
Reflection_Tuning
[ACL'24] Selective Reflection-Tuning: Student-Selected Data Recycling for LLM Instruction-Tuning
Stars: 124
Reflection-Tuning is a project focused on improving the quality of instruction-tuning data through a reflection-based method. It introduces Selective Reflection-Tuning, where the student model can decide whether to accept the improvements made by the teacher model. The project aims to generate high-quality instruction-response pairs by defining specific criteria for the oracle model to follow and respond to. It also evaluates the efficacy and relevance of instruction-response pairs using the r-IFD metric. The project provides code for reflection and selection processes, along with data and model weights for both V1 and V2 methods.
README:
[Method V1] Reflection-Tuning: Data Recycling Improves LLM Instruction-Tuning (NIPS'23 Wrokshop)
[Method V2] Selective Reflection-Tuning: Student-Selected Data Recycling for LLM Instruction-Tuning (ACL'24)
Chinese Version: [知乎]
This is the repo for the Reflection-Tuning project, which introduces a reflection-based method to improve the quality of instruction-tuning data.
The repo contains:
Data: (The detailed description will be found in Section Data and Model Weights V2 )
Recycled Data (V1): Alpaca, WizardLM70k
Selective Recycled Data (V2): Alpaca, WizardLM70k
Overall Reflected Data: Alpaca, WizardLM70k, WizardLM V2
Overall Reflected Data IFD scores:Alpaca llama2 7b, Alpaca llama2 13b, WizardLM70k llama2 7b, WizardLM70k llama2 13b
(Feel free to email Ming (Homepage, Email) for any questions or feedback.)
- [2024/05] Our Selective Reflection-Tuning has been accepted to the ACL 2024 findings!
- [2024/02] We release the paper of our Selective Reflection-Tuning.
- [2023/12] We add the complete data of Selective Instruction-Tuning (V2 method) and add the evaluation results.
- [2023/12] We add the description of Selective Instruction-Tuning (V2 method).
- [2023/10] The Reflection-Tuning has been accepted by the NeurIPS 2023 Workshop on Instruction Tuning and Instruction Following.
- [2023/10] We released the V2 model and pushed models to the Alpaca Eval leaderboard.
- [2023/10] We released codes for this project.
- Overview
- Highlights
- Selective Reflection-Tuning
- Install
- Code for Reflection
- Code for Selection
- Data and Model Weights V1
- Data and Model Weights V2
- Prompt and Hyperparameters
- ToDo
- Citation
- Our Related Works
We propose a reflection-based method for improving the quality of instruction-response pairs. Given the initial base dataset, we are motivated to generate a high-quality version of each data point with an oracle model, chatGPT for instance. However, a common problem with using LLMs as judges is the failure to obtain diverse results. To overcome this potential problem, inspired by Chain-of-Thought prompting, we further define several specific criteria for the oracle model to follow, and respond to those specific criteria with critical responses, respectively. Then the responses to these criteria can serve as bridges (chain of thought) to generate new instruction-response pairs that are satisfied.
In the original Reflection-Tuning, we propose a data improvement method through Reflection.
However, two research questions arise:
- Is the teacher-refined data compatible with the needs of the student model?
- How does the student model decide which enhanced data are most needed and critical to its training?
To answer the above questions, we propose Selective Reflection-Tuning, in which the student model can decide whether to accept the improvement of the teacher model.
- In Reflection-Tuning V1, we propose a reflection method that can improve the quality of the instruction-tuning dataset, which is a general method and can be utilized on almost ANY instruction-tuning dataset.
- We implement our method on both Alpaca and WizardLM datasets and release the newly-generated high-quality recycled datasets.
- We propose an interactive selection pipeline where the oracle model and student model cooperate to build a more coherent and model-compatible instruction-following dataset, which can be further adapted into other self-improvement scenarios.
- Our selectively recycled data has a supreme quality, with only instruction tuning on a few thousand of automatically generated data, our models achieve promising performances compared to models with dozens of thousands of data.
- We present a nuanced evaluation schema r-IFD that quantifies the efficacy and relevance of instruction-response pairs.
Existing methods of data enhancement usually do not take a critical criterion into account: Is the teacher-refined data compatible with the needs of the student model? These approaches typically do not account for the inherent randomness and potential degradation associated with the generative models' output, leading to an oversight in how the student model responds to these "improved" data samples. Consequently, a mechanism for the student model to selectively integrate these enhancements has been notably absent. To bridge this gap, our work introduces an interactive pipeline wherein an oracle generative model engages in a reflection process to enhance both the instruction and response of a data sample. The student model then evaluates whether to incorporate these improvements based on its unique attributes. This pipeline is versatile and can be adapted to various contexts where data enhancement is needed.
Then, another pivotal question arises: How does the student model decide which enhanced data are most needed and critical to its training? This question underpins the challenge of autonomously evaluating the quality of instructions and responses. Common practices involve utilizing sophisticated models like GPT-4 for assessment purposes or employing a secondary judge model equipped with evaluative capabilities. These methods, however, present limitations: they fail to address the discrepancies between the evaluating model and the actual student model undergoing training. Particularly in the latter approach, even though the judge model and the student model share the same structural framework, their weight distributions diverge once endowed with basic evaluative functions. Consequently, the preferences of the judge model may not align with the real student model's requirements. To circumvent these issues, we adopt a statistical method, utilizing the Instruction-Following Difficulty (IFD) score proposed by Cherry LLM. This score is derived directly from the raw student model, thereby mitigating potential domain shifts and ensuring that the evaluation is better aligned with the student model’s learning context. We further introduce a reversed version of IFD named reversed-IFD (r-IFD). This metric evaluates how much the response contributes to predicting the corresponding instruction.
We utilize the IFD score to select reflected instructions and utilize the r-IFD score to select reflected responses.
Below is the performance for pair-wise comparison between our model and other classic models on the WizardLM test set. We follow the implementation from AlpaGasus and Cherry LLM, which greatly eliminates the potential position bias of GPT4. The prompts can be found in our paper, and the data, code, and use cases for evaluation can be found in Cherry LLM Repo.
Below are the performance results on the Alapca Eval leaderboard. “Data” represents the number of data used for fine-tuning. “RLHF/AIF” represents whether the model utilizes an additional RLHF or RLAIF process.
Below are comparisons between model performances and data used for fine-tuning on the Alapca Eval benchmark and the open LLM leaderboard. We utilize star markers to represent our models, dot markers to represent other instruction-tuned models and triangle markers to represent RLHF/AIF models. Blue markers represent 7B models, red markers represent 13B models and purple markers represent models with larger weights.
It is astonishing that with less than 1k automatically generated instruction samples (2%, 926 samples), our model achieves really promising performance (74.29 win rate on alpaca eval rate, 57.80 averaged score on Open LLM Leaderboard), showing the supreme quality of our sRecycled data.
Install the dependencies with pip install -r requirements.txt
Reflecting on the whole dataset containing dozens of thousands of data will consume a lot, so we recommend using some tiny datasets for the beginning, for example, cherry data from Cherry LLM. Experiments show that simply reflecting on a subset of high-quality data can also get a promising performance.
In the below scripts, we directly run on data/cherry_alpaca_v1/cherry_alpaca_5_percent_compressed.json which contains only approximately 3k Alpaca data.
- Reflection
python reflection_code/reflecn_instruction.py \
--data_path data/cherry_alpaca_v1/cherry_alpaca_5_percent_compressed.json \
--save_path cherry_alpaca_5_percent_reflect_ins_raw.json \
--api_key xxx
--data_path: The targeted dataset in the Alpaca format
--save_path: The path to save the raw reflection texts
--api_key: Your openAI key
- Extract the instruction-response pairs:
python reflection_code/reflect_instruction_postprocess.py \
--raw_data_path cherry_alpaca_5_percent_reflect_ins_raw.json \
--ori_data_path data/cherry_alpaca_v1/cherry_alpaca_5_percent_compressed.json \
--save_path cherry_alpaca_5_percent_reflect_ins.json \
--save_intermediate_path cherry_alpaca_5_percent_reflect_ins_mid.json \
--api_key xxx
--raw_data_path: The path that saves the raw reflection texts
--ori_data_path: The original targeted dataset in the Alpaca format
--save_path: The path to save formated dataset in the Alpaca format
--save_intermediate_path: The path to save the middle results
--api_key: Your openAI key
- Reflection
python reflection_code/reflect_response.py \
--data_path data/cherry_alpaca_v1/cherry_alpaca_5_percent_compressed.json \
--save_path cherry_alpaca_5_percent_reflect_res_raw.json \
--api_key xxx
- Extract the instruction-response pairs:
python reflection_code/reflect_response_postprocess.py \
--raw_data_path cherry_alpaca_5_percent_reflect_res_raw.json \
--ori_data_path data/cherry_alpaca_v1/cherry_alpaca_5_percent_compressed.json \
--save_path cherry_alpaca_5_percent_reflect_res.json \
--save_intermediate_path cherry_alpaca_5_percent_reflect_res_mid.json \
--api_key xxx
Note: When reflecting on the instruction, we first compress the instruction and input it into one single instruction for easier processing by using chatGPT.
The whole compressed Alpaca data can be found in the data folder.
Note: The extraction of reflection results is based on regular expression and, thus is not perfect. We will release the raw output before the extraction in the future.
- Generate Data Statistics
python selection_code/data_analysis.py \
--data_path data/cherry_alpaca_v1/cherry_alpaca_5_percent_compressed.json \
--save_path cherry_alpaca_5_percent_analysis.jsonl \
--model_name_or_path meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf
This code calculates the necessary statistics for calculating IFD scores and r-IFD scores.
Please feel free to customize your own training prompt and model.
- Put the Statistics to Original Data
python selection_code/put_analysis_to_data.py \
--pt_data_path cherry_alpaca_5_percent_analysis.jsonl \
--json_data_path data/cherry_alpaca_v1/cherry_alpaca_5_percent_compressed.json \
--json_save_path cherry_alpaca_5_percent_with_analysis.json
After obtaining data with IFD scores and r-IFD scores, you can compare these scores to make the customized selection.
The following table provides a comparison between our recycled models (V1) and baseline models on the AlpacaEval Leaderboard and Huggingface Open LLM Leaderboard.
The Recycled Alpaca Data can be found here: [hf-Link]
The Recycled WizardLM (70k) Data can be found here: [hf-Link]
| AlpacaEval | Avg | ARC | HellaSwag | MMLU | TruthfulQA | Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpaca 7B | 26.46 | 50.21 | 42.65 | 76.91 | 41.73 | 39.55 | / | ||
| Recycled Alpaca 7B V1.0 | 76.99 | 56.18 | 53.92 | 77.68 | 47.55 | 45.55 | [hf-Link] | ||
| Recycled Alpaca 13B V1.0 | 83.42 | 58.93 | 58.70 | 80.80 | 53.11 | 43.12 | [Link] | ||
| WizardLM 7B | 67.64 | 54.18 | 51.60 | 77.70 | 42.70 | 44.70 | / | ||
| Recycled WizardLM 7B V1.0 | 78.88 | 56.21 | 53.92 | 77.05 | 48.35 | 45.52 | [hf-Link] | ||
In the repo, we name our Selective Reflection-Tuning as the V2 method for simplicity.
The following table provides a comparison between our sRecycled models (V2) and baseline models on the AlpacaEval Leaderboard and Huggingface Open LLM Leaderboard.
The data used for training llama2-7b model can be directly found here:
Selective Recycled Data (V2): Alpaca, WizardLM70k
The above data contains the model-selected data from data reflected on both instruction and response and data reflected on response.
The complete data reflected on instruction, response or both can be found here:
Overall Reflected Data: Alpaca, WizardLM70k, WizardLM V2
The complete data statistics on (loss, and perplexity) on llama2-7b and llama2-13b model can be found here, which can be directly used for computing IFD scores:
Overall Reflected Data IFD scores:Alpaca llama2 7b, Alpaca llama2 13b, WizardLM70k llama2 7b, WizardLM70k llama2 13b
| AlpacaEval | Avg | ARC | HellaSwag | MMLU | TruthfulQA | Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpaca 7B | 26.46 | 50.21 | 42.65 | 76.91 | 41.73 | 39.55 | / | ||
| Recycled Alpaca 7B V2.0 | 79.58 | 56.05 | 54.01 | 78.07 | 46.69 | 45.41 | [hf-Link] | ||
| WizardLM 7B | 67.64 | 54.18 | 51.60 | 77.70 | 42.70 | 44.70 | / | ||
| Recycled WizardLM 7B V2.0 | 83.48 | 56.79 | 54.78 | 77.86 | 45.63 | 48.91 | [hf-Link] | ||
We use the prompt from FastChat:
A chat between a curious user and an artificial intelligence assistant. The assistant gives helpful, detailed, and polite answers to the user's questions. USER: Hi ASSISTANT: Hello.</s>USER: Who are you? ASSISTANT: I am ...</s>......
| Hyperparameter | Global Batch Size | Learning rate | Epochs | Max length | Weight decay | Warmup Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recycled Models (7B) | 128 | 2e-5 | 3 | 2048 | 0 | 0.03 |
| Recycled Models (13B) | 128 | 2e-5 | 3 | 2048 | 0 | 0.03 |
- [x] Release the code, data, and models for V1.
- [x] Release the method for Selective Reflection-Tuning (V2).
- [x] Release the data for Selective Reflection-Tuning (V2).
- [x] Release the models for Selective Reflection-Tuning (V2).
Please consider citing our paper if you think our codes, data, or models are useful. Thank you!
@inproceedings{li2023reflectiontuning,
title={Reflection-Tuning: Recycling Data for Better Instruction-Tuning},
author={Ming Li and Lichang Chen and Jiuhai Chen and Shwai He and Tianyi Zhou},
booktitle={NeurIPS 2023 Workshop on Instruction Tuning and Instruction Following},
year={2023},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=xaqoZZqkPU}
}
@inproceedings{li-etal-2024-selective,
title = "Selective Reflection-Tuning: Student-Selected Data Recycling for {LLM} Instruction-Tuning",
author = "Li, Ming and
Chen, Lichang and
Chen, Jiuhai and
He, Shwai and
Gu, Jiuxiang and
Zhou, Tianyi",
editor = "Ku, Lun-Wei and
Martins, Andre and
Srikumar, Vivek",
booktitle = "Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics ACL 2024",
month = aug,
year = "2024",
address = "Bangkok, Thailand and virtual meeting",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2024.findings-acl.958",
pages = "16189--16211",
}
@inproceedings{li-etal-2024-quantity,
title = "From Quantity to Quality: Boosting {LLM} Performance with Self-Guided Data Selection for Instruction Tuning",
author = "Li, Ming and
Zhang, Yong and
Li, Zhitao and
Chen, Jiuhai and
Chen, Lichang and
Cheng, Ning and
Wang, Jianzong and
Zhou, Tianyi and
Xiao, Jing",
editor = "Duh, Kevin and
Gomez, Helena and
Bethard, Steven",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2024 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = jun,
year = "2024",
address = "Mexico City, Mexico",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2024.naacl-long.421",
pages = "7595--7628",
}
@inproceedings{li-etal-2024-superfiltering,
title = "Superfiltering: Weak-to-Strong Data Filtering for Fast Instruction-Tuning",
author = "Li, Ming and
Zhang, Yong and
He, Shwai and
Li, Zhitao and
Zhao, Hongyu and
Wang, Jianzong and
Cheng, Ning and
Zhou, Tianyi",
editor = "Ku, Lun-Wei and
Martins, Andre and
Srikumar, Vivek",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = aug,
year = "2024",
address = "Bangkok, Thailand",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2024.acl-long.769",
pages = "14255--14273",
}
If you are interested in Data Selection for Instruction Tuning, please see Cherry_LLM and Superfiltering.
If you are interested in human/LLM-free Data Augmentation for Instruction Tuning, please see Mosaic-IT and RuleR.
If you are interested in Data Improvement for Instruction Tuning, please see Reflection_Tuning.
If you are interested in Knowledge Distillation in the LLM era, please see this Survey.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Reflection_Tuning
Similar Open Source Tools

Reflection_Tuning
Reflection-Tuning is a project focused on improving the quality of instruction-tuning data through a reflection-based method. It introduces Selective Reflection-Tuning, where the student model can decide whether to accept the improvements made by the teacher model. The project aims to generate high-quality instruction-response pairs by defining specific criteria for the oracle model to follow and respond to. It also evaluates the efficacy and relevance of instruction-response pairs using the r-IFD metric. The project provides code for reflection and selection processes, along with data and model weights for both V1 and V2 methods.

magpie
This is the official repository for 'Alignment Data Synthesis from Scratch by Prompting Aligned LLMs with Nothing'. Magpie is a tool designed to synthesize high-quality instruction data at scale by extracting it directly from an aligned Large Language Models (LLMs). It aims to democratize AI by generating large-scale alignment data and enhancing the transparency of model alignment processes. Magpie has been tested on various model families and can be used to fine-tune models for improved performance on alignment benchmarks such as AlpacaEval, ArenaHard, and WildBench.
babilong
BABILong is a generative benchmark designed to evaluate the performance of NLP models in processing long documents with distributed facts. It consists of 20 tasks that simulate interactions between characters and objects in various locations, requiring models to distinguish important information from irrelevant details. The tasks vary in complexity and reasoning aspects, with test samples potentially containing millions of tokens. The benchmark aims to challenge and assess the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in handling complex, long-context information.
MME-RealWorld
MME-RealWorld is a benchmark designed to address real-world applications with practical relevance, featuring 13,366 high-resolution images and 29,429 annotations across 43 tasks. It aims to provide substantial recognition challenges and overcome common barriers in existing Multimodal Large Language Model benchmarks, such as small data scale, restricted data quality, and insufficient task difficulty. The dataset offers advantages in data scale, data quality, task difficulty, and real-world utility compared to existing benchmarks. It also includes a Chinese version with additional images and QA pairs focused on Chinese scenarios.
MMStar
MMStar is an elite vision-indispensable multi-modal benchmark comprising 1,500 challenge samples meticulously selected by humans. It addresses two key issues in current LLM evaluation: the unnecessary use of visual content in many samples and the existence of unintentional data leakage in LLM and LVLM training. MMStar evaluates 6 core capabilities across 18 detailed axes, ensuring a balanced distribution of samples across all dimensions.
Slow_Thinking_with_LLMs
STILL is an open-source project exploring slow-thinking reasoning systems, focusing on o1-like reasoning systems. The project has released technical reports on enhancing LLM reasoning with reward-guided tree search algorithms and implementing slow-thinking reasoning systems using an imitate, explore, and self-improve framework. The project aims to replicate the capabilities of industry-level reasoning systems by fine-tuning reasoning models with long-form thought data and iteratively refining training datasets.
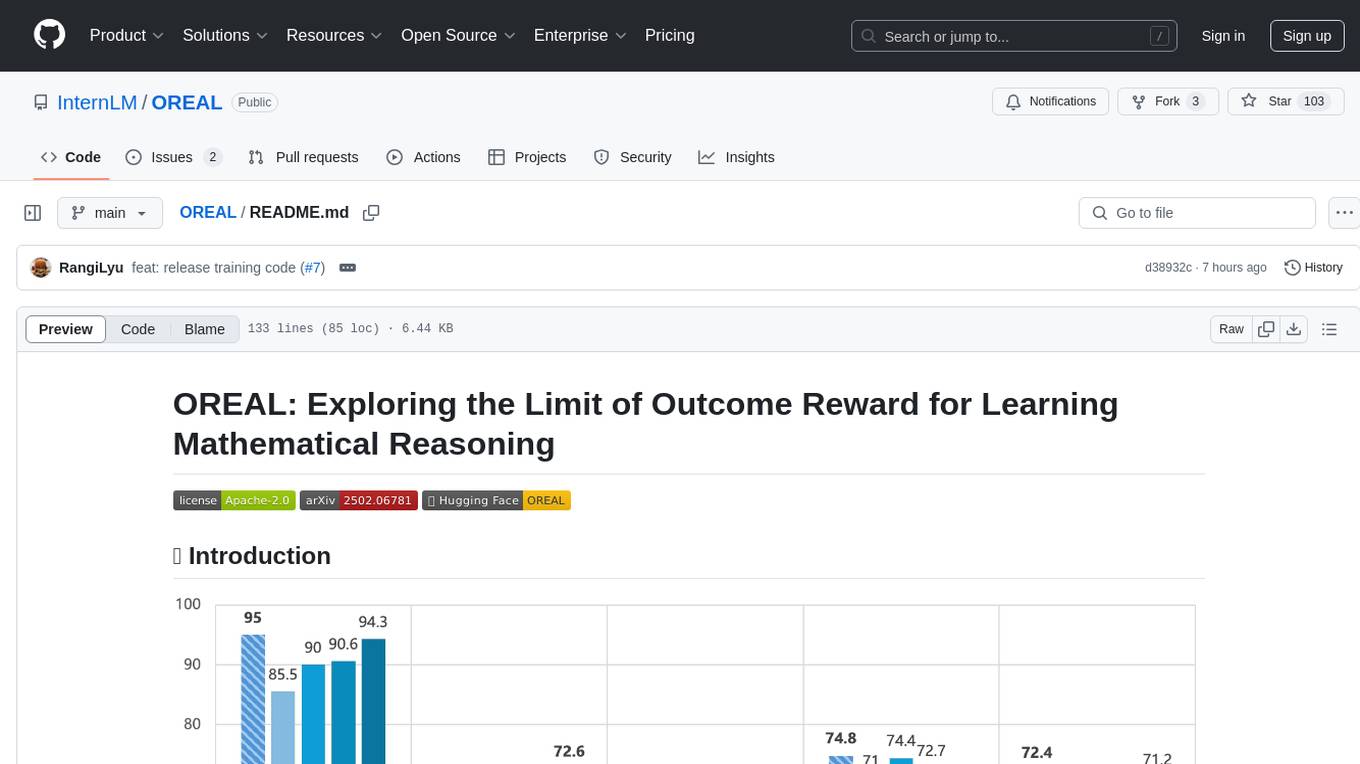
OREAL
OREAL is a reinforcement learning framework designed for mathematical reasoning tasks, aiming to achieve optimal performance through outcome reward-based learning. The framework utilizes behavior cloning, reshaping rewards, and token-level reward models to address challenges in sparse rewards and partial correctness. OREAL has achieved significant results, with a 7B model reaching 94.0 pass@1 accuracy on MATH-500 and surpassing previous 32B models. The tool provides training tutorials and Hugging Face model repositories for easy access and implementation.
k2
K2 (GeoLLaMA) is a large language model for geoscience, trained on geoscience literature and fine-tuned with knowledge-intensive instruction data. It outperforms baseline models on objective and subjective tasks. The repository provides K2 weights, core data of GeoSignal, GeoBench benchmark, and code for further pretraining and instruction tuning. The model is available on Hugging Face for use. The project aims to create larger and more powerful geoscience language models in the future.
MathCoder
MathCoder is a repository focused on enhancing mathematical reasoning by fine-tuning open-source language models to use code for modeling and deriving math equations. It introduces MathCodeInstruct dataset with solutions interleaving natural language, code, and execution results. The repository provides MathCoder models capable of generating code-based solutions for challenging math problems, achieving state-of-the-art scores on MATH and GSM8K datasets. It offers tools for model deployment, inference, and evaluation, along with a citation for referencing the work.
RLHF-Reward-Modeling
This repository contains code for training reward models for Deep Reinforcement Learning-based Reward-modulated Hierarchical Fine-tuning (DRL-based RLHF), Iterative Selection Fine-tuning (Rejection sampling fine-tuning), and iterative Decision Policy Optimization (DPO). The reward models are trained using a Bradley-Terry model based on the Gemma and Mistral language models. The resulting reward models achieve state-of-the-art performance on the RewardBench leaderboard for reward models with base models of up to 13B parameters.
Adaptive-MT-LLM-Fine-tuning
The repository Adaptive-MT-LLM-Fine-tuning contains code and data for the paper 'Fine-tuning Large Language Models for Adaptive Machine Translation'. It focuses on enhancing Mistral 7B, a large language model, for real-time adaptive machine translation in the medical domain. The fine-tuning process involves using zero-shot and one-shot translation prompts to improve terminology and style adherence. The repository includes training and test data, data processing code, fuzzy match retrieval techniques, fine-tuning methods, conversion to CTranslate2 format, tokenizers, translation codes, and evaluation metrics.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.
LongBench
LongBench v2 is a benchmark designed to assess the ability of large language models (LLMs) to handle long-context problems requiring deep understanding and reasoning across various real-world multitasks. It consists of 503 challenging multiple-choice questions with contexts ranging from 8k to 2M words, covering six major task categories. The dataset is collected from nearly 100 highly educated individuals with diverse professional backgrounds and is designed to be challenging even for human experts. The evaluation results highlight the importance of enhanced reasoning ability and scaling inference-time compute to tackle the long-context challenges in LongBench v2.

AgentCPM
AgentCPM is a series of open-source LLM agents jointly developed by THUNLP, Renmin University of China, ModelBest, and the OpenBMB community. It addresses challenges faced by agents in real-world applications such as limited long-horizon capability, autonomy, and generalization. The team focuses on building deep research capabilities for agents, releasing AgentCPM-Explore, a deep-search LLM agent, and AgentCPM-Report, a deep-research LLM agent. AgentCPM-Explore is the first open-source agent model with 4B parameters to appear on widely used long-horizon agent benchmarks. AgentCPM-Report is built on the 8B-parameter base model MiniCPM4.1, autonomously generating long-form reports with extreme performance and minimal footprint, designed for high-privacy scenarios with offline and agile local deployment.
gepa
GEPA (Genetic-Pareto) is a framework for optimizing arbitrary systems composed of text components like AI prompts, code snippets, or textual specs against any evaluation metric. It employs LLMs to reflect on system behavior, using feedback from execution and evaluation traces to drive targeted improvements. Through iterative mutation, reflection, and Pareto-aware candidate selection, GEPA evolves robust, high-performing variants with minimal evaluations, co-evolving multiple components in modular systems for domain-specific gains. The repository provides the official implementation of the GEPA algorithm as proposed in the paper titled 'GEPA: Reflective Prompt Evolution Can Outperform Reinforcement Learning'.
For similar tasks

Reflection_Tuning
Reflection-Tuning is a project focused on improving the quality of instruction-tuning data through a reflection-based method. It introduces Selective Reflection-Tuning, where the student model can decide whether to accept the improvements made by the teacher model. The project aims to generate high-quality instruction-response pairs by defining specific criteria for the oracle model to follow and respond to. It also evaluates the efficacy and relevance of instruction-response pairs using the r-IFD metric. The project provides code for reflection and selection processes, along with data and model weights for both V1 and V2 methods.
prometheus-eval
Prometheus-Eval is a repository dedicated to evaluating large language models (LLMs) in generation tasks. It provides state-of-the-art language models like Prometheus 2 (7B & 8x7B) for assessing in pairwise ranking formats and achieving high correlation scores with benchmarks. The repository includes tools for training, evaluating, and using these models, along with scripts for fine-tuning on custom datasets. Prometheus aims to address issues like fairness, controllability, and affordability in evaluations by simulating human judgments and proprietary LM-based assessments.
LLMs
LLMs is a Chinese large language model technology stack for practical use. It includes high-availability pre-training, SFT, and DPO preference alignment code framework. The repository covers pre-training data cleaning, high-concurrency framework, SFT dataset cleaning, data quality improvement, and security alignment work for Chinese large language models. It also provides open-source SFT dataset construction, pre-training from scratch, and various tools and frameworks for data cleaning, quality optimization, and task alignment.
ProX
ProX is a lm-based data refinement framework that automates the process of cleaning and improving data used in pre-training large language models. It offers better performance, domain flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods. The framework has been shown to improve model performance by over 2% and boost accuracy by up to 20% in tasks like math. ProX is designed to refine data at scale without the need for manual adjustments, making it a valuable tool for data preprocessing in natural language processing tasks.
For similar jobs
LLM-Agent-Survey
Autonomous agents are designed to achieve specific objectives through self-guided instructions. With the emergence and growth of large language models (LLMs), there is a growing trend in utilizing LLMs as fundamental controllers for these autonomous agents. This repository conducts a comprehensive survey study on the construction, application, and evaluation of LLM-based autonomous agents. It explores essential components of AI agents, application domains in natural sciences, social sciences, and engineering, and evaluation strategies. The survey aims to be a resource for researchers and practitioners in this rapidly evolving field.
AIProductHome
AI Product Home is a repository dedicated to collecting various AI commercial or open-source products. It provides assistance in submitting issues, self-recommendation, correcting resources, and more. The repository also features AI tools like Build Naidia, Autopod, Rytr, Mubert, and a virtual town driven by AI. It includes sections for AI models, chat dialogues, AI assistants, code assistance, artistic creation, content creation, and more. The repository covers a wide range of AI-related tools and resources for users interested in AI products and services.
AI-Catalog
AI-Catalog is a curated list of AI tools, platforms, and resources across various domains. It serves as a comprehensive repository for users to discover and explore a wide range of AI applications. The catalog includes tools for tasks such as text-to-image generation, summarization, prompt generation, writing assistance, code assistance, developer tools, low code/no code tools, audio editing, video generation, 3D modeling, search engines, chatbots, email assistants, fun tools, gaming, music generation, presentation tools, website builders, education assistants, autonomous AI agents, photo editing, AI extensions, deep face/deep fake detection, text-to-speech, startup tools, SQL-related AI tools, education tools, and text-to-video conversion.
awesome-ai-repositories
A curated list of open source repositories for AI Engineers. The repository provides a comprehensive collection of tools and frameworks for various AI-related tasks such as AI Gateway, AI Workload Manager, Copilot Development, Dataset Engineering, Evaluation, Fine Tuning, Function Calling, Graph RAG, Guardrails, Local Model Inference, LLM Agent Framework, Model Serving, Observability, Pre Training, Prompt Engineering, RAG Framework, Security, Structured Extraction, Structured Generation, Vector DB, and Voice Agent.
AI-Bootcamp
The AI Bootcamp is a comprehensive training program focusing on real-world applications to equip individuals with the skills and knowledge needed to excel as AI engineers. The bootcamp covers topics such as Real-World PyTorch, Machine Learning Projects, Fine-tuning Tiny LLM, Deployment of LLM to Production, AI Agents with GPT-4 Turbo, CrewAI, Llama 3, and more. Participants will learn foundational skills in Python for AI, ML Pipelines, Large Language Models (LLMs), AI Agents, and work on projects like RagBase for private document chat.
easyAi
EasyAi is a lightweight, beginner-friendly Java artificial intelligence algorithm framework. It can be seamlessly integrated into Java projects with Maven, requiring no additional environment configuration or dependencies. The framework provides pre-packaged modules for image object detection and AI customer service, as well as various low-level algorithm tools for deep learning, machine learning, reinforcement learning, heuristic learning, and matrix operations. Developers can easily develop custom micro-models tailored to their business needs.
awesome-ai-newsletters
Awesome AI Newsletters is a curated list of AI-related newsletters that provide the latest news, trends, tools, and insights in the field of Artificial Intelligence. It includes a variety of newsletters covering general AI news, prompts for marketing and productivity, AI job opportunities, and newsletters tailored for professionals in the AI industry. Whether you are a beginner looking to stay updated on AI advancements or a professional seeking to enhance your knowledge and skills, this repository offers a collection of valuable resources to help you navigate the world of AI.

Reflection_Tuning
Reflection-Tuning is a project focused on improving the quality of instruction-tuning data through a reflection-based method. It introduces Selective Reflection-Tuning, where the student model can decide whether to accept the improvements made by the teacher model. The project aims to generate high-quality instruction-response pairs by defining specific criteria for the oracle model to follow and respond to. It also evaluates the efficacy and relevance of instruction-response pairs using the r-IFD metric. The project provides code for reflection and selection processes, along with data and model weights for both V1 and V2 methods.




