
tinyllm
Develop, evaluate and monitor LLM applications at scale
Stars: 90
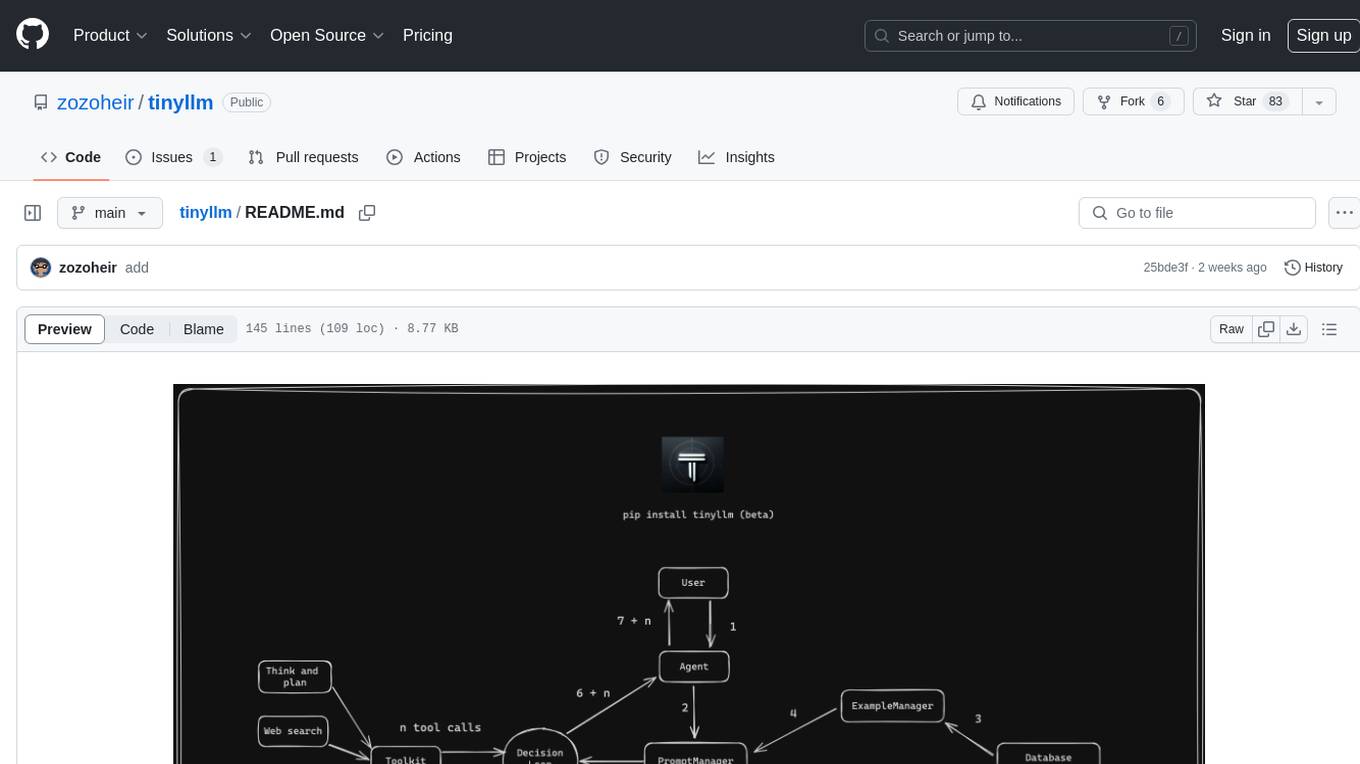
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.
README:
tinyllm is a lightweight framework for developing, debugging and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. The main goal of the library is to keep code as simple and readable as possible while allowing user to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production.
Function and its streaming equivalent FunctionStream are the core classes in tinyllm. They are designed to standardize and control LLM, ToolStore and any relevant calls for scalable production use in stream mode and otherwise.
It provides a structured approach to handle various aspects of function execution, including input/output validation, output processing, error handling, evaluation, all while keeping code readable. You can create a chain with its own prompt, LLM model and evaluators all in a single file. No need to jump through many class definitions, no spaghetti code. Any other library agent/chain (langchain/llama-index...) can also seamlessly be imported as a tinyllm Function.
pip install tinyllm
- LiteLLM integration: 20+ model providers available (OpenAI, Huggingface etc ...)
- Langfuse integration: Monitor trace and debug LLMs, Agents, Tools, RAG pipelines etc in structured run trees
- Agents: An agent is an LLM with Memory, a Toolkit and an ExampleManager
- ToolStore and Toolkits: let your Agent run python functions using ToolStore
- Example manager: constant examples + variable examples using and example selector with similarity search
- Memory: conversations history
- Retrieval Augmented Generation: RAG tools to search and generate answers
- Evaluation: Evaluators can be defined to evaluate and log the quality of the function's output in real-time
- PGVector store: PostgreSQL DB with the pgvector extension for vector storage.
- Prompt engineering tools: utility modules for prompt engineering, optimization and string formatting
- Layered validation: 3 validations happen during the Function lifecycle: input, output and output processing.
- IO Standardization: Maintains consistent response patterns and failure handling across different function implementations.
- Observability: Integrates with Langfuse for
- Logging: Records detailed logs for debugging and auditing purposes.
- Finite State Machine design: Manages the function's lifecycle through defined states, ensuring controlled and predictable execution.
class RiskScoreOutput(BaseModel):
risk_score: float
@tiny_function(output_model=RiskScoreOutput)
async def calculate_risk_score(bank_account_history: str, employment_history: str):
"""
<system>
Extract a Risk Score between 0 and 1 for a Credit Card application based on bank account and employment history.
</system>
<prompt>
Given the bank account history: {bank_account_history}
And the employment history: {employment_history}
Calculate the risk score for a credit card application.
</prompt>
"""
passMany of the LLM libraries today (langchain, llama-index, deep pavlov...) have made serious software design commitments which I believe were too early to make given the infancy of the industry. The goals of tinyllm are:
- Solve painpoints from current libraries: lack of composability (within + between libraries), complex software designs, code readability, debugging and logging.
- High level, robust abstractions: tinyllm is designed to be as simple as possible to use and integrate with existing and living codebases.
- Human and machine readable code to enable AI powered and autonomous chain development
LLM Functions are designed to behave like a web API. All Functions will always, even if failed, return a dictionary response.
Validations are defined through a Pydantic model and are provided to the Function using input_validator, output_validator and output_processing_validator args to a Function
tinyllm is integrated with Langfuse for tracing chains, functions and agents.
Configs are managed through a tinyllm.yaml file. It gets picked up at runtime in tinyllm.init and can be placed in any of /Documents, your root folder, or the current working directory. An empty tinyllm.yaml file is at the source of the repo to get you setup.
These tend to be confusing across the board. Here's a quick explanation:
- Concurrency : This means more than 1 Input/Ouput request at a time. Just like you can download 10 files concurrently on your web browser, you can call 10 APIs concurrently.
- Chaining : An ordered list of Functions where a Function's output is the input of the next Function in the chain.
- Parallelism : compute/calculations being performed on more than 1 process/CPU Core on the same machine. This is what model providers like OpenAI do using large GPU clusters (Nvidia, AMD...). This is used for "CPU Bound" tasks.
Tinyllm does not care about Parallelism. Parallelism is implemented by LLM providers on a GPU/CPU level and should be abstracted away using an LLM microservice. Tinyllm only cares about Concurrency, Chaining and organizing IO Bound tasks.
Finite state machine with predictable and controlled state transitions for easy debugging of your chains/compute graphs.
Below is the start and end of a trace for asking "What is the weather in Puerto Rico?" to an Agent with a get_weather Tool.
INFO | tinyllm.function | 2023-12-25 19:37:10,617 : [Standard example selector] transition to: States.INIT
INFO | tinyllm.function | 2023-12-25 19:37:12,720 : [BufferMemory] transition to: States.INIT
INFO | tinyllm.function | 2023-12-25 19:37:12,729 : [get_weather] transition to: States.INIT
INFO | tinyllm.function | 2023-12-25 19:37:12,729 : [Toolkit] transition to: States.INIT
INFO | tinyllm.function | 2023-12-25 19:37:12,731 : [LiteLLM] transition to: States.INIT
...
...
INFO | tinyllm.function | 2023-12-25 19:37:17,150 : [AnswerCorrectnessEvaluator] transition to: States.PROCESSING_OUTPUT
INFO | tinyllm.function | 2023-12-25 19:37:17,151 : [AnswerCorrectnessEvaluator] transition to: States.PROCESSED_OUTPUT_VALIDATION
INFO | tinyllm.function | 2023-12-25 19:37:17,151 : [AnswerCorrectnessEvaluator] transition to: States.COMPLETE
INFO | tinyllm.function | 2023-12-25 19:37:17,846 : [Agent] transition to: States.PROCESSING_OUTPUT
INFO | tinyllm.function | 2023-12-25 19:37:17,847 : [Agent] transition to: States.PROCESSED_OUTPUT_VALIDATION
INFO | tinyllm.function | 2023-12-25 19:37:17,847 : [Agent] transition to: States.COMPLETE
{'status': 'success', 'output': {'response': {'id': 'chatcmpl-8ZpjY0QmXbDiMIcSRwKuCUny4sxul', 'choices': [{'finish_reason': 'stop', 'index': 0, 'message': {'content': "It is 25 degrees celsius in Puerto Rico", 'role': 'assistant'}}], 'created': 1703551035, 'model': 'gpt-3.5-turbo-0613', 'object': 'chat.completion', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'usage': {'completion_tokens': 12, 'prompt_tokens': 138, 'total_tokens': 150}, '_response_ms': 785.606}}}
These tend to be confusing across the board. Here's a quick explanation:
- Concurrency : This means more than 1 Input/Ouput request at a time. Just like you can download 10 files concurrently on your web browser, you can call 10 APIs concurrently.
- Chaining : An ordered list of Functions where a Function's output is the input of the next Function in the chain.
- Parallelism : compute/calculations being performed on more than 1 process/CPU Core on the same machine. This is what model providers like OpenAI do using large GPU clusters (Nvidia, AMD...). This is used for "CPU Bound" tasks.
Tinyllm does not care about Parallelism. Parallelism is implemented by LLM providers on a GPU/CPU level and should be abstracted away using an LLM microservice. Tinyllm only cares about Concurrency, Chaining and organizing IO Bound tasks.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for tinyllm
Similar Open Source Tools

tinyllm
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.
arbigent
Arbigent (Arbiter-Agent) is an AI agent testing framework designed to make AI agent testing practical for modern applications. It addresses challenges faced by traditional UI testing frameworks and AI agents by breaking down complex tasks into smaller, dependent scenarios. The framework is customizable for various AI providers, operating systems, and form factors, empowering users with extensive customization capabilities. Arbigent offers an intuitive UI for scenario creation and a powerful code interface for seamless test execution. It supports multiple form factors, optimizes UI for AI interaction, and is cost-effective by utilizing models like GPT-4o mini. With a flexible code interface and open-source nature, Arbigent aims to revolutionize AI agent testing in modern applications.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
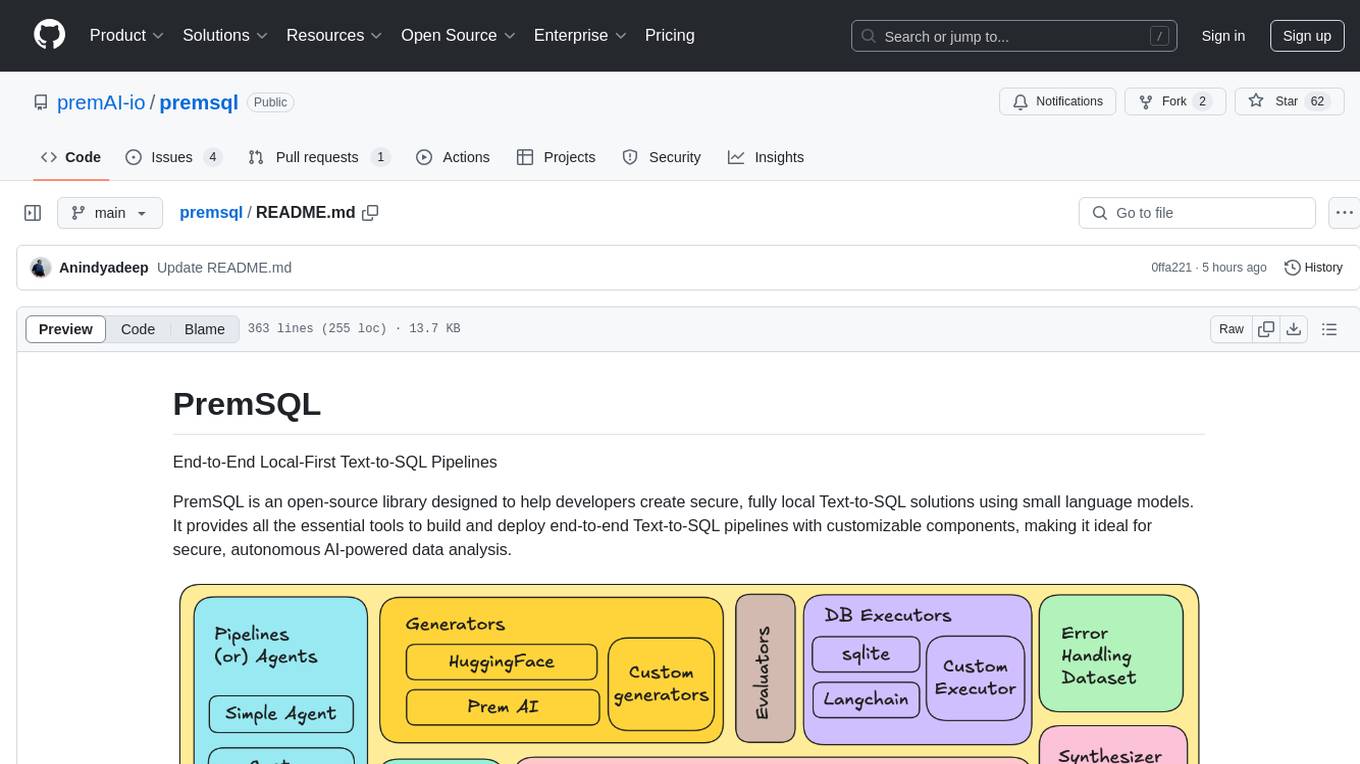
premsql
PremSQL is an open-source library designed to help developers create secure, fully local Text-to-SQL solutions using small language models. It provides essential tools for building and deploying end-to-end Text-to-SQL pipelines with customizable components, ideal for secure, autonomous AI-powered data analysis. The library offers features like Local-First approach, Customizable Datasets, Robust Executors and Evaluators, Advanced Generators, Error Handling and Self-Correction, Fine-Tuning Support, and End-to-End Pipelines. Users can fine-tune models, generate SQL queries from natural language inputs, handle errors, and evaluate model performance against predefined metrics. PremSQL is extendible for customization and private data usage.

embodied-agents
Embodied Agents is a toolkit for integrating large multi-modal models into existing robot stacks with just a few lines of code. It provides consistency, reliability, scalability, and is configurable to any observation and action space. The toolkit is designed to reduce complexities involved in setting up inference endpoints, converting between different model formats, and collecting/storing datasets. It aims to facilitate data collection and sharing among roboticists by providing Python-first abstractions that are modular, extensible, and applicable to a wide range of tasks. The toolkit supports asynchronous and remote thread-safe agent execution for maximal responsiveness and scalability, and is compatible with various APIs like HuggingFace Spaces, Datasets, Gymnasium Spaces, Ollama, and OpenAI. It also offers automatic dataset recording and optional uploads to the HuggingFace hub.
LightAgent
LightAgent is a lightweight, open-source Agentic AI development framework with memory, tools, and a tree of thought. It supports multi-agent collaboration, autonomous learning, tool integration, complex task handling, and multi-model support. It also features a streaming API, tool generator, agent self-learning, adaptive tool mechanism, and more. LightAgent is designed for intelligent customer service, data analysis, automated tools, and educational assistance.
deep-research
Deep Research is a lightning-fast tool that uses powerful AI models to generate comprehensive research reports in just a few minutes. It leverages advanced 'Thinking' and 'Task' models, combined with an internet connection, to provide fast and insightful analysis on various topics. The tool ensures privacy by processing and storing all data locally. It supports multi-platform deployment, offers support for various large language models, web search functionality, knowledge graph generation, research history preservation, local and server API support, PWA technology, multi-key payload support, multi-language support, and is built with modern technologies like Next.js and Shadcn UI. Deep Research is open-source under the MIT License.

exospherehost
Exosphere is an open source infrastructure designed to run AI agents at scale for large data and long running flows. It allows developers to define plug and playable nodes that can be run on a reliable backbone in the form of a workflow, with features like dynamic state creation at runtime, infinite parallel agents, persistent state management, and failure handling. This enables the deployment of production agents that can scale beautifully to build robust autonomous AI workflows.

zenml
ZenML is an extensible, open-source MLOps framework for creating portable, production-ready machine learning pipelines. By decoupling infrastructure from code, ZenML enables developers across your organization to collaborate more effectively as they develop to production.

axar
AXAR AI is a lightweight framework designed for building production-ready agentic applications using TypeScript. It aims to simplify the process of creating robust, production-grade LLM-powered apps by focusing on familiar coding practices without unnecessary abstractions or steep learning curves. The framework provides structured, typed inputs and outputs, familiar and intuitive patterns like dependency injection and decorators, explicit control over agent behavior, real-time logging and monitoring tools, minimalistic design with little overhead, model agnostic compatibility with various AI models, and streamed outputs for fast and accurate results. AXAR AI is ideal for developers working on real-world AI applications who want a tool that gets out of the way and allows them to focus on shipping reliable software.
Memori
Memori is a memory fabric designed for enterprise AI that seamlessly integrates into existing software and infrastructure. It is agnostic to LLM, datastore, and framework, providing support for major foundational models and databases. With features like vectorized memories, in-memory semantic search, and a knowledge graph, Memori simplifies the process of attributing LLM interactions and managing sessions. It offers Advanced Augmentation for enhancing memories at different levels and supports various platforms, frameworks, database integrations, and datastores. Memori is designed to reduce development overhead and provide efficient memory management for AI applications.
langmanus
LangManus is a community-driven AI automation framework that combines language models with specialized tools for tasks like web search, crawling, and Python code execution. It implements a hierarchical multi-agent system with agents like Coordinator, Planner, Supervisor, Researcher, Coder, Browser, and Reporter. The framework supports LLM integration, search and retrieval tools, Python integration, workflow management, and visualization. LangManus aims to give back to the open-source community and welcomes contributions in various forms.
RainbowGPT
RainbowGPT is a versatile tool that offers a range of functionalities, including Stock Analysis for financial decision-making, MySQL Management for database navigation, and integration of AI technologies like GPT-4 and ChatGlm3. It provides a user-friendly interface suitable for all skill levels, ensuring seamless information flow and continuous expansion of emerging technologies. The tool enhances adaptability, creativity, and insight, making it a valuable asset for various projects and tasks.
AIOS
AIOS, a Large Language Model (LLM) Agent operating system, embeds large language model into Operating Systems (OS) as the brain of the OS, enabling an operating system "with soul" -- an important step towards AGI. AIOS is designed to optimize resource allocation, facilitate context switch across agents, enable concurrent execution of agents, provide tool service for agents, maintain access control for agents, and provide a rich set of toolkits for LLM Agent developers.
llm-answer-engine
This repository contains the code and instructions needed to build a sophisticated answer engine that leverages the capabilities of Groq, Mistral AI's Mixtral, Langchain.JS, Brave Search, Serper API, and OpenAI. Designed to efficiently return sources, answers, images, videos, and follow-up questions based on user queries, this project is an ideal starting point for developers interested in natural language processing and search technologies.
BentoML
BentoML is an open-source model serving library for building performant and scalable AI applications with Python. It comes with everything you need for serving optimization, model packaging, and production deployment.
For similar tasks
honcho
Honcho is a platform for creating personalized AI agents and LLM powered applications for end users. The repository is a monorepo containing the server/API for managing database interactions and storing application state, along with a Python SDK. It utilizes FastAPI for user context management and Poetry for dependency management. The API can be run using Docker or manually by setting environment variables. The client SDK can be installed using pip or Poetry. The project is open source and welcomes contributions, following a fork and PR workflow. Honcho is licensed under the AGPL-3.0 License.
sagentic-af
Sagentic.ai Agent Framework is a tool for creating AI agents with hot reloading dev server. It allows users to spawn agents locally by calling specific endpoint. The framework comes with detailed documentation and supports contributions, issues, and feature requests. It is MIT licensed and maintained by Ahyve Inc.

tinyllm
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.
council
Council is an open-source platform designed for the rapid development and deployment of customized generative AI applications using teams of agents. It extends the LLM tool ecosystem by providing advanced control flow and scalable oversight for AI agents. Users can create sophisticated agents with predictable behavior by leveraging Council's powerful approach to control flow using Controllers, Filters, Evaluators, and Budgets. The framework allows for automated routing between agents, comparing, evaluating, and selecting the best results for a task. Council aims to facilitate packaging and deploying agents at scale on multiple platforms while enabling enterprise-grade monitoring and quality control.
mentals-ai
Mentals AI is a tool designed for creating and operating agents that feature loops, memory, and various tools, all through straightforward markdown syntax. This tool enables you to concentrate solely on the agent’s logic, eliminating the necessity to compose underlying code in Python or any other language. It redefines the foundational frameworks for future AI applications by allowing the creation of agents with recursive decision-making processes, integration of reasoning frameworks, and control flow expressed in natural language. Key concepts include instructions with prompts and references, working memory for context, short-term memory for storing intermediate results, and control flow from strings to algorithms. The tool provides a set of native tools for message output, user input, file handling, Python interpreter, Bash commands, and short-term memory. The roadmap includes features like a web UI, vector database tools, agent's experience, and tools for image generation and browsing. The idea behind Mentals AI originated from studies on psychoanalysis executive functions and aims to integrate 'System 1' (cognitive executor) with 'System 2' (central executive) to create more sophisticated agents.
AgentPilot
Agent Pilot is an open source desktop app for creating, managing, and chatting with AI agents. It features multi-agent, branching chats with various providers through LiteLLM. Users can combine models from different providers, configure interactions, and run code using the built-in Open Interpreter. The tool allows users to create agents, manage chats, work with multi-agent workflows, branching workflows, context blocks, tools, and plugins. It also supports a code interpreter, scheduler, voice integration, and integration with various AI providers. Contributions to the project are welcome, and users can report known issues for improvement.
shinkai-apps
Shinkai apps unlock the full capabilities/automation of first-class LLM (AI) support in the web browser. It enables creating multiple agents, each connected to either local or 3rd-party LLMs (ex. OpenAI GPT), which have permissioned (meaning secure) access to act in every webpage you visit. There is a companion repo called Shinkai Node, that allows you to set up the node anywhere as the central unit of the Shinkai Network, handling tasks such as agent management, job processing, and secure communications.
llm-functions
LLM Functions is a project that enables the enhancement of large language models (LLMs) with custom tools and agents developed in bash, javascript, and python. Users can create tools for their LLM to execute system commands, access web APIs, or perform other complex tasks triggered by natural language prompts. The project provides a framework for building tools and agents, with tools being functions written in the user's preferred language and automatically generating JSON declarations based on comments. Agents combine prompts, function callings, and knowledge (RAG) to create conversational AI agents. The project is designed to be user-friendly and allows users to easily extend the capabilities of their language models.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.