
xFasterTransformer
None
Stars: 247

xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for Large Language Models (LLMs) on the X86 platform, providing high performance and scalability for inference on mainstream LLM models. It offers C++ and Python APIs for easy integration, along with example codes and benchmark scripts. Users can prepare models in a different format, convert them, and use the APIs for tasks like encoding input prompts, generating token ids, and serving inference requests. The tool supports various data types and models, and can run in single or multi-rank modes using MPI. A web demo based on Gradio is available for popular LLM models like ChatGLM and Llama2. Benchmark scripts help evaluate model inference performance quickly, and MLServer enables serving with REST and gRPC interfaces.
README:
xFasterTransformer is an exceptionally optimized solution for large language models (LLM) on the X86 platform, which is similar to FasterTransformer on the GPU platform. xFasterTransformer is able to operate in distributed mode across multiple sockets and nodes to support inference on larger models. Additionally, it provides both C++ and Python APIs, spanning from high-level to low-level interfaces, making it easy to adopt and integrate.
- xFasterTransformer
Large Language Models (LLMs) develops very fast and are more widely used in many AI scenarios. xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for LLM inference using the mainstream and popular LLM models on Xeon. xFasterTransformer fully leverages the hardware capabilities of Xeon platforms to achieve the high performance and high scalability of LLM inference both on single socket and multiple sockets/multiple nodes.
xFasterTransformer provides a series of APIs, both of C++ and Python, for end users to integrate xFasterTransformer into their own solutions or services directly. Many kinds of example codes are also provided to demonstrate the usage. Benchmark codes and scripts are provided for users to show the performance. Web demos for popular LLM models are also provided.
| Models | Framework | Distribution | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PyTorch | C++ | ||
| ChatGLM | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| ChatGLM2 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| ChatGLM3 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Llama | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Llama2 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Llama3 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Baichuan | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| QWen | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| QWen2 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| SecLLM(YaRN-Llama) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Opt | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Deepseek-coder | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| gemma | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| gemma-1.1 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| codegemma | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
- FP16
- BF16
- INT8
- W8A8
- INT4
- NF4
- BF16_FP16
- BF16_INT8
- BF16_W8A8
- BF16_INT4
- BF16_NF4
- W8A8_INT8
- W8A8_int4
- W8A8_NF4
xFasterTransformer Documents and Wiki provides the following resources:
- An introduction to xFasterTransformer.
- Comprehensive API references for both high-level and low-level interfaces in C++ and PyTorch.
- Practical API usage examples for xFasterTransformer in both C++ and PyTorch.
pip install xfastertransformerdocker pull intel/xfastertransformer:latestRun the docker with the command (Assume model files are in /data/ directory):
docker run -it \
--name xfastertransformer \
--privileged \
--shm-size=16g \
-v /data/:/data/ \
-e "http_proxy=$http_proxy" \
-e "https_proxy=$https_proxy" \
intel/xfastertransformer:latestNotice!!!: Please enlarge --shm-size if bus error occurred while running in the multi-ranks mode . The default docker limits the shared memory size to 64MB and our implementation uses many shared memories to achieve a better performance.
-
PyTorch v2.0 (When using the PyTorch API, it's required, but it's not needed when using the C++ API.)
pip install torch --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
-
For GPU, xFT needs ABI=1 from torch==2.0.1+cpu.cxx11.abi in torch-whl-list due to DPC++ need ABI=1.
Please install libnuma package:
- CentOS: yum install libnuma-devel
- Ubuntu: apt-get install libnuma-dev
- Using 'CMake'
# Build xFasterTransformer git clone https://github.com/intel/xFasterTransformer.git xFasterTransformer cd xFasterTransformer git checkout <latest-tag> # Please make sure torch is installed when run python example mkdir build && cd build cmake .. make -j
- Using
python setup.py# Build xFasterTransformer library and C++ example. python setup.py build # Install xFasterTransformer into pip environment. # Notice: Run `python setup.py build` before installation! python setup.py install
xFasterTransformer supports a different model format from Huggingface, but it's compatible with FasterTransformer's format.
-
Download the huggingface format model firstly.
-
After that, convert the model into xFasterTransformer format by using model convert module in xfastertransformer. If output directory is not provided, converted model will be placed into
${HF_DATASET_DIR}-xft.python -c 'import xfastertransformer as xft; xft.LlamaConvert().convert("${HF_DATASET_DIR}","${OUTPUT_DIR}")'PS: Due to the potential compatibility issues between the model file and the
transformersversion, please select the appropriatetransformersversion.Supported model convert list:
- LlamaConvert
- YiConvert
- GemmaConvert
- ChatGLMConvert
- ChatGLM2Convert
- ChatGLM3Convert
- OPTConvert
- BaichuanConvert
- QwenConvert
- Qwen2Convert
- DeepseekConvert
For more details, please see API document and examples.
Firstly, please install the dependencies.
- Python dependencies
PS: Due to the potential compatibility issues between the model file and the
pip install -r requirements.txt
transformersversion, please select the appropriatetransformersversion. - oneCCL (For multi ranks)
Install oneCCL and setup the environment. Please refer to Prepare Environment.
xFasterTransformer's Python API is similar to transformers and also supports transformers's streamer to achieve the streaming output. In the example, we use transformers to encode input prompts to token ids.
import xfastertransformer
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, TextStreamer
# Assume huggingface model dir is `/data/chatglm-6b-hf` and converted model dir is `/data/chatglm-6b-xft`.
MODEL_PATH="/data/chatglm-6b-xft"
TOKEN_PATH="/data/chatglm-6b-hf"
INPUT_PROMPT = "Once upon a time, there existed a little girl who liked to have adventures."
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(TOKEN_PATH, use_fast=False, padding_side="left", trust_remote_code=True)
streamer = TextStreamer(tokenizer, skip_special_tokens=True, skip_prompt=False)
input_ids = tokenizer(INPUT_PROMPT, return_tensors="pt", padding=False).input_ids
model = xfastertransformer.AutoModel.from_pretrained(MODEL_PATH, dtype="bf16")
generated_ids = model.generate(input_ids, max_length=200, streamer=streamer)SentencePiece can be used to tokenizer and detokenizer text.
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include "xfastertransformer.h"
// ChatGLM token ids for prompt "Once upon a time, there existed a little girl who liked to have adventures."
std::vector<int> input(
{3393, 955, 104, 163, 6, 173, 9166, 104, 486, 2511, 172, 7599, 103, 127, 17163, 7, 130001, 130004});
// Assume converted model dir is `/data/chatglm-6b-xft`.
xft::AutoModel model("/data/chatglm-6b-xft", xft::DataType::bf16);
model.config(/*max length*/ 100, /*num beams*/ 1);
model.input(/*input token ids*/ input, /*batch size*/ 1);
while (!model.isDone()) {
std::vector<int> nextIds = model.generate();
}
std::vector<int> result = model.finalize();
for (auto id : result) {
std::cout << id << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;Recommend preloading libiomp5.so to get a better performance. libiomp5.so file will be in 3rdparty/mklml/lib directory after building xFasterTransformer successfully.
FasterTransformer will automatically check the MPI environment, or you can use the SINGLE_INSTANCE=1 environment variable to forcefully deactivate MPI.
Use MPI to run in the multi-ranks mode, please install oneCCL firstly.
-
- If you have built xfastertransformer from source, oneCCL is installed in 3rdparty when compilation.
source ./3rdparty/oneccl/build/_install/env/setvars.sh -
[Recommended] Use provided scripts to build it from source code.
cd 3rdparty sh prepare_oneccl.sh source ./oneccl/build/_install/env/setvars.sh
- Install oneCCL through installing Intel® oneAPI Base Toolkit.(Notice:It is recommended to use versions 2023.x and below.) And source the enviroment by:
source /opt/intel/oneapi/setvars.sh
- If you have built xfastertransformer from source, oneCCL is installed in 3rdparty when compilation.
-
Here is a example on local.
OMP_NUM_THREADS=48 LD_PRELOAD=libiomp5.so mpirun \ -n 1 numactl -N 0 -m 0 ${RUN_WORKLOAD} : \ -n 1 numactl -N 1 -m 1 ${RUN_WORKLOAD}
For more details, please refer to examples.
model.rank can get the process's rank, model.rank == 0 is the Master.
For Slaves, after loading the model, the only thing needs to do is model.generate(). The input and generation configuration will be auto synced.
model = xfastertransformer.AutoModel.from_pretrained("/data/chatglm-6b-xft", dtype="bf16")
# Slave
while True:
model.generate()model.getRank() can get the process's rank, model.getRank() == 0 is the Master.
For Slaves, any value can be input to model.config() and model.input since Master's value will be synced.
xft::AutoModel model("/data/chatglm-6b-xft", xft::DataType::bf16);
// Slave
while (1) {
model.config();
std::vector<int> input_ids;
model.input(/*input token ids*/ input_ids, /*batch size*/ 1);
while (!model.isDone()) {
model.generate();
}
}A web demo based on Gradio is provided in repo. Now support ChatGLM, ChatGLM2 and Llama2 models.
- Perpare the model.
- Install the dependencies
PS: Due to the potential compatibility issues between the model file and the
pip install -r examples/web_demo/requirements.txt
transformersversion, please select the appropriatetransformersversion. - Run the script corresponding to the model. After the web server started, open the output URL in the browser to use the demo. Please specify the paths of model and tokenizer directory, and data type.
transformer's tokenizer is used to encode and decode text so${TOKEN_PATH}means the huggingface model directory. This demo also support multi-rank.
# Recommend preloading `libiomp5.so` to get a better performance.
# `libiomp5.so` file will be in `3rdparty/mklml/lib` directory after build xFasterTransformer.
LD_PRELOAD=libiomp5.so python examples/web_demo/ChatGLM.py \
--dtype=bf16 \
--token_path=${TOKEN_PATH} \
--model_path=${MODEL_PATH}A example serving of MLServer is provided which supports REST and gRPC interface and adaptive batching feature to group inference requests together on the fly.
Benchmark scripts are provided to get the model inference performance quickly.
- Prepare the model.
- Install the dependencies, including oneCCL and python dependencies.
- Enter the
benchmarkfolder and runrun_benchmark.sh. Please refer to Benchmark README for more information.
Notes!!!: The system and CPU configuration may be different. For the best performance, please try to modify OMP_NUM_THREADS, datatype and the memory nodes number (check the memory nodes using numactl -H) according to your test environment.
- xFasterTransformer email: [email protected]
- xFasterTransformer wechat
-
Q: Can xFasterTransformer run on a Intel® Core™ CPU?
A: No. xFasterTransformer requires support for the AMX and AVX512 instruction sets, which are not available on Intel® Core™ CPUs. -
Q: Can xFasterTransformer run on the Windows system?
A: There is no native support for Windows, and all compatibility tests are only conducted on Linux, so Linux is recommended. -
Q: Why does the program freeze or exit with errors when running in multi-rank mode after installing the latest version of oneCCL through oneAPI?
A: Please try downgrading oneAPI to version 2023.x or below, or use the provided script to install oneCCL from source code. -
Q: Why does running the program using two CPU sockets result in much lower performance compared to running on a single CPU socket?
A: Running in this way causes the program to engage in many unnecessary cross-socket communications, significantly impacting performance. If there is a need for cross-socket deployment, consider running in a multi-rank mode with one rank on each socket. -
Q:The performance is normal when running in a single rank, but why is the performance very slow and the CPU utilization very low when using MPI to run multiple ranks?
A:This is because the program launched through MPI readsOMP_NUM_THREADS=1, which cannot correctly retrieve the appropriate value from the environment. It is necessary to manually set the value ofOMP_NUM_THREADSbased on the actual situation. -
Q: Why do I still encounter errors when converting already supported models?
A: Try downgradingtransformerto an appropriate version, such as the version specified in therequirements.txt. This is because different versions of Transformer may change the names of certain variables.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for xFasterTransformer
Similar Open Source Tools

xFasterTransformer
xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for Large Language Models (LLMs) on the X86 platform, providing high performance and scalability for inference on mainstream LLM models. It offers C++ and Python APIs for easy integration, along with example codes and benchmark scripts. Users can prepare models in a different format, convert them, and use the APIs for tasks like encoding input prompts, generating token ids, and serving inference requests. The tool supports various data types and models, and can run in single or multi-rank modes using MPI. A web demo based on Gradio is available for popular LLM models like ChatGLM and Llama2. Benchmark scripts help evaluate model inference performance quickly, and MLServer enables serving with REST and gRPC interfaces.
MockingBird
MockingBird is a toolbox designed for Mandarin speech synthesis using PyTorch. It supports multiple datasets such as aidatatang_200zh, magicdata, aishell3, and data_aishell. The toolbox can run on Windows, Linux, and M1 MacOS, providing easy and effective speech synthesis with pretrained encoder/vocoder models. It is webserver ready for remote calling. Users can train their own models or use existing ones for the encoder, synthesizer, and vocoder. The toolbox offers a demo video and detailed setup instructions for installation and model training.

HuixiangDou
HuixiangDou is a **group chat** assistant based on LLM (Large Language Model). Advantages: 1. Design a two-stage pipeline of rejection and response to cope with group chat scenario, answer user questions without message flooding, see arxiv2401.08772 2. Low cost, requiring only 1.5GB memory and no need for training 3. Offers a complete suite of Web, Android, and pipeline source code, which is industrial-grade and commercially viable Check out the scenes in which HuixiangDou are running and join WeChat Group to try AI assistant inside. If this helps you, please give it a star ⭐
evalchemy
Evalchemy is a unified and easy-to-use toolkit for evaluating language models, focusing on post-trained models. It integrates multiple existing benchmarks such as RepoBench, AlpacaEval, and ZeroEval. Key features include unified installation, parallel evaluation, simplified usage, and results management. Users can run various benchmarks with a consistent command-line interface and track results locally or integrate with a database for systematic tracking and leaderboard submission.

ragflow
RAGFlow is an open-source Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) engine that combines deep document understanding with Large Language Models (LLMs) to provide accurate question-answering capabilities. It offers a streamlined RAG workflow for businesses of all sizes, enabling them to extract knowledge from unstructured data in various formats, including Word documents, slides, Excel files, images, and more. RAGFlow's key features include deep document understanding, template-based chunking, grounded citations with reduced hallucinations, compatibility with heterogeneous data sources, and an automated and effortless RAG workflow. It supports multiple recall paired with fused re-ranking, configurable LLMs and embedding models, and intuitive APIs for seamless integration with business applications.

LEANN
LEANN is an innovative vector database that democratizes personal AI, transforming your laptop into a powerful RAG system that can index and search through millions of documents using 97% less storage than traditional solutions without accuracy loss. It achieves this through graph-based selective recomputation and high-degree preserving pruning, computing embeddings on-demand instead of storing them all. LEANN allows semantic search of file system, emails, browser history, chat history, codebase, or external knowledge bases on your laptop with zero cloud costs and complete privacy. It is a drop-in semantic search MCP service fully compatible with Claude Code, enabling intelligent retrieval without changing your workflow.
UCAgent
UCAgent is an AI-powered automated UT verification agent for chip design. It automates chip verification workflow, supports functional and code coverage analysis, ensures consistency among documentation, code, and reports, and collaborates with mainstream Code Agents via MCP protocol. It offers three intelligent interaction modes and requires Python 3.11+, Linux/macOS OS, 4GB+ memory, and access to an AI model API. Users can clone the repository, install dependencies, configure qwen, and start verification. UCAgent supports various verification quality improvement options and basic operations through TUI shortcuts and stage color indicators. It also provides documentation build and preview using MkDocs, PDF manual build using Pandoc + XeLaTeX, and resources for further help and contribution.
llmfit
llmfit is a terminal tool designed to optimize LLM models for your system's RAM, CPU, and GPU. It detects your hardware, scores models based on quality, speed, fit, and context, and recommends models that will run well on your machine. It supports multi-GPU setups, MoE architectures, dynamic quantization selection, and speed estimation. The tool provides an interactive TUI and a classic CLI mode for ease of use. It includes a database of 94 models from 30 providers sourced from the HuggingFace API, with memory requirements computed from parameter counts across a quantization hierarchy. llmfit uses multi-dimensional scoring to rank models and estimates speed based on backend-specific constants. It also offers dynamic quantization selection to fit models to available memory efficiently.
RepairAgent
RepairAgent is an autonomous LLM-based agent for automated program repair targeting the Defects4J benchmark. It uses an LLM-driven loop to localize, analyze, and fix Java bugs. The tool requires Docker, VS Code with Dev Containers extension, OpenAI API key, disk space of ~40 GB, and internet access. Users can get started with RepairAgent using either VS Code Dev Container or Docker Image. Running RepairAgent involves checking out the buggy project version, autonomous bug analysis, fix candidate generation, and testing against the project's test suite. Users can configure hyperparameters for budget control, repetition handling, commands limit, and external fix strategy. The tool provides output structure, experiment overview, individual analysis scripts, and data on fixed bugs from the Defects4J dataset.
plexe
Plexe is a tool that allows users to create machine learning models by describing them in plain language. Users can explain their requirements, provide a dataset, and the AI-powered system will build a fully functional model through an automated agentic approach. It supports multiple AI agents and model building frameworks like XGBoost, CatBoost, and Keras. Plexe also provides Docker images with pre-configured environments, YAML configuration for customization, and support for multiple LiteLLM providers. Users can visualize experiment results using the built-in Streamlit dashboard and extend Plexe's functionality through custom integrations.
iloom-cli
iloom is a tool designed to streamline AI-assisted development by focusing on maintaining alignment between human developers and AI agents. It treats context as a first-class concern, persisting AI reasoning in issue comments rather than temporary chats. The tool allows users to collaborate with AI agents in an isolated environment, switch between complex features without losing context, document AI decisions publicly, and capture key insights and lessons learned from AI sessions. iloom is not just a tool for managing git worktrees, but a control plane for maintaining alignment between users and their AI assistants.
uLoopMCP
uLoopMCP is a Unity integration tool designed to let AI drive your Unity project forward with minimal human intervention. It provides a 'self-hosted development loop' where an AI can compile, run tests, inspect logs, and fix issues using tools like compile, run-tests, get-logs, and clear-console. It also allows AI to operate the Unity Editor itself—creating objects, calling menu items, inspecting scenes, and refining UI layouts from screenshots via tools like execute-dynamic-code, execute-menu-item, and capture-window. The tool enables AI-driven development loops to run autonomously inside existing Unity projects.
DB-GPT
DB-GPT is a personal database administrator that can solve database problems by reading documents, using various tools, and writing analysis reports. It is currently undergoing an upgrade. **Features:** * **Online Demo:** * Import documents into the knowledge base * Utilize the knowledge base for well-founded Q&A and diagnosis analysis of abnormal alarms * Send feedbacks to refine the intermediate diagnosis results * Edit the diagnosis result * Browse all historical diagnosis results, used metrics, and detailed diagnosis processes * **Language Support:** * English (default) * Chinese (add "language: zh" in config.yaml) * **New Frontend:** * Knowledgebase + Chat Q&A + Diagnosis + Report Replay * **Extreme Speed Version for localized llms:** * 4-bit quantized LLM (reducing inference time by 1/3) * vllm for fast inference (qwen) * Tiny LLM * **Multi-path extraction of document knowledge:** * Vector database (ChromaDB) * RESTful Search Engine (Elasticsearch) * **Expert prompt generation using document knowledge** * **Upgrade the LLM-based diagnosis mechanism:** * Task Dispatching -> Concurrent Diagnosis -> Cross Review -> Report Generation * Synchronous Concurrency Mechanism during LLM inference * **Support monitoring and optimization tools in multiple levels:** * Monitoring metrics (Prometheus) * Flame graph in code level * Diagnosis knowledge retrieval (dbmind) * Logical query transformations (Calcite) * Index optimization algorithms (for PostgreSQL) * Physical operator hints (for PostgreSQL) * Backup and Point-in-time Recovery (Pigsty) * **Continuously updated papers and experimental reports** This project is constantly evolving with new features. Don't forget to star ⭐ and watch 👀 to stay up to date.
factorio-learning-environment
Factorio Learning Environment is an open source framework designed for developing and evaluating LLM agents in the game of Factorio. It provides two settings: Lab-play with structured tasks and Open-play for building large factories. Results show limitations in spatial reasoning and automation strategies. Agents interact with the environment through code synthesis, observation, action, and feedback. Tools are provided for game actions and state representation. Agents operate in episodes with observation, planning, and action execution. Tasks specify agent goals and are implemented in JSON files. The project structure includes directories for agents, environment, cluster, data, docs, eval, and more. A database is used for checkpointing agent steps. Benchmarks show performance metrics for different configurations.
AirConnect-Synology
AirConnect-Synology is a minimal Synology package that allows users to use AirPlay to stream to UPnP/Sonos & Chromecast devices that do not natively support AirPlay. It is compatible with DSM 7.0 and DSM 7.1, and provides detailed information on installation, configuration, supported devices, troubleshooting, and more. The package automates the installation and usage of AirConnect on Synology devices, ensuring compatibility with various architectures and firmware versions. Users can customize the configuration using the airconnect.conf file and adjust settings for specific speakers like Sonos, Bose SoundTouch, and Pioneer/Phorus/Play-Fi.
aim
Aim is a command-line tool for downloading and uploading files with resume support. It supports various protocols including HTTP, FTP, SFTP, SSH, and S3. Aim features an interactive mode for easy navigation and selection of files, as well as the ability to share folders over HTTP for easy access from other devices. Additionally, it offers customizable progress indicators and output formats, and can be integrated with other commands through piping. Aim can be installed via pre-built binaries or by compiling from source, and is also available as a Docker image for platform-independent usage.
For similar tasks
Ollama-Colab-Integration
Ollama Colab Integration V4 is a tool designed to enhance the interaction and management of large language models. It allows users to quantize models within their notebook environment, access a variety of models through a user-friendly interface, and manage public endpoints efficiently. The tool also provides features like LiteLLM proxy control, model insights, and customizable model file templating. Users can troubleshoot model loading issues, CPU fallback strategies, and manage VRAM and RAM effectively. Additionally, the tool offers functionalities for downloading model files from Hugging Face, model conversion with high precision, model quantization using Q and Kquants, and securely uploading converted models to Hugging Face.
rknn-llm
RKLLM software stack is a toolkit designed to help users quickly deploy AI models to Rockchip chips. It consists of RKLLM-Toolkit for model conversion and quantization, RKLLM Runtime for deploying models on Rockchip NPU platform, and RKNPU kernel driver for hardware interaction. The toolkit supports RK3588 and RK3576 series chips and various models like TinyLLAMA, Qwen, Phi, ChatGLM3, Gemma, InternLM2, and MiniCPM. Users can download packages, docker images, examples, and docs from RKLLM_SDK. Additionally, RKNN-Toolkit2 SDK is available for deploying additional AI models.
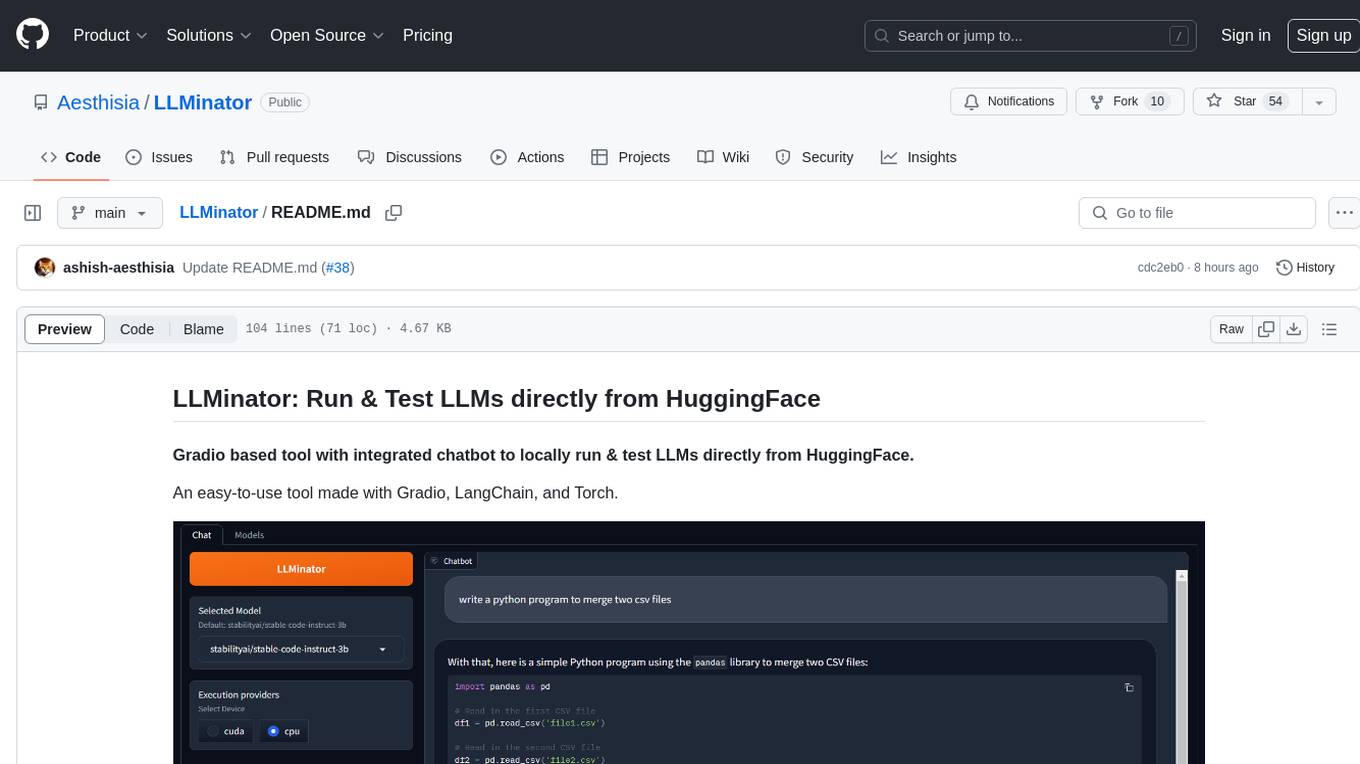
LLMinator
LLMinator is a Gradio-based tool with an integrated chatbot designed to locally run and test Language Model Models (LLMs) directly from HuggingFace. It provides an easy-to-use interface made with Gradio, LangChain, and Torch, offering features such as context-aware streaming chatbot, inbuilt code syntax highlighting, loading any LLM repo from HuggingFace, support for both CPU and CUDA modes, enabling LLM inference with llama.cpp, and model conversion capabilities.

xFasterTransformer
xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for Large Language Models (LLMs) on the X86 platform, providing high performance and scalability for inference on mainstream LLM models. It offers C++ and Python APIs for easy integration, along with example codes and benchmark scripts. Users can prepare models in a different format, convert them, and use the APIs for tasks like encoding input prompts, generating token ids, and serving inference requests. The tool supports various data types and models, and can run in single or multi-rank modes using MPI. A web demo based on Gradio is available for popular LLM models like ChatGLM and Llama2. Benchmark scripts help evaluate model inference performance quickly, and MLServer enables serving with REST and gRPC interfaces.
ai-edge-torch
AI Edge Torch is a Python library that supports converting PyTorch models into a .tflite format for on-device applications on Android, iOS, and IoT devices. It offers broad CPU coverage with initial GPU and NPU support, closely integrating with PyTorch and providing good coverage of Core ATen operators. The library includes a PyTorch converter for model conversion and a Generative API for authoring mobile-optimized PyTorch Transformer models, enabling easy deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) on mobile devices.
BodhiApp
Bodhi App runs Open Source Large Language Models locally, exposing LLM inference capabilities as OpenAI API compatible REST APIs. It leverages llama.cpp for GGUF format models and huggingface.co ecosystem for model downloads. Users can run fine-tuned models for chat completions, create custom aliases, and convert Huggingface models to GGUF format. The CLI offers commands for environment configuration, model management, pulling files, serving API, and more.
lm.rs
lm.rs is a tool that allows users to run inference on Language Models locally on the CPU using Rust. It supports LLama3.2 1B and 3B models, with a WebUI also available. The tool provides benchmarks and download links for models and tokenizers, with recommendations for quantization options. Users can convert models from Google/Meta on huggingface using provided scripts. The tool can be compiled with cargo and run with various arguments for model weights, tokenizer, temperature, and more. Additionally, a backend for the WebUI can be compiled and run to connect via the web interface.
LiteRT
LiteRT is Google's open-source high-performance runtime for on-device AI, previously known as TensorFlow Lite. The repository is currently not intended for open-source development, but aims to evolve to allow direct building and contributions. LiteRT supports Python versions 3.9, 3.10, 3.11 on Linux and MacOS. It ensures compatibility with existing .tflite file extension and format, offering conversion tools and continued active development under the name LiteRT.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.