
katib
Automated Machine Learning on Kubernetes
Stars: 1626

Katib is a Kubernetes-native project for automated machine learning (AutoML). Katib supports Hyperparameter Tuning, Early Stopping and Neural Architecture Search. Katib is the project which is agnostic to machine learning (ML) frameworks. It can tune hyperparameters of applications written in any language of the users’ choice and natively supports many ML frameworks, such as TensorFlow, Apache MXNet, PyTorch, XGBoost, and others. Katib can perform training jobs using any Kubernetes Custom Resources with out of the box support for Kubeflow Training Operator, Argo Workflows, Tekton Pipelines and many more.
README:
Kubeflow Katib is a Kubernetes-native project for automated machine learning (AutoML). Katib supports Hyperparameter Tuning, Early Stopping and Neural Architecture Search.
Katib is the project which is agnostic to machine learning (ML) frameworks. It can tune hyperparameters of applications written in any language of the users’ choice and natively supports many ML frameworks, such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, and others.
Katib can perform training jobs using any Kubernetes Custom Resources with out of the box support for Kubeflow Training Operator, Argo Workflows, Tekton Pipelines and many more.
Katib stands for secretary in Arabic.
Katib supports several search algorithms. Follow the Kubeflow documentation to know more about each algorithm and check the this guide to implement your custom algorithm.
| Hyperparameter Tuning | Neural Architecture Search | Early Stopping |
| Random Search | ENAS | Median Stop |
| Grid Search | DARTS | |
| Bayesian Optimization | ||
| TPE | ||
| Multivariate TPE | ||
| CMA-ES | ||
| Sobol's Quasirandom Sequence | ||
| HyperBand | ||
| Population Based Training |
To perform the above algorithms Katib supports the following frameworks:
Please check the official Kubeflow documentation for prerequisites to install Katib.
Please follow the Kubeflow Katib guide for the detailed instructions on how to install Katib.
Run the following command to install the latest stable release of Katib control plane:
kubectl apply -k "github.com/kubeflow/katib.git/manifests/v1beta1/installs/katib-standalone?ref=v0.17.0"
Run the following command to install the latest changes of Katib control plane:
kubectl apply -k "github.com/kubeflow/katib.git/manifests/v1beta1/installs/katib-standalone?ref=master"
For the Katib Experiments check the complete examples list.
Katib implements a Python SDK to simplify creation of hyperparameter tuning jobs for Data Scientists.
Run the following command to install the latest stable release of Katib SDK:
pip install -U kubeflow-katibPlease refer to the getting started guide to quickly create your first hyperparameter tuning Experiment using the Python SDK.
The following links provide information on how to get involved in the community:
- Attend the bi-weekly AutoML and Training Working Group community meeting.
- Join our
#kubeflow-katibSlack channel. - Check out who is using Katib and presentations about Katib project.
Please refer to the CONTRIBUTING guide.
If you use Katib in a scientific publication, we would appreciate citations to the following paper:
A Scalable and Cloud-Native Hyperparameter Tuning System, George et al., arXiv:2006.02085, 2020.
Bibtex entry:
@misc{george2020katib,
title={A Scalable and Cloud-Native Hyperparameter Tuning System},
author={Johnu George and Ce Gao and Richard Liu and Hou Gang Liu and Yuan Tang and Ramdoot Pydipaty and Amit Kumar Saha},
year={2020},
eprint={2006.02085},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.DC}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for katib
Similar Open Source Tools

katib
Katib is a Kubernetes-native project for automated machine learning (AutoML). Katib supports Hyperparameter Tuning, Early Stopping and Neural Architecture Search. Katib is the project which is agnostic to machine learning (ML) frameworks. It can tune hyperparameters of applications written in any language of the users’ choice and natively supports many ML frameworks, such as TensorFlow, Apache MXNet, PyTorch, XGBoost, and others. Katib can perform training jobs using any Kubernetes Custom Resources with out of the box support for Kubeflow Training Operator, Argo Workflows, Tekton Pipelines and many more.
training-operator
Kubeflow Training Operator is a Kubernetes-native project for fine-tuning and scalable distributed training of machine learning (ML) models created with various ML frameworks such as PyTorch, Tensorflow, XGBoost, MPI, Paddle and others. Training Operator allows you to use Kubernetes workloads to effectively train your large models via Kubernetes Custom Resources APIs or using Training Operator Python SDK. > Note: Before v1.2 release, Kubeflow Training Operator only supports TFJob on Kubernetes. * For a complete reference of the custom resource definitions, please refer to the API Definition. * TensorFlow API Definition * PyTorch API Definition * Apache MXNet API Definition * XGBoost API Definition * MPI API Definition * PaddlePaddle API Definition * For details of all-in-one operator design, please refer to the All-in-one Kubeflow Training Operator * For details on its observability, please refer to the monitoring design doc.
ChatDev
ChatDev is a virtual software company powered by intelligent agents like CEO, CPO, CTO, programmer, reviewer, tester, and art designer. These agents collaborate to revolutionize the digital world through programming. The platform offers an easy-to-use, highly customizable, and extendable framework based on large language models, ideal for studying collective intelligence. ChatDev introduces innovative methods like Iterative Experience Refinement and Experiential Co-Learning to enhance software development efficiency. It supports features like incremental development, Docker integration, Git mode, and Human-Agent-Interaction mode. Users can customize ChatChain, Phase, and Role settings, and share their software creations easily. The project is open-source under the Apache 2.0 License and utilizes data licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0.
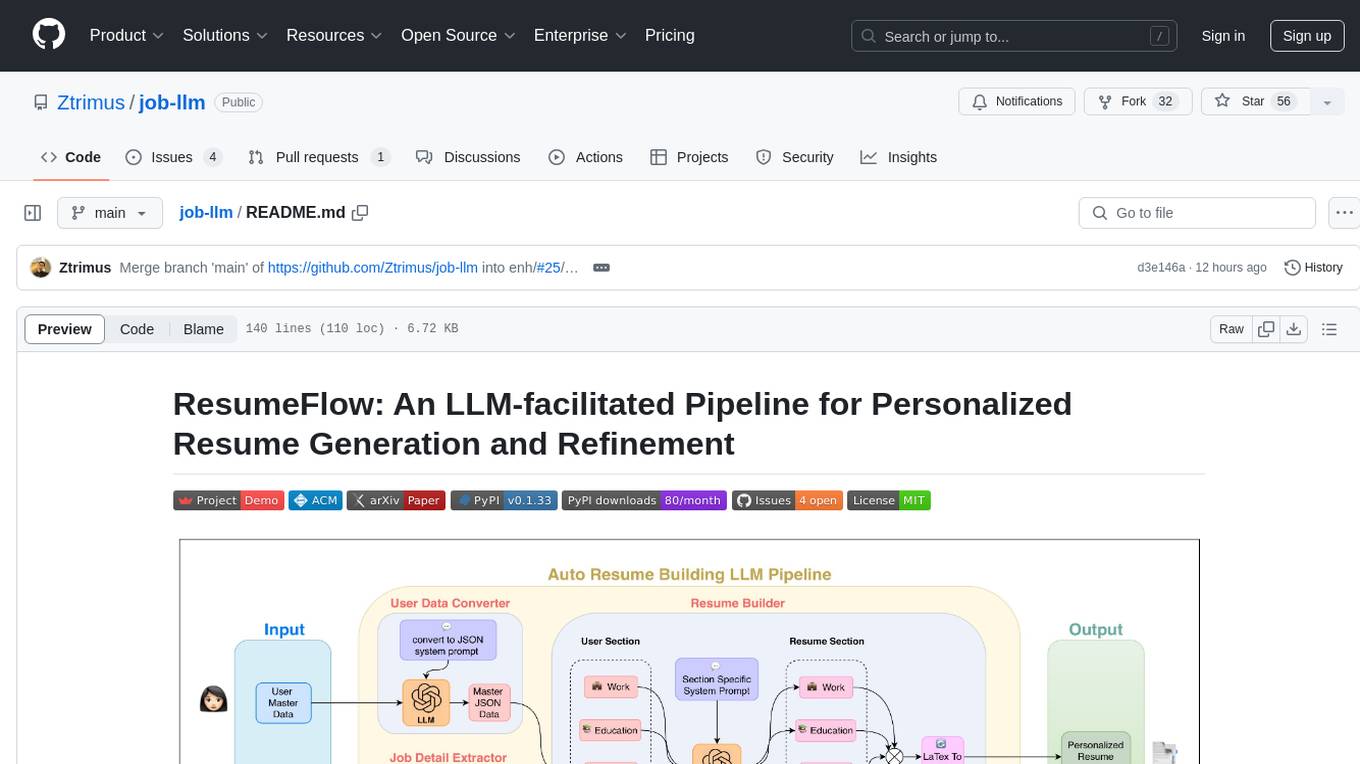
job-llm
ResumeFlow is an automated system utilizing Large Language Models (LLMs) to streamline the job application process. It aims to reduce human effort in various steps of job hunting by integrating LLM technology. Users can access ResumeFlow as a web tool, install it as a Python package, or download the source code. The project focuses on leveraging LLMs to automate tasks such as resume generation and refinement, making job applications smoother and more efficient.
DemoGPT
DemoGPT is an all-in-one agent library that provides tools, prompts, frameworks, and LLM models for streamlined agent development. It leverages GPT-3.5-turbo to generate LangChain code, creating interactive Streamlit applications. The tool is designed for creating intelligent, interactive, and inclusive solutions in LLM-based application development. It offers model flexibility, iterative development, and a commitment to user engagement. Future enhancements include integrating Gorilla for autonomous API usage and adding a publicly available database for refining the generation process.
embedchain
Embedchain is an Open Source Framework for personalizing LLM responses. It simplifies the creation and deployment of personalized AI applications by efficiently managing unstructured data, generating relevant embeddings, and storing them in a vector database. With diverse APIs, users can extract contextual information, find precise answers, and engage in interactive chat conversations tailored to their data. The framework follows the design principle of being 'Conventional but Configurable' to cater to both software engineers and machine learning engineers.

agent-lightning
Agent Lightning is a lightweight and efficient tool for automating repetitive tasks in the field of data analysis and machine learning. It provides a user-friendly interface to create and manage automated workflows, allowing users to easily schedule and execute data processing, model training, and evaluation tasks. With its intuitive design and powerful features, Agent Lightning streamlines the process of building and deploying machine learning models, making it ideal for data scientists, machine learning engineers, and AI enthusiasts looking to boost their productivity and efficiency in their projects.

superduper
superduper.io is a Python framework that integrates AI models, APIs, and vector search engines directly with existing databases. It allows hosting of models, streaming inference, and scalable model training/fine-tuning. Key features include integration of AI with data infrastructure, inference via change-data-capture, scalable model training, model chaining, simple Python interface, Python-first approach, working with difficult data types, feature storing, and vector search capabilities. The tool enables users to turn their existing databases into centralized repositories for managing AI model inputs and outputs, as well as conducting vector searches without the need for specialized databases.
dify
Dify is an open-source LLM app development platform that combines AI workflow, RAG pipeline, agent capabilities, model management, observability features, and more. It allows users to quickly go from prototype to production. Key features include: 1. Workflow: Build and test powerful AI workflows on a visual canvas. 2. Comprehensive model support: Seamless integration with hundreds of proprietary / open-source LLMs from dozens of inference providers and self-hosted solutions. 3. Prompt IDE: Intuitive interface for crafting prompts, comparing model performance, and adding additional features. 4. RAG Pipeline: Extensive RAG capabilities that cover everything from document ingestion to retrieval. 5. Agent capabilities: Define agents based on LLM Function Calling or ReAct, and add pre-built or custom tools. 6. LLMOps: Monitor and analyze application logs and performance over time. 7. Backend-as-a-Service: All of Dify's offerings come with corresponding APIs for easy integration into your own business logic.

tracecat
Tracecat is an open-source automation platform for security teams. It's designed to be simple but powerful, with a focus on AI features and a practitioner-obsessed UI/UX. Tracecat can be used to automate a variety of tasks, including phishing email investigation, evidence collection, and remediation plan generation.

AdalFlow
AdalFlow is a library designed to help developers build and optimize Large Language Model (LLM) task pipelines. It follows a design pattern similar to PyTorch, offering a light, modular, and robust codebase. Named in honor of Ada Lovelace, AdalFlow aims to inspire more women to enter the AI field. The library is tailored for various GenAI applications like chatbots, translation, summarization, code generation, and autonomous agents, as well as classical NLP tasks such as text classification and named entity recognition. AdalFlow emphasizes modularity, robustness, and readability to support users in customizing and iterating code for their specific use cases.
OpenDevin
OpenDevin is an open-source project aiming to replicate Devin, an autonomous AI software engineer capable of executing complex engineering tasks and collaborating actively with users on software development projects. The project aspires to enhance and innovate upon Devin through the power of the open-source community. Users can contribute to the project by developing core functionalities, frontend interface, or sandboxing solutions, participating in research and evaluation of LLMs in software engineering, and providing feedback and testing on the OpenDevin toolset.
NeMo
NVIDIA NeMo Framework is a scalable and cloud-native generative AI framework built for researchers and PyTorch developers working on Large Language Models (LLMs), Multimodal Models (MMs), Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Text to Speech (TTS), and Computer Vision (CV) domains. It is designed to help you efficiently create, customize, and deploy new generative AI models by leveraging existing code and pre-trained model checkpoints.
NeMo
NeMo Framework is a generative AI framework built for researchers and pytorch developers working on large language models (LLMs), multimodal models (MM), automatic speech recognition (ASR), and text-to-speech synthesis (TTS). The primary objective of NeMo is to provide a scalable framework for researchers and developers from industry and academia to more easily implement and design new generative AI models by being able to leverage existing code and pretrained models.
OpenHands
OpenDevin is a platform for autonomous software engineers powered by AI and LLMs. It allows human developers to collaborate with agents to write code, fix bugs, and ship features. The tool operates in a secured docker sandbox and provides access to different LLM providers for advanced configuration options. Users can contribute to the project through code contributions, research and evaluation of LLMs in software engineering, and providing feedback and testing. OpenDevin is community-driven and welcomes contributions from developers, researchers, and enthusiasts looking to advance software engineering with AI.

trainer
Kubeflow Trainer is a Kubernetes-native project for fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) and enabling scalable, distributed training of machine learning (ML) models across various frameworks. It allows integration with ML libraries like HuggingFace, DeepSpeed, or Megatron-LM to orchestrate ML training on Kubernetes. Develop LLMs effortlessly with the Kubeflow Python SDK and build Kubernetes-native Training Runtimes with Kubernetes Custom Resources APIs.
For similar tasks

katib
Katib is a Kubernetes-native project for automated machine learning (AutoML). Katib supports Hyperparameter Tuning, Early Stopping and Neural Architecture Search. Katib is the project which is agnostic to machine learning (ML) frameworks. It can tune hyperparameters of applications written in any language of the users’ choice and natively supports many ML frameworks, such as TensorFlow, Apache MXNet, PyTorch, XGBoost, and others. Katib can perform training jobs using any Kubernetes Custom Resources with out of the box support for Kubeflow Training Operator, Argo Workflows, Tekton Pipelines and many more.
cog
Cog is an open-source tool that lets you package machine learning models in a standard, production-ready container. You can deploy your packaged model to your own infrastructure, or to Replicate.
mosec
Mosec is a high-performance and flexible model serving framework for building ML model-enabled backend and microservices. It bridges the gap between any machine learning models you just trained and the efficient online service API. * **Highly performant** : web layer and task coordination built with Rust 🦀, which offers blazing speed in addition to efficient CPU utilization powered by async I/O * **Ease of use** : user interface purely in Python 🐍, by which users can serve their models in an ML framework-agnostic manner using the same code as they do for offline testing * **Dynamic batching** : aggregate requests from different users for batched inference and distribute results back * **Pipelined stages** : spawn multiple processes for pipelined stages to handle CPU/GPU/IO mixed workloads * **Cloud friendly** : designed to run in the cloud, with the model warmup, graceful shutdown, and Prometheus monitoring metrics, easily managed by Kubernetes or any container orchestration systems * **Do one thing well** : focus on the online serving part, users can pay attention to the model optimization and business logic
web-llm
WebLLM is a modular and customizable javascript package that directly brings language model chats directly onto web browsers with hardware acceleration. Everything runs inside the browser with no server support and is accelerated with WebGPU. WebLLM is fully compatible with OpenAI API. That is, you can use the same OpenAI API on any open source models locally, with functionalities including json-mode, function-calling, streaming, etc. We can bring a lot of fun opportunities to build AI assistants for everyone and enable privacy while enjoying GPU acceleration.
data-scientist-roadmap2024
The Data Scientist Roadmap2024 provides a comprehensive guide to mastering essential tools for data science success. It includes programming languages, machine learning libraries, cloud platforms, and concepts categorized by difficulty. The roadmap covers a wide range of topics from programming languages to machine learning techniques, data visualization tools, and DevOps/MLOps tools. It also includes web development frameworks and specific concepts like supervised and unsupervised learning, NLP, deep learning, reinforcement learning, and statistics. Additionally, it delves into DevOps tools like Airflow and MLFlow, data visualization tools like Tableau and Matplotlib, and other topics such as ETL processes, optimization algorithms, and financial modeling.
aibydoing-feedback
AI By Doing is a hands-on artificial intelligence tutorial series that aims to help beginners understand the principles of machine learning and deep learning while providing practical applications. The content covers various supervised and unsupervised learning algorithms, machine learning engineering, deep learning fundamentals, frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch, and applications in computer vision and natural language processing. The tutorials are written in Jupyter Notebook format, combining theory, mathematical derivations, and Python code implementations to facilitate learning and understanding.
runbooks
Runbooks is a repository that is no longer active. The project has been deprecated in favor of KubeAI, a platform designed to simplify the operationalization of AI on Kubernetes. For more information, please refer to the new repository at https://github.com/substratusai/kubeai.
Ultimate-Data-Science-Toolkit---From-Python-Basics-to-GenerativeAI
Ultimate Data Science Toolkit is a comprehensive repository covering Python basics to Generative AI. It includes modules on Python programming, data analysis, statistics, machine learning, MLOps, case studies, and deep learning. The repository provides detailed tutorials on various topics such as Python data structures, control statements, functions, modules, object-oriented programming, exception handling, file handling, web API, databases, list comprehension, lambda functions, Pandas, Numpy, data visualization, statistical analysis, supervised and unsupervised machine learning algorithms, model serialization, ML pipeline orchestration, case studies, and deep learning concepts like neural networks and autoencoders.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.


