
training-operator
Distributed ML Training and Fine-Tuning on Kubernetes
Stars: 1662
Kubeflow Training Operator is a Kubernetes-native project for fine-tuning and scalable distributed training of machine learning (ML) models created with various ML frameworks such as PyTorch, Tensorflow, XGBoost, MPI, Paddle and others. Training Operator allows you to use Kubernetes workloads to effectively train your large models via Kubernetes Custom Resources APIs or using Training Operator Python SDK. > Note: Before v1.2 release, Kubeflow Training Operator only supports TFJob on Kubernetes. * For a complete reference of the custom resource definitions, please refer to the API Definition. * TensorFlow API Definition * PyTorch API Definition * Apache MXNet API Definition * XGBoost API Definition * MPI API Definition * PaddlePaddle API Definition * For details of all-in-one operator design, please refer to the All-in-one Kubeflow Training Operator * For details on its observability, please refer to the monitoring design doc.
README:
Kubeflow Training Operator is a Kubernetes-native project for fine-tuning and scalable distributed training of machine learning (ML) models created with various ML frameworks such as PyTorch, TensorFlow, HuggingFace, JAX, DeepSpeed, XGBoost, PaddlePaddle and others.
You can run high-performance computing (HPC) tasks with the Training Operator and MPIJob since it
supports running Message Passing Interface (MPI) on Kubernetes which is heavily used for HPC.
The Training Operator implements the V1 API version of MPI Operator. For the MPI Operator V2 version,
please follow this guide to
install MPI Operator V2.
The Training Operator allows you to use Kubernetes workloads to effectively train your large models via Kubernetes Custom Resources APIs or using the Training Operator Python SDK.
Please check the official Kubeflow documentation for prerequisites to install the Training Operator.
Please follow the Kubeflow Training Operator guide for the detailed instructions on how to install Training Operator.
Run the following command to install the latest stable release of the Training Operator control plane: v1.8.0.
kubectl apply --server-side -k "github.com/kubeflow/training-operator.git/manifests/overlays/standalone?ref=v1.8.0"Run the following command to install the latest changes of the Training Operator control plane:
kubectl apply --server-side -k "github.com/kubeflow/training-operator/manifests/overlays/standalone"The Training Operator implements a Python SDK to simplify creation of distributed training and fine-tuning jobs for Data Scientists.
Run the following command to install the latest stable release of the Training SDK:
pip install -U kubeflow-training
Please refer to the getting started guide to quickly create your first distributed training job using the Python SDK.
If you want to work directly with Kubernetes Custom Resources provided by Training Operator, follow the PyTorchJob MNIST guide.
The following links provide information on how to get involved in the community:
- Attend the bi-weekly AutoML and Training Working Group community meeting.
- Join our
#kubeflow-trainingSlack channel. - Check out who is using the Training Operator.
This is a part of Kubeflow, so please see readme in kubeflow/kubeflow to get in touch with the community.
Please refer to the CONTRIBUTING guide.
Please refer to the CHANGELOG.
The following table lists the most recent few versions of the operator.
| Operator Version | API Version | Kubernetes Version |
|---|---|---|
v1.4.x |
v1 |
1.23+ |
v1.5.x |
v1 |
1.23+ |
v1.6.x |
v1 |
1.23+ |
v1.7.x |
v1 |
1.25+ |
v1.8.x |
v1 |
1.27+ |
latest (master HEAD) |
v1 |
1.27+ |
For a complete reference of the custom resource definitions, please refer to the API Definition.
- TensorFlow API Definition
- PyTorch API Definition
- XGBoost API Definition
- MPI API Definition
- PaddlePaddle API Definition
- JAX API Definition
For details on the Training Operator custom resources APIs, refer to the following API documentation
This project was originally started as a distributed training operator for TensorFlow and later we merged efforts from other Kubeflow Training Operators to provide a unified and simplified experience for both users and developers. We are very grateful to all who filed issues or helped resolve them, asked and answered questions, and were part of inspiring discussions. We'd also like to thank everyone who's contributed to and maintained the original operators.
- PyTorch Operator: list of contributors and maintainers.
- MPI Operator: list of contributors and maintainers.
- XGBoost Operator: list of contributors and maintainers.
- Common library: list of contributors and maintainers.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for training-operator
Similar Open Source Tools

training-operator
Kubeflow Training Operator is a Kubernetes-native project for fine-tuning and scalable distributed training of machine learning (ML) models created with various ML frameworks such as PyTorch, Tensorflow, XGBoost, MPI, Paddle and others. Training Operator allows you to use Kubernetes workloads to effectively train your large models via Kubernetes Custom Resources APIs or using Training Operator Python SDK. > Note: Before v1.2 release, Kubeflow Training Operator only supports TFJob on Kubernetes. * For a complete reference of the custom resource definitions, please refer to the API Definition. * TensorFlow API Definition * PyTorch API Definition * Apache MXNet API Definition * XGBoost API Definition * MPI API Definition * PaddlePaddle API Definition * For details of all-in-one operator design, please refer to the All-in-one Kubeflow Training Operator * For details on its observability, please refer to the monitoring design doc.
agentok
Agentok Studio is a tool built upon AG2, a powerful agent framework from Microsoft, offering intuitive visual tools to streamline the creation and management of complex agent-based workflows. It simplifies the process for creators and developers by generating native Python code with minimal dependencies, enabling users to create self-contained code that can be executed anywhere. The tool is currently under development and not recommended for production use, but contributions are welcome from the community to enhance its capabilities and functionalities.
BotServer
General Bot is a chat bot server that accelerates bot development by providing code base, resources, deployment to the cloud, and templates for creating new bots. It allows modification of bot packages without code through a database and service backend. Users can develop bot packages using custom code in editors like Visual Studio Code, Atom, or Brackets. The tool supports creating bots by copying and pasting files and using favorite tools from Office or Photoshop. It also enables building custom dialogs with BASIC for extending bots.
agentok
Agentok Studio is a visual tool built for AutoGen, a cutting-edge agent framework from Microsoft and various contributors. It offers intuitive visual tools to simplify the construction and management of complex agent-based workflows. Users can create workflows visually as graphs, chat with agents, and share flow templates. The tool is designed to streamline the development process for creators and developers working on next-generation Multi-Agent Applications.
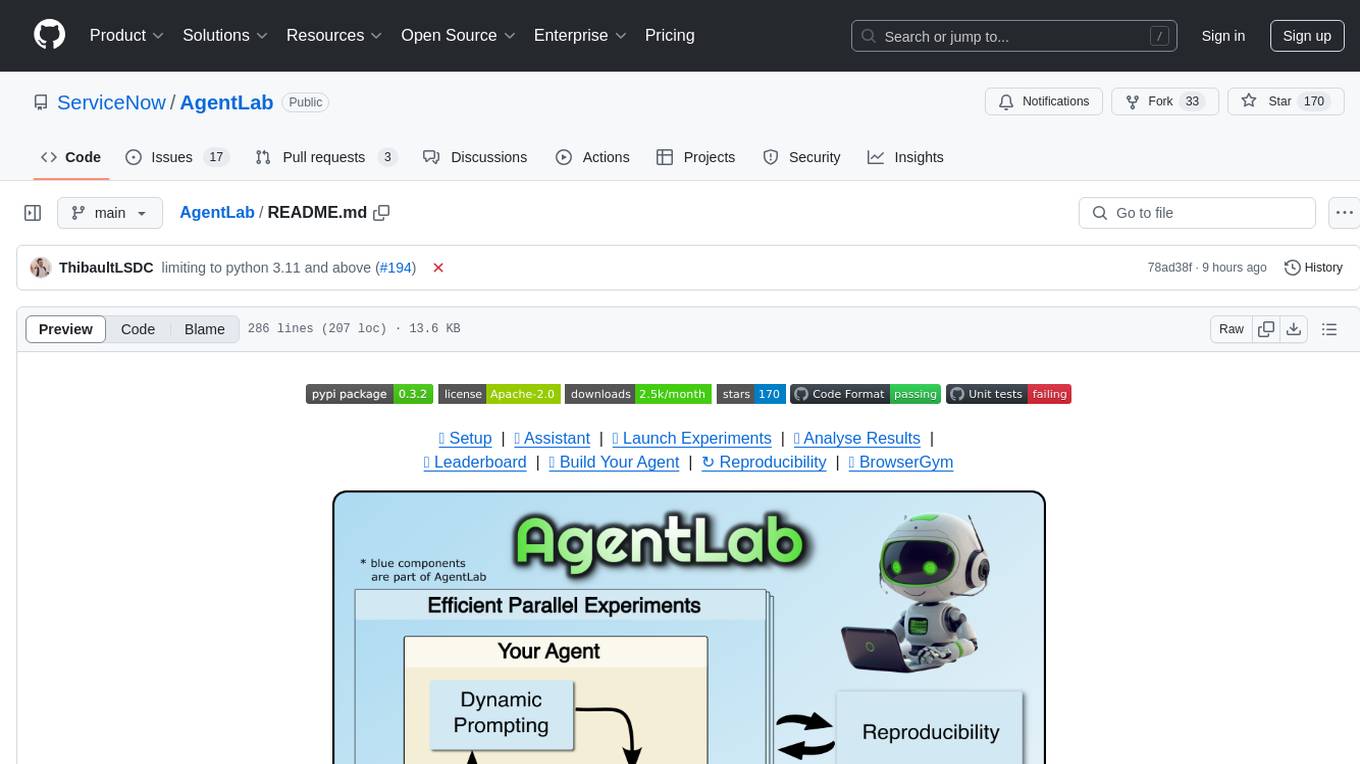
AgentLab
AgentLab is an open, easy-to-use, and extensible framework designed to accelerate web agent research. It provides features for developing and evaluating agents on various benchmarks supported by BrowserGym. The framework allows for large-scale parallel agent experiments using ray, building blocks for creating agents over BrowserGym, and a unified LLM API for OpenRouter, OpenAI, Azure, or self-hosted using TGI. AgentLab also offers reproducibility features, a unified LeaderBoard, and supports multiple benchmarks like WebArena, WorkArena, WebLinx, VisualWebArena, AssistantBench, GAIA, Mind2Web-live, and MiniWoB.
swt-bench
SWT-Bench is a benchmark tool for evaluating large language models on testing generation for real world software issues collected from GitHub. It tasks a language model with generating a reproducing test that fails in the original state of the code base and passes after a patch resolving the issue has been applied. The tool operates in unit test mode or reproduction script mode to assess model predictions and success rates. Users can run evaluations on SWT-Bench Lite using the evaluation harness with specific commands. The tool provides instructions for setting up and building SWT-Bench, as well as guidelines for contributing to the project. It also offers datasets and evaluation results for public access and provides a citation for referencing the work.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.
botpress
Botpress is a platform for building next-generation chatbots and assistants powered by OpenAI. It provides a range of tools and integrations to help developers quickly and easily create and deploy chatbots for various use cases.
LaVague
LaVague is an open-source Large Action Model framework that uses advanced AI techniques to compile natural language instructions into browser automation code. It leverages Selenium or Playwright for browser actions. Users can interact with LaVague through an interactive Gradio interface to automate web interactions. The tool requires an OpenAI API key for default examples and offers a Playwright integration guide. Contributors can help by working on outlined tasks, submitting PRs, and engaging with the community on Discord. The project roadmap is available to track progress, but users should exercise caution when executing LLM-generated code using 'exec'.
agents
Polymarket Agents is a developer framework and set of utilities for building AI agents to trade autonomously on Polymarket. It integrates with Polymarket API, provides AI agent utilities for prediction markets, supports local and remote RAG, sources data from various services, and offers comprehensive LLM tools for prompt engineering. The architecture features modular components like APIs and scripts for managing local environments, server set-up, and CLI for end-user commands.
contoso-chat
Contoso Chat is a Python sample demonstrating how to build, evaluate, and deploy a retail copilot application with Azure AI Studio using Promptflow with Prompty assets. The sample implements a Retrieval Augmented Generation approach to answer customer queries based on the company's product catalog and customer purchase history. It utilizes Azure AI Search, Azure Cosmos DB, Azure OpenAI, text-embeddings-ada-002, and GPT models for vectorizing user queries, AI-assisted evaluation, and generating chat responses. By exploring this sample, users can learn to build a retail copilot application, define prompts using Prompty, design, run & evaluate a copilot using Promptflow, provision and deploy the solution to Azure using the Azure Developer CLI, and understand Responsible AI practices for evaluation and content safety.
open-source-slack-ai
This repository provides a ready-to-run basic Slack AI solution that allows users to summarize threads and channels using OpenAI. Users can generate thread summaries, channel overviews, channel summaries since a specific time, and full channel summaries. The tool is powered by GPT-3.5-Turbo and an ensemble of NLP models. It requires Python 3.8 or higher, an OpenAI API key, Slack App with associated API tokens, Poetry package manager, and ngrok for local development. Users can customize channel and thread summaries, run tests with coverage using pytest, and contribute to the project for future enhancements.
OpenHands
OpenDevin is a platform for autonomous software engineers powered by AI and LLMs. It allows human developers to collaborate with agents to write code, fix bugs, and ship features. The tool operates in a secured docker sandbox and provides access to different LLM providers for advanced configuration options. Users can contribute to the project through code contributions, research and evaluation of LLMs in software engineering, and providing feedback and testing. OpenDevin is community-driven and welcomes contributions from developers, researchers, and enthusiasts looking to advance software engineering with AI.
piccolo
Piccolo AI is an open-source software development toolkit for constructing sensor-based AI inference models optimized to run on low-power microcontrollers and IoT edge platforms. It includes SensiML's ML Engine, Embedded ML SDK, Analytic Studio UI, and SensiML Python Client. The tool is intended for individual developers, researchers, and AI enthusiasts, offering support for time-series sensor data classification and various applications such as acoustic event detection, activity recognition, gesture detection, anomaly detection, keyword spotting, and vibration classification.

superduper
superduper.io is a Python framework that integrates AI models, APIs, and vector search engines directly with existing databases. It allows hosting of models, streaming inference, and scalable model training/fine-tuning. Key features include integration of AI with data infrastructure, inference via change-data-capture, scalable model training, model chaining, simple Python interface, Python-first approach, working with difficult data types, feature storing, and vector search capabilities. The tool enables users to turn their existing databases into centralized repositories for managing AI model inputs and outputs, as well as conducting vector searches without the need for specialized databases.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.
For similar tasks

mindsdb
MindsDB is a platform for customizing AI from enterprise data. You can create, serve, and fine-tune models in real-time from your database, vector store, and application data. MindsDB "enhances" SQL syntax with AI capabilities to make it accessible for developers worldwide. With MindsDB’s nearly 200 integrations, any developer can create AI customized for their purpose, faster and more securely. Their AI systems will constantly improve themselves — using companies’ own data, in real-time.

training-operator
Kubeflow Training Operator is a Kubernetes-native project for fine-tuning and scalable distributed training of machine learning (ML) models created with various ML frameworks such as PyTorch, Tensorflow, XGBoost, MPI, Paddle and others. Training Operator allows you to use Kubernetes workloads to effectively train your large models via Kubernetes Custom Resources APIs or using Training Operator Python SDK. > Note: Before v1.2 release, Kubeflow Training Operator only supports TFJob on Kubernetes. * For a complete reference of the custom resource definitions, please refer to the API Definition. * TensorFlow API Definition * PyTorch API Definition * Apache MXNet API Definition * XGBoost API Definition * MPI API Definition * PaddlePaddle API Definition * For details of all-in-one operator design, please refer to the All-in-one Kubeflow Training Operator * For details on its observability, please refer to the monitoring design doc.
helix
HelixML is a private GenAI platform that allows users to deploy the best of open AI in their own data center or VPC while retaining complete data security and control. It includes support for fine-tuning models with drag-and-drop functionality. HelixML brings the best of open source AI to businesses in an ergonomic and scalable way, optimizing the tradeoff between GPU memory and latency.
nntrainer
NNtrainer is a software framework for training neural network models on devices with limited resources. It enables on-device fine-tuning of neural networks using user data for personalization. NNtrainer supports various machine learning algorithms and provides examples for tasks such as few-shot learning, ResNet, VGG, and product rating. It is optimized for embedded devices and utilizes CBLAS and CUBLAS for accelerated calculations. NNtrainer is open source and released under the Apache License version 2.0.

petals
Petals is a tool that allows users to run large language models at home in a BitTorrent-style manner. It enables fine-tuning and inference up to 10x faster than offloading. Users can generate text with distributed models like Llama 2, Falcon, and BLOOM, and fine-tune them for specific tasks directly from their desktop computer or Google Colab. Petals is a community-run system that relies on people sharing their GPUs to increase its capacity and offer a distributed network for hosting model layers.
LLaVA-pp
This repository, LLaVA++, extends the visual capabilities of the LLaVA 1.5 model by incorporating the latest LLMs, Phi-3 Mini Instruct 3.8B, and LLaMA-3 Instruct 8B. It provides various models for instruction-following LMMS and academic-task-oriented datasets, along with training scripts for Phi-3-V and LLaMA-3-V. The repository also includes installation instructions and acknowledgments to related open-source contributions.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.
Firefly
Firefly is an open-source large model training project that supports pre-training, fine-tuning, and DPO of mainstream large models. It includes models like Llama3, Gemma, Qwen1.5, MiniCPM, Llama, InternLM, Baichuan, ChatGLM, Yi, Deepseek, Qwen, Orion, Ziya, Xverse, Mistral, Mixtral-8x7B, Zephyr, Vicuna, Bloom, etc. The project supports full-parameter training, LoRA, QLoRA efficient training, and various tasks such as pre-training, SFT, and DPO. Suitable for users with limited training resources, QLoRA is recommended for fine-tuning instructions. The project has achieved good results on the Open LLM Leaderboard with QLoRA training process validation. The latest version has significant updates and adaptations for different chat model templates.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.