServe helps developers deploy `LangChain` runnables and chains as a REST API. This library is integrated with FastAPI and uses pydantic for data validation. In addition, it provides a client that can be used to call into runnables deployed on a server. A JavaScript client is available in LangChain.js.
pr-pilot
PR Pilot is an AI-powered tool designed to assist users in their daily workflow by delegating routine work to AI with confidence and predictability. It integrates seamlessly with popular development tools and allows users to interact with it through a Command-Line Interface, Python SDK, REST API, and Smart Workflows. Users can automate tasks such as generating PR titles and descriptions, summarizing and posting issues, and formatting README files. The tool aims to save time and enhance productivity by providing AI-powered solutions for common development tasks.
client-python
The Mistral Python Client is a tool inspired by cohere-python that allows users to interact with the Mistral AI API. It provides functionalities to access and utilize the AI capabilities offered by Mistral. Users can easily install the client using pip and manage dependencies using poetry. The client includes examples demonstrating how to use the API for various tasks, such as chat interactions. To get started, users need to obtain a Mistral API Key and set it as an environment variable. Overall, the Mistral Python Client simplifies the integration of Mistral AI services into Python applications.
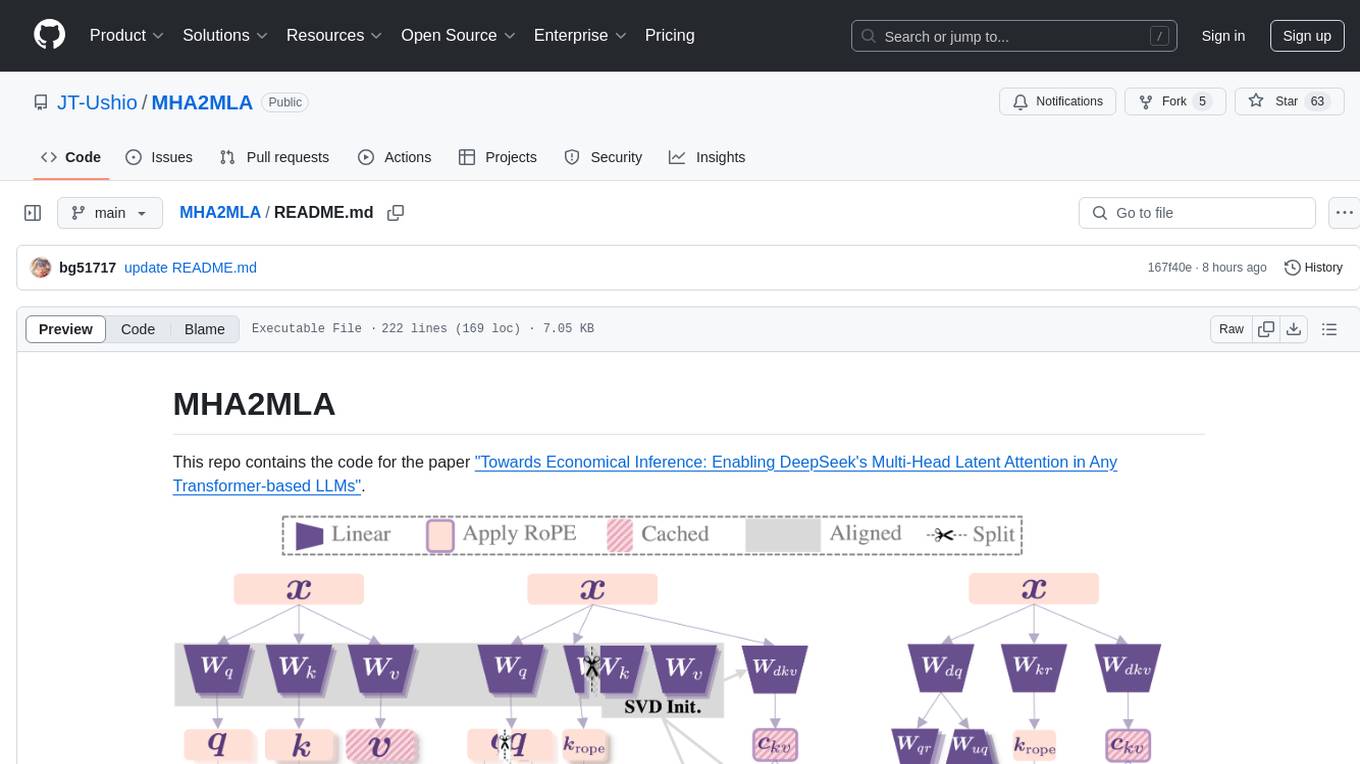
MHA2MLA
This repository contains the code for the paper 'Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs'. It provides tools for fine-tuning and evaluating Llama models, converting models between different frameworks, processing datasets, and performing specific model training tasks like Partial-RoPE Fine-Tuning and Multiple-Head Latent Attention Fine-Tuning. The repository also includes commands for model evaluation using Lighteval and LongBench, along with necessary environment setup instructions.
mcpdoc
The MCP LLMS-TXT Documentation Server is an open-source server that provides developers full control over tools used by applications like Cursor, Windsurf, and Claude Code/Desktop. It allows users to create a user-defined list of `llms.txt` files and use a `fetch_docs` tool to read URLs within these files, enabling auditing of tool calls and context returned. The server supports various applications and provides a way to connect to them, configure rules, and test tool calls for tasks related to documentation retrieval and processing.
For similar tasks

mLoRA
mLoRA (Multi-LoRA Fine-Tune) is an open-source framework for efficient fine-tuning of multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) using LoRA and its variants. It allows concurrent fine-tuning of multiple LoRA adapters with a shared base model, efficient pipeline parallelism algorithm, support for various LoRA variant algorithms, and reinforcement learning preference alignment algorithms. mLoRA helps save computational and memory resources when training multiple adapters simultaneously, achieving high performance on consumer hardware.
InstructGraph
InstructGraph is a framework designed to enhance large language models (LLMs) for graph-centric tasks by utilizing graph instruction tuning and preference alignment. The tool collects and decomposes 29 standard graph datasets into four groups, enabling LLMs to better understand and generate graph data. It introduces a structured format verbalizer to transform graph data into a code-like format, facilitating code understanding and generation. Additionally, it addresses hallucination problems in graph reasoning and generation through direct preference optimization (DPO). The tool aims to bridge the gap between textual LLMs and graph data, offering a comprehensive solution for graph-related tasks.
FedLLM-Bench
FedLLM-Bench is a realistic benchmark for the Federated Learning of Large Language Models community. It includes datasets for federated instruction tuning and preference alignment tasks, exhibiting diversities in language, quality, quantity, instruction, sequence length, embedding, and preference. The repository provides training scripts and code for open-ended evaluation, aiming to facilitate research and development in federated learning of large language models.

mindsdb
MindsDB is a platform for customizing AI from enterprise data. You can create, serve, and fine-tune models in real-time from your database, vector store, and application data. MindsDB "enhances" SQL syntax with AI capabilities to make it accessible for developers worldwide. With MindsDB’s nearly 200 integrations, any developer can create AI customized for their purpose, faster and more securely. Their AI systems will constantly improve themselves — using companies’ own data, in real-time.
training-operator
Kubeflow Training Operator is a Kubernetes-native project for fine-tuning and scalable distributed training of machine learning (ML) models created with various ML frameworks such as PyTorch, Tensorflow, XGBoost, MPI, Paddle and others. Training Operator allows you to use Kubernetes workloads to effectively train your large models via Kubernetes Custom Resources APIs or using Training Operator Python SDK. > Note: Before v1.2 release, Kubeflow Training Operator only supports TFJob on Kubernetes. * For a complete reference of the custom resource definitions, please refer to the API Definition. * TensorFlow API Definition * PyTorch API Definition * Apache MXNet API Definition * XGBoost API Definition * MPI API Definition * PaddlePaddle API Definition * For details of all-in-one operator design, please refer to the All-in-one Kubeflow Training Operator * For details on its observability, please refer to the monitoring design doc.
helix
HelixML is a private GenAI platform that allows users to deploy the best of open AI in their own data center or VPC while retaining complete data security and control. It includes support for fine-tuning models with drag-and-drop functionality. HelixML brings the best of open source AI to businesses in an ergonomic and scalable way, optimizing the tradeoff between GPU memory and latency.
nntrainer
NNtrainer is a software framework for training neural network models on devices with limited resources. It enables on-device fine-tuning of neural networks using user data for personalization. NNtrainer supports various machine learning algorithms and provides examples for tasks such as few-shot learning, ResNet, VGG, and product rating. It is optimized for embedded devices and utilizes CBLAS and CUBLAS for accelerated calculations. NNtrainer is open source and released under the Apache License version 2.0.

petals
Petals is a tool that allows users to run large language models at home in a BitTorrent-style manner. It enables fine-tuning and inference up to 10x faster than offloading. Users can generate text with distributed models like Llama 2, Falcon, and BLOOM, and fine-tune them for specific tasks directly from their desktop computer or Google Colab. Petals is a community-run system that relies on people sharing their GPUs to increase its capacity and offer a distributed network for hosting model layers.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.





