
zep
Zep | The Memory Foundation For Your AI Stack
Stars: 2446
Zep is a long-term memory service for AI Assistant apps. With Zep, you can provide AI assistants with the ability to recall past conversations, no matter how distant, while also reducing hallucinations, latency, and cost. Zep persists and recalls chat histories, and automatically generates summaries and other artifacts from these chat histories. It also embeds messages and summaries, enabling you to search Zep for relevant context from past conversations. Zep does all of this asyncronously, ensuring these operations don't impact your user's chat experience. Data is persisted to database, allowing you to scale out when growth demands. Zep also provides a simple, easy to use abstraction for document vector search called Document Collections. This is designed to complement Zep's core memory features, but is not designed to be a general purpose vector database. Zep allows you to be more intentional about constructing your prompt: 1. automatically adding a few recent messages, with the number customized for your app; 2. a summary of recent conversations prior to the messages above; 3. and/or contextually relevant summaries or messages surfaced from the entire chat session. 4. and/or relevant Business data from Zep Document Collections.
README:
Quick Start | Documentation | Zep Cloud Docs
Zep continually learns from user interactions, improving your AI agent's knowledge over time. With Zep, you can personalize user experiences and significantly improve agent accuracy.
Zep is powered by a temporal Knowledge Graph. As your user's conversation with an agent progresses, new facts are added to the graph. Zep maintains historical context, helping your agent reason with state change and offering data provenance insights.
Retrieving facts is simple and very fast. Both semantic and graph search are used to ensure facts are relevant to the current conversation. Fact retrieval does not require LLM inference; the slowest activity is embedding the search query.
Zep supports:
- Adding chat history messages.
- Ingestion of JSON and unstructured text.
- Session, user, and group-level graphs. Group graphs allow for capturing organizational knowledge.
Please see the Zep Quick Start Guide for important configuration information.
./zep pull
./zep up[!NOTE] Make sure to set the
secretvalue in thezep.yamlconfiguration file.Additionally, make sure that you expose an
OPENAI_API_KEYenvironment variable either in a local .env file or by runningexport OPENAI_API_KEY=your_openai_api_key
pip install zep-pythonor
npm i @getzep/zep-jsPersisting chat history memory is simple and fast.
result = await client.memory.add(session_id, messages=messages)Zep's high-level memory API offers an opinionated retrieval API, which uses BM25, semantic, and graph search to retrieve facts relevant to the current conversation. Results are reranked by distance from the user node, further improving relevance.
memory = client.memory.get(session_id="session_id")Lower-level APIs for search and CRUD are also available.
A Knowledge Graph is a network of interconnected facts, such as “Kendra loves Adidas shoes.” Each fact is a “triplet” represented by two entities, or nodes (”Kendra”, “Adidas shoes”), and their relationship, or edge (”loves”).
Knowledge Graphs allow us to model an agent's complex world and offer a superior retrieval approach than semantic search alone, which is commonly used in RAG. Most approaches to building Knowledge Graphs don't reason well with state changes. Facts inevitably change over time as users provide new information or business data changes.
Most graph-building tools don't reason well with state changes. Zep incorporates a temporal Knowledge Graph library, Graphiti, which we developed to address this challenge. What makes Graphiti unique is its ability to autonomously build a Knowledge Graph while handling changing relationships and maintaining historical context.
Graphiti also offers Zep the ability to ingest chat history, JSON business data, and unstructured text.
Zep is framework agnostic. It can be used with LangChain, LangGraph, Chainlit, Microsoft Autogen, and more.
Zep Community Edition is an open-source Zep distribution. It shares APIs with Zep Cloud and has comprehensive documentation available.
Zep Cloud is a managed service with Zep Community Edition at its core. In addition to Zep Community Edition's memory layer, Zep Cloud offers:
- Low Latency, Scalability, High Availability: Our cloud is designed to scale to the needs of customers with millions of DAUs and is SOC II Type 2 certified. Zep utilizes self-hosted LLMs and embedding models, offering customers very low-latency memory retrieval and graph-building.
- Dialog Classification: Instantly and accurately classify chat dialog. Understand user intent and emotion, segment users, and more. Route chains based on semantic context, and trigger events.
- Structured Data Extraction: Quickly extract business data from chat conversations using a schema you define. Understand what your assistant should ask for next to complete the task.
With increased LLM context lengths, including the entire chat history, RAG results, and other instructions in a prompt may be tempting. Unfortunately, this has resulted in poor temporal reasoning, poor recall, hallucinations, and slow and expensive inference.
As discussed above, providing just the chat history to an LLM can often result in poor temporal reasoning.
Users, Sessions, and Chat Messages are first-class abstractions in Zep. This allows simple and flexible management of chat memory, including the execution of Right To Be Forgetten requests and other privacy compliance-related tasks with single-API call.
Yes - Zep offers Python & TypeScript/JS SDKs for easy integration with your Assistant app. We also have examples of using Zep with popular frameworks - see below.
Yes - the Zep team and community contributors have built integrations with Zep, making it simple to, for example, drop Zep's memory components into a LangChain app. Please see the Zep Documentation and your favorite framework's documentation.
Zep Community Edition relies on an external LLM API service to function. Any OpenAI-compatible LLM API is supported. Providers such as Anthropic can be used via a proxy such as LiteLLM. You will also need to configure LiteLLM with an embedding service.
import uuid
from zep_python.client import AsyncZep
from zep_python.types import Message
client = AsyncZep(
api_key=API_KEY,
base_url=BASE_URL,
)
user_id = uuid.uuid4().hex # A new user identifier
new_user = await client.user.add(
user_id=user_id,
email="[email protected]",
first_name="Jane",
last_name="Smith",
metadata={"foo": "bar"},
)
# create a chat session
session_id = uuid.uuid4().hex # A new session identifier
session = await client.memory.add_session(
session_id=session_id,
user_id=user_id,
metadata={"foo" : "bar"}
)
# Add a memory to the session
await client.memory.add_memory(
session_id=session_id,
messages=[
Message(
role_type = "user", # One of ("system", "assistant", "user", "function", "tool")
role = "Researcher", # Optional, a use case specific string representing the role of the user
content = "Who was Octavia Butler?", # The message content
)
],
)
# Get session memory
memory = await client.memory.get(session_id=session_id)
messages = memory.messages # List of messages in the session (quantity determined by optional lastn parameter in memory.get)
relevant_facts = memory.relevant_facts # List of facts relevant to the recent messages in the session
# Search user facts across all sessions
search_response = await client.memory.search_sessions(
user_id=user_id,
search_scope="facts",
text="What science fiction books did I recently read?",
)
facts = [r.fact for r in search_response.results]import { v4 as uuidv4 } from 'uuid';
import { ZepClient } from '@getzep/zep-js';
import type { CreateUserRequest, CreateSessionRequest, SessionSearchQuery } from '@getzep/zep-js/api';
const client = new ZepClient({
apiKey: API_KEY,
baseUrl: BASE_URL,
});
// A new user identifier
const userId = uuidv4();
const userRequest: CreateUserRequest = {
userId: userId,
email: "[email protected]",
firstName: "Jane",
lastName: "Smith",
metadata: { foo: "bar" },
};
const newUser = await client.user.add(userRequest);
// Create a chat session
const sessionId = uuidv4();
const sessionRequest: CreateSessionRequest = {
sessionId: sessionId,
userId: userId,
metadata: { foo: "bar" },
};
// A new session identifier
const session = await client.memory.addSession(sessionRequest);
// Add a memory to the session
await client.memory.add(sessionId, {
messages: [
{
role: "Researcher",
roleType: "user",
content: "Who was Octavia Butler?",
},
],
});
// Get session memory
const memory = await client.memory.get(sessionId);
const messages = memory.messages; // List of messages in the session (quantity determined by optional lastN parameter in memory.get)
const relevantFacts = memory.relevantFacts; // List of facts relevant to the recent messages in the session
// Search user facts across all sessions
const searchQuery: SessionSearchQuery = {
userId: userId,
searchScope: "facts",
text: "What science fiction books did I recently read?",
};
const searchResponse = await client.memory.searchSessions(searchQuery);
const facts = searchResponse.results?.map(result => result.fact);Zep Open Source is an older version of Zep that did not use a Knowledge Graph to persist and recall memory.
Some additional changes:
- The Zep OSS web UI has been deprecated in favor of significantly expanded SDK support.
- Zep CE supports many LLM services and local servers that offer OpenAI-compatible APIs. Other services may be used with an LLM proxy.
- Zep CE no longer ships with a local embedding service and named entity extractor.
Significant changes have been made to Zep, and unfortunately, we have not been able to devise a migration path from Zep OSS to Zep CE.
Zep OSS will remain available in our container repo, but we will not see future enhancements or bug fixes. The code is available in the legacy branch in this repo.
We welcome contributions. For more, see the CONTRIBUTING file in this repo.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for zep
Similar Open Source Tools

zep
Zep is a long-term memory service for AI Assistant apps. With Zep, you can provide AI assistants with the ability to recall past conversations, no matter how distant, while also reducing hallucinations, latency, and cost. Zep persists and recalls chat histories, and automatically generates summaries and other artifacts from these chat histories. It also embeds messages and summaries, enabling you to search Zep for relevant context from past conversations. Zep does all of this asyncronously, ensuring these operations don't impact your user's chat experience. Data is persisted to database, allowing you to scale out when growth demands. Zep also provides a simple, easy to use abstraction for document vector search called Document Collections. This is designed to complement Zep's core memory features, but is not designed to be a general purpose vector database. Zep allows you to be more intentional about constructing your prompt: 1. automatically adding a few recent messages, with the number customized for your app; 2. a summary of recent conversations prior to the messages above; 3. and/or contextually relevant summaries or messages surfaced from the entire chat session. 4. and/or relevant Business data from Zep Document Collections.
langchain
LangChain is a framework for developing Elixir applications powered by language models. It enables applications to connect language models to other data sources and interact with the environment. The library provides components for working with language models and off-the-shelf chains for specific tasks. It aims to assist in building applications that combine large language models with other sources of computation or knowledge. LangChain is written in Elixir and is not aimed for parity with the JavaScript and Python versions due to differences in programming paradigms and design choices. The library is designed to make it easy to integrate language models into applications and expose features, data, and functionality to the models.
agentscript
AgentScript is an open-source framework for building AI agents that think in code. It prompts a language model to generate JavaScript code, which is then executed in a dedicated runtime with resumability, state persistence, and interactivity. The framework allows for abstract task execution without needing to know all the data beforehand, making it flexible and efficient. AgentScript supports tools, deterministic functions, and LLM-enabled functions, enabling dynamic data processing and decision-making. It also provides state management and human-in-the-loop capabilities, allowing for pausing, serialization, and resumption of execution.
neuron-ai
Neuron is a PHP framework for creating and orchestrating AI Agents, providing tools for the entire agentic application development lifecycle. It allows integration of AI entities in existing PHP applications with a powerful and flexible architecture. Neuron offers tutorials and educational content to help users get started using AI Agents in their projects. The framework supports various LLM providers, tools, and toolkits, enabling users to create fully functional agents for tasks like data analysis, chatbots, and structured output. Neuron also facilitates monitoring and debugging of AI applications, ensuring control over agent behavior and decision-making processes.
lotus
LOTUS (LLMs Over Tables of Unstructured and Structured Data) is a query engine that provides a declarative programming model and an optimized query engine for reasoning-based query pipelines over structured and unstructured data. It offers a simple and intuitive Pandas-like API with semantic operators for fast and easy LLM-powered data processing. The tool implements a semantic operator programming model, allowing users to write AI-based pipelines with high-level logic and leaving the rest of the work to the query engine. LOTUS supports various semantic operators like sem_map, sem_filter, sem_extract, sem_agg, sem_topk, sem_join, sem_sim_join, and sem_search, enabling users to perform tasks like mapping records, filtering data, aggregating records, and more. The tool also supports different model classes such as LM, RM, and Reranker for language modeling, retrieval, and reranking tasks respectively.
pgai
pgai simplifies the process of building search and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) AI applications with PostgreSQL. It brings embedding and generation AI models closer to the database, allowing users to create embeddings, retrieve LLM chat completions, reason over data for classification, summarization, and data enrichment directly from within PostgreSQL in a SQL query. The tool requires an OpenAI API key and a PostgreSQL client to enable AI functionality in the database. Users can install pgai from source, run it in a pre-built Docker container, or enable it in a Timescale Cloud service. The tool provides functions to handle API keys using psql or Python, and offers various AI functionalities like tokenizing, detokenizing, embedding, chat completion, and content moderation.

project_alice
Alice is an agentic workflow framework that integrates task execution and intelligent chat capabilities. It provides a flexible environment for creating, managing, and deploying AI agents for various purposes, leveraging a microservices architecture with MongoDB for data persistence. The framework consists of components like APIs, agents, tasks, and chats that interact to produce outputs through files, messages, task results, and URL references. Users can create, test, and deploy agentic solutions in a human-language framework, making it easy to engage with by both users and agents. The tool offers an open-source option, user management, flexible model deployment, and programmatic access to tasks and chats.
gel
Gel is a graph-relational database that combines the best parts of relational databases, graph databases, and ORMs. It introduces a new way of schema modeling with object types, properties, and links. Gel's query language, EdgeQL, produces structured objects and supports features like subqueries and nested mutations. It offers a comprehensive standard library, computed properties, transactions, and more. Gel is not just a mapper but a full-fledged database with a powerful query language, migrations system, client libraries, and a CLI. The goal is to revolutionize how developers model, migrate, manage, and query their database.
multilspy
Multilspy is a Python library developed for research purposes to facilitate the creation of language server clients for querying and obtaining results of static analyses from various language servers. It simplifies the process by handling server setup, communication, and configuration parameters, providing a common interface for different languages. The library supports features like finding function/class definitions, callers, completions, hover information, and document symbols. It is designed to work with AI systems like Large Language Models (LLMs) for tasks such as Monitor-Guided Decoding to ensure code generation correctness and boost compilability.
airflow-ai-sdk
This repository contains an SDK for working with LLMs from Apache Airflow, based on Pydantic AI. It allows users to call LLMs and orchestrate agent calls directly within their Airflow pipelines using decorator-based tasks. The SDK leverages the familiar Airflow `@task` syntax with extensions like `@task.llm`, `@task.llm_branch`, and `@task.agent`. Users can define tasks that call language models, orchestrate multi-step AI reasoning, change the control flow of a DAG based on LLM output, and support various models in the Pydantic AI library. The SDK is designed to integrate LLM workflows into Airflow pipelines, from simple LLM calls to complex agentic workflows.
Tools4AI
Tools4AI is a Java-based Agentic Framework for building AI agents to integrate with enterprise Java applications. It enables the conversion of natural language prompts into actionable behaviors, streamlining user interactions with complex systems. By leveraging AI capabilities, it enhances productivity and innovation across diverse applications. The framework allows for seamless integration of AI with various systems, such as customer service applications, to interpret user requests, trigger actions, and streamline workflows. Prompt prediction anticipates user actions based on input prompts, enhancing user experience by proactively suggesting relevant actions or services based on context.
backtrack_sampler
Backtrack Sampler is a framework for experimenting with custom sampling algorithms that can backtrack the latest generated tokens. It provides a simple and easy-to-understand codebase for creating new sampling strategies. Users can implement their own strategies by creating new files in the `/strategy` directory. The repo includes examples for usage with llama.cpp and transformers, showcasing different strategies like Creative Writing, Anti-slop, Debug, Human Guidance, Adaptive Temperature, and Replace. The goal is to encourage experimentation and customization of backtracking algorithms for language models.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.
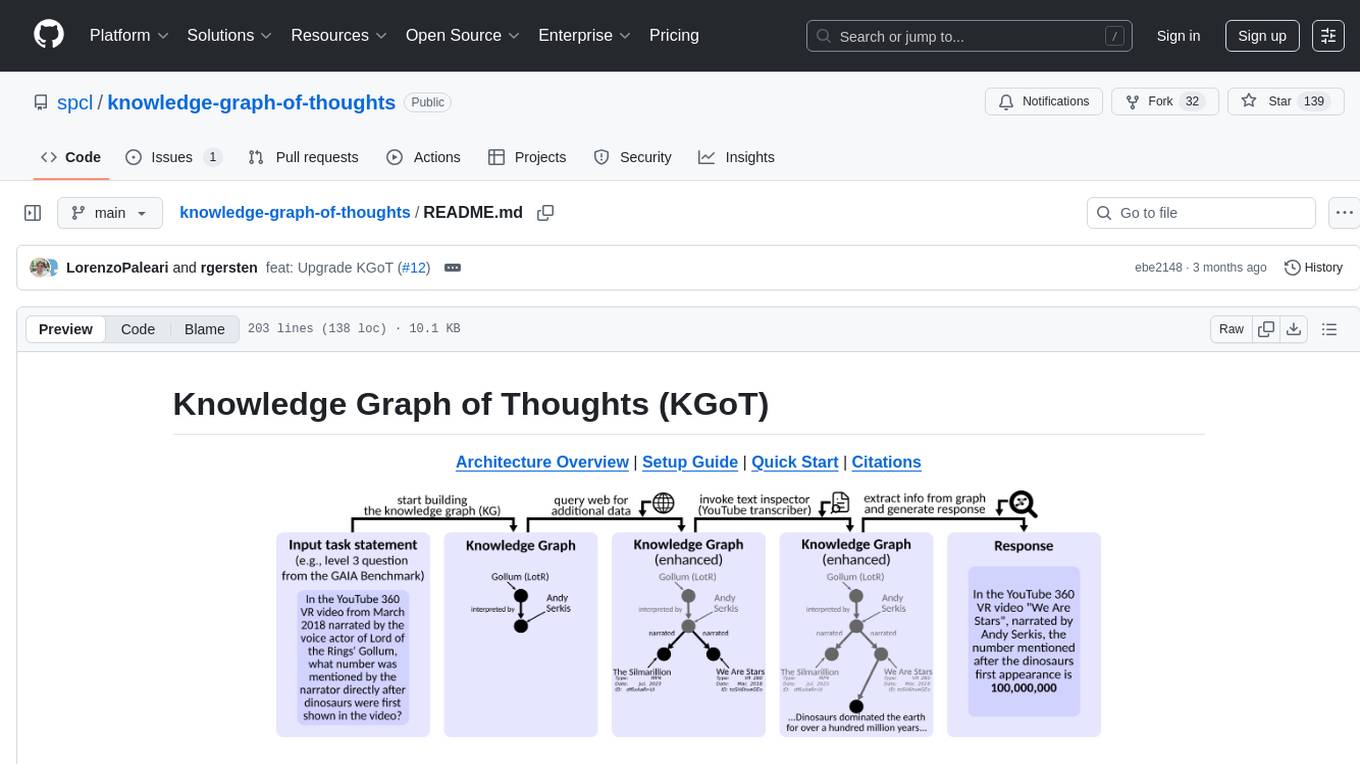
knowledge-graph-of-thoughts
Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT) is an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively. The KGoT system consists of three main components: the Controller, the Graph Store, and the Integrated Tools, each playing a critical role in the task-solving process.
aici
The Artificial Intelligence Controller Interface (AICI) lets you build Controllers that constrain and direct output of a Large Language Model (LLM) in real time. Controllers are flexible programs capable of implementing constrained decoding, dynamic editing of prompts and generated text, and coordinating execution across multiple, parallel generations. Controllers incorporate custom logic during the token-by-token decoding and maintain state during an LLM request. This allows diverse Controller strategies, from programmatic or query-based decoding to multi-agent conversations to execute efficiently in tight integration with the LLM itself.
kafka-ml
Kafka-ML is a framework designed to manage the pipeline of Tensorflow/Keras and PyTorch machine learning models on Kubernetes. It enables the design, training, and inference of ML models with datasets fed through Apache Kafka, connecting them directly to data streams like those from IoT devices. The Web UI allows easy definition of ML models without external libraries, catering to both experts and non-experts in ML/AI.
For similar tasks

zep
Zep is a long-term memory service for AI Assistant apps. With Zep, you can provide AI assistants with the ability to recall past conversations, no matter how distant, while also reducing hallucinations, latency, and cost. Zep persists and recalls chat histories, and automatically generates summaries and other artifacts from these chat histories. It also embeds messages and summaries, enabling you to search Zep for relevant context from past conversations. Zep does all of this asyncronously, ensuring these operations don't impact your user's chat experience. Data is persisted to database, allowing you to scale out when growth demands. Zep also provides a simple, easy to use abstraction for document vector search called Document Collections. This is designed to complement Zep's core memory features, but is not designed to be a general purpose vector database. Zep allows you to be more intentional about constructing your prompt: 1. automatically adding a few recent messages, with the number customized for your app; 2. a summary of recent conversations prior to the messages above; 3. and/or contextually relevant summaries or messages surfaced from the entire chat session. 4. and/or relevant Business data from Zep Document Collections.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.
mslearn-ai-language
This repository contains lab files for Azure AI Language modules. It provides hands-on exercises and resources for learning about various AI language technologies on the Azure platform. The labs cover topics such as natural language processing, text analytics, language understanding, and more. By following the exercises in this repository, users can gain practical experience in implementing AI language solutions using Azure services.
summary-of-a-haystack
This repository contains data and code for the experiments in the SummHay paper. It includes publicly released Haystacks in conversational and news domains, along with scripts for running the pipeline, visualizing results, and benchmarking automatic evaluation. The data structure includes topics, subtopics, insights, queries, retrievers, summaries, evaluation summaries, and documents. The pipeline involves scripts for retriever scores, summaries, and evaluation scores using GPT-4o. Visualization scripts are provided for compiling and visualizing results. The repository also includes annotated samples for benchmarking and citation information for the SummHay paper.
llm-book
The 'llm-book' repository is dedicated to the introduction of large-scale language models, focusing on natural language processing tasks. The code is designed to run on Google Colaboratory and utilizes datasets and models available on the Hugging Face Hub. Note that as of July 28, 2023, there are issues with the MARC-ja dataset links, but an alternative notebook using the WRIME Japanese sentiment analysis dataset has been added. The repository covers various chapters on topics such as Transformers, fine-tuning language models, entity recognition, summarization, document embedding, question answering, and more.
Controllable-RAG-Agent
This repository contains a sophisticated deterministic graph-based solution for answering complex questions using a controllable autonomous agent. The solution is designed to ensure that answers are solely based on the provided data, avoiding hallucinations. It involves various steps such as PDF loading, text preprocessing, summarization, database creation, encoding, and utilizing large language models. The algorithm follows a detailed workflow involving planning, retrieval, answering, replanning, content distillation, and performance evaluation. Heuristics and techniques implemented focus on content encoding, anonymizing questions, task breakdown, content distillation, chain of thought answering, verification, and model performance evaluation.
summarize
The 'summarize' tool is designed to transcribe and summarize videos from various sources using AI models. It helps users efficiently summarize lengthy videos, take notes, and extract key insights by providing timestamps, original transcripts, and support for auto-generated captions. Users can utilize different AI models via Groq, OpenAI, or custom local models to generate grammatically correct video transcripts and extract wisdom from video content. The tool simplifies the process of summarizing video content, making it easier to remember and reference important information.
For similar jobs

zep
Zep is a long-term memory service for AI Assistant apps. With Zep, you can provide AI assistants with the ability to recall past conversations, no matter how distant, while also reducing hallucinations, latency, and cost. Zep persists and recalls chat histories, and automatically generates summaries and other artifacts from these chat histories. It also embeds messages and summaries, enabling you to search Zep for relevant context from past conversations. Zep does all of this asyncronously, ensuring these operations don't impact your user's chat experience. Data is persisted to database, allowing you to scale out when growth demands. Zep also provides a simple, easy to use abstraction for document vector search called Document Collections. This is designed to complement Zep's core memory features, but is not designed to be a general purpose vector database. Zep allows you to be more intentional about constructing your prompt: 1. automatically adding a few recent messages, with the number customized for your app; 2. a summary of recent conversations prior to the messages above; 3. and/or contextually relevant summaries or messages surfaced from the entire chat session. 4. and/or relevant Business data from Zep Document Collections.
doc2plan
doc2plan is a browser-based application that helps users create personalized learning plans by extracting content from documents. It features a Creator for manual or AI-assisted plan construction and a Viewer for interactive plan navigation. Users can extract chapters, key topics, generate quizzes, and track progress. The application includes AI-driven content extraction, quiz generation, progress tracking, plan import/export, assistant management, customizable settings, viewer chat with text-to-speech and speech-to-text support, and integration with various Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) models. It aims to simplify the creation of comprehensive learning modules tailored to individual needs.
whatsapp-chatgpt
This repository contains a WhatsApp bot that utilizes OpenAI's GPT and DALL-E 2 to respond to user inputs. Users can interact with the bot through voice messages, which are transcribed and responded to. The bot requires Node.js, npm, an OpenAI API key, and a WhatsApp account. It uses Puppeteer to run a real instance of Whatsapp Web to avoid being blocked. However, there is a risk of being blocked by WhatsApp as it does not allow bots or unofficial clients on its platform. The bot is not free to use, and users will be charged by OpenAI for each request made.

OmniSteward
OmniSteward is an AI-powered steward system based on large language models that can interact with users through voice or text to help control smart home devices and computer programs. It supports multi-turn dialogue, tool calling for complex tasks, multiple LLM models, voice recognition, smart home control, computer program management, online information retrieval, command line operations, and file management. The system is highly extensible, allowing users to customize and share their own tools.
chatgpt-wechat
ChatGPT-WeChat is a personal assistant application that can be safely used on WeChat through enterprise WeChat without the risk of being banned. The project is open source and free, with no paid sections or external traffic operations except for advertising on the author's public account '积木成楼'. It supports various features such as secure usage on WeChat, multi-channel customer service message integration, proxy support, session management, rapid message response, voice and image messaging, drawing capabilities, private data storage, plugin support, and more. Users can also develop their own capabilities following the rules provided. The project is currently in development with stable versions available for use.
mcp-agent
mcp-agent is a simple, composable framework designed to build agents using the Model Context Protocol. It handles the lifecycle of MCP server connections and implements patterns for building production-ready AI agents in a composable way. The framework also includes OpenAI's Swarm pattern for multi-agent orchestration in a model-agnostic manner, making it the simplest way to build robust agent applications. It is purpose-built for the shared protocol MCP, lightweight, and closer to an agent pattern library than a framework. mcp-agent allows developers to focus on the core business logic of their AI applications by handling mechanics such as server connections, working with LLMs, and supporting external signals like human input.
Gmail-MCP-Server
Gmail AutoAuth MCP Server is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server designed for Gmail integration in Claude Desktop. It supports auto authentication and enables AI assistants to manage Gmail through natural language interactions. The server provides comprehensive features for sending emails, reading messages, managing labels, searching emails, and batch operations. It offers full support for international characters, email attachments, and Gmail API integration. Users can install and authenticate the server via Smithery or manually with Google Cloud Project credentials. The server supports both Desktop and Web application credentials, with global credential storage for convenience. It also includes Docker support and instructions for cloud server authentication.
Operit
Operit AI is a fully functional AI assistant application for mobile devices, running independently on Android devices with powerful tool invocation capabilities. It offers over 40 built-in tools for file system operations, HTTP requests, system operations, UI automation, and media processing. The app combines these tools with rich plugins to enable a wide range of tasks, from simple to complex, providing a comprehensive experience of a smartphone AI assistant.


