
LiteRT
LiteRT continues the legacy of TensorFlow Lite as the trusted, high-performance runtime for on-device AI. Now with LiteRT Next, we're expanding our vision with a new generation of APIs designed for superior performance and simplified hardware acceleration. Discover what's next for on-device AI.
Stars: 815
LiteRT is Google's open-source high-performance runtime for on-device AI, previously known as TensorFlow Lite. The repository is currently not intended for open-source development, but aims to evolve to allow direct building and contributions. LiteRT supports Python versions 3.9, 3.10, 3.11 on Linux and MacOS. It ensures compatibility with existing .tflite file extension and format, offering conversion tools and continued active development under the name LiteRT.
README:
Google's On-device framework for high-performance ML & GenAI deployment on edge platforms, via efficient conversion, runtime, and optimization
📖 Get Started | 🤝 Contributing | 📜 License | 🛡 Security Policy | 📄 Documentation
LiteRT continues the legacy of TensorFlow Lite as the trusted, high-performance runtime for on-device AI.
LiteRT V2 (aka Next as announced at Google IO '25), introduced a new set of APIs, featuring advanced GPU/NPU acceleration, delivering superior performance, and making on-device ML inference easier than ever.
- LiteRT V2 is an alpha release and under active development.
- Join LiteRT NPU Early access program: g.co/ai/LiteRT-NPU-EAP
-
🆕 New LiteRT v2 API: Streamline development with automated accelerator selection, true async execution, and efficient I/O buffer handling.
- Automated accelerator selection vs explicit delegate creation
- Async execution for faster overall execution time
- Easy NPU runtime and model distribution
- Efficient I/O buffer handling
-
🤖 Unified NPU Acceleration: Offer seamless access to NPUs from major chipset providers with a consistent developer experience. LiteRT NPU acceleration is available through an Early Access Program.
-
⚡ Best-in-class GPU Performance: Use state-of-the-art GPU acceleration for on-device ML. The new buffer interoperability enables zero-copy and minimizes latency across various GPU buffer types.
-
🧠 Superior Generative AI inference: Enable the simplest integration with the best performance for GenAI models.
LiteRT is designed for cross-platform deployment on a wide range of hardware.
| Platform | CPU Support | GPU Support | NPU Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🤖 Android | ✅ | ✅ OpenCL WebGPU* |
Google Tensor* ✅ Qualcomm ✅ MediaTek S.SLI* |
| 🍎 iOS | ✅ | Metal* | ANE* |
| 🐧 Linux | ✅ | WebGPU* | N/A |
| 🍎 macOS | ✅ | Metal* | ANE* |
| 💻 Windows | ✅ | WebGPU* | Intel* |
| 🌐 Web | Coming soon | Coming soon | Coming soon |
| 🧩 Embedded | Broadcom* Raspberry Pi* |
*Coming soon
Coming soon...
For a comprehensive guide to setting up your application with LiteRT Next, see the Get Started guide.
You can build LiteRT from source:
- Start a docker daemon.
- Run
build_with_docker.shunderdocker_build/
The script automatically creates a Linux Docker image, which allows you to build artifacts for Linux and Android (through cross compilation). See build instructions in BUILD_INSTRUCTIONS.md for more information on how to build runtime libraries with the docker container.
For more information about using docker interactive shell or building different
targets, please refer to docker_build/README.md.
Every developer's path is different. Here are a few common journeys to help you get started based on your goals:
- Goal: Convert a model from PyTorch to run on LiteRT.
-
Path1 (classic models): Use the
AI Edge Torch Converter to
transform your PyTorch model into the
.tfliteformat, and use AI Edge Quantizer to optimize the model for optimal performance under resource constraints. From there, you can deploy it using the standard LiteRT runtime. - Path2 (LLMs): Use Torch Generative API to reauthor and convert your PyTorch LLMs into Apache format, and deploy it using LiteRT LM.
- Goal: Run a pre-trained model (like image segmentation) in a mobile app for the first time.
- Path1 (Beginner dev): Follow step-by-step instructions via Android Studio to create a Real-time segmentation App for CPU/GPU/NPU inference. Source code link.
- Path2 (Experienced dev): Start with the Get Started guide, find a pre-trained .tflite model on Kaggle Models, and use the standard LiteRT runtime to integrate it into your Android or iOS app.
- Goal: Accelerate an existing model to run faster and more efficiently on-device.
-
Path:
- Explore the LiteRT API to easily leverage hardware acceleration. Learn how to enable the GPU acceleration or the NPU acceleration (NPU EAP: g.co/ai/LiteRT-NPU-EAP).
- For working with Generative AI: Dive into LiteRT LM, our specialized solution for running GenAI models.
- Goal: Deploy a large language model (LLM) or diffusion model on a mobile device.
- Path: Dive into LiteRT LM, our specialized solution for running GenAI models. You'll focus on model quantization and optimizations specific to large model architectures.
Where Next:
Beta by Dec 2025:
- Achieve feature parity with TensorFlow Lite
- Upgrade GPU Acceleration to ML SDK, Metal and more advanced version
- Simplify Android development with Maven, Android Studio, and Google Tensor
- Proactively increase ML and GenAI model coverage
- Enable Certain support
- Broader LiteRT Runtime/Converter upgrades from TensorFlow Lite
General Availability by Google IO, May 2026
Our commitment is to make LiteRT the best runtime for any on-device ML deployment. The above roadmap is defined based on the following product strategy:
- Expanding Hardware Acceleration: Broadening our support for NPUs and improving performance across all major hardware accelerators.
- Generative AI Optimizations: Introducing new optimizations and features specifically for the next wave of on-device generative AI models.
- Improving Developer Tools: Building better tools for debugging, profiling, and optimizing models.
- Platform Support: Enhancing support for core platforms and exploring new ones.
Going forward, LiteRT will establish a release cadence for minor release every 4-6 weeks.
This roadmap is subject to change. We encourage community feedback—please open an issue to discuss proposals or ideas!
We welcome contributions to LiteRT. Please see the CONTRIBUTING.md file for more information on how to contribute.
We encourage you to reach out if you need help.
- GitHub Issues: For bug reports and feature requests, please file a new issue on our GitHub Issues page.
- GitHub Discussions: For questions, general discussions, and community support, please visit our GitHub Discussions.
LiteRT is part of a larger ecosystem of tools for on-device machine learning. Check out these other projects from Google:
- LiteRT Samples: A collection of LiteRT sample apps.
- AI Edge Torch Converter: A tool in LiteRT to convert PyTorch models into the LiteRT(.tflite) format for on-device deployment.
- Torch Generative API: A library in LiteRT to reauthor LLMs for efficient conversion and on-device inference.
- LiteRT-LM: A library to efficiently run Large Language Models (LLMs) across edge platforms, built on top of LiteRT.
- XNNPACK: A highly optimized library of neural network inference operators for ARM, x86, and WebAssembly architectures that provides high-performance CPU acceleration for LiteRT.
- V2 GPU Delegate - Coming soon
- MediaPipe: A framework for building cross-platform, customizable ML solutions for live and streaming media.
This project is dedicated to fostering an open and welcoming environment. Please read our Code of Conduct to understand the standards of behavior we expect from all participants in our community.
LiteRT is licensed under the Apache-2.0 License.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LiteRT
Similar Open Source Tools

LiteRT
LiteRT is Google's open-source high-performance runtime for on-device AI, previously known as TensorFlow Lite. The repository is currently not intended for open-source development, but aims to evolve to allow direct building and contributions. LiteRT supports Python versions 3.9, 3.10, 3.11 on Linux and MacOS. It ensures compatibility with existing .tflite file extension and format, offering conversion tools and continued active development under the name LiteRT.
Simplifine
Simplifine is an open-source library designed for easy LLM finetuning, enabling users to perform tasks such as supervised fine tuning, question-answer finetuning, contrastive loss for embedding tasks, multi-label classification finetuning, and more. It provides features like WandB logging, in-built evaluation tools, automated finetuning parameters, and state-of-the-art optimization techniques. The library offers bug fixes, new features, and documentation updates in its latest version. Users can install Simplifine via pip or directly from GitHub. The project welcomes contributors and provides comprehensive documentation and support for users.

UltraRAG
The UltraRAG framework is a researcher and developer-friendly RAG system solution that simplifies the process from data construction to model fine-tuning in domain adaptation. It introduces an automated knowledge adaptation technology system, supporting no-code programming, one-click synthesis and fine-tuning, multidimensional evaluation, and research-friendly exploration work integration. The architecture consists of Frontend, Service, and Backend components, offering flexibility in customization and optimization. Performance evaluation in the legal field shows improved results compared to VanillaRAG, with specific metrics provided. The repository is licensed under Apache-2.0 and encourages citation for support.
saga-reader
Saga Reader is an AI-driven think tank-style reader that automatically retrieves information from the internet based on user-specified topics and preferences. It uses cloud or local large models to summarize and provide guidance, and it includes an AI-driven interactive companion reading function, allowing you to discuss and exchange ideas with AI about the content you've read. Saga Reader is completely free and open-source, meaning all data is securely stored on your own computer and is not controlled by third-party service providers. Additionally, you can manage your subscription keywords based on your interests and preferences without being disturbed by advertisements and commercialized content.
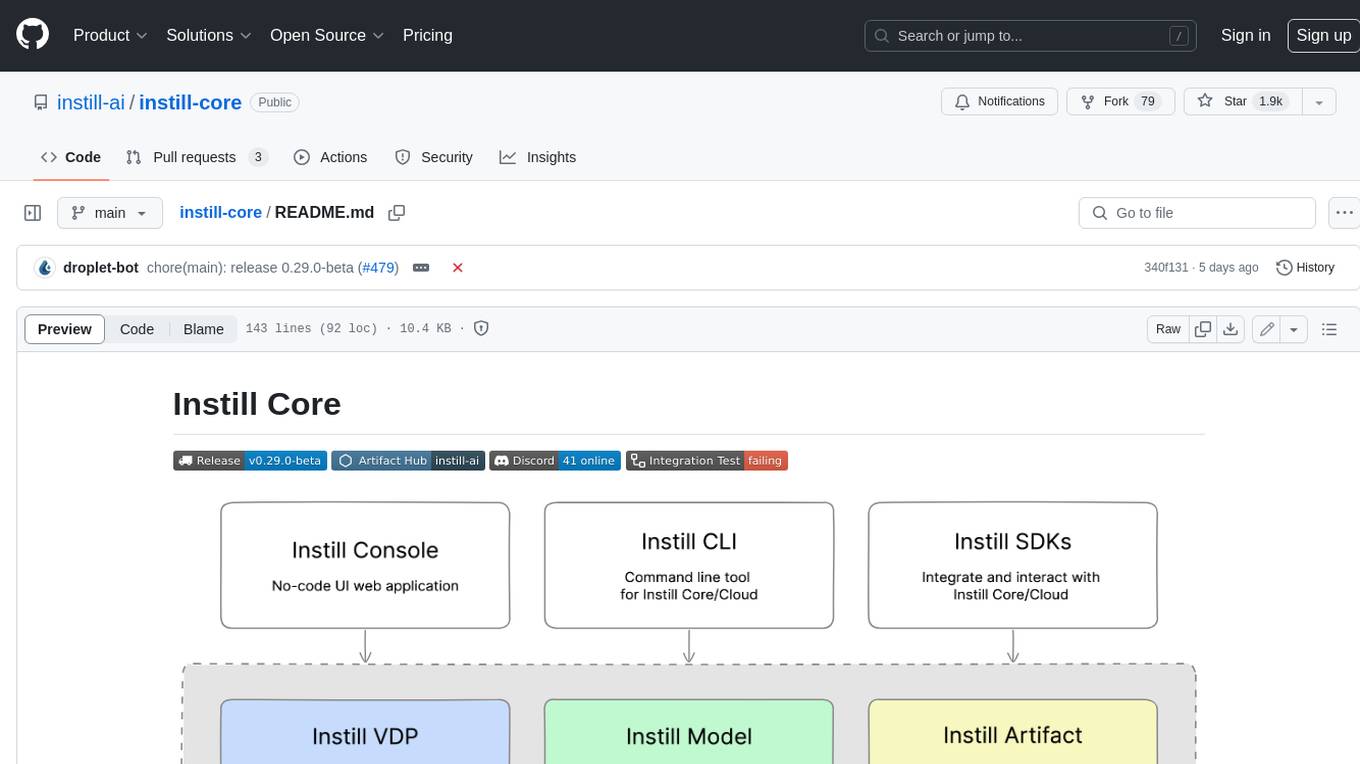
instill-core
Instill Core is an open-source orchestrator comprising a collection of source-available projects designed to streamline every aspect of building versatile AI features with unstructured data. It includes Instill VDP (Versatile Data Pipeline) for unstructured data, AI, and pipeline orchestration, Instill Model for scalable MLOps and LLMOps for open-source or custom AI models, and Instill Artifact for unified unstructured data management. Instill Core can be used for tasks such as building, testing, and sharing pipelines, importing, serving, fine-tuning, and monitoring ML models, and transforming documents, images, audio, and video into a unified AI-ready format.

nanobrowser
Nanobrowser is an open-source AI web automation tool that runs in your browser. It is a free alternative to OpenAI Operator with flexible LLM options and a multi-agent system. Nanobrowser offers premium web automation capabilities while keeping users in complete control, with features like a multi-agent system, interactive side panel, task automation, follow-up questions, and multiple LLM support. Users can easily download and install Nanobrowser as a Chrome extension, configure agent models, and accomplish tasks such as news summary, GitHub research, and shopping research with just a sentence. The tool uses a specialized multi-agent system powered by large language models to understand and execute complex web tasks. Nanobrowser is actively developed with plans to expand LLM support, implement security measures, optimize memory usage, enable session replay, and develop specialized agents for domain-specific tasks. Contributions from the community are welcome to improve Nanobrowser and build the future of web automation.
openvino
OpenVINO™ is an open-source toolkit for optimizing and deploying AI inference. It provides a common API to deliver inference solutions on various platforms, including CPU, GPU, NPU, and heterogeneous devices. OpenVINO™ supports pre-trained models from Open Model Zoo and popular frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and ONNX. Key components of OpenVINO™ include the OpenVINO™ Runtime, plugins for different hardware devices, frontends for reading models from native framework formats, and the OpenVINO Model Converter (OVC) for adjusting models for optimal execution on target devices.
ProjectAirSim
Project AirSim is a simulation platform for drones, robots, and autonomous systems. Leveraging Unreal Engine 5, it provides photo-realistic visuals and a simulation framework for custom physics, controllers, actuators, and sensors. It consists of three main layers: Sim Libs, Plugin, and Client Library. It supports Windows 11 and Ubuntu 22, inviting collaboration and enterprise support. Users can join the community, contribute to the roadmap, and get started with pre-built binaries or building from source. It offers headless running options and references for configuration settings, API, controllers, sensors, scene, physics, and FAQ.
wanwu
Wanwu AI Agent Platform is an enterprise-grade one-stop commercially friendly AI agent development platform designed for business scenarios. It provides enterprises with a safe, efficient, and compliant one-stop AI solution. The platform integrates cutting-edge technologies such as large language models and business process automation to build an AI engineering platform covering model full life-cycle management, MCP, web search, AI agent rapid development, enterprise knowledge base construction, and complex workflow orchestration. It supports modular architecture design, flexible functional expansion, and secondary development, reducing the application threshold of AI technology while ensuring security and privacy protection of enterprise data. It accelerates digital transformation, cost reduction, efficiency improvement, and business innovation for enterprises of all sizes.
TaskingAI
TaskingAI brings Firebase's simplicity to **AI-native app development**. The platform enables the creation of GPTs-like multi-tenant applications using a wide range of LLMs from various providers. It features distinct, modular functions such as Inference, Retrieval, Assistant, and Tool, seamlessly integrated to enhance the development process. TaskingAI’s cohesive design ensures an efficient, intelligent, and user-friendly experience in AI application development.
sail
Sail is a tool designed to unify stream processing, batch processing, and compute-intensive workloads, serving as a drop-in replacement for Spark SQL and the Spark DataFrame API in single-process settings. It aims to streamline data processing tasks and facilitate AI workloads.
refact
This repository contains Refact WebUI for fine-tuning and self-hosting of code models, which can be used inside Refact plugins for code completion and chat. Users can fine-tune open-source code models, self-host them, download and upload Lloras, use models for code completion and chat inside Refact plugins, shard models, host multiple small models on one GPU, and connect GPT-models for chat using OpenAI and Anthropic keys. The repository provides a Docker container for running the self-hosted server and supports various models for completion, chat, and fine-tuning. Refact is free for individuals and small teams under the BSD-3-Clause license, with custom installation options available for GPU support. The community and support include contributing guidelines, GitHub issues for bugs, a community forum, Discord for chatting, and Twitter for product news and updates.
AI-Gateway
The AI-Gateway repository explores the AI Gateway pattern through a series of experimental labs, focusing on Azure API Management for handling AI services APIs. The labs provide step-by-step instructions using Jupyter notebooks with Python scripts, Bicep files, and APIM policies. The goal is to accelerate experimentation of advanced use cases and pave the way for further innovation in the rapidly evolving field of AI. The repository also includes a Mock Server to mimic the behavior of the OpenAI API for testing and development purposes.
AgentForge
AgentForge is a low-code framework tailored for the rapid development, testing, and iteration of AI-powered autonomous agents and Cognitive Architectures. It is compatible with a range of LLM models and offers flexibility to run different models for different agents based on specific needs. The framework is designed for seamless extensibility and database-flexibility, making it an ideal playground for various AI projects. AgentForge is a beta-testing ground and future-proof hub for crafting intelligent, model-agnostic autonomous agents.
beeai-platform
BeeAI is an open-source platform that simplifies the discovery, running, and sharing of AI agents across different frameworks. It addresses challenges such as framework fragmentation, deployment complexity, and discovery issues by providing a standardized platform for individuals and teams to access agents easily. With features like a centralized agent catalog, framework-agnostic interfaces, containerized agents, and consistent user experiences, BeeAI aims to streamline the process of working with AI agents for both developers and teams.
LLMstudio
LLMstudio by TensorOps is a platform that offers prompt engineering tools for accessing models from providers like OpenAI, VertexAI, and Bedrock. It provides features such as Python Client Gateway, Prompt Editing UI, History Management, and Context Limit Adaptability. Users can track past runs, log costs and latency, and export history to CSV. The tool also supports automatic switching to larger-context models when needed. Coming soon features include side-by-side comparison of LLMs, automated testing, API key administration, project organization, and resilience against rate limits. LLMstudio aims to streamline prompt engineering, provide execution history tracking, and enable effortless data export, offering an evolving environment for teams to experiment with advanced language models.
For similar tasks

LiteRT
LiteRT is Google's open-source high-performance runtime for on-device AI, previously known as TensorFlow Lite. The repository is currently not intended for open-source development, but aims to evolve to allow direct building and contributions. LiteRT supports Python versions 3.9, 3.10, 3.11 on Linux and MacOS. It ensures compatibility with existing .tflite file extension and format, offering conversion tools and continued active development under the name LiteRT.
Ollama-Colab-Integration
Ollama Colab Integration V4 is a tool designed to enhance the interaction and management of large language models. It allows users to quantize models within their notebook environment, access a variety of models through a user-friendly interface, and manage public endpoints efficiently. The tool also provides features like LiteLLM proxy control, model insights, and customizable model file templating. Users can troubleshoot model loading issues, CPU fallback strategies, and manage VRAM and RAM effectively. Additionally, the tool offers functionalities for downloading model files from Hugging Face, model conversion with high precision, model quantization using Q and Kquants, and securely uploading converted models to Hugging Face.
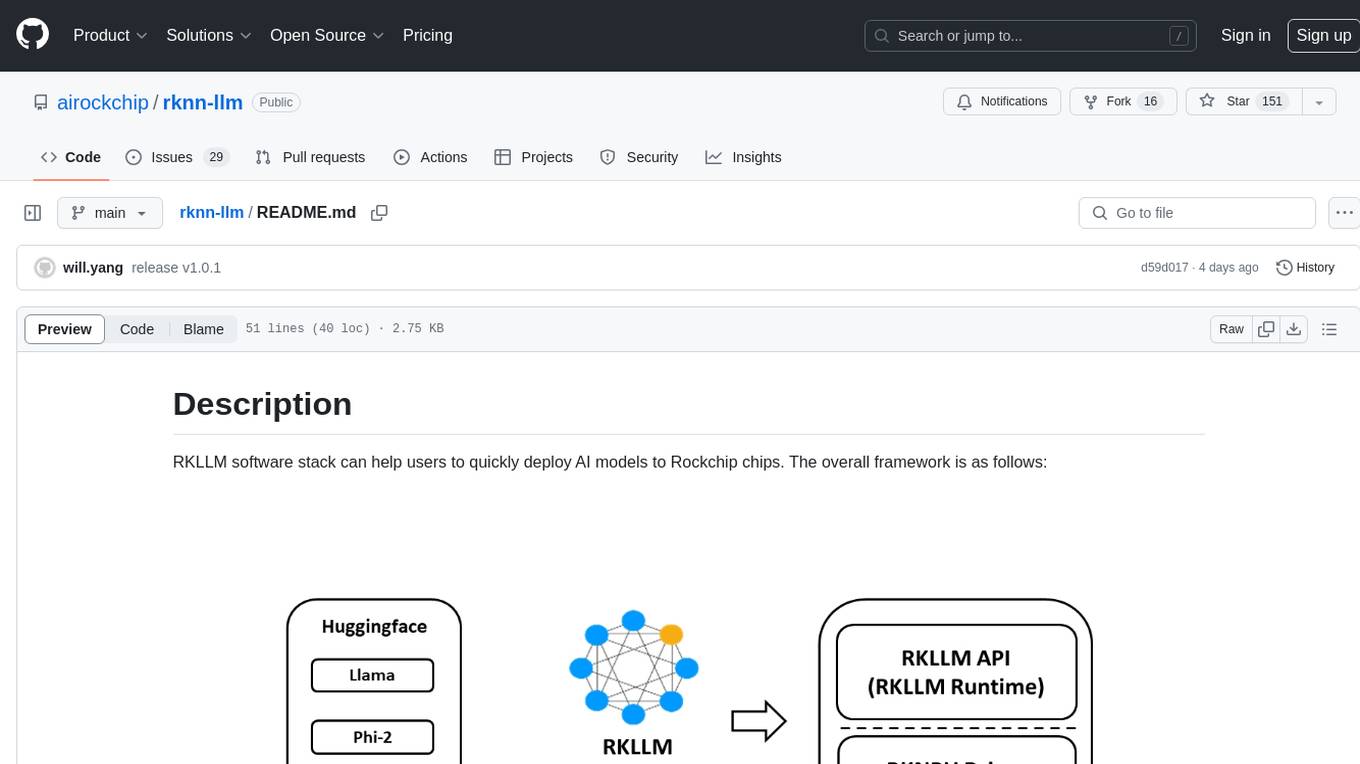
rknn-llm
RKLLM software stack is a toolkit designed to help users quickly deploy AI models to Rockchip chips. It consists of RKLLM-Toolkit for model conversion and quantization, RKLLM Runtime for deploying models on Rockchip NPU platform, and RKNPU kernel driver for hardware interaction. The toolkit supports RK3588 and RK3576 series chips and various models like TinyLLAMA, Qwen, Phi, ChatGLM3, Gemma, InternLM2, and MiniCPM. Users can download packages, docker images, examples, and docs from RKLLM_SDK. Additionally, RKNN-Toolkit2 SDK is available for deploying additional AI models.
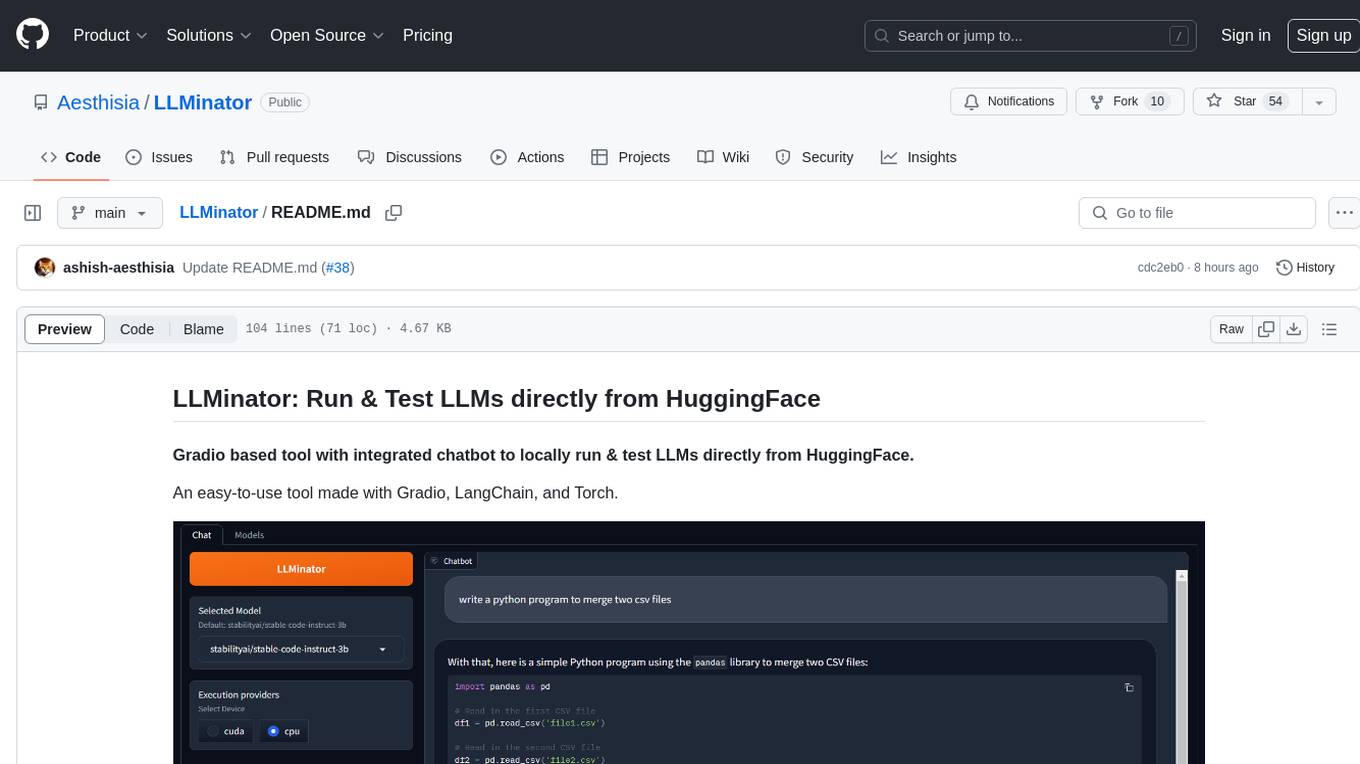
LLMinator
LLMinator is a Gradio-based tool with an integrated chatbot designed to locally run and test Language Model Models (LLMs) directly from HuggingFace. It provides an easy-to-use interface made with Gradio, LangChain, and Torch, offering features such as context-aware streaming chatbot, inbuilt code syntax highlighting, loading any LLM repo from HuggingFace, support for both CPU and CUDA modes, enabling LLM inference with llama.cpp, and model conversion capabilities.

xFasterTransformer
xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for Large Language Models (LLMs) on the X86 platform, providing high performance and scalability for inference on mainstream LLM models. It offers C++ and Python APIs for easy integration, along with example codes and benchmark scripts. Users can prepare models in a different format, convert them, and use the APIs for tasks like encoding input prompts, generating token ids, and serving inference requests. The tool supports various data types and models, and can run in single or multi-rank modes using MPI. A web demo based on Gradio is available for popular LLM models like ChatGLM and Llama2. Benchmark scripts help evaluate model inference performance quickly, and MLServer enables serving with REST and gRPC interfaces.
ai-edge-torch
AI Edge Torch is a Python library that supports converting PyTorch models into a .tflite format for on-device applications on Android, iOS, and IoT devices. It offers broad CPU coverage with initial GPU and NPU support, closely integrating with PyTorch and providing good coverage of Core ATen operators. The library includes a PyTorch converter for model conversion and a Generative API for authoring mobile-optimized PyTorch Transformer models, enabling easy deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) on mobile devices.
BodhiApp
Bodhi App runs Open Source Large Language Models locally, exposing LLM inference capabilities as OpenAI API compatible REST APIs. It leverages llama.cpp for GGUF format models and huggingface.co ecosystem for model downloads. Users can run fine-tuned models for chat completions, create custom aliases, and convert Huggingface models to GGUF format. The CLI offers commands for environment configuration, model management, pulling files, serving API, and more.
lm.rs
lm.rs is a tool that allows users to run inference on Language Models locally on the CPU using Rust. It supports LLama3.2 1B and 3B models, with a WebUI also available. The tool provides benchmarks and download links for models and tokenizers, with recommendations for quantization options. Users can convert models from Google/Meta on huggingface using provided scripts. The tool can be compiled with cargo and run with various arguments for model weights, tokenizer, temperature, and more. Additionally, a backend for the WebUI can be compiled and run to connect via the web interface.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
