
CogVideo
text and image to video generation: CogVideoX (2024) and CogVideo (ICLR 2023)
Stars: 11017

CogVideo is an open-source repository that provides pretrained text-to-video models for generating videos based on input text. It includes models like CogVideoX-2B and CogVideo, offering powerful video generation capabilities. The repository offers tools for inference, fine-tuning, and model conversion, along with demos showcasing the model's capabilities through CLI, web UI, and online experiences. CogVideo aims to facilitate the creation of high-quality videos from textual descriptions, catering to a wide range of applications.
README:
Experience the CogVideoX-5B model online at 🤗 Huggingface Space or 🤖 ModelScope Space
📚 View the paper and user guide
📍 Visit QingYing and API Platform to experience larger-scale commercial video generation models.
- 🔥 News:
2025/02/28: DDIM Inverse is now supported inCogVideoX-5BandCogVideoX1.5-5B. Check here. - 🔥 News:
2025/01/08: We have updated the code forLorafine-tuning based on thediffusersversion model, which uses less GPU memory. For more details, please see here. - 🔥 News:
2024/11/15: We released theCogVideoX1.5model in the diffusers version. Only minor parameter adjustments are needed to continue using previous code. - 🔥 News:
2024/11/08: We have released the CogVideoX1.5 model. CogVideoX1.5 is an upgraded version of the open-source model CogVideoX. The CogVideoX1.5-5B series supports 10-second videos with higher resolution, and CogVideoX1.5-5B-I2V supports video generation at any resolution. The SAT code has already been updated, while the diffusers version is still under adaptation. Download the SAT version code here. - 🔥 News:
2024/10/13: A more cost-effective fine-tuning framework forCogVideoX-5Bthat works with a single 4090 GPU, cogvideox-factory, has been released. It supports fine-tuning with multiple resolutions. Feel free to use it! - 🔥 News:
2024/10/10: We have updated our technical report. Please click here to view it. More training details and a demo have been added. To see the demo, click here.- 🔥 News:2024/10/09: We have publicly released the technical documentation for CogVideoX fine-tuning on Feishu, further increasing distribution flexibility. All examples in the public documentation can be fully reproduced. - 🔥 News:
2024/9/19: We have open-sourced the CogVideoX series image-to-video model CogVideoX-5B-I2V. This model can take an image as a background input and generate a video combined with prompt words, offering greater controllability. With this, the CogVideoX series models now support three tasks: text-to-video generation, video continuation, and image-to-video generation. Welcome to try it online at Experience. - 🔥
2024/9/19: The Caption model CogVLM2-Caption, used in the training process of CogVideoX to convert video data into text descriptions, has been open-sourced. Welcome to download and use it. - 🔥
2024/8/27: We have open-sourced a larger model in the CogVideoX series, CogVideoX-5B. We have significantly optimized the model's inference performance, greatly lowering the inference threshold. You can run CogVideoX-2B on older GPUs likeGTX 1080TI, and CogVideoX-5B on desktop GPUs likeRTX 3060. Please strictly follow the requirements to update and install dependencies, and refer to cli_demo for inference code. Additionally, the open-source license for the CogVideoX-2B model has been changed to the Apache 2.0 License. - 🔥
2024/8/6: We have open-sourced 3D Causal VAE, used for CogVideoX-2B, which can reconstruct videos with almost no loss. - 🔥
2024/8/6: We have open-sourced the first model of the CogVideoX series video generation models, **CogVideoX-2B **. - 🌱 Source:
2022/5/19: We have open-sourced the CogVideo video generation model (now you can see it in theCogVideobranch). This is the first open-source large Transformer-based text-to-video generation model. You can access the ICLR'23 paper for technical details.
Jump to a specific section:
- Quick Start
- Gallery
- Model Introduction
- Friendly Links
- Project Structure
- CogVideo(ICLR'23)
- Citation
- Model-License
Before running the model, please refer to this guide to see how we use large models like GLM-4 (or other comparable products, such as GPT-4) to optimize the model. This is crucial because the model is trained with long prompts, and a good prompt directly impacts the quality of the video generation.
Please make sure your Python version is between 3.10 and 3.12, inclusive of both 3.10 and 3.12.
Follow instructions in sat_demo: Contains the inference code and fine-tuning code of SAT weights. It is recommended to improve based on the CogVideoX model structure. Innovative researchers use this code to better perform rapid stacking and development.
Please make sure your Python version is between 3.10 and 3.12, inclusive of both 3.10 and 3.12.
pip install -r requirements.txt
Then follow diffusers_demo: A more detailed explanation of the inference code, mentioning the significance of common parameters.
For more details on quantized inference, please refer to diffusers-torchao. With Diffusers and TorchAO, quantized inference is also possible leading to memory-efficient inference as well as speedup in some cases when compiled. A full list of memory and time benchmarks with various settings on A100 and H100 has been published at diffusers-torchao.
To view the corresponding prompt words for the gallery, please click here
CogVideoX is an open-source version of the video generation model originating from QingYing. The table below displays the list of video generation models we currently offer, along with their foundational information.
| Model Name | CogVideoX1.5-5B (Latest) | CogVideoX1.5-5B-I2V (Latest) | CogVideoX-2B | CogVideoX-5B | CogVideoX-5B-I2V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Release Date | November 8, 2024 | November 8, 2024 | August 6, 2024 | August 27, 2024 | September 19, 2024 |
| Video Resolution | 1360 * 768 | Min(W, H) = 768 768 ≤ Max(W, H) ≤ 1360 Max(W, H) % 16 = 0 |
720 * 480 | ||
| Number of Frames | Should be 16N + 1 where N <= 10 (default 81) | Should be 8N + 1 where N <= 6 (default 49) | |||
| Inference Precision | BF16 (Recommended), FP16, FP32, FP8*, INT8, Not supported: INT4 | FP16*(Recommended), BF16, FP32, FP8*, INT8, Not supported: INT4 | BF16 (Recommended), FP16, FP32, FP8*, INT8, Not supported: INT4 | ||
| Single GPU Memory Usage |
SAT BF16: 76GB diffusers BF16: from 10GB* diffusers INT8(torchao): from 7GB* |
SAT FP16: 18GB diffusers FP16: 4GB minimum* diffusers INT8 (torchao): 3.6GB minimum* |
SAT BF16: 26GB diffusers BF16 : 5GB minimum* diffusers INT8 (torchao): 4.4GB minimum* |
||
| Multi-GPU Memory Usage |
BF16: 24GB* using diffusers |
FP16: 10GB* using diffusers |
BF16: 15GB* using diffusers |
||
| Inference Speed (Step = 50, FP/BF16) |
Single A100: ~1000 seconds (5-second video) Single H100: ~550 seconds (5-second video) |
Single A100: ~90 seconds Single H100: ~45 seconds |
Single A100: ~180 seconds Single H100: ~90 seconds |
||
| Prompt Language | English* | ||||
| Prompt Token Limit | 224 Tokens | 226 Tokens | |||
| Video Length | 5 seconds or 10 seconds | 6 seconds | |||
| Frame Rate | 16 frames / second | 8 frames / second | |||
| Position Encoding | 3d_rope_pos_embed | 3d_sincos_pos_embed | 3d_rope_pos_embed | 3d_rope_pos_embed + learnable_pos_embed | |
| Download Link (Diffusers) |
🤗 HuggingFace 🤖 ModelScope 🟣 WiseModel |
🤗 HuggingFace 🤖 ModelScope 🟣 WiseModel |
🤗 HuggingFace 🤖 ModelScope 🟣 WiseModel |
🤗 HuggingFace 🤖 ModelScope 🟣 WiseModel |
🤗 HuggingFace 🤖 ModelScope 🟣 WiseModel |
| Download Link (SAT) |
🤗 HuggingFace 🤖 ModelScope 🟣 WiseModel |
SAT | |||
Data Explanation
- While testing using the diffusers library, all optimizations included in the diffusers library were enabled. This scheme has not been tested for actual memory usage on devices outside of NVIDIA A100 / H100 architectures. Generally, this scheme can be adapted to all NVIDIA Ampere architecture and above devices. If optimizations are disabled, memory consumption will multiply, with peak memory usage being about 3 times the value in the table. However, speed will increase by about 3-4 times. You can selectively disable some optimizations, including:
pipe.enable_sequential_cpu_offload()
pipe.vae.enable_slicing()
pipe.vae.enable_tiling()
- For multi-GPU inference, the
enable_sequential_cpu_offload()optimization needs to be disabled. - Using INT8 models will slow down inference, which is done to accommodate lower-memory GPUs while maintaining minimal video quality loss, though inference speed will significantly decrease.
- The CogVideoX-2B model was trained in
FP16precision, and all CogVideoX-5B models were trained inBF16precision. We recommend using the precision in which the model was trained for inference. -
PytorchAO and Optimum-quanto can be
used to quantize the text encoder, transformer, and VAE modules to reduce the memory requirements of CogVideoX. This
allows the model to run on free T4 Colabs or GPUs with smaller memory! Also, note that TorchAO quantization is fully
compatible with
torch.compile, which can significantly improve inference speed. FP8 precision must be used on devices with NVIDIA H100 and above, requiring source installation oftorch,torchaoPython packages. CUDA 12.4 is recommended. - The inference speed tests also used the above memory optimization scheme. Without memory optimization, inference speed
increases by about 10%. Only the
diffusersversion of the model supports quantization. - The model only supports English input; other languages can be translated into English for use via large model refinement.
We highly welcome contributions from the community and actively contribute to the open-source community. The following works have already been adapted for CogVideoX, and we invite everyone to use them:
-
RIFLEx-CogVideoX:
RIFLEx extends the video with just one line of code:
freq[k-1]=(2np.pi)/(Ls). The framework not only supports training-free inference, but also offers models fine-tuned based on CogVideoX. By fine-tuning the model for just 1,000 steps on original-length videos, RIFLEx significantly enhances its length extrapolation capability. - CogVideoX-Fun: CogVideoX-Fun is a modified pipeline based on the CogVideoX architecture, supporting flexible resolutions and multiple launch methods.
- CogStudio: A separate repository for CogVideo's Gradio Web UI, which supports more functional Web UIs.
- Xorbits Inference: A powerful and comprehensive distributed inference framework, allowing you to easily deploy your own models or the latest cutting-edge open-source models with just one click.
- ComfyUI-CogVideoXWrapper Use the ComfyUI framework to integrate CogVideoX into your workflow.
- VideoSys: VideoSys provides a user-friendly, high-performance infrastructure for video generation, with full pipeline support and continuous integration of the latest models and techniques.
- AutoDL Space: A one-click deployment Huggingface Space image provided by community members.
- Interior Design Fine-Tuning Model: is a fine-tuned model based on CogVideoX, specifically designed for interior design.
-
xDiT: xDiT is a scalable inference engine for Diffusion Transformers (DiTs)
on multiple GPU Clusters. xDiT supports real-time image and video generations services.
cogvideox-factory: A cost-effective
fine-tuning framework for CogVideoX, compatible with the
diffusersversion model. Supports more resolutions, and fine-tuning CogVideoX-5B can be done with a single 4090 GPU. - CogVideoX-Interpolation: A pipeline based on the modified CogVideoX structure, aimed at providing greater flexibility for keyframe interpolation generation.
- DiffSynth-Studio: DiffSynth Studio is a diffusion engine. It has restructured the architecture, including text encoders, UNet, VAE, etc., enhancing computational performance while maintaining compatibility with open-source community models. The framework has been adapted for CogVideoX.
- CogVideoX-Controlnet: A simple ControlNet module code that includes the CogVideoX model.
- VideoTuna: VideoTuna is the first repo that integrates multiple AI video generation models for text-to-video, image-to-video, text-to-image generation.
- ConsisID: An identity-preserving text-to-video generation model, bases on CogVideoX-5B, which keep the face consistent in the generated video by frequency decomposition.
- A Step by Step Tutorial: A step-by-step guide on installing and optimizing the CogVideoX1.5-5B-I2V model in Windows and cloud environments. Special thanks to the FurkanGozukara for his effort and support!
This open-source repository will guide developers to quickly get started with the basic usage and fine-tuning examples of the CogVideoX open-source model.
Here provide three projects that can be run directly on free Colab T4 instances:
- CogVideoX-5B-T2V-Colab.ipynb: CogVideoX-5B Text-to-Video Colab code.
- CogVideoX-5B-T2V-Int8-Colab.ipynb: CogVideoX-5B Quantized Text-to-Video Inference Colab code, which takes about 30 minutes per run.
- CogVideoX-5B-I2V-Colab.ipynb: CogVideoX-5B Image-to-Video Colab code.
- CogVideoX-5B-V2V-Colab.ipynb: CogVideoX-5B Video-to-Video Colab code.
- dcli_demo: A more detailed inference code explanation, including the significance of common parameters. All of this is covered here.
- cli_demo_quantization: Quantized model inference code that can run on devices with lower memory. You can also modify this code to support running CogVideoX models in FP8 precision.
- diffusers_vae_demo: Code for running VAE inference separately.
- space demo: The same GUI code as used in the Huggingface Space, with frame interpolation and super-resolution tools integrated.
- convert_demo: How to convert user input into long-form input suitable for CogVideoX. Since CogVideoX is trained on long texts, we need to transform the input text distribution to match the training data using an LLM. The script defaults to using GLM-4, but it can be replaced with GPT, Gemini, or any other large language model.
- gradio_web_demo: A simple Gradio web application demonstrating how to use the CogVideoX-2B / 5B model to generate videos. Similar to our Huggingface Space, you can use this script to run a simple web application for video generation.
- finetune_demo: Fine-tuning scheme and details of the diffusers version of the CogVideoX model.
- sat_demo: Contains the inference code and fine-tuning code of SAT weights. It is recommended to improve based on the CogVideoX model structure. Innovative researchers use this code to better perform rapid stacking and development.
This folder contains some tools for model conversion / caption generation, etc.
- convert_weight_sat2hf: Converts SAT model weights to Huggingface model weights.
- caption_demo: Caption tool, a model that understands videos and outputs descriptions in text.
- export_sat_lora_weight: SAT fine-tuning model export tool, exports the SAT Lora Adapter in diffusers format.
- load_cogvideox_lora: Tool code for loading the diffusers version of fine-tuned Lora Adapter.
- llm_flux_cogvideox: Automatically generate videos using an open-source local large language model + Flux + CogVideoX.
- parallel_inference_xdit: Supported by xDiT, parallelize the video generation process on multiple GPUs.
The official repo for the paper: CogVideo: Large-scale Pretraining for Text-to-Video Generation via Transformers is on the CogVideo branch
CogVideo is able to generate relatively high-frame-rate videos. A 4-second clip of 32 frames is shown below.
The demo for CogVideo is at https://models.aminer.cn/cogvideo, where you can get hands-on practice on text-to-video generation. The original input is in Chinese.
🌟 If you find our work helpful, please leave us a star and cite our paper.
@article{yang2024cogvideox,
title={CogVideoX: Text-to-Video Diffusion Models with An Expert Transformer},
author={Yang, Zhuoyi and Teng, Jiayan and Zheng, Wendi and Ding, Ming and Huang, Shiyu and Xu, Jiazheng and Yang, Yuanming and Hong, Wenyi and Zhang, Xiaohan and Feng, Guanyu and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.06072},
year={2024}
}
@article{hong2022cogvideo,
title={CogVideo: Large-scale Pretraining for Text-to-Video Generation via Transformers},
author={Hong, Wenyi and Ding, Ming and Zheng, Wendi and Liu, Xinghan and Tang, Jie},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.15868},
year={2022}
}
We welcome your contributions! You can click here for more information.
The code in this repository is released under the Apache 2.0 License.
The CogVideoX-2B model (including its corresponding Transformers module and VAE module) is released under the Apache 2.0 License.
The CogVideoX-5B model (Transformers module, include I2V and T2V) is released under the CogVideoX LICENSE.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for CogVideo
Similar Open Source Tools

CogVideo
CogVideo is an open-source repository that provides pretrained text-to-video models for generating videos based on input text. It includes models like CogVideoX-2B and CogVideo, offering powerful video generation capabilities. The repository offers tools for inference, fine-tuning, and model conversion, along with demos showcasing the model's capabilities through CLI, web UI, and online experiences. CogVideo aims to facilitate the creation of high-quality videos from textual descriptions, catering to a wide range of applications.

magpie
This is the official repository for 'Alignment Data Synthesis from Scratch by Prompting Aligned LLMs with Nothing'. Magpie is a tool designed to synthesize high-quality instruction data at scale by extracting it directly from an aligned Large Language Models (LLMs). It aims to democratize AI by generating large-scale alignment data and enhancing the transparency of model alignment processes. Magpie has been tested on various model families and can be used to fine-tune models for improved performance on alignment benchmarks such as AlpacaEval, ArenaHard, and WildBench.
eole
EOLE is an open language modeling toolkit based on PyTorch. It aims to provide a research-friendly approach with a comprehensive yet compact and modular codebase for experimenting with various types of language models. The toolkit includes features such as versatile training and inference, dynamic data transforms, comprehensive large language model support, advanced quantization, efficient finetuning, flexible inference, and tensor parallelism. EOLE is a work in progress with ongoing enhancements in configuration management, command line entry points, reproducible recipes, core API simplification, and plans for further simplification, refactoring, inference server development, additional recipes, documentation enhancement, test coverage improvement, logging enhancements, and broader model support.
saga-reader
Saga Reader is an AI-driven think tank-style reader that automatically retrieves information from the internet based on user-specified topics and preferences. It uses cloud or local large models to summarize and provide guidance, and it includes an AI-driven interactive companion reading function, allowing you to discuss and exchange ideas with AI about the content you've read. Saga Reader is completely free and open-source, meaning all data is securely stored on your own computer and is not controlled by third-party service providers. Additionally, you can manage your subscription keywords based on your interests and preferences without being disturbed by advertisements and commercialized content.
wunjo.wladradchenko.ru
Wunjo AI is a comprehensive tool that empowers users to explore the realm of speech synthesis, deepfake animations, video-to-video transformations, and more. Its user-friendly interface and privacy-first approach make it accessible to both beginners and professionals alike. With Wunjo AI, you can effortlessly convert text into human-like speech, clone voices from audio files, create multi-dialogues with distinct voice profiles, and perform real-time speech recognition. Additionally, you can animate faces using just one photo combined with audio, swap faces in videos, GIFs, and photos, and even remove unwanted objects or enhance the quality of your deepfakes using the AI Retouch Tool. Wunjo AI is an all-in-one solution for your voice and visual AI needs, offering endless possibilities for creativity and expression.
LiteRT
LiteRT is Google's open-source high-performance runtime for on-device AI, previously known as TensorFlow Lite. The repository is currently not intended for open-source development, but aims to evolve to allow direct building and contributions. LiteRT supports Python versions 3.9, 3.10, 3.11 on Linux and MacOS. It ensures compatibility with existing .tflite file extension and format, offering conversion tools and continued active development under the name LiteRT.
krita-ai-diffusion
Krita-AI-Diffusion is a plugin for Krita that allows users to generate images from within the program. It offers a variety of features, including inpainting, outpainting, generating images from scratch, refining existing content, live painting, and control over image creation. The plugin is designed to fit into an interactive workflow where AI generation is used as just another tool while painting. It is meant to synergize with traditional tools and the layer stack.

deepdoctection
**deep** doctection is a Python library that orchestrates document extraction and document layout analysis tasks using deep learning models. It does not implement models but enables you to build pipelines using highly acknowledged libraries for object detection, OCR and selected NLP tasks and provides an integrated framework for fine-tuning, evaluating and running models. For more specific text processing tasks use one of the many other great NLP libraries. **deep** doctection focuses on applications and is made for those who want to solve real world problems related to document extraction from PDFs or scans in various image formats. **deep** doctection provides model wrappers of supported libraries for various tasks to be integrated into pipelines. Its core function does not depend on any specific deep learning library. Selected models for the following tasks are currently supported: * Document layout analysis including table recognition in Tensorflow with **Tensorpack**, or PyTorch with **Detectron2**, * OCR with support of **Tesseract**, **DocTr** (Tensorflow and PyTorch implementations available) and a wrapper to an API for a commercial solution, * Text mining for native PDFs with **pdfplumber**, * Language detection with **fastText**, * Deskewing and rotating images with **jdeskew**. * Document and token classification with all LayoutLM models provided by the **Transformer library**. (Yes, you can use any LayoutLM-model with any of the provided OCR-or pdfplumber tools straight away!). * Table detection and table structure recognition with **table-transformer**. * There is a small dataset for token classification available and a lot of new tutorials to show, how to train and evaluate this dataset using LayoutLMv1, LayoutLMv2, LayoutXLM and LayoutLMv3. * Comprehensive configuration of **analyzer** like choosing different models, output parsing, OCR selection. Check this notebook or the docs for more infos. * Document layout analysis and table recognition now runs with **Torchscript** (CPU) as well and **Detectron2** is not required anymore for basic inference. * [**new**] More angle predictors for determining the rotation of a document based on **Tesseract** and **DocTr** (not contained in the built-in Analyzer). * [**new**] Token classification with **LiLT** via **transformers**. We have added a model wrapper for token classification with LiLT and added a some LiLT models to the model catalog that seem to look promising, especially if you want to train a model on non-english data. The training script for LayoutLM can be used for LiLT as well and we will be providing a notebook on how to train a model on a custom dataset soon. **deep** doctection provides on top of that methods for pre-processing inputs to models like cropping or resizing and to post-process results, like validating duplicate outputs, relating words to detected layout segments or ordering words into contiguous text. You will get an output in JSON format that you can customize even further by yourself. Have a look at the **introduction notebook** in the notebook repo for an easy start. Check the **release notes** for recent updates. **deep** doctection or its support libraries provide pre-trained models that are in most of the cases available at the **Hugging Face Model Hub** or that will be automatically downloaded once requested. For instance, you can find pre-trained object detection models from the Tensorpack or Detectron2 framework for coarse layout analysis, table cell detection and table recognition. Training is a substantial part to get pipelines ready on some specific domain, let it be document layout analysis, document classification or NER. **deep** doctection provides training scripts for models that are based on trainers developed from the library that hosts the model code. Moreover, **deep** doctection hosts code to some well established datasets like **Publaynet** that makes it easy to experiment. It also contains mappings from widely used data formats like COCO and it has a dataset framework (akin to **datasets** so that setting up training on a custom dataset becomes very easy. **This notebook** shows you how to do this. **deep** doctection comes equipped with a framework that allows you to evaluate predictions of a single or multiple models in a pipeline against some ground truth. Check again **here** how it is done. Having set up a pipeline it takes you a few lines of code to instantiate the pipeline and after a for loop all pages will be processed through the pipeline.
persian-license-plate-recognition
The Persian License Plate Recognition (PLPR) system is a state-of-the-art solution designed for detecting and recognizing Persian license plates in images and video streams. Leveraging advanced deep learning models and a user-friendly interface, it ensures reliable performance across different scenarios. The system offers advanced detection using YOLOv5 models, precise recognition of Persian characters, real-time processing capabilities, and a user-friendly GUI. It is well-suited for applications in traffic monitoring, automated vehicle identification, and similar fields. The system's architecture includes modules for resident management, entrance management, and a detailed flowchart explaining the process from system initialization to displaying results in the GUI. Hardware requirements include an Intel Core i5 processor, 8 GB RAM, a dedicated GPU with at least 4 GB VRAM, and an SSD with 20 GB of free space. The system can be installed by cloning the repository and installing required Python packages. Users can customize the video source for processing and run the application to upload and process images or video streams. The system's GUI allows for parameter adjustments to optimize performance, and the Wiki provides in-depth information on the system's architecture and model training.
MME-RealWorld
MME-RealWorld is a benchmark designed to address real-world applications with practical relevance, featuring 13,366 high-resolution images and 29,429 annotations across 43 tasks. It aims to provide substantial recognition challenges and overcome common barriers in existing Multimodal Large Language Model benchmarks, such as small data scale, restricted data quality, and insufficient task difficulty. The dataset offers advantages in data scale, data quality, task difficulty, and real-world utility compared to existing benchmarks. It also includes a Chinese version with additional images and QA pairs focused on Chinese scenarios.
Video-MME
Video-MME is the first-ever comprehensive evaluation benchmark of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in Video Analysis. It assesses the capabilities of MLLMs in processing video data, covering a wide range of visual domains, temporal durations, and data modalities. The dataset comprises 900 videos with 256 hours and 2,700 human-annotated question-answer pairs. It distinguishes itself through features like duration variety, diversity in video types, breadth in data modalities, and quality in annotations.

UltraRAG
The UltraRAG framework is a researcher and developer-friendly RAG system solution that simplifies the process from data construction to model fine-tuning in domain adaptation. It introduces an automated knowledge adaptation technology system, supporting no-code programming, one-click synthesis and fine-tuning, multidimensional evaluation, and research-friendly exploration work integration. The architecture consists of Frontend, Service, and Backend components, offering flexibility in customization and optimization. Performance evaluation in the legal field shows improved results compared to VanillaRAG, with specific metrics provided. The repository is licensed under Apache-2.0 and encourages citation for support.
llm-course
The LLM course is divided into three parts: 1. 🧩 **LLM Fundamentals** covers essential knowledge about mathematics, Python, and neural networks. 2. 🧑🔬 **The LLM Scientist** focuses on building the best possible LLMs using the latest techniques. 3. 👷 **The LLM Engineer** focuses on creating LLM-based applications and deploying them. For an interactive version of this course, I created two **LLM assistants** that will answer questions and test your knowledge in a personalized way: * 🤗 **HuggingChat Assistant**: Free version using Mixtral-8x7B. * 🤖 **ChatGPT Assistant**: Requires a premium account. ## 📝 Notebooks A list of notebooks and articles related to large language models. ### Tools | Notebook | Description | Notebook | |----------|-------------|----------| | 🧐 LLM AutoEval | Automatically evaluate your LLMs using RunPod |  | | 🥱 LazyMergekit | Easily merge models using MergeKit in one click. |  | | 🦎 LazyAxolotl | Fine-tune models in the cloud using Axolotl in one click. |  | | ⚡ AutoQuant | Quantize LLMs in GGUF, GPTQ, EXL2, AWQ, and HQQ formats in one click. |  | | 🌳 Model Family Tree | Visualize the family tree of merged models. |  | | 🚀 ZeroSpace | Automatically create a Gradio chat interface using a free ZeroGPU. |  |

AgentCPM
AgentCPM is a series of open-source LLM agents jointly developed by THUNLP, Renmin University of China, ModelBest, and the OpenBMB community. It addresses challenges faced by agents in real-world applications such as limited long-horizon capability, autonomy, and generalization. The team focuses on building deep research capabilities for agents, releasing AgentCPM-Explore, a deep-search LLM agent, and AgentCPM-Report, a deep-research LLM agent. AgentCPM-Explore is the first open-source agent model with 4B parameters to appear on widely used long-horizon agent benchmarks. AgentCPM-Report is built on the 8B-parameter base model MiniCPM4.1, autonomously generating long-form reports with extreme performance and minimal footprint, designed for high-privacy scenarios with offline and agile local deployment.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.
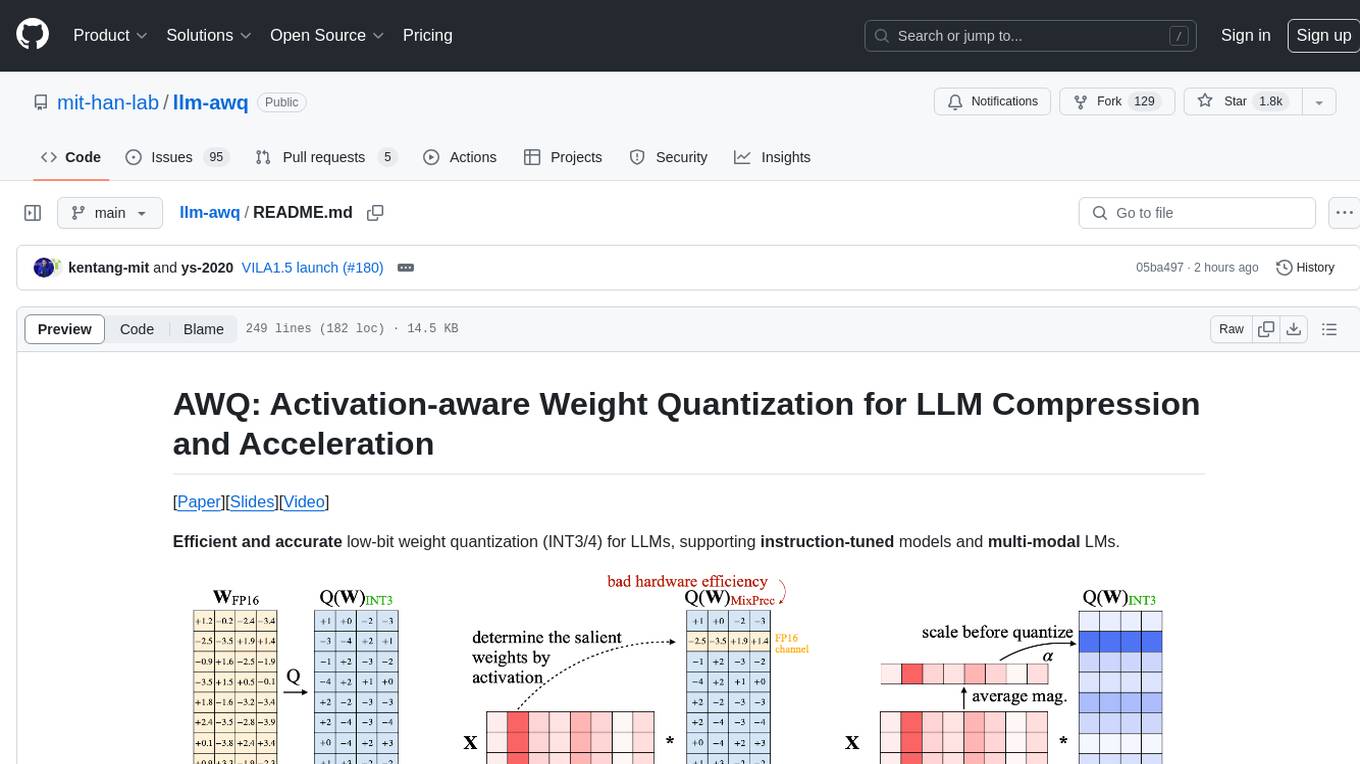
llm-awq
AWQ (Activation-aware Weight Quantization) is a tool designed for efficient and accurate low-bit weight quantization (INT3/4) for Large Language Models (LLMs). It supports instruction-tuned models and multi-modal LMs, providing features such as AWQ search for accurate quantization, pre-computed AWQ model zoo for various LLMs, memory-efficient 4-bit linear in PyTorch, and efficient CUDA kernel implementation for fast inference. The tool enables users to run large models on resource-constrained edge platforms, delivering more efficient responses with LLM/VLM chatbots through 4-bit inference.
For similar tasks

CogVideo
CogVideo is an open-source repository that provides pretrained text-to-video models for generating videos based on input text. It includes models like CogVideoX-2B and CogVideo, offering powerful video generation capabilities. The repository offers tools for inference, fine-tuning, and model conversion, along with demos showcasing the model's capabilities through CLI, web UI, and online experiences. CogVideo aims to facilitate the creation of high-quality videos from textual descriptions, catering to a wide range of applications.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.


