
XLearning
AI on Hadoop
Stars: 1733
XLearning is a scheduling platform for big data and artificial intelligence, supporting various machine learning and deep learning frameworks. It runs on Hadoop Yarn and integrates frameworks like TensorFlow, MXNet, Caffe, Theano, PyTorch, Keras, XGBoost. XLearning offers scalability, compatibility, multiple deep learning framework support, unified data management based on HDFS, visualization display, and compatibility with code at native frameworks. It provides functions for data input/output strategies, container management, TensorBoard service, and resource usage metrics display. XLearning requires JDK >= 1.7 and Maven >= 3.3 for compilation, and deployment on CentOS 7.2 with Java >= 1.7 and Hadoop 2.6, 2.7, 2.8.
README:
Hbox is a convenient and efficient scheduling platform combined with the big data and artificial intelligence, support for a variety of machine learning, deep learning frameworks. Hbox is running on the Hadoop Yarn and has integrated deep learning frameworks such as TensorFlow, MXNet, Caffe, Theano, PyTorch, Keras, XGBoost. Hbox has the satisfactory scalability and compatibility.

There are three essential components in Hbox:
- Client: start and get the state of the application.
- ApplicationMaster(AM): the role for the internal schedule and lifecycle manager, including the input data distribution and containers management.
- Container: the actual executor of the application to start the progress of Worker or PS(Parameter Server), monitor and report the status of the progress to AM, and save the output, especially start the TensorBoard service for TensorFlow application.
Besides the distributed mode of TensorFlow and MXNet frameworks, Hbox supports the standalone mode of all deep learning frameworks such as Caffe, Theano, PyTorch. Moreover, Hbox allows the custom versions and multi-version of frameworks flexibly.
Hbox is enable to specify the input strategy for the input data --input by setting the --input-strategy parameter or hbox.input.strategy configuration. Hbox support three ways to read the HDFS input data:
- Download: AM traverses all files under the specified HDFS path and distributes data to workers in files. Each worker download files from the remote to local.
- Placeholder: The difference with Download mode is that AM send the related HDFS file list to workers. The process in worker read the data from HDFS directly.
- InputFormat: Integrated the InputFormat function of MapReduce, Hbox allows the user to specify any of the implementation of InputFormat for the input data. AM splits the input data and assigns fragments to the different workers. Each worker passes the assigned fragments through the pipeline to the execution progress.
Similar with the read strategy, Hbox allows to specify the output strategy for the output data --output by setting the --output-strategy parameter or hbox.output.strategy configuration. There are two kinds of result output modes:
- Upload: After the program finished, each worker upload the local directory of the output to specified HDFS path directly. The button, "Saved Model", on the web interface allows user to upload the intermediate result to remote during the execution.
- OutputFormat: Integrated the OutputFormat function of MapReduce, Hbox allows the user to specify any of the implementation of OutputFormat for saving the result to HDFS.
More detail see data management
The application interface can be divided into four parts:
- All Containers:display the container list and corresponding information, including the container host, container role, current state of container, start time, finish time, current progress.
- View TensorBoard:If set to start the service of TensorBoard when the type of application is TensorFlow, provide the link to enter the TensorBoard for real-time view.
- Save Model:If the application has the output, user can upload the intermediate output to specified HDFS path during the execution of the application through the button of "Save Model". After the upload finished, display the list of the intermediate saved path.
-
Worker Metrix:display the resource usage information metrics of each worker.
As shown below:
Except the automatic construction of the ClusterSpec at the distributed mode TensorFlow framework, the program at standalone mode TensorFlow and other deep learning frameworks can be executed at Hbox directly.
- jdk >= 1.7
- Maven >= 3.3
Run the following command in the root directory of the source code:
mvn package
After compiling, a distribution package named hbox-1.1-dist.tar.gz will be generated under target in the root directory.
Unpacking the distribution package, the following subdirectories will be generated under the root directory:
- bin: scripts for application commit
- lib: jars for Hbox and dependencies
- conf: configuration files
- sbin: scripts for history service
- data: data and files for examples
- examples: Hbox examples
- CentOS 7.2
- Java >= 1.7
- Hadoop = 2.6, 2.7, 2.8
- [optional] Dependent environment for deep learning frameworks at the cluster nodes, such as TensorFlow, numpy, Caffe.
Under the "conf" directory of the unpacking distribution package "$HBOX_HOME", configure the related files:
-
hbox-env.sh: set the environment variables, such as:
- JAVA_HOME
- HADOOP_CONF_DIR
-
hbox-site.xml: configure related properties. Note that the properties associated with the history service needs to be consistent with what has configured when the history service started.For more details, please see the Configuration part。
-
log4j.properties:configure the log level
- run
$HBOX_HOME/sbin/start-history-server.sh.
Use $HBOX_HOME/bin/xl-submit to submit the application to cluster in the Hbox client.
Here are the submit example for the TensorFlow application.
upload the "data" directory under the root of unpacking distribution package to HDFS
cd $HBOX_HOME
hadoop fs -put data /tmp/
cd $HBOX_HOME/examples/tensorflow
$HBOX_HOME/bin/xl-submit \
--app-type "tensorflow" \
--app-name "tf-demo" \
--input /tmp/data/tensorflow#data \
--output /tmp/tensorflow_model#model \
--files demo.py,dataDeal.py \
--launch-cmd "python demo.py --data_path=./data --save_path=./model --log_dir=./eventLog --training_epochs=10" \
--worker-memory 10G \
--worker-num 2 \
--worker-cores 3 \
--ps-memory 1G \
--ps-num 1 \
--ps-cores 2 \
--queue default \
The meaning of the parameters are as follows:
| Property Name | Meaning |
|---|---|
| app-name | application name as "tf-demo" |
| app-type | application type as "tensorflow" |
| input | input file, HDFS path is "/tmp/data/tensorflow" related to local dir "./data" |
| output | output file,HDFS path is "/tmp/tensorflow_model" related to local dir "./model" |
| files | application program and required local files, including demo.py, dataDeal.py |
| launch-cmd | execute command |
| worker-memory | amount of memory to use for the worker process is 10GB |
| worker-num | number of worker containers to use for the application is 2 |
| worker-cores | number of cores to use for the worker process is 3 |
| ps-memory | amount of memory to use for the ps process is 1GB |
| ps-num | number of ps containers to use for the application is 1 |
| ps-cores | number of cores to use for the ps process is 2 |
| queue | the queue that application submit to |
For more details, set the Submit Parameter part。
Hbox is designed, authored, reviewed and tested by the team at the github:
@Yuance Li, @Wen OuYang, @Runying Jia, @YuHan Jia, @Lei Wang
Mail: [email protected]
QQ群:588356340

For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for XLearning
Similar Open Source Tools

XLearning
XLearning is a scheduling platform for big data and artificial intelligence, supporting various machine learning and deep learning frameworks. It runs on Hadoop Yarn and integrates frameworks like TensorFlow, MXNet, Caffe, Theano, PyTorch, Keras, XGBoost. XLearning offers scalability, compatibility, multiple deep learning framework support, unified data management based on HDFS, visualization display, and compatibility with code at native frameworks. It provides functions for data input/output strategies, container management, TensorBoard service, and resource usage metrics display. XLearning requires JDK >= 1.7 and Maven >= 3.3 for compilation, and deployment on CentOS 7.2 with Java >= 1.7 and Hadoop 2.6, 2.7, 2.8.
langmanus
LangManus is a community-driven AI automation framework that combines language models with specialized tools for tasks like web search, crawling, and Python code execution. It implements a hierarchical multi-agent system with agents like Coordinator, Planner, Supervisor, Researcher, Coder, Browser, and Reporter. The framework supports LLM integration, search and retrieval tools, Python integration, workflow management, and visualization. LangManus aims to give back to the open-source community and welcomes contributions in various forms.
deep-research
Deep Research is a lightning-fast tool that uses powerful AI models to generate comprehensive research reports in just a few minutes. It leverages advanced 'Thinking' and 'Task' models, combined with an internet connection, to provide fast and insightful analysis on various topics. The tool ensures privacy by processing and storing all data locally. It supports multi-platform deployment, offers support for various large language models, web search functionality, knowledge graph generation, research history preservation, local and server API support, PWA technology, multi-key payload support, multi-language support, and is built with modern technologies like Next.js and Shadcn UI. Deep Research is open-source under the MIT License.
graphiti
Graphiti is a framework for building and querying temporally-aware knowledge graphs, tailored for AI agents in dynamic environments. It continuously integrates user interactions, structured and unstructured data, and external information into a coherent, queryable graph. The framework supports incremental data updates, efficient retrieval, and precise historical queries without complete graph recomputation, making it suitable for developing interactive, context-aware AI applications.
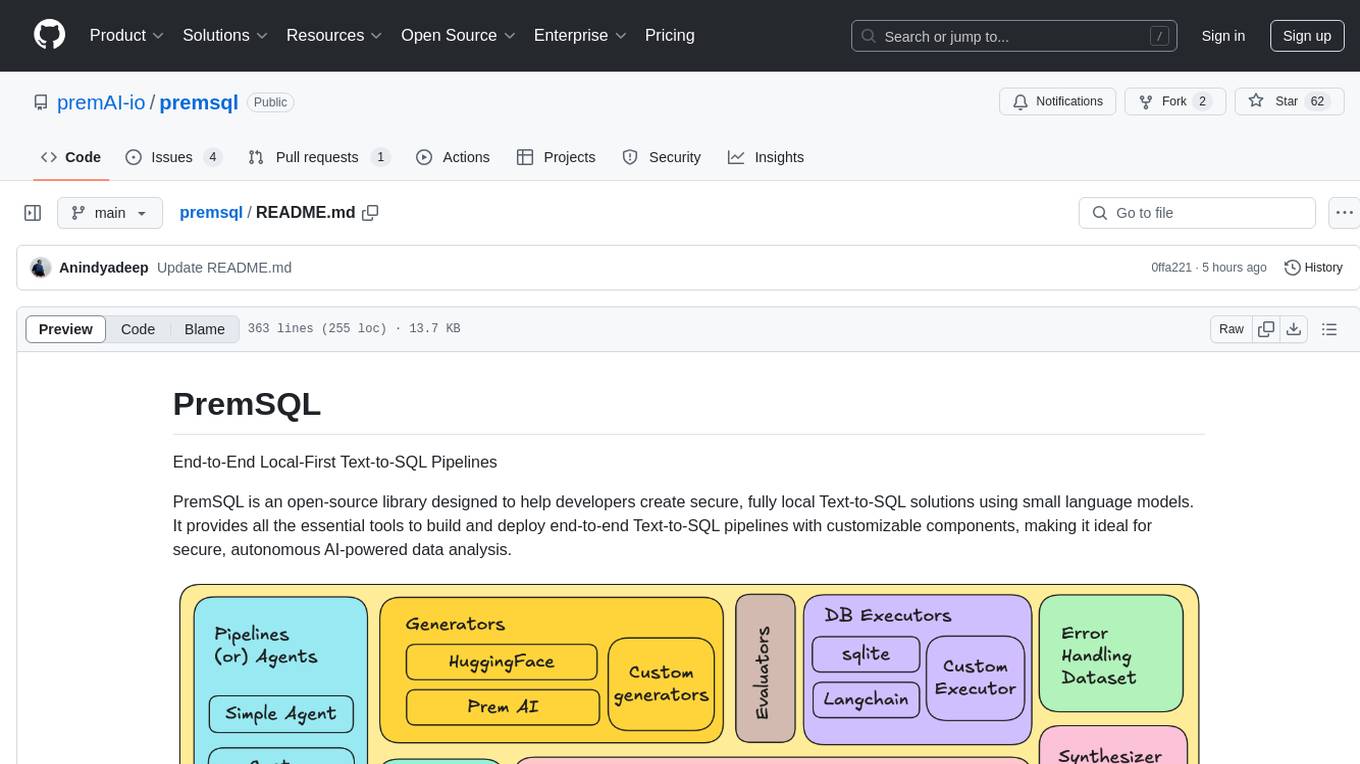
premsql
PremSQL is an open-source library designed to help developers create secure, fully local Text-to-SQL solutions using small language models. It provides essential tools for building and deploying end-to-end Text-to-SQL pipelines with customizable components, ideal for secure, autonomous AI-powered data analysis. The library offers features like Local-First approach, Customizable Datasets, Robust Executors and Evaluators, Advanced Generators, Error Handling and Self-Correction, Fine-Tuning Support, and End-to-End Pipelines. Users can fine-tune models, generate SQL queries from natural language inputs, handle errors, and evaluate model performance against predefined metrics. PremSQL is extendible for customization and private data usage.
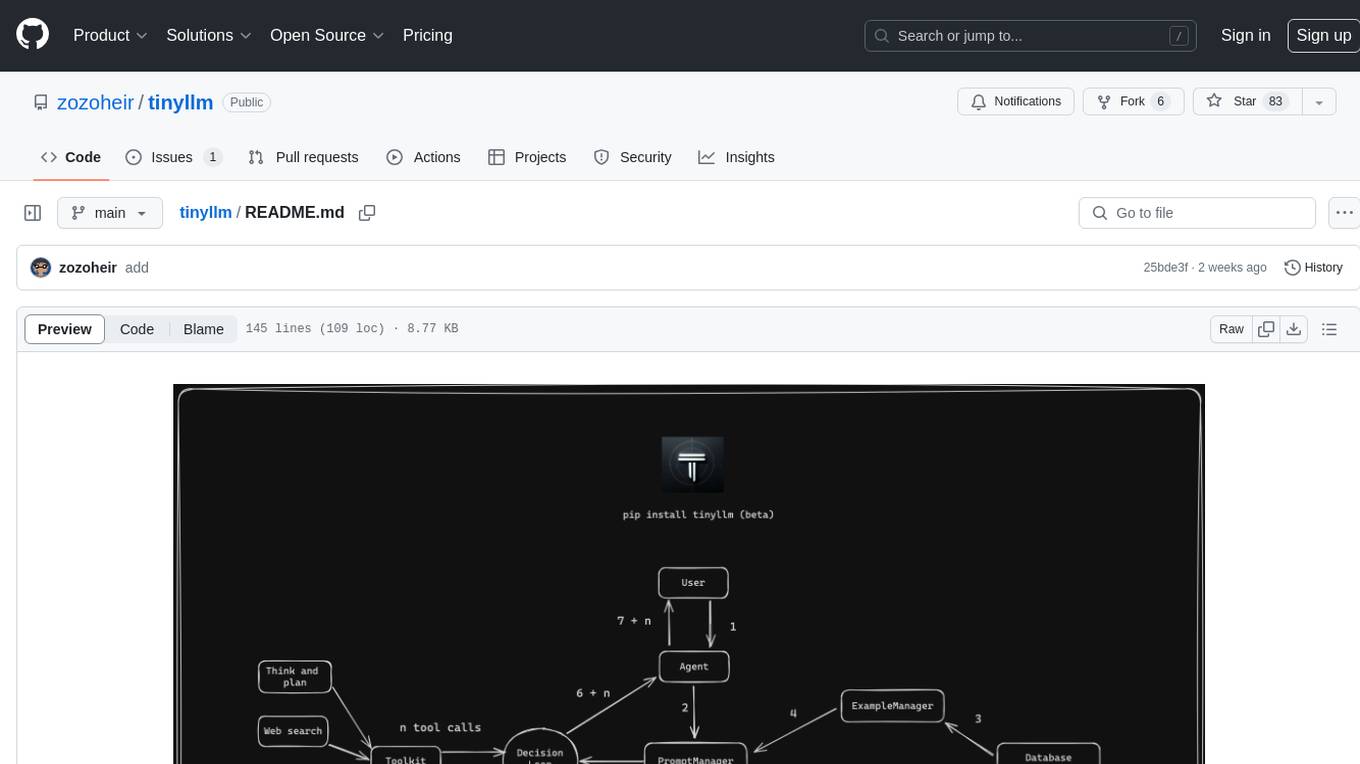
tinyllm
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
fastagency
FastAgency is an open-source framework designed to accelerate the transition from prototype to production for multi-agent AI workflows. It provides a unified programming interface for deploying agentic workflows written in AG2 agentic framework in both development and productional settings. With features like seamless external API integration, a Tester Class for continuous integration, and a Command-Line Interface (CLI) for orchestration, FastAgency streamlines the deployment process, saving time and effort while maintaining flexibility and performance. Whether orchestrating complex AI agents or integrating external APIs, FastAgency helps users quickly transition from concept to production, reducing development cycles and optimizing multi-agent systems.
fastagency
FastAgency is a powerful tool that leverages the AutoGen framework to quickly build applications with multi-agent workflows. It supports various interfaces like ConsoleUI and MesopUI, allowing users to create interactive applications. The tool enables defining workflows between agents, such as students and teachers, and summarizing conversations. FastAgency aims to expand its capabilities by integrating with additional agentic frameworks like CrewAI, providing more options for workflow definition and AI tool integration.
RooFlow
RooFlow is a VS Code extension that enhances AI-assisted development by providing persistent project context and optimized mode interactions. It reduces token consumption and streamlines workflow by integrating Architect, Code, Test, Debug, and Ask modes. The tool simplifies setup, offers real-time updates, and provides clearer instructions through YAML-based rule files. It includes components like Memory Bank, System Prompts, VS Code Integration, and Real-time Updates. Users can install RooFlow by downloading specific files, placing them in the project structure, and running an insert-variables script. They can then start a chat, select a mode, interact with Roo, and use the 'Update Memory Bank' command for synchronization. The Memory Bank structure includes files for active context, decision log, product context, progress tracking, and system patterns. RooFlow features persistent context, real-time updates, mode collaboration, and reduced token consumption.
clearml-server
ClearML Server is a backend service infrastructure for ClearML, facilitating collaboration and experiment management. It includes a web app, RESTful API, and file server for storing images and models. Users can deploy ClearML Server using Docker, AWS EC2 AMI, or Kubernetes. The system design supports single IP or sub-domain configurations with specific open ports. ClearML-Agent Services container allows launching long-lasting jobs and various use cases like auto-scaler service, controllers, optimizer, and applications. Advanced functionality includes web login authentication and non-responsive experiments watchdog. Upgrading ClearML Server involves stopping containers, backing up data, downloading the latest docker-compose.yml file, configuring ClearML-Agent Services, and spinning up docker containers. Community support is available through ClearML FAQ, Stack Overflow, GitHub issues, and email contact.
Memori
Memori is a memory fabric designed for enterprise AI that seamlessly integrates into existing software and infrastructure. It is agnostic to LLM, datastore, and framework, providing support for major foundational models and databases. With features like vectorized memories, in-memory semantic search, and a knowledge graph, Memori simplifies the process of attributing LLM interactions and managing sessions. It offers Advanced Augmentation for enhancing memories at different levels and supports various platforms, frameworks, database integrations, and datastores. Memori is designed to reduce development overhead and provide efficient memory management for AI applications.
tinystruct
Tinystruct is a simple Java framework designed for easy development with better performance. It offers a modern approach with features like CLI and web integration, built-in lightweight HTTP server, minimal configuration philosophy, annotation-based routing, and performance-first architecture. Developers can focus on real business logic without dealing with unnecessary complexities, making it transparent, predictable, and extensible.
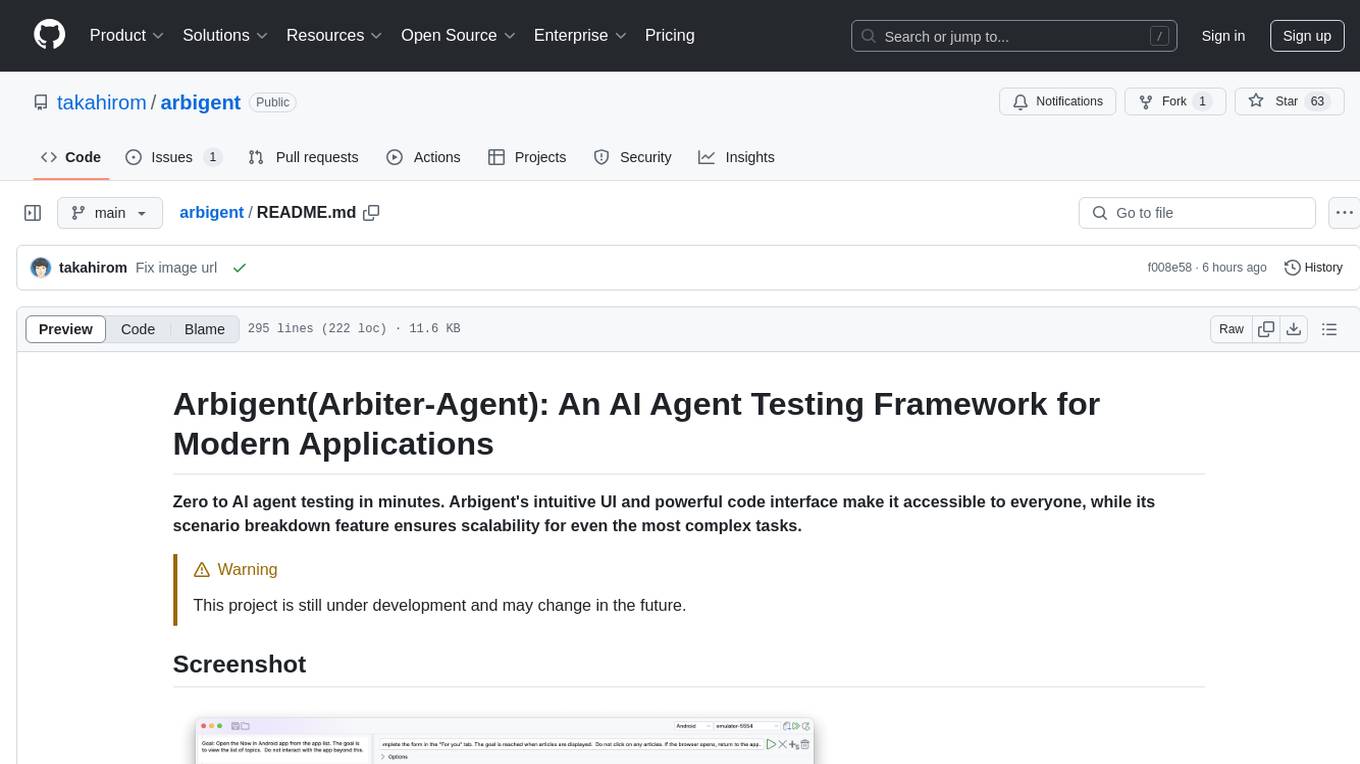
arbigent
Arbigent (Arbiter-Agent) is an AI agent testing framework designed to make AI agent testing practical for modern applications. It addresses challenges faced by traditional UI testing frameworks and AI agents by breaking down complex tasks into smaller, dependent scenarios. The framework is customizable for various AI providers, operating systems, and form factors, empowering users with extensive customization capabilities. Arbigent offers an intuitive UI for scenario creation and a powerful code interface for seamless test execution. It supports multiple form factors, optimizes UI for AI interaction, and is cost-effective by utilizing models like GPT-4o mini. With a flexible code interface and open-source nature, Arbigent aims to revolutionize AI agent testing in modern applications.
llm-d-inference-sim
The `llm-d-inference-sim` is a lightweight, configurable, and real-time simulator designed to mimic the behavior of vLLM without the need for GPUs or running heavy models. It operates as an OpenAI-compliant server, allowing developers to test clients, schedulers, and infrastructure using realistic request-response cycles, token streaming, and latency patterns. The simulator offers modes of operation, response generation from predefined text or real datasets, latency simulation, tokenization options, LoRA management, KV cache simulation, failure injection, and deployment options for standalone or Kubernetes testing. It supports a subset of standard vLLM Prometheus metrics for observability.
RainbowGPT
RainbowGPT is a versatile tool that offers a range of functionalities, including Stock Analysis for financial decision-making, MySQL Management for database navigation, and integration of AI technologies like GPT-4 and ChatGlm3. It provides a user-friendly interface suitable for all skill levels, ensuring seamless information flow and continuous expansion of emerging technologies. The tool enhances adaptability, creativity, and insight, making it a valuable asset for various projects and tasks.
For similar tasks

XLearning
XLearning is a scheduling platform for big data and artificial intelligence, supporting various machine learning and deep learning frameworks. It runs on Hadoop Yarn and integrates frameworks like TensorFlow, MXNet, Caffe, Theano, PyTorch, Keras, XGBoost. XLearning offers scalability, compatibility, multiple deep learning framework support, unified data management based on HDFS, visualization display, and compatibility with code at native frameworks. It provides functions for data input/output strategies, container management, TensorBoard service, and resource usage metrics display. XLearning requires JDK >= 1.7 and Maven >= 3.3 for compilation, and deployment on CentOS 7.2 with Java >= 1.7 and Hadoop 2.6, 2.7, 2.8.
parllama
PAR LLAMA is a Text UI application for managing and using LLMs, designed with Textual and Rich and PAR AI Core. It runs on major OS's including Windows, Windows WSL, Mac, and Linux. Supports Dark and Light mode, custom themes, and various workflows like Ollama chat, image chat, and OpenAI provider chat. Offers features like custom prompts, themes, environment variables configuration, and remote instance connection. Suitable for managing and using LLMs efficiently.
mcp-ts-template
The MCP TypeScript Server Template is a production-grade framework for building powerful and scalable Model Context Protocol servers with TypeScript. It features built-in observability, declarative tooling, robust error handling, and a modular, DI-driven architecture. The template is designed to be AI-agent-friendly, providing detailed rules and guidance for developers to adhere to best practices. It enforces architectural principles like 'Logic Throws, Handler Catches' pattern, full-stack observability, declarative components, and dependency injection for decoupling. The project structure includes directories for configuration, container setup, server resources, services, storage, utilities, tests, and more. Configuration is done via environment variables, and key scripts are available for development, testing, and publishing to the MCP Registry.
receipt-ocr
An efficient OCR engine for receipt image processing, providing a comprehensive solution for Optical Character Recognition (OCR) on receipt images. The repository includes a dedicated Tesseract OCR module and a general receipt processing package using LLMs. Users can extract structured data from receipts, configure environment variables for multiple LLM providers, process receipts using CLI or programmatically in Python, and run the OCR engine as a Docker web service. The project also offers direct OCR capabilities using Tesseract and provides troubleshooting tips, contribution guidelines, and license information under the MIT license.
For similar jobs
llmops-promptflow-template
LLMOps with Prompt flow is a template and guidance for building LLM-infused apps using Prompt flow. It provides centralized code hosting, lifecycle management, variant and hyperparameter experimentation, A/B deployment, many-to-many dataset/flow relationships, multiple deployment targets, comprehensive reporting, BYOF capabilities, configuration-based development, local prompt experimentation and evaluation, endpoint testing, and optional Human-in-loop validation. The tool is customizable to suit various application needs.
azure-search-vector-samples
This repository provides code samples in Python, C#, REST, and JavaScript for vector support in Azure AI Search. It includes demos for various languages showcasing vectorization of data, creating indexes, and querying vector data. Additionally, it offers tools like Azure AI Search Lab for experimenting with AI-enabled search scenarios in Azure and templates for deploying custom chat-with-your-data solutions. The repository also features documentation on vector search, hybrid search, creating and querying vector indexes, and REST API references for Azure AI Search and Azure OpenAI Service.
geti-sdk
The Intel® Geti™ SDK is a python package that enables teams to rapidly develop AI models by easing the complexities of model development and enhancing collaboration between teams. It provides tools to interact with an Intel® Geti™ server via the REST API, allowing for project creation, downloading, uploading, deploying for local inference with OpenVINO, setting project and model configuration, launching and monitoring training jobs, and media upload and prediction. The SDK also includes tutorial-style Jupyter notebooks demonstrating its usage.

booster
Booster is a powerful inference accelerator designed for scaling large language models within production environments or for experimental purposes. It is built with performance and scaling in mind, supporting various CPUs and GPUs, including Nvidia CUDA, Apple Metal, and OpenCL cards. The tool can split large models across multiple GPUs, offering fast inference on machines with beefy GPUs. It supports both regular FP16/FP32 models and quantised versions, along with popular LLM architectures. Additionally, Booster features proprietary Janus Sampling for code generation and non-English languages.

xFasterTransformer
xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for Large Language Models (LLMs) on the X86 platform, providing high performance and scalability for inference on mainstream LLM models. It offers C++ and Python APIs for easy integration, along with example codes and benchmark scripts. Users can prepare models in a different format, convert them, and use the APIs for tasks like encoding input prompts, generating token ids, and serving inference requests. The tool supports various data types and models, and can run in single or multi-rank modes using MPI. A web demo based on Gradio is available for popular LLM models like ChatGLM and Llama2. Benchmark scripts help evaluate model inference performance quickly, and MLServer enables serving with REST and gRPC interfaces.
amazon-transcribe-live-call-analytics
The Amazon Transcribe Live Call Analytics (LCA) with Agent Assist Sample Solution is designed to help contact centers assess and optimize caller experiences in real time. It leverages Amazon machine learning services like Amazon Transcribe, Amazon Comprehend, and Amazon SageMaker to transcribe and extract insights from contact center audio. The solution provides real-time supervisor and agent assist features, integrates with existing contact centers, and offers a scalable, cost-effective approach to improve customer interactions. The end-to-end architecture includes features like live call transcription, call summarization, AI-powered agent assistance, and real-time analytics. The solution is event-driven, ensuring low latency and seamless processing flow from ingested speech to live webpage updates.
ai-lab-recipes
This repository contains recipes for building and running containerized AI and LLM applications with Podman. It provides model servers that serve machine-learning models via an API, allowing developers to quickly prototype new AI applications locally. The recipes include components like model servers and AI applications for tasks such as chat, summarization, object detection, etc. Images for sample applications and models are available in `quay.io`, and bootable containers for AI training on Linux OS are enabled.

XLearning
XLearning is a scheduling platform for big data and artificial intelligence, supporting various machine learning and deep learning frameworks. It runs on Hadoop Yarn and integrates frameworks like TensorFlow, MXNet, Caffe, Theano, PyTorch, Keras, XGBoost. XLearning offers scalability, compatibility, multiple deep learning framework support, unified data management based on HDFS, visualization display, and compatibility with code at native frameworks. It provides functions for data input/output strategies, container management, TensorBoard service, and resource usage metrics display. XLearning requires JDK >= 1.7 and Maven >= 3.3 for compilation, and deployment on CentOS 7.2 with Java >= 1.7 and Hadoop 2.6, 2.7, 2.8.




