
AutoNode
AutoNode: A Neuro-Graphic Self-Learnable Engine for Cognitive GUI Automation
Stars: 116
AutoNode is a self-operating computer system designed to automate web interactions and data extraction processes. It leverages advanced technologies like OCR (Optical Character Recognition), YOLO (You Only Look Once) models for object detection, and a custom site-graph to navigate and interact with web pages programmatically. Users can define objectives, create site-graphs, and utilize AutoNode via API to automate tasks on websites. The tool also supports training custom YOLO models for object detection and OCR for text recognition on web pages. AutoNode can be used for tasks such as extracting product details, automating web interactions, and more.
README:
Generalized Super Intelligence Research, Infrastructure & Autonomous Apps
Follow SuperAGI
Connect with the Creator
Share This Repository
AutoNode is a self-operating computer system designed to automate web interactions and data extraction processes. It leverages advanced technologies like OCR (Optical Character Recognition), YOLO (You Only Look Once) models for object detection, and a custom site-graph to navigate and interact with web pages programmatically.
To get started with AutoNode, you need to have Python installed on your system. Follow these steps to install AutoNode:
- Open your terminal and clone the SuperAGI repository.
git clone https://github.com/TransformerOptimus/AutoNode.git
- Navigate to the root of the cloned repository directory using the command:
cd AutoNode
-
Create a copy of .env.example , and name it .env. Repeat this step for all the three modules - autonode, yolo, ocr
-
Ensure that Docker is installed on your system. You can download and install it from here.
-
Once you have Docker Desktop running, run the following command in the AutoNode directory:
docker compose -f docker-compose.yaml up --build
- Open your web browser and navigate to http://localhost:8001/health to check server is running
AutoNode operates based on a site-graph that defines the navigation and actions to be performed on a website. Here's a basic overview of how to use AutoNode:
-
Define Your Objective: Specify what you want to achieve with AutoNode, such as data extraction or automation of specific web interactions.
-
Prepare Your Autonode-Site-Graph: Create a JSON file that represents the site-graph. This graph outlines the nodes (web elements) and edges (actions) that AutoNode will navigate and interact with.
-
Prepare you AutoNode initiator planner prompt : Using the template structure given for planner prompts in openai_prompts.py, for OpenAI LLM, you can create a new prompt file in the prompts directory with structure <llm_prompts.py>
-
Run AutoNode:
AutoNode can be controlled and utilized through its API, allowing users to automate web interactions and data extraction tasks programmatically. This guide will walk you through the process of sending requests to AutoNode using its API endpoint.
Before you start, ensure that AutoNode is running on your local machine. Once AutoNode is up and running, you can access the API documentation by visiting:
http://localhost:8001/docsThis URL will take you to the Swagger UI, where you can find detailed documentation on all available API endpoints, including the one used to initiate AutoNode tasks.
To automate a task with AutoNode, you will use the /api/autonode/initiate endpoint. This endpoint accepts a JSON payload that specifies the task's objective, the path to the site-graph JSON file, the root node to start traversal, and the URL of the website you wish to interact with.
Here is the structure of the JSON payload you need to send to the
/api/autonode/initiateendpoint:{ "site_url": "string", "objective": "string", "graph_path": "string", "planer_prompt": "string" }Example request: { "site_url": "https://app.apollo.io/#/login", "objective": "Find the list of 20 ceo, cto of tech companies in san francisco. Login into apollo using the creds [email protected] and password dummypassword@123", "graph_path": "autonode/site_trees/apollo.json" "planner_prompt": "apollo" }
-
site_url: The URL of the website AutoNode will visit and interact with.
-
objective: The goal you want to achieve on the website. This could be anything from data extraction to automating a series of web interactions. Make sure you provide the login instructions along with the credentials if login is required in your use-case
-
graph_path: The path to the JSON file that contains your site-graph. The site-graph defines the structure and navigation flow of the website for AutoNode.
-
planner_prompt: The key for planning prompt. You can change or map new key in planning_agent.py for AutoNode planner prompt.
curl -X 'POST' \ 'http://localhost:8001/api/autonode/initiate' \ -H 'accept: application/json' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -d '{ "site_url": "https://example.com/products", "objective": "Extract product details", "graph_path": "/path/to/your/site-graph.json" "planner_prompt": "planner_key" }' -
AutoNode utilizes YOLO models for object detection and OCR for text recognition on web pages. These models are crucial for identifying clickable elements, reading text from images, and interacting with web pages dynamically.
We are providing some general yolo models trained on YOLO-V8 over thousands of web-screenshots
Navigate to - yolo/web_detection_models/ dir to find those
-
Collect a Dataset: Gather images of the web elements you want to detect and annotate them with bounding boxes.
-
Prepare the Dataset: Split your dataset into training and validation sets.
-
Train the Model: Use a YOLO training script to train your model on the prepared dataset. Adjust the training parameters according to your needs.
-
Evaluate the Model: Test your trained model on a separate test set to evaluate its performance.
-
Integrate with AutoNode: Once trained, integrate your custom YOLO model with AutoNode by specifying the model path in the configuration.
If you don't have enough resources on your local machine, you can host the OCR and YOLO modules on any cloud server. Following steps can be taken:
-
In your ocr/.env file, add USE_REMOTE_OCR=True and set the url for the remote service in OCR_REMOTE_URL
-
In your yolo/.env file, add USE_REMOTE_YOLO=True and set the url for the remote service in YOLO_REMOTE_URL
-
Update the yolo web detection model path in your yolo/.env file, add SAHI_MODEL_PATH and ULTRALYTICS_MODEL_PATH. Example: SAHI_MODEL_PATH = yolo/web_detection_models/twitter.pt
The site-graph is a JSON file that describes the structure and navigation flow of a website for AutoNode. Here's how to prepare it:
-
Identify Web Elements: Navigate through your target website and identify the key elements you want to interact with, such as buttons, text-boxes, and links.
-
Define Nodes: For each web element, define a node in the JSON file. Include properties like node_name, actionable_element_type, location, and is_type.
-
Define Edges: Specify the relationships between nodes using adjacent_to and adjacent_from properties to represent the navigation flow.
-
Include Action Details: For nodes that require typing or clicking, provide additional details like type_description or click_action.
Example of a simple site-graph:
{
"1": {
"node_type": "clickable_and_typeable",
"node_name": "Login Button",
"actionable_element_type": "button",
"location": [100, 200],
"is_type": false,
"adjacent_to": ["2"]
},
"2": {
"node_type": "clickable_and_typeable",
"node_name": "Username Field",
"actionable_element_type": "textbox",
"location": [150, 250],
"is_type": true,
"type_description": "Enter username here",
"adjacent_to": []
}
}
Screenshots at every node for web element detection is stored in requests directory in the root folder. You can store them on an AWS s3 account in case you wish to, or persist them locally or neither as per your choice. For use-cases which require downloading output, downloadable content (like output in apollo) needs to be stored either locally or remotely.
- Storing Screenshots & Downloads Remotely
- In your autonode/.env file, configure AWS keys AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY from your AWS console
- In autonode/services/autonode.py, uncomment the following snippet at line 35,
# Uncomment If you have aws account and want to store result in your AWS S3
# self.s3_client = S3Helper(access_key=self.config.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,
# secret_key=self.config.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY,
# bucket_name=self.config.bucket_name)
and pass s3_client=self.s3_client at line 84
s3_client=None
- In autonode/utils/screenshot_generator.py uncomment this on line 18,
# Uncomment If you have aws account and want to store result in your AWS S3
s3_client.upload_file(file_path=screenshot_filename)
- In autonode/nodes/download.py uncomment this on line 44
# Uncomment If you have aws account and want to store result in your AWS S3
s3_client.upload_file(file_path=download_file_path)
- Storing Screenshots & Downloaded files locally
- By default, the screenshots and downloaded output are stored locally during execution and are deleted as the task completes or fails
- In autonode/worker.py comment this finally block on line 79 to persist screenshots locally,
finally:
# Comment if you don't want to delete screenshots locally
if os.path.exists(screenshots_dir):
logger.info(f"Deleting request directory {screenshots_dir}")
shutil.rmtree(screenshots_dir)
session.close()
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AutoNode
Similar Open Source Tools

AutoNode
AutoNode is a self-operating computer system designed to automate web interactions and data extraction processes. It leverages advanced technologies like OCR (Optical Character Recognition), YOLO (You Only Look Once) models for object detection, and a custom site-graph to navigate and interact with web pages programmatically. Users can define objectives, create site-graphs, and utilize AutoNode via API to automate tasks on websites. The tool also supports training custom YOLO models for object detection and OCR for text recognition on web pages. AutoNode can be used for tasks such as extracting product details, automating web interactions, and more.
palimpzest
Palimpzest (PZ) is a tool for managing and optimizing workloads, particularly for data processing tasks. It provides a CLI tool and Python demos for users to register datasets, run workloads, and access results. Users can easily initialize their system, register datasets, and manage configurations using the CLI commands provided. Palimpzest also supports caching intermediate results and configuring for parallel execution with remote services like OpenAI and together.ai. The tool aims to streamline the workflow of working with datasets and optimizing performance for data extraction tasks.
vscode-pddl
The vscode-pddl extension provides comprehensive support for Planning Domain Description Language (PDDL) in Visual Studio Code. It enables users to model planning domains, validate them, industrialize planning solutions, and run planners. The extension offers features like syntax highlighting, auto-completion, plan visualization, plan validation, plan happenings evaluation, search debugging, and integration with Planning.Domains. Users can create PDDL files, run planners, visualize plans, and debug search algorithms efficiently within VS Code.
oasis
OASIS is a scalable, open-source social media simulator that integrates large language models with rule-based agents to realistically mimic the behavior of up to one million users on platforms like Twitter and Reddit. It facilitates the study of complex social phenomena such as information spread, group polarization, and herd behavior, offering a versatile tool for exploring diverse social dynamics and user interactions in digital environments. With features like scalability, dynamic environments, diverse action spaces, and integrated recommendation systems, OASIS provides a comprehensive platform for simulating social media interactions at a large scale.

open-deep-research
Open Deep Research is an open-source tool designed to generate AI-powered reports from web search results efficiently. It combines Bing Search API for search results retrieval, JinaAI for content extraction, and customizable report generation. Users can customize settings, export reports in multiple formats, and benefit from rate limiting for stability. The tool aims to streamline research and report creation in a user-friendly platform.
vectara-answer
Vectara Answer is a sample app for Vectara-powered Summarized Semantic Search (or question-answering) with advanced configuration options. For examples of what you can build with Vectara Answer, check out Ask News, LegalAid, or any of the other demo applications.
bia-bob
BIA `bob` is a Jupyter-based assistant for interacting with data using large language models to generate Python code. It can utilize OpenAI's chatGPT, Google's Gemini, Helmholtz' blablador, and Ollama. Users need respective accounts to access these services. Bob can assist in code generation, bug fixing, code documentation, GPU-acceleration, and offers a no-code custom Jupyter Kernel. It provides example notebooks for various tasks like bio-image analysis, model selection, and bug fixing. Installation is recommended via conda/mamba environment. Custom endpoints like blablador and ollama can be used. Google Cloud AI API integration is also supported. The tool is extensible for Python libraries to enhance Bob's functionality.
promptwright
Promptwright is a Python library designed for generating large synthetic datasets using a local LLM and various LLM service providers. It offers flexible interfaces for generating prompt-led synthetic datasets. The library supports multiple providers, configurable instructions and prompts, YAML configuration for tasks, command line interface for running tasks, push to Hugging Face Hub for dataset upload, and system message control. Users can define generation tasks using YAML configuration or Python code. Promptwright integrates with LiteLLM to interface with LLM providers and supports automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub.
kaito
KAITO is an operator that automates the AI/ML model inference or tuning workload in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, provides preset configurations to avoid adjusting workload parameters based on GPU hardware, supports popular open-sourced inference runtimes, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry. Using KAITO simplifies the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes.
promptwright
Promptwright is a Python library designed for generating large synthetic datasets using local LLM and various LLM service providers. It offers flexible interfaces for generating prompt-led synthetic datasets. The library supports multiple providers, configurable instructions and prompts, YAML configuration, command line interface, push to Hugging Face Hub, and system message control. Users can define generation tasks using YAML configuration files or programmatically using Python code. Promptwright integrates with LiteLLM for LLM providers and supports automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub. The library is not responsible for the content generated by models and advises users to review the data before using it in production environments.
TaskWeaver
TaskWeaver is a code-first agent framework designed for planning and executing data analytics tasks. It interprets user requests through code snippets, coordinates various plugins to execute tasks in a stateful manner, and preserves both chat history and code execution history. It supports rich data structures, customized algorithms, domain-specific knowledge incorporation, stateful execution, code verification, easy debugging, security considerations, and easy extension. TaskWeaver is easy to use with CLI and WebUI support, and it can be integrated as a library. It offers detailed documentation, demo examples, and citation guidelines.
deep-research
Deep Research is a lightning-fast tool that uses powerful AI models to generate comprehensive research reports in just a few minutes. It leverages advanced 'Thinking' and 'Task' models, combined with an internet connection, to provide fast and insightful analysis on various topics. The tool ensures privacy by processing and storing all data locally. It supports multi-platform deployment, offers support for various large language models, web search functionality, knowledge graph generation, research history preservation, local and server API support, PWA technology, multi-key payload support, multi-language support, and is built with modern technologies like Next.js and Shadcn UI. Deep Research is open-source under the MIT License.
otto-m8
otto-m8 is a flowchart based automation platform designed to run deep learning workloads with minimal to no code. It provides a user-friendly interface to spin up a wide range of AI models, including traditional deep learning models and large language models. The tool deploys Docker containers of workflows as APIs for integration with existing workflows, building AI chatbots, or standalone applications. Otto-m8 operates on an Input, Process, Output paradigm, simplifying the process of running AI models into a flowchart-like UI.
aiconfig
AIConfig is a framework that makes it easy to build generative AI applications for production. It manages generative AI prompts, models and model parameters as JSON-serializable configs that can be version controlled, evaluated, monitored and opened in a local editor for rapid prototyping. It allows you to store and iterate on generative AI behavior separately from your application code, offering a streamlined AI development workflow.
kafka-ml
Kafka-ML is a framework designed to manage the pipeline of Tensorflow/Keras and PyTorch machine learning models on Kubernetes. It enables the design, training, and inference of ML models with datasets fed through Apache Kafka, connecting them directly to data streams like those from IoT devices. The Web UI allows easy definition of ML models without external libraries, catering to both experts and non-experts in ML/AI.
ai-component-generator
AI Component Generator with ChatGPT is a project that utilizes OpenAI's ChatGPT and Vercel Edge functions to generate various UI components based on user input. It allows users to export components in HTML format or choose combinations of Tailwind CSS, Next.js, React.js, or Material UI. The tool can be used to quickly bootstrap projects and create custom UI components. Users can run the project locally with Next.js and TailwindCSS, and customize ChatGPT prompts to generate specific components or code snippets. The project is open for contributions and aims to simplify the process of creating UI components with AI assistance.
For similar tasks
genaiscript
GenAIScript is a scripting environment designed to facilitate file ingestion, prompt development, and structured data extraction. Users can define metadata and model configurations, specify data sources, and define tasks to extract specific information. The tool provides a convenient way to analyze files and extract desired content in a structured format. It offers a user-friendly interface for working with data and automating data extraction processes, making it suitable for various data processing tasks.

AutoNode
AutoNode is a self-operating computer system designed to automate web interactions and data extraction processes. It leverages advanced technologies like OCR (Optical Character Recognition), YOLO (You Only Look Once) models for object detection, and a custom site-graph to navigate and interact with web pages programmatically. Users can define objectives, create site-graphs, and utilize AutoNode via API to automate tasks on websites. The tool also supports training custom YOLO models for object detection and OCR for text recognition on web pages. AutoNode can be used for tasks such as extracting product details, automating web interactions, and more.
oxylabs-mcp
The Oxylabs MCP Server acts as a bridge between AI models and the web, providing clean, structured data from any site. It enables scraping of URLs, rendering JavaScript-heavy pages, content extraction for AI use, bypassing anti-scraping measures, and accessing geo-restricted web data from 195+ countries. The implementation utilizes the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to facilitate secure interactions between AI assistants and web content. Key features include scraping content from any site, automatic data cleaning and conversion, bypassing blocks and geo-restrictions, flexible setup with cross-platform support, and built-in error handling and request management.
LaVague
LaVague is an open-source Large Action Model framework that uses advanced AI techniques to compile natural language instructions into browser automation code. It leverages Selenium or Playwright for browser actions. Users can interact with LaVague through an interactive Gradio interface to automate web interactions. The tool requires an OpenAI API key for default examples and offers a Playwright integration guide. Contributors can help by working on outlined tasks, submitting PRs, and engaging with the community on Discord. The project roadmap is available to track progress, but users should exercise caution when executing LLM-generated code using 'exec'.
PulsarRPA
PulsarRPA is a high-performance, distributed, open-source Robotic Process Automation (RPA) framework designed to handle large-scale RPA tasks with ease. It provides a comprehensive solution for browser automation, web content understanding, and data extraction. PulsarRPA addresses challenges of browser automation and accurate web data extraction from complex and evolving websites. It incorporates innovative technologies like browser rendering, RPA, intelligent scraping, advanced DOM parsing, and distributed architecture to ensure efficient, accurate, and scalable web data extraction. The tool is open-source, customizable, and supports cutting-edge information extraction technology, making it a preferred solution for large-scale web data extraction.
agent-browser
agent-browser is a headless browser automation CLI tool designed for AI agents. It is a fast Rust CLI tool with Node.js fallback. The tool allows users to automate web interactions, perform various browser actions, interact with elements using semantic locators, wait for specific conditions, control mouse and keyboard events, manage browser settings, handle cookies and storage, monitor network requests, work with tabs and windows, interact with frames and dialogs, debug browser sessions, navigate pages, set up sessions, use persistent profiles, take snapshots with filtering options, control browser via CDP, stream browser viewport, work with iOS simulators and real devices, utilize Browserbase, Browser Use, and Kernel cloud browser infrastructure, and more. It supports multiple platforms and browsers, provides a comprehensive set of commands for web automation, and is suitable for AI agents and coding assistants.
playword
PlayWord is a tool designed to supercharge web test automation experience with AI. It provides core features such as enabling browser operations and validations using natural language inputs, as well as monitoring interface to record and dry-run test steps. PlayWord supports multiple AI services including Anthropic, Google, and OpenAI, allowing users to select the appropriate provider based on their requirements. The tool also offers features like assertion handling, frame handling, custom variables, test recordings, and an Observer module to track user interactions on web pages. With PlayWord, users can interact with web pages using natural language commands, reducing the need to worry about element locators and providing AI-powered adaptation to UI changes.
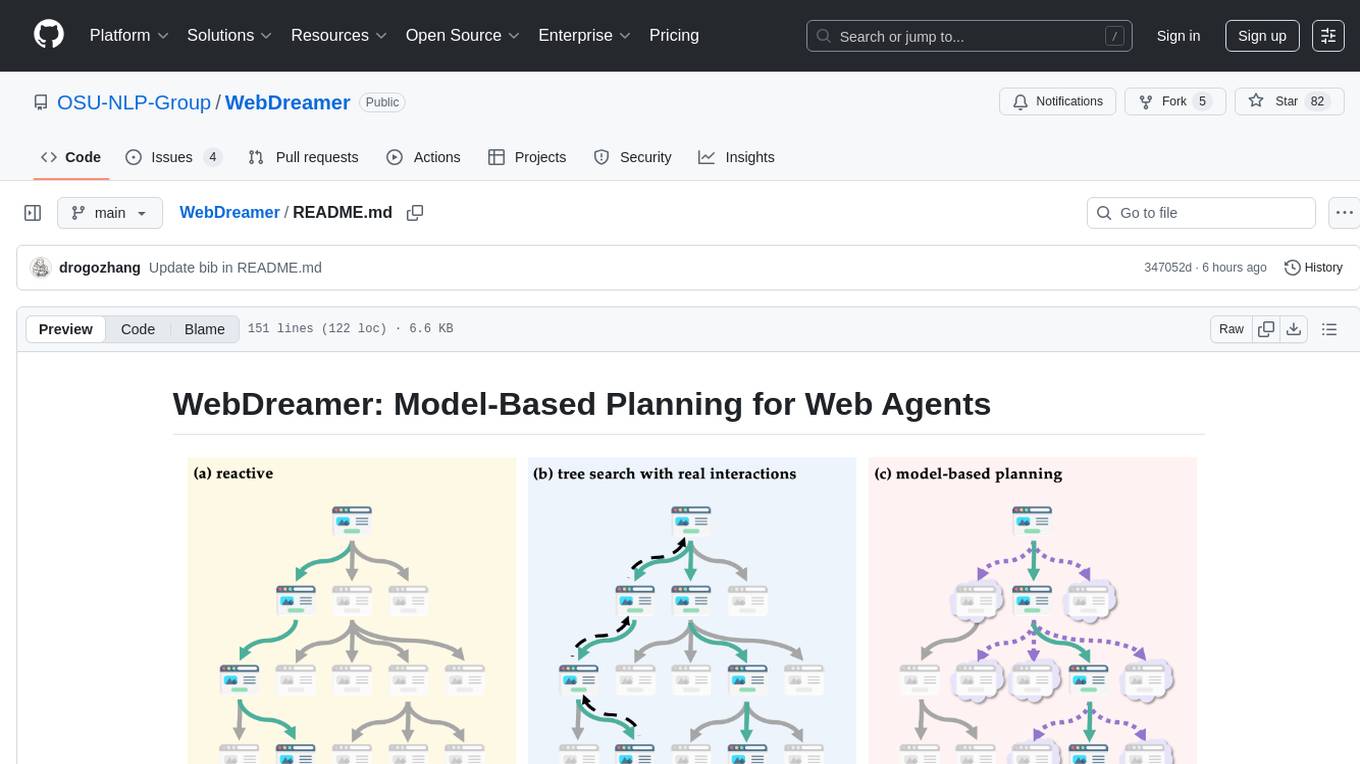
WebDreamer
WebDreamer is a model-based planning tool for web agents that uses large language models (LLMs) as a world model of the internet to predict outcomes of actions on websites. It employs LLM-based simulation for speculative planning on the web, offering greater safety and flexibility compared to traditional tree search methods. The tool provides modules for world model prediction, simulation scoring, and controller actions, enabling users to interact with web pages and achieve specific goals through simulated actions.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.









