
marly
Context-aware structured outputs. Search your documents or the web for specific data and get it back in JSON or Markdown.
Stars: 135
Marly is a tool that allows users to search for and extract context-specific data from various types of documents such as PDFs, Word files, Powerpoints, and websites. It provides the ability to extract data in structured formats like JSON or Markdown, making it easy to integrate into workflows. Marly supports multi-schema and multi-document extraction, offers built-in caching for rapid repeat extractions, and ensures no vendor lock-in by allowing flexibility in choosing model providers.
README:
Marly allows you to search for and extract context specific data from your PDFs, WRDs, Powerpoints, Websites etc in a structured format like JSON or Markdown.
📄 Extract Relevant Information Seamlessly: Give your applications the ability to identify and extract relevant data from one or many large documents and websites with just a single API call. Get the content back in JSON or Markdown formats, making it easy to integrate into your workflows.
🔍 Multi-Schema/Multi-Document Support: Extract data based one or many predefined schemas from a variety of document types, without needing a vector database or specifying page numbers.
🔄 Built-in Caching: With built-in caching, previously extracted schemas can be instantly retrieved, enabling rapid repeat extractions without having to reprocess the original documents.
🚫 No Vendor Lock-In: Enjoy complete flexibility with your choice of model provider. Whether using open-source or closed-source models, you're never tied to a specific vendor, ensuring full control.
A schema is a set of key-value pairs describing what needs to be extracted from a particular document.
📋 Example Schema
{
"Firm": "The name of the firm",
"Number of Funds": "The number of funds managed by the firm",
"Commitment": "The commitment amount in millions of dollars",
"% of Total Comm": "The percentage of total commitment",
"Exposure (FMV + Unfunded)": "The exposure including fair market value and unfunded commitments in millions of dollars",
"% of Total Exposure": "The percentage of total exposure",
"TVPI": "Total Value to Paid-In multiple",
"Net IRR": "Net Internal Rate of Return as a percentage"
}
| 💼 Financial Report Analysis | 📊 Customer Feedback Processing | 🔬 Research Assistant | 🧠 Legal Contract Parsing |
| Extract key financial metrics from quarterly PDF reports | Categorize feedback from various document types | Process research papers, extracting methodologies and findings | Extract key legal terms and conditions from contracts |
To install the python package, run the following command:
pip install marly
To build the platform from source, run the following command:
./start-marly.shOnce the Marly platform is running you can test it out by trying one of our examples
-
Navigate to the examples folder:
cd examples -
Navigate to the scripts or notebooks folder:
cd scriptsor
cd notebooks/autogen_example -
Run one of our example scripts:
python azure_example.py
For more detailed information, please refer to our documentation.
We welcome contributions! Please see our Contributing Guide for more details.
This project is licensed under the Elastic License 2.0 (ELv2).
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for marly
Similar Open Source Tools

marly
Marly is a tool that allows users to search for and extract context-specific data from various types of documents such as PDFs, Word files, Powerpoints, and websites. It provides the ability to extract data in structured formats like JSON or Markdown, making it easy to integrate into workflows. Marly supports multi-schema and multi-document extraction, offers built-in caching for rapid repeat extractions, and ensures no vendor lock-in by allowing flexibility in choosing model providers.
chroma
Chroma is an open-source embedding database that provides a simple, scalable, and feature-rich way to build Python or JavaScript LLM apps with memory. It offers a fully-typed, fully-tested, and fully-documented API that makes it easy to get started and scale your applications. Chroma also integrates with popular tools like LangChain and LlamaIndex, and supports a variety of embedding models, including Sentence Transformers, OpenAI embeddings, and Cohere embeddings. With Chroma, you can easily add documents to your database, query relevant documents with natural language, and compose documents into the context window of an LLM like GPT3 for additional summarization or analysis.
reductstore
ReductStore is a high-performance time series database designed for storing and managing large amounts of unstructured blob data. It offers features such as real-time querying, batching data, and HTTP(S) API for edge computing, computer vision, and IoT applications. The database ensures data integrity, implements retention policies, and provides efficient data access, making it a cost-effective solution for applications requiring unstructured data storage and access at specific time intervals.

crewAI
CrewAI is a cutting-edge framework designed to orchestrate role-playing autonomous AI agents. By fostering collaborative intelligence, CrewAI empowers agents to work together seamlessly, tackling complex tasks. It enables AI agents to assume roles, share goals, and operate in a cohesive unit, much like a well-oiled crew. Whether you're building a smart assistant platform, an automated customer service ensemble, or a multi-agent research team, CrewAI provides the backbone for sophisticated multi-agent interactions. With features like role-based agent design, autonomous inter-agent delegation, flexible task management, and support for various LLMs, CrewAI offers a dynamic and adaptable solution for both development and production workflows.
draive
draive is an open-source Python library designed to simplify and accelerate the development of LLM-based applications. It offers abstract building blocks for connecting functionalities with large language models, flexible integration with various AI solutions, and a user-friendly framework for building scalable data processing pipelines. The library follows a function-oriented design, allowing users to represent complex programs as simple functions. It also provides tools for measuring and debugging functionalities, ensuring type safety and efficient asynchronous operations for modern Python apps.
Conversation-Knowledge-Mining-Solution-Accelerator
The Conversation Knowledge Mining Solution Accelerator enables customers to leverage intelligence to uncover insights, relationships, and patterns from conversational data. It empowers users to gain valuable knowledge and drive targeted business impact by utilizing Azure AI Foundry, Azure OpenAI, Microsoft Fabric, and Azure Search for topic modeling, key phrase extraction, speech-to-text transcription, and interactive chat experiences.

qdrant
Qdrant is a vector similarity search engine and vector database. It is written in Rust, which makes it fast and reliable even under high load. Qdrant can be used for a variety of applications, including: * Semantic search * Image search * Product recommendations * Chatbots * Anomaly detection Qdrant offers a variety of features, including: * Payload storage and filtering * Hybrid search with sparse vectors * Vector quantization and on-disk storage * Distributed deployment * Highlighted features such as query planning, payload indexes, SIMD hardware acceleration, async I/O, and write-ahead logging Qdrant is available as a fully managed cloud service or as an open-source software that can be deployed on-premises.
CosmosAIGraph
CosmosAIGraph is an AI-powered graph and RAG implementation of OmniRAG pattern, utilizing Azure Cosmos DB and other sources. It includes presentations, reference application documentation, FAQs, and a reference dataset of Python libraries pre-vectorized. The project focuses on Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL and Apache Jena implementation for the in-memory RDF graph. It provides DockerHub images, with plans to add RBAC and Microsoft Entra ID/AAD authentication support, update AI model to gpt-4.5, and offer generic graph examples with a graph generation solution.
poml
POML (Prompt Orchestration Markup Language) is a novel markup language designed to bring structure, maintainability, and versatility to advanced prompt engineering for Large Language Models (LLMs). It addresses common challenges in prompt development, such as lack of structure, complex data integration, format sensitivity, and inadequate tooling. POML provides a systematic way to organize prompt components, integrate diverse data types seamlessly, and manage presentation variations, empowering developers to create more sophisticated and reliable LLM applications.

nucliadb
NucliaDB is a robust database that allows storing and searching on unstructured data. It is an out of the box hybrid search database, utilizing vector, full text and graph indexes. NucliaDB is written in Rust and Python. We designed it to index large datasets and provide multi-teanant support. When utilizing NucliaDB with Nuclia cloud, you are able to the power of an NLP database without the hassle of data extraction, enrichment and inference. We do all the hard work for you.

Instrukt
Instrukt is a terminal-based AI integrated environment that allows users to create and instruct modular AI agents, generate document indexes for question-answering, and attach tools to any agent. It provides a platform for users to interact with AI agents in natural language and run them inside secure containers for performing tasks. The tool supports custom AI agents, chat with code and documents, tools customization, prompt console for quick interaction, LangChain ecosystem integration, secure containers for agent execution, and developer console for debugging and introspection. Instrukt aims to make AI accessible to everyone by providing tools that empower users without relying on external APIs and services.
deep-research-web-ui
This web UI tool is designed to enhance the user experience of the deep-research repository by providing a safe and secure environment for conducting AI research. It offers features such as real-time feedback, search visualization, export as PDF, support for various AI models, and Docker deployment. Users can interact with multiple AI providers and web search services, making research processes more efficient and accessible. The tool also includes recent updates that improve functionality and fix bugs, ensuring a seamless experience for users.

fenic
fenic is an opinionated DataFrame framework from typedef.ai for building AI and agentic applications. It transforms unstructured and structured data into insights using familiar DataFrame operations enhanced with semantic intelligence. With support for markdown, transcripts, and semantic operators, plus efficient batch inference across various model providers. fenic is purpose-built for LLM inference, providing a query engine designed for AI workloads, semantic operators as first-class citizens, native unstructured data support, production-ready infrastructure, and a familiar DataFrame API.
LabelLLM
LabelLLM is an open-source data annotation platform designed to optimize the data annotation process for LLM development. It offers flexible configuration, multimodal data support, comprehensive task management, and AI-assisted annotation. Users can access a suite of annotation tools, enjoy a user-friendly experience, and enhance efficiency. The platform allows real-time monitoring of annotation progress and quality control, ensuring data integrity and timeliness.

cosdata
Cosdata is a cutting-edge AI data platform designed to power the next generation search pipelines. It features immutability, version control, and excels in semantic search, structured knowledge graphs, hybrid search capabilities, real-time search at scale, and ML pipeline integration. The platform is customizable, scalable, efficient, enterprise-grade, easy to use, and can manage multi-modal data. It offers high performance, indexing, low latency, and high requests per second. Cosdata is designed to meet the demands of modern search applications, empowering businesses to harness the full potential of their data.

PrivateDocBot
PrivateDocBot is a local LLM-powered chatbot designed for secure document interactions. It seamlessly merges Chainlit user-friendly interface with localized language models, tailored for sensitive data. The project streamlines data access by deciphering intricate user guides and extracting vital insights from complex PDF reports. Equipped with advanced technology, it offers an engaging conversational experience, redefining data interaction and empowering users with control.
For similar tasks

marly
Marly is a tool that allows users to search for and extract context-specific data from various types of documents such as PDFs, Word files, Powerpoints, and websites. It provides the ability to extract data in structured formats like JSON or Markdown, making it easy to integrate into workflows. Marly supports multi-schema and multi-document extraction, offers built-in caching for rapid repeat extractions, and ensures no vendor lock-in by allowing flexibility in choosing model providers.
open-extract
open-extract simplifies the ingestion and processing of unstructured data for those building AI Agents/Agentic Workflows using frameworks such as LangGraph, AG2, and CrewAI. It allows applications to identify and extract relevant data from large documents and websites with a single API call, supporting multi-schema/multi-document extraction without vendor lock-in. The tool includes built-in caching for rapid repeat extractions, providing flexibility in model provider choice.
For similar jobs
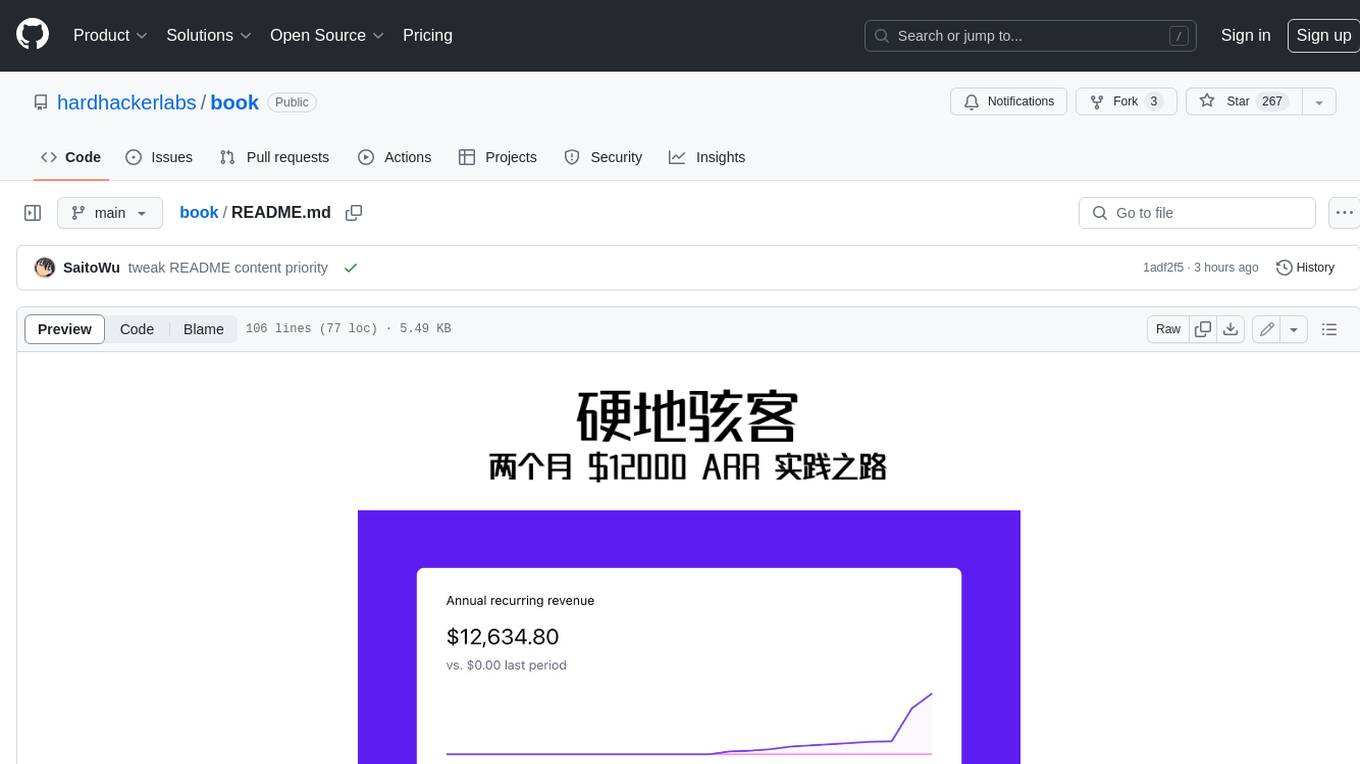
book
Podwise is an AI knowledge management app designed specifically for podcast listeners. With the Podwise platform, you only need to follow your favorite podcasts, such as "Hardcore Hackers". When a program is released, Podwise will use AI to transcribe, extract, summarize, and analyze the podcast content, helping you to break down the hard-core podcast knowledge. At the same time, it is connected to platforms such as Notion, Obsidian, Logseq, and Readwise, embedded in your knowledge management workflow, and integrated with content from other channels including news, newsletters, and blogs, helping you to improve your second brain 🧠.
extractor
Extractor is an AI-powered data extraction library for Laravel that leverages OpenAI's capabilities to effortlessly extract structured data from various sources, including images, PDFs, and emails. It features a convenient wrapper around OpenAI Chat and Completion endpoints, supports multiple input formats, includes a flexible Field Extractor for arbitrary data extraction, and integrates with Textract for OCR functionality. Extractor utilizes JSON Mode from the latest GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models, providing accurate and efficient data extraction.
Scrapegraph-ai
ScrapeGraphAI is a Python library that uses Large Language Models (LLMs) and direct graph logic to create web scraping pipelines for websites, documents, and XML files. It allows users to extract specific information from web pages by providing a prompt describing the desired data. ScrapeGraphAI supports various LLMs, including Ollama, OpenAI, Gemini, and Docker, enabling users to choose the most suitable model for their needs. The library provides a user-friendly interface through its `SmartScraper` class, which simplifies the process of building and executing scraping pipelines. ScrapeGraphAI is open-source and available on GitHub, with extensive documentation and examples to guide users. It is particularly useful for researchers and data scientists who need to extract structured data from web pages for analysis and exploration.
databerry
Chaindesk is a no-code platform that allows users to easily set up a semantic search system for personal data without technical knowledge. It supports loading data from various sources such as raw text, web pages, files (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, PDF, Markdown, Plain Text), and upcoming support for web sites, Notion, and Airtable. The platform offers a user-friendly interface for managing datastores, querying data via a secure API endpoint, and auto-generating ChatGPT Plugins for each datastore. Chaindesk utilizes a Vector Database (Qdrant), Openai's text-embedding-ada-002 for embeddings, and has a chunk size of 1024 tokens. The technology stack includes Next.js, Joy UI, LangchainJS, PostgreSQL, Prisma, and Qdrant, inspired by the ChatGPT Retrieval Plugin.

auto-news
Auto-News is an automatic news aggregator tool that utilizes Large Language Models (LLM) to pull information from various sources such as Tweets, RSS feeds, YouTube videos, web articles, Reddit, and journal notes. The tool aims to help users efficiently read and filter content based on personal interests, providing a unified reading experience and organizing information effectively. It features feed aggregation with summarization, transcript generation for videos and articles, noise reduction, task organization, and deep dive topic exploration. The tool supports multiple LLM backends, offers weekly top-k aggregations, and can be deployed on Linux/MacOS using docker-compose or Kubernetes.
SemanticFinder
SemanticFinder is a frontend-only live semantic search tool that calculates embeddings and cosine similarity client-side using transformers.js and SOTA embedding models from Huggingface. It allows users to search through large texts like books with pre-indexed examples, customize search parameters, and offers data privacy by keeping input text in the browser. The tool can be used for basic search tasks, analyzing texts for recurring themes, and has potential integrations with various applications like wikis, chat apps, and personal history search. It also provides options for building browser extensions and future ideas for further enhancements and integrations.
1filellm
1filellm is a command-line data aggregation tool designed for LLM ingestion. It aggregates and preprocesses data from various sources into a single text file, facilitating the creation of information-dense prompts for large language models. The tool supports automatic source type detection, handling of multiple file formats, web crawling functionality, integration with Sci-Hub for research paper downloads, text preprocessing, and token count reporting. Users can input local files, directories, GitHub repositories, pull requests, issues, ArXiv papers, YouTube transcripts, web pages, Sci-Hub papers via DOI or PMID. The tool provides uncompressed and compressed text outputs, with the uncompressed text automatically copied to the clipboard for easy pasting into LLMs.
Agently-Daily-News-Collector
Agently Daily News Collector is an open-source project showcasing a workflow powered by the Agent ly AI application development framework. It allows users to generate news collections on various topics by inputting the field topic. The AI agents automatically perform the necessary tasks to generate a high-quality news collection saved in a markdown file. Users can edit settings in the YAML file, install Python and required packages, input their topic idea, and wait for the news collection to be generated. The process involves tasks like outlining, searching, summarizing, and preparing column data. The project dependencies include Agently AI Development Framework, duckduckgo-search, BeautifulSoup4, and PyYAM.


