
playword
Automate browsers with AI to boost productivity and make testing more enjoyable!
Stars: 52
PlayWord is a tool designed to supercharge web test automation experience with AI. It provides core features such as enabling browser operations and validations using natural language inputs, as well as monitoring interface to record and dry-run test steps. PlayWord supports multiple AI services including Anthropic, Google, and OpenAI, allowing users to select the appropriate provider based on their requirements. The tool also offers features like assertion handling, frame handling, custom variables, test recordings, and an Observer module to track user interactions on web pages. With PlayWord, users can interact with web pages using natural language commands, reducing the need to worry about element locators and providing AI-powered adaptation to UI changes.
README:
Supercharge your web test automation experience with AI.
Choose the package that best suits your needs.
The @playword/core package provides the core features of PlayWord and can be used as Node.js modules.
It includes the following modules:
- PlayWord: Enables browser operations and validations using natural language inputs to interact with web pages.
- Observer: Mounts a monitoring interface on the browser to record and dry-run captured test steps.
# Install with any package manager you prefer
npm install @playword/core --save-devThe @playword/cli package enables you to use the features of PlayWord directly through the command line.
For ease of use, I recommend running this package with npx.
# Run a PlayWord test
npx @playword/cli test --headed --verbose -b webkit
# Start the Observer
npx @playword/cli observe -b chromium -vSee documentation for usage examples and options.
PlayWord supports multiple AI services, including Anthropic, Google, and OpenAI. You can select the appropriate provider based on your requirements.
There are two ways to provide the required API key to PlayWord:
1. Export the API key as an environment variable:
export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-..."2. Pass the API key as a parameter during initialization:
import { chromium } from 'playwright'
const browser = await chromium.launch()
const context = await browser.newContext()
const playword = new PlayWord(context, {
aiOptions: {
baseURL: 'https://...', // Custom API endpoint (If applicable)
openAIApiKey: 'sk-...',
model: 'gpt-4o' // If not specified, the default model is gpt-4o-mini.
}
})1. Export the API key as an environment variable:
export GOOGLE_API_KEY="AI..."2. Pass the API key as a parameter during initialization:
const playword = new PlayWord(context, {
aiOptions: {
googleApiKey: 'AI...',
model: 'gemini-2.0-flash' // If not specified, the default model is gemini-2.0-flash-lite.
}
})Since Anthropic does not offer its own embeddings model, integrating Anthropic requires an additional API key for embeddings.
Currently, PlayWord supports the following providers for embeddings:
- VoyageAI (officially recommended by Anthropic)
- OpenAI
1. Export API keys as environment variables:
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="sk-..."
export VOYAGEAI_API_KEY="pa-..."2. Pass the API keys as parameters during initialization:
const playword = new PlayWord(context, {
aiOptions: {
anthropicApiKey: 'sk-...',
voyageAIApiKey: 'pa-...',
model: 'claude-3-7-sonnet-latest' // If not specified, the default model is claude-3-5-haiku-latest.
}
})| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| aiOptions | object | {} | Configuration options for the AI instance. |
| debug | boolean | false | Whether to enable debug mode. |
| delay | number | 250 | Delay between each step in milliseconds. |
| record | boolean | string | false | Whether to record actions performed and where to save the recordings. |
In its basic usage, you can use the say method to interact with the page.
No need to worry about locating elements or performing interactions—PlayWord handles all of that for you.
await playword.say('Navigate to https://www.google.com')
await playword.say('Type "Hello, World!" in the search bar')
await playword.say('Press enter')PlayWord uses keywords to identify whether a step is an assertion. This approach ensures more stable results compared to relying solely on AI judgment.
Using PlayWord within Playwright Test
import { PlayWord } from '@playword/core'
import { expect, test } from '@playwright/test'
test('get started link', async ({ context }) => {
const playword = new PlayWord(context, { debug: true, record: 'recordings/getStartLink.json' })
await playword.say('go to https://playwright.dev/')
await playword.say('click the link "Get started"')
expect(await playword.say('Verify if the installation heading is visible')).toBe(true)
})The input starting with any of the following case-insensitive keywords will be recognized as an assertion:
- are
- assert
- assure
- can
- check
- compare
- confirm
- could
- did
- do
- does
- ensure
- expect
- guarantee
- has
- have
- is
- match
- satisfy
- shall
- should
- test
- then
- was
- were
- validate
- verify
To interact with elements inside frames, simply instruct PlayWord to switch to the desired frame.
await playword.say('Go to https://iframetester.com')
await playword.say('Type "https://www.saucedemo.com" in the URL field')
await playword.say('Click the render button')
await playword.say('Switch to the frame with the url "https://www.saucedemo.com"')
// Perform actions inside the frame
await playword.say('Type standard_user into the username field')Hardcoding sensitive information in your test cases is not a good practice.
Instead, use custom variables with the syntax {VARIABLE_NAME} and define them in your environment settings.
# .env
USERNAME=standard_user
PASSWORD=secret_sauce// Load environment variables
import 'dotenv/config'
// {USERNAME} and {PASSWORD} will be replaced with the values from the environment
await playword.say('Input {USERNAME} in the username field')
await playword.say('Input {PASSWORD} in the password field')PlayWord supports recording test executions and replaying them later for efficient and consistent testing.
// Save recordings to the default path (.playword/recordings.json)
const playword = new PlayWord(context, { record: true })
// Save recordings to a custom path (Must be `.json`)
const playword = new PlayWord(context, { record: 'spec/test-shopping-cart.json' })If recordings are available, PlayWord prioritizes using them to execute tests, reducing the need to consume API tokens.
If a recorded action fails, PlayWord automatically retries it using AI.
To ensure PlayWord uses AI for specific steps during playback, start the input with [AI].
await playword.say('[AI] click the "Login" button')
await playword.say('[AI] verify the URL matches "https://www.saucedemo.com/inventory.html"')The Observer module tracks user interactions on web pages and swiftly generates accurate test steps using AI.
Upon activation, Playwright injects the Observer UI into every launched browser webpage. As you manually interact with the page, the AI interprets your actions, generates corresponding test steps, and records action details.
The Observer provides several controls to manage and interact with your test recordings:
-
Accept: Add test steps to the recording. (Can also be invoked by pressing the
akey) -
Cancel: Skip test steps without adding them to the recording. (Can also be invoked by pressing the
ckey) - Preview: View the test steps recorded so far.
- Clear: Delete recorded test steps.
-
Dry Run: Trial-run the recorded test steps. (Can press the
esckey to stop the dry-run process)
And it captures various user interactions on the webpage as follows:
- Click: Triggered when an element on the webpage is clicked.
- Hover: Triggered when hovering over an element for more than three seconds
- Input: Triggered after entering content into an input field and then clicking the input field again.
- Navigate: Triggered when the page navigates to a new URL or is refreshed.
- Select: Triggered after selecting an option from a dropdown menu.
For complex actions and assertions that the Observer cannot directly record, you can manually edit the step descriptions, enabling the AI to accurately capture your intentions.
To start using the Observer, create a PlayWord instance in headed mode, pass it to the Observer, and initiate observation with Playwright.
import { chromium } from 'playwright'
import { Observer, PlayWord } from '@playword/core'
const browser = await chromium.launch({ headless: false /** Enable headed mode */ })
const context = await browser.newContext()
const playword = new PlayWord(context)
const observer = new Observer(playword, {
delay: 500,
recordPath: 'spec/test-login.json'
})
// Start the Observer
await observer.observe()
// Open a new page to observe
await context.newPage()| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| delay | number | 250 | Delay between each step in milliseconds during the dry-run process. |
| recordPath | string | .playword/recordings.json | Where to save the recordings. (Must be .json) |
| Aspect | Traditional Testing | PlayWord |
|---|---|---|
| Dev Experience | Locating elements is very frustrating. | AI takes care of locating elements. Say goodbye to locators. |
| Dev Speed | Time is needed for writing both test cases and code. | Test cases serve both as documentation and executable tests. |
| Maintainance | High maintenance cost due to UI changes. | AI-powered adaption to UI changes. |
| Learning Curve | Requires knowledge of testing frameworks and tools. | Just use natural language to execute tests. |
- Click on an element
- Go to a specific URL
- Hover over an element
- Press a key or keys
- Scroll in a specific direction (top, bottom, up, down)
- Select an option from a select element
- Sleep for a specific duration in milliseconds
- Switch to a specific frame
- Switch to other pages
- Type text into an input field or textarea
- Wait for text to appear on the page
- Check if an element contains specific text
- Check if an element does not contain specific text
- Check if an element content is equal to specific text
- Check if an element content is not equal to specific text
- Check if an element is visible
- Check if an element is not visible
- Check if the page contains specific text
- Check if the page does not contain specific text
- Check if the page title is equal to specific text
- Check if the page URL matches specific RegExp patterns
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for playword
Similar Open Source Tools

playword
PlayWord is a tool designed to supercharge web test automation experience with AI. It provides core features such as enabling browser operations and validations using natural language inputs, as well as monitoring interface to record and dry-run test steps. PlayWord supports multiple AI services including Anthropic, Google, and OpenAI, allowing users to select the appropriate provider based on their requirements. The tool also offers features like assertion handling, frame handling, custom variables, test recordings, and an Observer module to track user interactions on web pages. With PlayWord, users can interact with web pages using natural language commands, reducing the need to worry about element locators and providing AI-powered adaptation to UI changes.

langserve
LangServe helps developers deploy `LangChain` runnables and chains as a REST API. This library is integrated with FastAPI and uses pydantic for data validation. In addition, it provides a client that can be used to call into runnables deployed on a server. A JavaScript client is available in LangChain.js.
chatgpt-cli
ChatGPT CLI provides a powerful command-line interface for seamless interaction with ChatGPT models via OpenAI and Azure. It features streaming capabilities, extensive configuration options, and supports various modes like streaming, query, and interactive mode. Users can manage thread-based context, sliding window history, and provide custom context from any source. The CLI also offers model and thread listing, advanced configuration options, and supports GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo, and Perplexity's models. Installation is available via Homebrew or direct download, and users can configure settings through default values, a config.yaml file, or environment variables.
monacopilot
Monacopilot is a powerful and customizable AI auto-completion plugin for the Monaco Editor. It supports multiple AI providers such as Anthropic, OpenAI, Groq, and Google, providing real-time code completions with an efficient caching system. The plugin offers context-aware suggestions, customizable completion behavior, and framework agnostic features. Users can also customize the model support and trigger completions manually. Monacopilot is designed to enhance coding productivity by providing accurate and contextually appropriate completions in daily spoken language.
consult-llm-mcp
Consult LLM MCP is an MCP server that enables users to consult powerful AI models like GPT-5.2, Gemini 3.0 Pro, and DeepSeek Reasoner for complex problem-solving. It supports multi-turn conversations, direct queries with optional file context, git changes inclusion for code review, comprehensive logging with cost estimation, and various CLI modes for Gemini and Codex. The tool is designed to simplify the process of querying AI models for assistance in resolving coding issues and improving code quality.
OpenAI-sublime-text
The OpenAI Completion plugin for Sublime Text provides first-class code assistant support within the editor. It utilizes LLM models to manipulate code, engage in chat mode, and perform various tasks. The plugin supports OpenAI, llama.cpp, and ollama models, allowing users to customize their AI assistant experience. It offers separated chat histories and assistant settings for different projects, enabling context-specific interactions. Additionally, the plugin supports Markdown syntax with code language syntax highlighting, server-side streaming for faster response times, and proxy support for secure connections. Users can configure the plugin's settings to set their OpenAI API key, adjust assistant modes, and manage chat history. Overall, the OpenAI Completion plugin enhances the Sublime Text editor with powerful AI capabilities, streamlining coding workflows and fostering collaboration with AI assistants.
agenticSeek
AgenticSeek is a voice-enabled AI assistant powered by DeepSeek R1 agents, offering a fully local alternative to cloud-based AI services. It allows users to interact with their filesystem, code in multiple languages, and perform various tasks autonomously. The tool is equipped with memory to remember user preferences and past conversations, and it can divide tasks among multiple agents for efficient execution. AgenticSeek prioritizes privacy by running entirely on the user's hardware without sending data to the cloud.
auto-playwright
Auto Playwright is a tool that allows users to run Playwright tests using AI. It eliminates the need for selectors by determining actions at runtime based on plain-text instructions. Users can automate complex scenarios, write tests concurrently with or before functionality development, and benefit from rapid test creation. The tool supports various Playwright actions and offers additional options for debugging and customization. It uses HTML sanitization to reduce costs and improve text quality when interacting with the OpenAI API.

skyvern
Skyvern automates browser-based workflows using LLMs and computer vision. It provides a simple API endpoint to fully automate manual workflows, replacing brittle or unreliable automation solutions. Traditional approaches to browser automations required writing custom scripts for websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions which would break whenever the website layouts changed. Instead of only relying on code-defined XPath interactions, Skyvern adds computer vision and LLMs to the mix to parse items in the viewport in real-time, create a plan for interaction and interact with them. This approach gives us a few advantages: 1. Skyvern can operate on websites it’s never seen before, as it’s able to map visual elements to actions necessary to complete a workflow, without any customized code 2. Skyvern is resistant to website layout changes, as there are no pre-determined XPaths or other selectors our system is looking for while trying to navigate 3. Skyvern leverages LLMs to reason through interactions to ensure we can cover complex situations. Examples include: 1. If you wanted to get an auto insurance quote from Geico, the answer to a common question “Were you eligible to drive at 18?” could be inferred from the driver receiving their license at age 16 2. If you were doing competitor analysis, it’s understanding that an Arnold Palmer 22 oz can at 7/11 is almost definitely the same product as a 23 oz can at Gopuff (even though the sizes are slightly different, which could be a rounding error!) Want to see examples of Skyvern in action? Jump to #real-world-examples-of- skyvern
wcgw
wcgw is a shell and coding agent designed for Claude and Chatgpt. It provides full shell access with no restrictions, desktop control on Claude for screen capture and control, interactive command handling, large file editing, and REPL support. Users can use wcgw to create, execute, and iterate on tasks, such as solving problems with Python, finding code instances, setting up projects, creating web apps, editing large files, and running server commands. Additionally, wcgw supports computer use on Docker containers for desktop control. The tool can be extended with a VS Code extension for pasting context on Claude app and integrates with Chatgpt for custom GPT interactions.

blinkid-ios
BlinkID iOS is a mobile SDK that enables developers to easily integrate ID scanning and data extraction capabilities into their iOS applications. The SDK supports scanning and processing various types of identity documents, such as passports, driver's licenses, and ID cards. It provides accurate and fast data extraction, including personal information and document details. With BlinkID iOS, developers can enhance their apps with secure and reliable ID verification functionality, improving user experience and streamlining identity verification processes.
cortex
Cortex is a tool that simplifies and accelerates the process of creating applications utilizing modern AI models like chatGPT and GPT-4. It provides a structured interface (GraphQL or REST) to a prompt execution environment, enabling complex augmented prompting and abstracting away model connection complexities like input chunking, rate limiting, output formatting, caching, and error handling. Cortex offers a solution to challenges faced when using AI models, providing a simple package for interacting with NL AI models.
kwaak
Kwaak is a tool that allows users to run a team of autonomous AI agents locally from their own machine. It enables users to write code, improve test coverage, update documentation, and enhance code quality while focusing on building innovative projects. Kwaak is designed to run multiple agents in parallel, interact with codebases, answer questions about code, find examples, write and execute code, create pull requests, and more. It is free and open-source, allowing users to bring their own API keys or models via Ollama. Kwaak is part of the bosun.ai project, aiming to be a platform for autonomous code improvement.
runpod-worker-comfy
runpod-worker-comfy is a serverless API tool that allows users to run any ComfyUI workflow to generate an image. Users can provide input images as base64-encoded strings, and the generated image can be returned as a base64-encoded string or uploaded to AWS S3. The tool is built on Ubuntu + NVIDIA CUDA and provides features like built-in checkpoints and VAE models. Users can configure environment variables to upload images to AWS S3 and interact with the RunPod API to generate images. The tool also supports local testing and deployment to Docker hub using Github Actions.
llm-vscode
llm-vscode is an extension designed for all things LLM, utilizing llm-ls as its backend. It offers features such as code completion with 'ghost-text' suggestions, the ability to choose models for code generation via HTTP requests, ensuring prompt size fits within the context window, and code attribution checks. Users can configure the backend, suggestion behavior, keybindings, llm-ls settings, and tokenization options. Additionally, the extension supports testing models like Code Llama 13B, Phind/Phind-CodeLlama-34B-v2, and WizardLM/WizardCoder-Python-34B-V1.0. Development involves cloning llm-ls, building it, and setting up the llm-vscode extension for use.
aire
Aire is a modern Laravel form builder with a focus on expressive and beautiful code. It allows easy configuration of form components using fluent method calls or Blade components. Aire supports customization through config files and custom views, data binding with Eloquent models or arrays, method spoofing, CSRF token injection, server-side and client-side validation, and translations. It is designed to run on Laravel 5.8.28 and higher, with support for PHP 7.1 and higher. Aire is actively maintained and under consideration for additional features like read-only plain text, cross-browser support for custom checkboxes and radio buttons, support for Choices.js or similar libraries, improved file input handling, and better support for content prepending or appending to inputs.
For similar tasks

playword
PlayWord is a tool designed to supercharge web test automation experience with AI. It provides core features such as enabling browser operations and validations using natural language inputs, as well as monitoring interface to record and dry-run test steps. PlayWord supports multiple AI services including Anthropic, Google, and OpenAI, allowing users to select the appropriate provider based on their requirements. The tool also offers features like assertion handling, frame handling, custom variables, test recordings, and an Observer module to track user interactions on web pages. With PlayWord, users can interact with web pages using natural language commands, reducing the need to worry about element locators and providing AI-powered adaptation to UI changes.
AutoNode
AutoNode is a self-operating computer system designed to automate web interactions and data extraction processes. It leverages advanced technologies like OCR (Optical Character Recognition), YOLO (You Only Look Once) models for object detection, and a custom site-graph to navigate and interact with web pages programmatically. Users can define objectives, create site-graphs, and utilize AutoNode via API to automate tasks on websites. The tool also supports training custom YOLO models for object detection and OCR for text recognition on web pages. AutoNode can be used for tasks such as extracting product details, automating web interactions, and more.
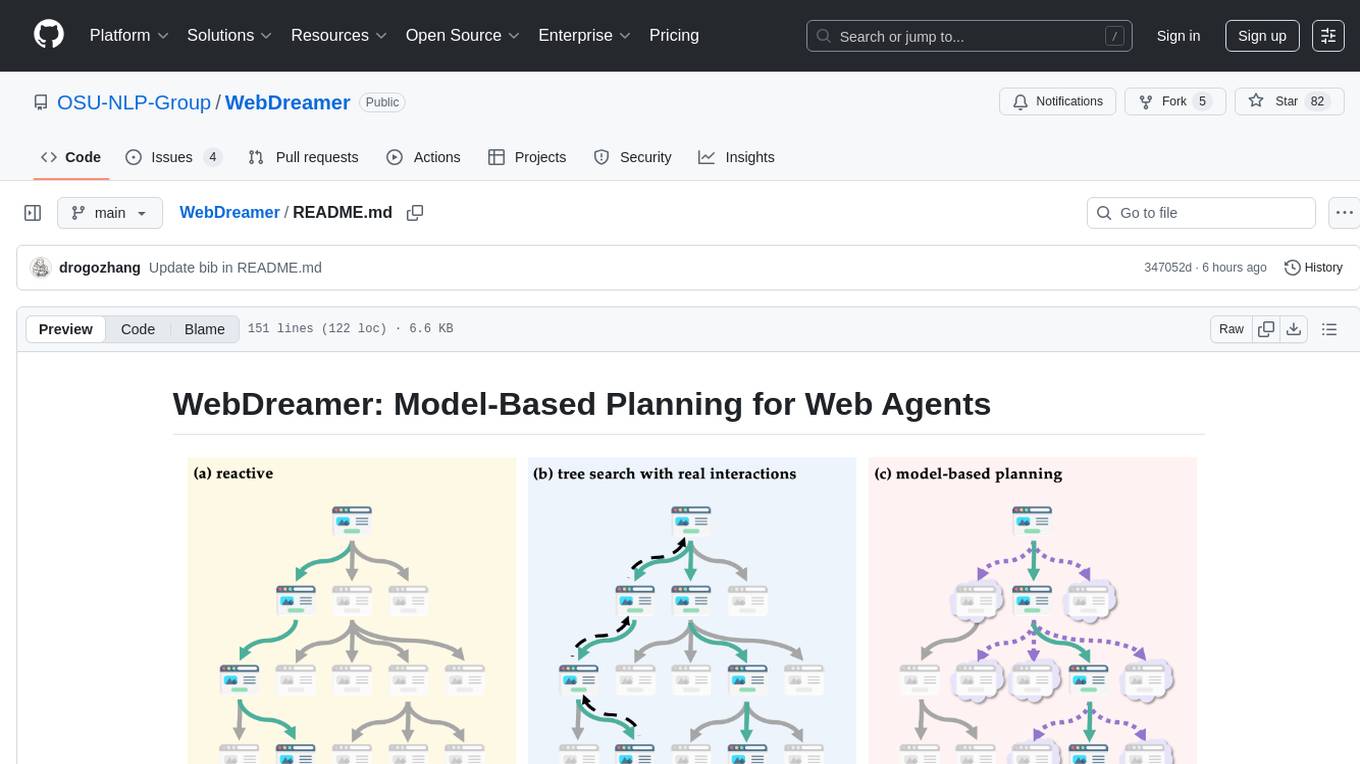
WebDreamer
WebDreamer is a model-based planning tool for web agents that uses large language models (LLMs) as a world model of the internet to predict outcomes of actions on websites. It employs LLM-based simulation for speculative planning on the web, offering greater safety and flexibility compared to traditional tree search methods. The tool provides modules for world model prediction, simulation scoring, and controller actions, enabling users to interact with web pages and achieve specific goals through simulated actions.
For similar jobs
aiscript
AiScript is a lightweight scripting language that runs on JavaScript. It supports arrays, objects, and functions as first-class citizens, and is easy to write without the need for semicolons or commas. AiScript runs in a secure sandbox environment, preventing infinite loops from freezing the host. It also allows for easy provision of variables and functions from the host.
askui
AskUI is a reliable, automated end-to-end automation tool that only depends on what is shown on your screen instead of the technology or platform you are running on.
bots
The 'bots' repository is a collection of guides, tools, and example bots for programming bots to play video games. It provides resources on running bots live, installing the BotLab client, debugging bots, testing bots in simulated environments, and more. The repository also includes example bots for games like EVE Online, Tribal Wars 2, and Elvenar. Users can learn about developing bots for specific games, syntax of the Elm programming language, and tools for memory reading development. Additionally, there are guides on bot programming, contributing to BotLab, and exploring Elm syntax and core library.
ain
Ain is a terminal HTTP API client designed for scripting input and processing output via pipes. It allows flexible organization of APIs using files and folders, supports shell-scripts and executables for common tasks, handles url-encoding, and enables sharing the resulting curl, wget, or httpie command-line. Users can put things that change in environment variables or .env-files, and pipe the API output for further processing. Ain targets users who work with many APIs using a simple file format and uses curl, wget, or httpie to make the actual calls.
LaVague
LaVague is an open-source Large Action Model framework that uses advanced AI techniques to compile natural language instructions into browser automation code. It leverages Selenium or Playwright for browser actions. Users can interact with LaVague through an interactive Gradio interface to automate web interactions. The tool requires an OpenAI API key for default examples and offers a Playwright integration guide. Contributors can help by working on outlined tasks, submitting PRs, and engaging with the community on Discord. The project roadmap is available to track progress, but users should exercise caution when executing LLM-generated code using 'exec'.
robocorp
Robocorp is a platform that allows users to create, deploy, and operate Python automations and AI actions. It provides an easy way to extend the capabilities of AI agents, assistants, and copilots with custom actions written in Python. Users can create and deploy tools, skills, loaders, and plugins that securely connect any AI Assistant platform to their data and applications. The Robocorp Action Server makes Python scripts compatible with ChatGPT and LangChain by automatically creating and exposing an API based on function declaration, type hints, and docstrings. It simplifies the process of developing and deploying AI actions, enabling users to interact with AI frameworks effortlessly.
Open-Interface
Open Interface is a self-driving software that automates computer tasks by sending user requests to a language model backend (e.g., GPT-4V) and simulating keyboard and mouse inputs to execute the steps. It course-corrects by sending current screenshots to the language models. The tool supports MacOS, Linux, and Windows, and requires setting up the OpenAI API key for access to GPT-4V. It can automate tasks like creating meal plans, setting up custom language model backends, and more. Open Interface is currently not efficient in accurate spatial reasoning, tracking itself in tabular contexts, and navigating complex GUI-rich applications. Future improvements aim to enhance the tool's capabilities with better models trained on video walkthroughs. The tool is cost-effective, with user requests priced between $0.05 - $0.20, and offers features like interrupting the app and primary display visibility in multi-monitor setups.
AI-Case-Sorter-CS7.1
AI-Case-Sorter-CS7.1 is a project focused on building a case sorter using machine vision and machine learning AI to sort cases by headstamp. The repository includes Arduino code and 3D models necessary for the project.



