
Ollama-Colab-Integration
Jupyter Notebooks for Ollama integration
Stars: 93
Ollama Colab Integration V4 is a tool designed to enhance the interaction and management of large language models. It allows users to quantize models within their notebook environment, access a variety of models through a user-friendly interface, and manage public endpoints efficiently. The tool also provides features like LiteLLM proxy control, model insights, and customizable model file templating. Users can troubleshoot model loading issues, CPU fallback strategies, and manage VRAM and RAM effectively. Additionally, the tool offers functionalities for downloading model files from Hugging Face, model conversion with high precision, model quantization using Q and Kquants, and securely uploading converted models to Hugging Face.
README:
Will update coming days. Mismatch with orginal versions so will update soon with alot of performance gains. Will be able to run within 2 minutes
Dive into the world of large language models with Ollama Colab Integration V4. This update brings an exciting feature: the ability to quantize models right within your notebook, coupled with the streamlined Ollama Companion, now powered by a Streamlit-based WebUI.
- Run Notebook Cells: Simply run the cells in the provided notebook to set up all dependencies automatically. It's designed for a hassle-free setup experience, perfect for both beginners and seasoned users.
- Get Public URL: Upon loading, you'll receive a public URL. This URL grants you access to the Ollama-Companion, where you can interact with various language models and leverage the tool's full potential.
- Seamless Quantization: Perform model quantization directly in your notebook environment.
- Integrated Streamlit UI: Experience an intuitive interaction with models through the Streamlit-based Ollama Companion.
- Secure Cloudflared Tunneling: Create endpoints independently and securely.
- Accessible Model Library: Easily access a wide range of models via a user-friendly interface.
- Customizable ModelFile Templater: Tailor model parameters to your requirements.
- In-depth Model Insights: Obtain detailed information about model specifications and licensing.
- Efficient Public Endpoint Management: Manage your public endpoints for both original and OpenAI models with ease.
- LiteLLM Proxy Control: Directly manage LiteLLM proxy and its automated polling.
- Utility Tools: Additional features include CURL command creation and manual model setup.
- Model Loading Issues: Tips for handling GPU crashes with large models.
- CPU Fallback Strategy: Guidelines for reverting to CPU post-crash.
- VRAM and RAM Management: Best practices for managing VRAM and RAM limitations.
- Kaggle for Enhanced Performance: Using Kaggle for better VRAM and RAM capabilities.
Contributions to Ollama Colab Integration V4 are always welcome. Enhance, suggest, and report to help us improve.
This Notebook git clones from https://github.com/Luxadevi/Ollama-Companion branch Colab-installer for its optimized installation file.
Want to un Ollama-Companion on your Mac, Windows or Linux machine, download from Ollama-Companion GitHub Repository
Ollama-Companion is developed to enhance the interaction and management of Ollama and other large language model (LLM) applications. It aims to support all Ollama API endpoints, facilitate model conversion, and ensure seamless connectivity, even in environments behind NAT. This tool is crafted to construct a versatile and user-friendly LLM software stack, meeting a diverse range of user requirements.
Transitioning from Gradio to Streamlit necessitated the development of new tunneling methods to maintain compatibility with Jupyter Notebooks, like Google Colab.
Explore our Colab Integration to set up the companion within minutes and obtain a public-facing URL.
Interact with Ollama API without typing commands and using a interface to manage your models. Run Ollama or connect to a client an use this WebUI to manage.
Ollama-Companion, developed for enhancing the interaction and management of Ollama and other large language model (LLM) applications, now features Streamlit integration. This tool aims to support all Ollama API endpoints, facilitate model conversion, and ensure seamless connectivity, even in environments behind NAT. Transitioning from Gradio to Streamlit has led to the development of new tunneling methods, maintaining compatibility with Jupyter Notebooks like Google Colab.
Explore our Colab Integration and set up the companion within minutes to obtain a public-facing URL for accessing Ollama-Companion. Visit the Ollama-Companion GitHub page for more details and repository access.
Develop your own Streamlit components and integrate them into Ollama-Companion. See examples using LangChain and other software stacks within Streamlit. management. You can also manage a remote Ollama instance by setting the Ollama endpoint in the UI.
Develop your own Streamlit components and integrate them into Ollama-Companion. See examples using LangChain and other software stacks within Streamlit.
This part allows you to manage and interact with the LiteLLM Proxy, which is used to convert over 100 LLM providers to the OpenAI API standard.
Check LiteLLM out at LiteLLM proxy
- Start LiteLLM Proxy: Click this button to start the LiteLLM Proxy. The proxy will run in the background and facilitate the conversion process.
- Read LiteLLM Log: Use this button to read the LiteLLM Proxy log, which contains relevant information about its operation.
- Start Polling: Click to initiate polling. Polling checks for updates to the ollama API and adds any new models to the configuration.
- Stop Polling: Use this button to stop polling for updates.
- Kill Existing LiteLLM Processes: If there are existing LiteLLM processes running, this button will terminate them.
- Free Up Port 8000: Click this button to free up port 8000 if it's currently in use.
Please note that starting the LiteLLM Proxy and performing other actions may take some time, so be patient and wait for the respective success messages.
The "Log Output" section will display relevant information from the LiteLLM Proxy log, providing insights into its operation and status.
To download model files from Hugging Face, follow these steps:
-
Visit the Model Page: Go to the Hugging Face model page you wish to download. For example: Mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2.
-
Copy Username/RepositoryName: On the model page, locate the icon next to the username of the model's author (usually a clipboard or copy symbol). Click to copy the Username/RepositoryName, e.g.,
mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2. -
Paste in the Input Field: Paste the copied Username/RepositoryName directly into the designated input field in your application.
-
Get File List: Click the "Get file list" button to retrieve a list of available files in this repository.
-
Review File List: Ensure the list contains the correct model files you wish to download.
-
Download Model: Click the "Download Model" button to start the download process for the selected model files.
-
File Storage: The model files will be saved in the
llama.cpp/modelsdirectory on your device.
By following these steps, you have successfully downloaded the model files from Hugging Face, and they are now stored in the llama.cpp/models directory for your use.
-
Select a Model Folder: Choose a folder within
llama.cpp/modelsthat contains the model you wish to convert. -
Set Conversion Options: Select your desired conversion options from the provided checkboxes, F32 F16 or Q8_0.
-
Docker Container Option: Optionally, use a Docker container for added flexibility and compatibility.
-
Execute Conversion: Click the "Run Commands" button to start the conversion process.
-
Output Location: Converted models will be saved in the
High-Precision-Quantizationsubfolder within the selected model folder.
Utilize this process to efficiently convert models while maintaining high precision and compatibility with llama.cpp.
-
Select GGUF File: Choose the GGUF file you wish to quantize from the dropdown list.
-
Quantization Options: Check the boxes next to the quantization options you want to apply (Q, Kquants).
-
Execution Environment: Choose to use either the native
llama.cppor a Docker container for compatibility. -
Run Quantization: Click the "Run Selected Commands" button to schedule and execute the quantization tasks.
-
Save Location: The quantized models will be saved in the
/modelname/Medium-Precision-Quantizationfolder.
Follow these steps to perform model quantization using Q and Kquants, saving the quantized models in the specified directory. Schedule multiple options in a row they will remember and run eventually.
Use this section to securely upload your converted models to Hugging Face.
-
Select a Model: Choose a model from the dropdown list. These models are located in the
llama.cpp/modelsdirectory. -
Enter Repository Name: Specify a name for the new Hugging Face repository where your model will be uploaded.
-
Choose Files for Upload: Select the files you wish to upload from the subfolders of the chosen model.
-
Add README Content: Optionally, write content for the README.md file of your new repository.
- For enhanced security, use an encrypted token. Encrypt your Hugging Face token on the Token Encrypt page and enter it in the "Enter Encrypted Token" field.
- Alternatively, enter an unencrypted Hugging Face token directly.
- Upload Files: Click the "Upload Selected Files" button to initiate the upload to Hugging Face.
After completing these steps, your uploaded models will be accessible at https://huggingface.co/your-username/your-repo-name.
- Intuitive and Responsive UI
- Advanced Modelfile Management
- Dynamic UI Building Blocks
- Download and Convert PyTorch Models from Huggingface
- Multiple Format Conversion Options
- Easy API Connectivity via Secure Tunnels
- Options for Sharing and Cloud Testing
- Accessible from Any Network Setup
- Easy Model Upload to Huggingface
- Capability to Queue Multiple Workloads
- Integrated LLAVA Image Analysis
- Configurable Security Features
- Advanced Token Encryption
We are dedicated to the continuous enhancement of Ollama-Companion, with a focus on user experience and expanded functionality.
Check the docs for more information
Licensed under the Apache License.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Ollama-Colab-Integration
Similar Open Source Tools

Ollama-Colab-Integration
Ollama Colab Integration V4 is a tool designed to enhance the interaction and management of large language models. It allows users to quantize models within their notebook environment, access a variety of models through a user-friendly interface, and manage public endpoints efficiently. The tool also provides features like LiteLLM proxy control, model insights, and customizable model file templating. Users can troubleshoot model loading issues, CPU fallback strategies, and manage VRAM and RAM effectively. Additionally, the tool offers functionalities for downloading model files from Hugging Face, model conversion with high precision, model quantization using Q and Kquants, and securely uploading converted models to Hugging Face.
Local-Multimodal-AI-Chat
Local Multimodal AI Chat is a multimodal chat application that integrates various AI models to manage audio, images, and PDFs seamlessly within a single interface. It offers local model processing with Ollama for data privacy, integration with OpenAI API for broader AI capabilities, audio chatting with Whisper AI for accurate voice interpretation, and PDF chatting with Chroma DB for efficient PDF interactions. The application is designed for AI enthusiasts and developers seeking a comprehensive solution for multimodal AI technologies.
comfyui_LLM_Polymath
LLM Polymath Chat Node is an advanced Chat Node for ComfyUI that integrates large language models to build text-driven applications and automate data processes, enhancing prompt responses by incorporating real-time web search, linked content extraction, and custom agent instructions. It supports both OpenAI’s GPT-like models and alternative models served via a local Ollama API. The core functionalities include Comfy Node Finder and Smart Assistant, along with additional agents like Flux Prompter, Custom Instructors, Python debugger, and scripter. The tool offers features for prompt processing, web search integration, model & API integration, custom instructions, image handling, logging & debugging, output compression, and more.

nanobrowser
Nanobrowser is an open-source AI web automation tool that runs in your browser. It is a free alternative to OpenAI Operator with flexible LLM options and a multi-agent system. Nanobrowser offers premium web automation capabilities while keeping users in complete control, with features like a multi-agent system, interactive side panel, task automation, follow-up questions, and multiple LLM support. Users can easily download and install Nanobrowser as a Chrome extension, configure agent models, and accomplish tasks such as news summary, GitHub research, and shopping research with just a sentence. The tool uses a specialized multi-agent system powered by large language models to understand and execute complex web tasks. Nanobrowser is actively developed with plans to expand LLM support, implement security measures, optimize memory usage, enable session replay, and develop specialized agents for domain-specific tasks. Contributions from the community are welcome to improve Nanobrowser and build the future of web automation.
LLMstudio
LLMstudio by TensorOps is a platform that offers prompt engineering tools for accessing models from providers like OpenAI, VertexAI, and Bedrock. It provides features such as Python Client Gateway, Prompt Editing UI, History Management, and Context Limit Adaptability. Users can track past runs, log costs and latency, and export history to CSV. The tool also supports automatic switching to larger-context models when needed. Coming soon features include side-by-side comparison of LLMs, automated testing, API key administration, project organization, and resilience against rate limits. LLMstudio aims to streamline prompt engineering, provide execution history tracking, and enable effortless data export, offering an evolving environment for teams to experiment with advanced language models.

deepdoctection
**deep** doctection is a Python library that orchestrates document extraction and document layout analysis tasks using deep learning models. It does not implement models but enables you to build pipelines using highly acknowledged libraries for object detection, OCR and selected NLP tasks and provides an integrated framework for fine-tuning, evaluating and running models. For more specific text processing tasks use one of the many other great NLP libraries. **deep** doctection focuses on applications and is made for those who want to solve real world problems related to document extraction from PDFs or scans in various image formats. **deep** doctection provides model wrappers of supported libraries for various tasks to be integrated into pipelines. Its core function does not depend on any specific deep learning library. Selected models for the following tasks are currently supported: * Document layout analysis including table recognition in Tensorflow with **Tensorpack**, or PyTorch with **Detectron2**, * OCR with support of **Tesseract**, **DocTr** (Tensorflow and PyTorch implementations available) and a wrapper to an API for a commercial solution, * Text mining for native PDFs with **pdfplumber**, * Language detection with **fastText**, * Deskewing and rotating images with **jdeskew**. * Document and token classification with all LayoutLM models provided by the **Transformer library**. (Yes, you can use any LayoutLM-model with any of the provided OCR-or pdfplumber tools straight away!). * Table detection and table structure recognition with **table-transformer**. * There is a small dataset for token classification available and a lot of new tutorials to show, how to train and evaluate this dataset using LayoutLMv1, LayoutLMv2, LayoutXLM and LayoutLMv3. * Comprehensive configuration of **analyzer** like choosing different models, output parsing, OCR selection. Check this notebook or the docs for more infos. * Document layout analysis and table recognition now runs with **Torchscript** (CPU) as well and **Detectron2** is not required anymore for basic inference. * [**new**] More angle predictors for determining the rotation of a document based on **Tesseract** and **DocTr** (not contained in the built-in Analyzer). * [**new**] Token classification with **LiLT** via **transformers**. We have added a model wrapper for token classification with LiLT and added a some LiLT models to the model catalog that seem to look promising, especially if you want to train a model on non-english data. The training script for LayoutLM can be used for LiLT as well and we will be providing a notebook on how to train a model on a custom dataset soon. **deep** doctection provides on top of that methods for pre-processing inputs to models like cropping or resizing and to post-process results, like validating duplicate outputs, relating words to detected layout segments or ordering words into contiguous text. You will get an output in JSON format that you can customize even further by yourself. Have a look at the **introduction notebook** in the notebook repo for an easy start. Check the **release notes** for recent updates. **deep** doctection or its support libraries provide pre-trained models that are in most of the cases available at the **Hugging Face Model Hub** or that will be automatically downloaded once requested. For instance, you can find pre-trained object detection models from the Tensorpack or Detectron2 framework for coarse layout analysis, table cell detection and table recognition. Training is a substantial part to get pipelines ready on some specific domain, let it be document layout analysis, document classification or NER. **deep** doctection provides training scripts for models that are based on trainers developed from the library that hosts the model code. Moreover, **deep** doctection hosts code to some well established datasets like **Publaynet** that makes it easy to experiment. It also contains mappings from widely used data formats like COCO and it has a dataset framework (akin to **datasets** so that setting up training on a custom dataset becomes very easy. **This notebook** shows you how to do this. **deep** doctection comes equipped with a framework that allows you to evaluate predictions of a single or multiple models in a pipeline against some ground truth. Check again **here** how it is done. Having set up a pipeline it takes you a few lines of code to instantiate the pipeline and after a for loop all pages will be processed through the pipeline.
mikupad
mikupad is a lightweight and efficient language model front-end powered by ReactJS, all packed into a single HTML file. Inspired by the likes of NovelAI, it provides a simple yet powerful interface for generating text with the help of various backends.

kairon
Kairon is an open-source conversational digital transformation platform that helps build LLM-based digital assistants at scale. It provides a no-coding web interface for adapting, training, testing, and maintaining AI assistants. Kairon focuses on pre-processing data for chatbots, including question augmentation, knowledge graph generation, and post-processing metrics. It offers end-to-end lifecycle management, low-code/no-code interface, secure script injection, telemetry monitoring, chat client designer, analytics module, and real-time struggle analytics. Kairon is suitable for teams and individuals looking for an easy interface to create, train, test, and deploy digital assistants.
Simplifine
Simplifine is an open-source library designed for easy LLM finetuning, enabling users to perform tasks such as supervised fine tuning, question-answer finetuning, contrastive loss for embedding tasks, multi-label classification finetuning, and more. It provides features like WandB logging, in-built evaluation tools, automated finetuning parameters, and state-of-the-art optimization techniques. The library offers bug fixes, new features, and documentation updates in its latest version. Users can install Simplifine via pip or directly from GitHub. The project welcomes contributors and provides comprehensive documentation and support for users.

Instrukt
Instrukt is a terminal-based AI integrated environment that allows users to create and instruct modular AI agents, generate document indexes for question-answering, and attach tools to any agent. It provides a platform for users to interact with AI agents in natural language and run them inside secure containers for performing tasks. The tool supports custom AI agents, chat with code and documents, tools customization, prompt console for quick interaction, LangChain ecosystem integration, secure containers for agent execution, and developer console for debugging and introspection. Instrukt aims to make AI accessible to everyone by providing tools that empower users without relying on external APIs and services.

swark
Swark is a VS Code extension that automatically generates architecture diagrams from code using large language models (LLMs). It is directly integrated with GitHub Copilot, requires no authentication or API key, and supports all languages. Swark helps users learn new codebases, review AI-generated code, improve documentation, understand legacy code, spot design flaws, and gain test coverage insights. It saves output in a 'swark-output' folder with diagram and log files. Source code is only shared with GitHub Copilot for privacy. The extension settings allow customization for file reading, file extensions, exclusion patterns, and language model selection. Swark is open source under the GNU Affero General Public License v3.0.
MyDeviceAI
MyDeviceAI is a personal AI assistant app for iPhone that brings the power of artificial intelligence directly to the device. It focuses on privacy, performance, and personalization by running AI models locally and integrating with privacy-focused web services. The app offers seamless user experience, web search integration, advanced reasoning capabilities, personalization features, chat history access, and broad device support. It requires macOS, Xcode, CocoaPods, Node.js, and a React Native development environment for installation. The technical stack includes React Native framework, AI models like Qwen 3 and BGE Small, SearXNG integration, Redux for state management, AsyncStorage for storage, Lucide for UI components, and tools like ESLint and Prettier for code quality.
ROSGPT_Vision
ROSGPT_Vision is a new robotic framework designed to command robots using only two prompts: a Visual Prompt for visual semantic features and an LLM Prompt to regulate robotic reactions. It is based on the Prompting Robotic Modalities (PRM) design pattern and is used to develop CarMate, a robotic application for monitoring driver distractions and providing real-time vocal notifications. The framework leverages state-of-the-art language models to facilitate advanced reasoning about image data and offers a unified platform for robots to perceive, interpret, and interact with visual data through natural language. LangChain is used for easy customization of prompts, and the implementation includes the CarMate application for driver monitoring and assistance.
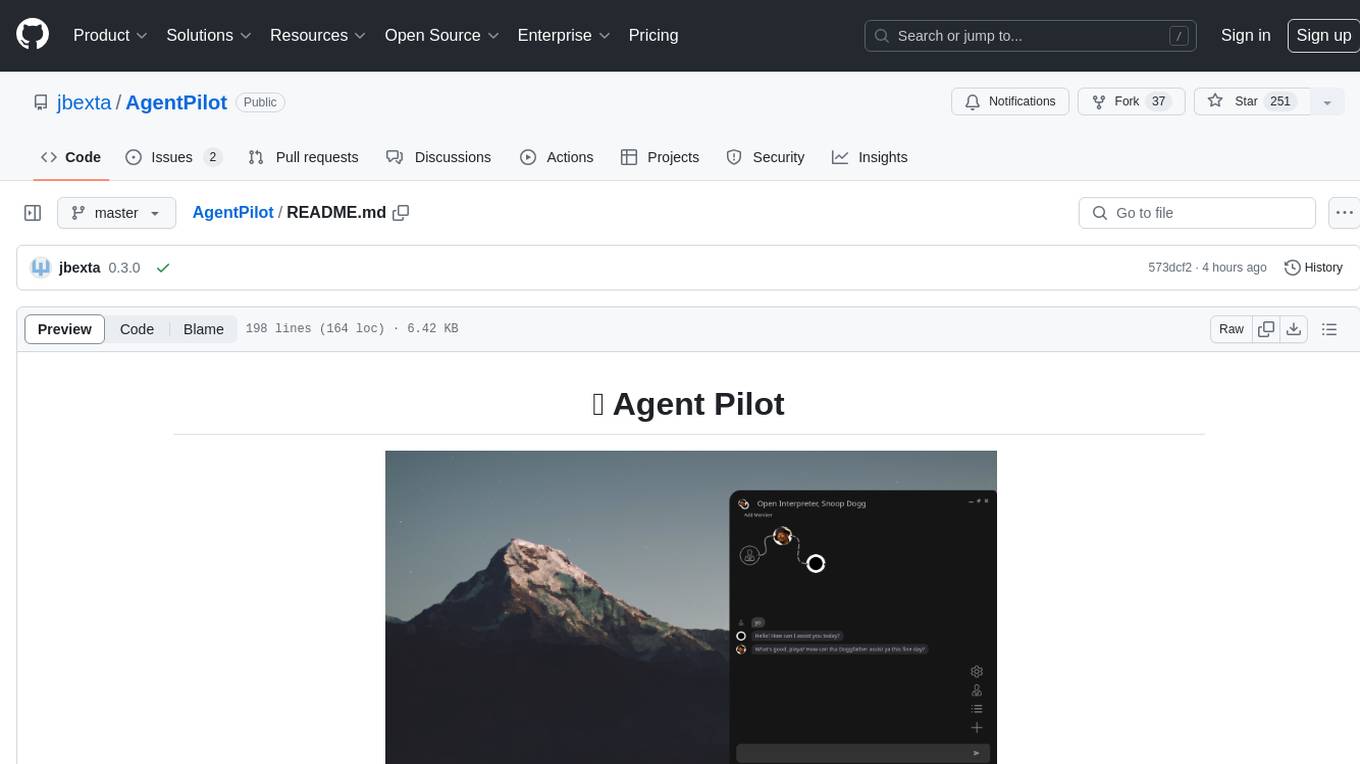
AgentPilot
Agent Pilot is an open source desktop app for creating, managing, and chatting with AI agents. It features multi-agent, branching chats with various providers through LiteLLM. Users can combine models from different providers, configure interactions, and run code using the built-in Open Interpreter. The tool allows users to create agents, manage chats, work with multi-agent workflows, branching workflows, context blocks, tools, and plugins. It also supports a code interpreter, scheduler, voice integration, and integration with various AI providers. Contributions to the project are welcome, and users can report known issues for improvement.
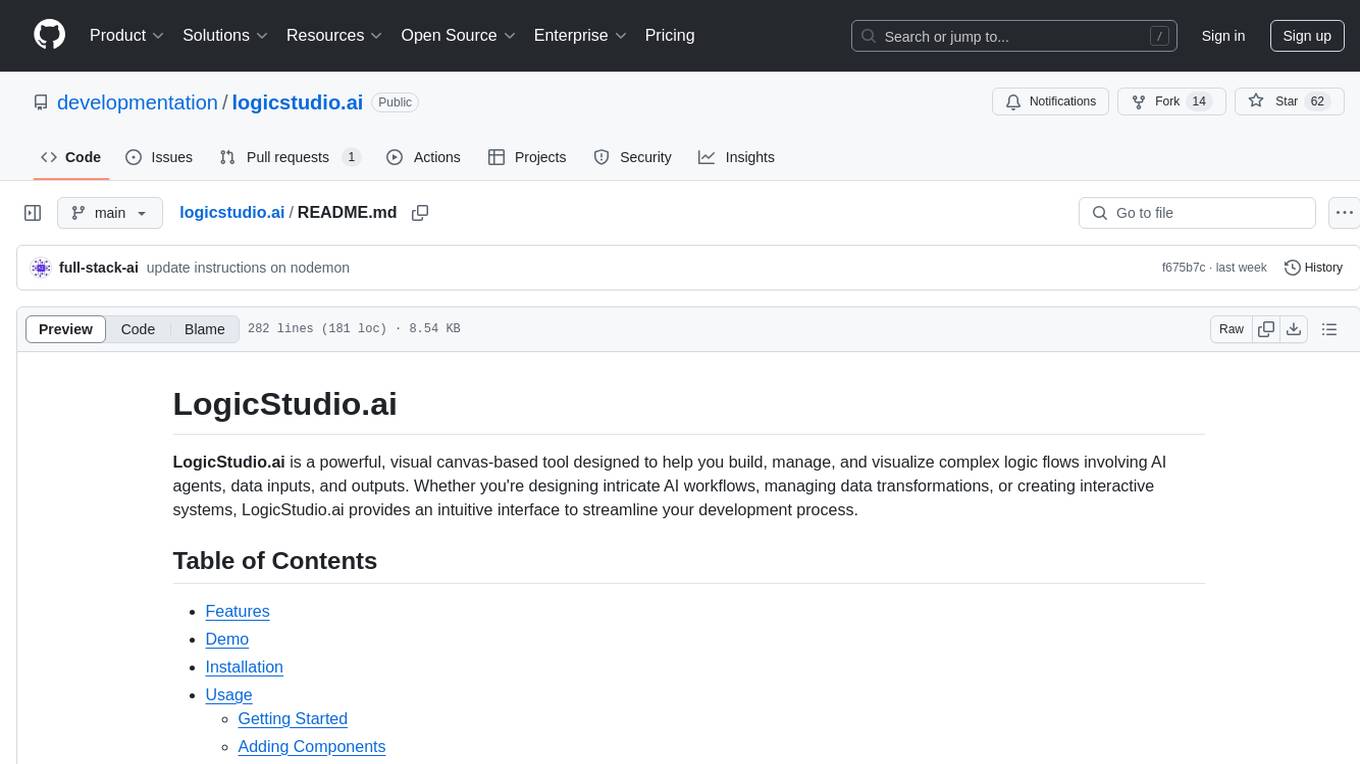
logicstudio.ai
LogicStudio.ai is a powerful visual canvas-based tool for building, managing, and visualizing complex logic flows involving AI agents, data inputs, and outputs. It provides an intuitive interface to streamline development processes by offering features like drag-and-drop canvas design, dynamic components, real-time connections, import/export capabilities, zoom & pan controls, file management, AI integration, editable views, and various output formats. Users can easily add, connect, configure, and manage components to create interactive systems and workflows.
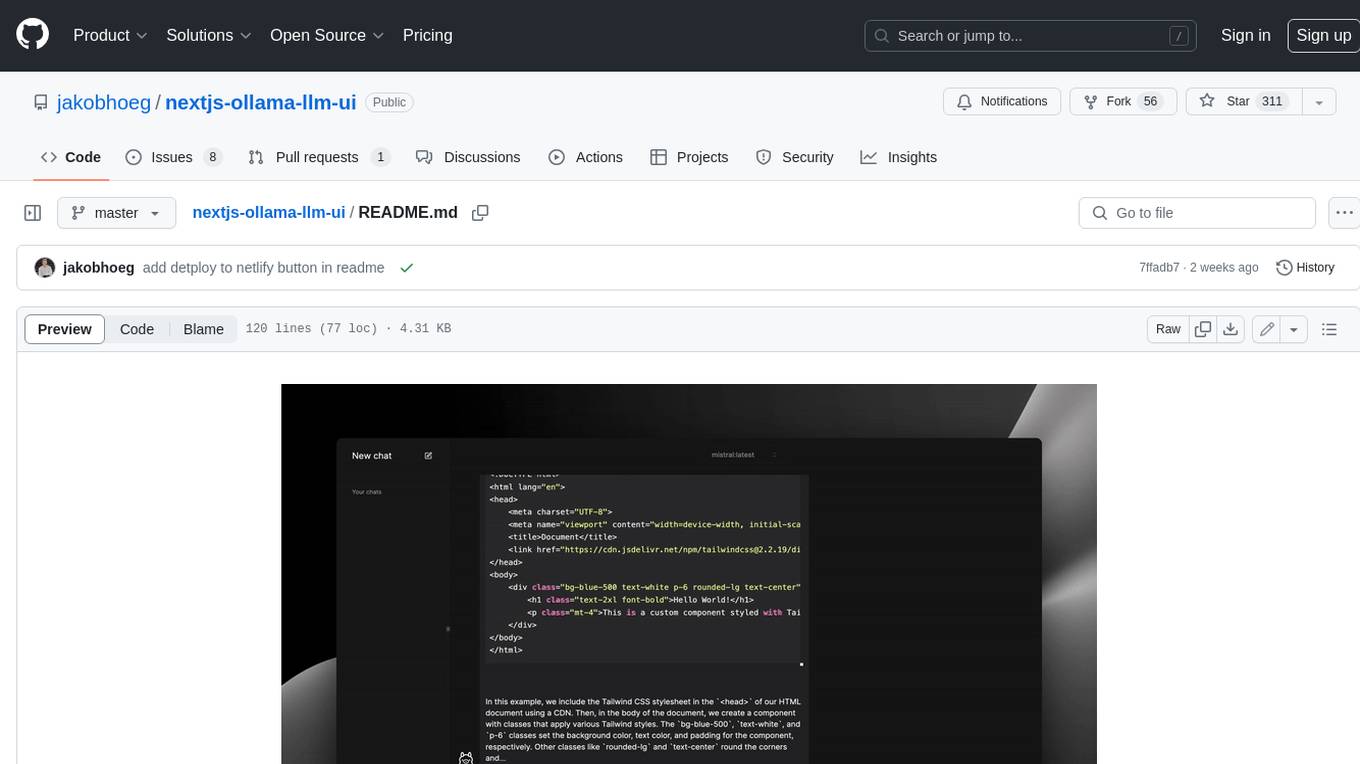
nextjs-ollama-llm-ui
This web interface provides a user-friendly and feature-rich platform for interacting with Ollama Large Language Models (LLMs). It offers a beautiful and intuitive UI inspired by ChatGPT, making it easy for users to get started with LLMs. The interface is fully local, storing chats in local storage for convenience, and fully responsive, allowing users to chat on their phones with the same ease as on a desktop. It features easy setup, code syntax highlighting, and the ability to easily copy codeblocks. Users can also download, pull, and delete models directly from the interface, and switch between models quickly. Chat history is saved and easily accessible, and users can choose between light and dark mode. To use the web interface, users must have Ollama downloaded and running, and Node.js (18+) and npm installed. Installation instructions are provided for running the interface locally. Upcoming features include the ability to send images in prompts, regenerate responses, import and export chats, and add voice input support.
For similar tasks

Ollama-Colab-Integration
Ollama Colab Integration V4 is a tool designed to enhance the interaction and management of large language models. It allows users to quantize models within their notebook environment, access a variety of models through a user-friendly interface, and manage public endpoints efficiently. The tool also provides features like LiteLLM proxy control, model insights, and customizable model file templating. Users can troubleshoot model loading issues, CPU fallback strategies, and manage VRAM and RAM effectively. Additionally, the tool offers functionalities for downloading model files from Hugging Face, model conversion with high precision, model quantization using Q and Kquants, and securely uploading converted models to Hugging Face.
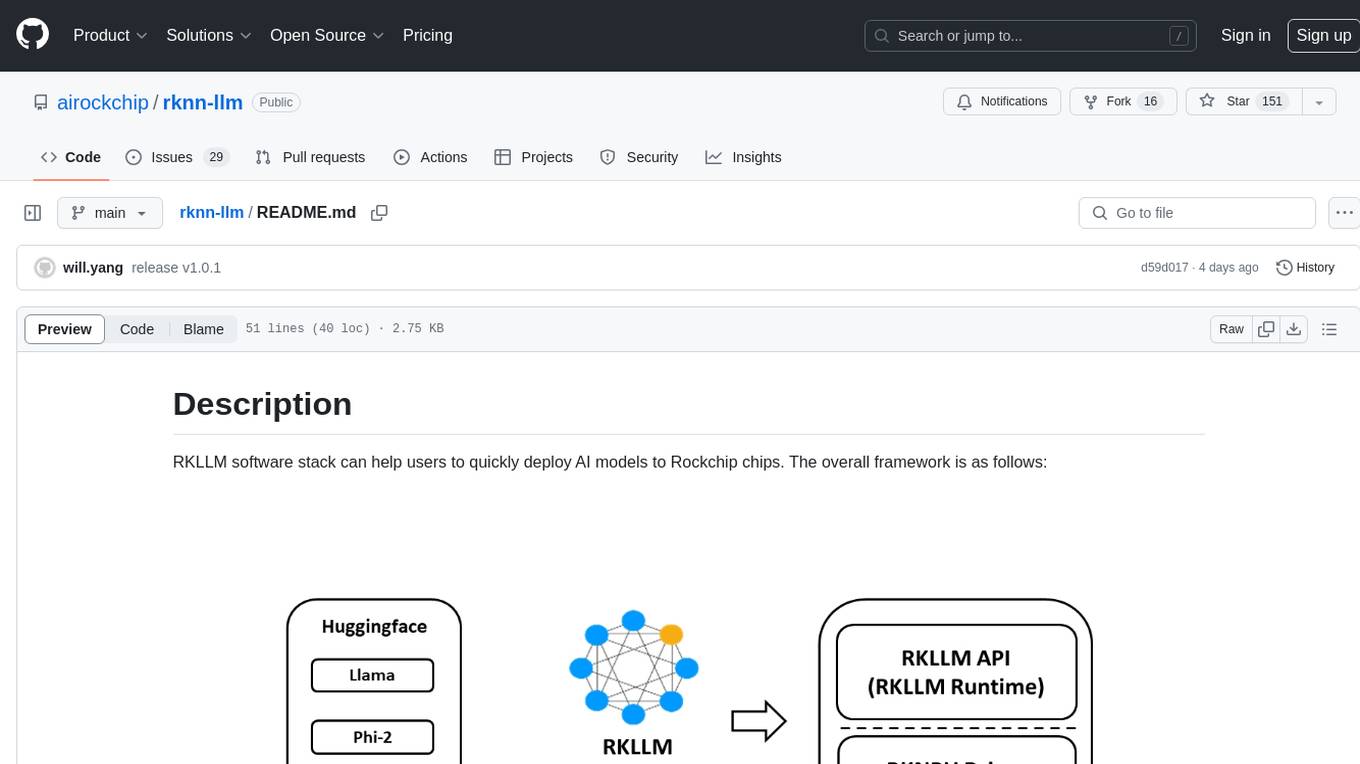
rknn-llm
RKLLM software stack is a toolkit designed to help users quickly deploy AI models to Rockchip chips. It consists of RKLLM-Toolkit for model conversion and quantization, RKLLM Runtime for deploying models on Rockchip NPU platform, and RKNPU kernel driver for hardware interaction. The toolkit supports RK3588 and RK3576 series chips and various models like TinyLLAMA, Qwen, Phi, ChatGLM3, Gemma, InternLM2, and MiniCPM. Users can download packages, docker images, examples, and docs from RKLLM_SDK. Additionally, RKNN-Toolkit2 SDK is available for deploying additional AI models.
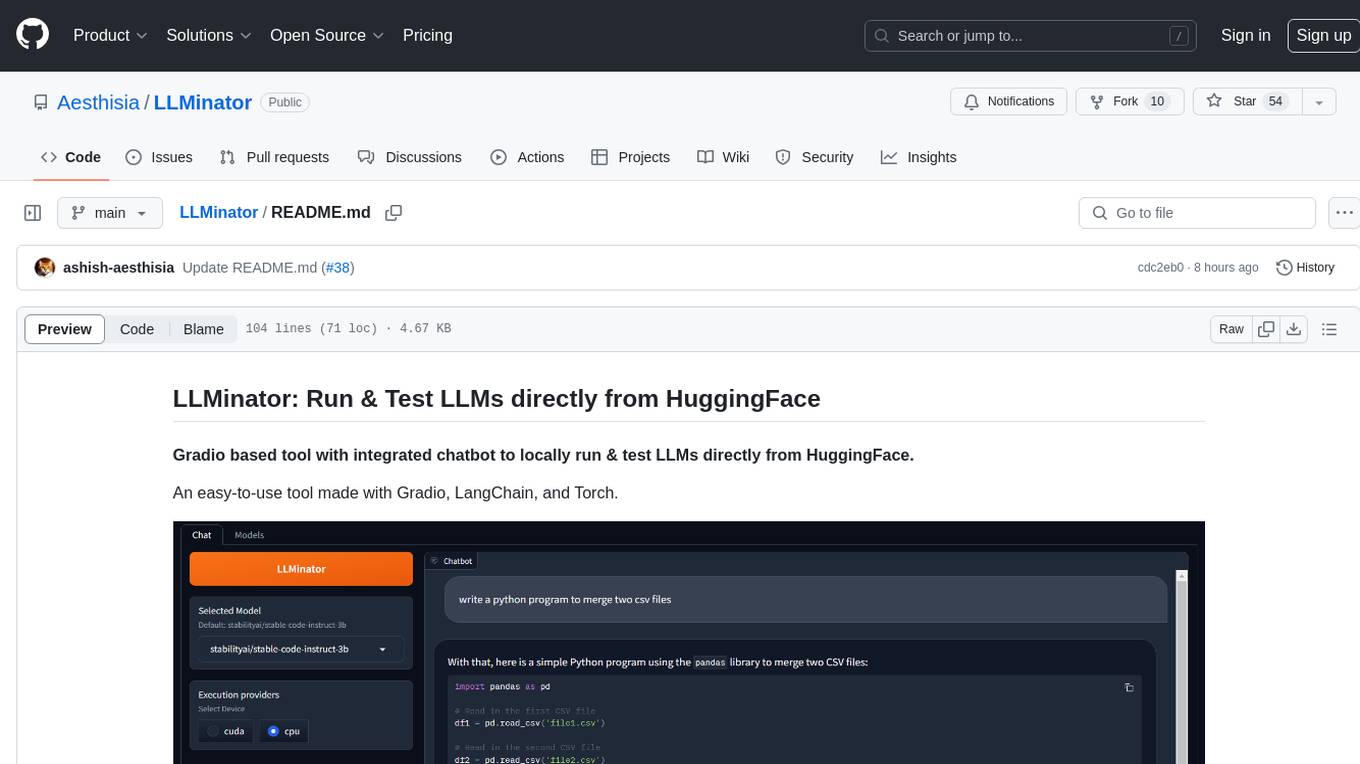
LLMinator
LLMinator is a Gradio-based tool with an integrated chatbot designed to locally run and test Language Model Models (LLMs) directly from HuggingFace. It provides an easy-to-use interface made with Gradio, LangChain, and Torch, offering features such as context-aware streaming chatbot, inbuilt code syntax highlighting, loading any LLM repo from HuggingFace, support for both CPU and CUDA modes, enabling LLM inference with llama.cpp, and model conversion capabilities.

xFasterTransformer
xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for Large Language Models (LLMs) on the X86 platform, providing high performance and scalability for inference on mainstream LLM models. It offers C++ and Python APIs for easy integration, along with example codes and benchmark scripts. Users can prepare models in a different format, convert them, and use the APIs for tasks like encoding input prompts, generating token ids, and serving inference requests. The tool supports various data types and models, and can run in single or multi-rank modes using MPI. A web demo based on Gradio is available for popular LLM models like ChatGLM and Llama2. Benchmark scripts help evaluate model inference performance quickly, and MLServer enables serving with REST and gRPC interfaces.
ai-edge-torch
AI Edge Torch is a Python library that supports converting PyTorch models into a .tflite format for on-device applications on Android, iOS, and IoT devices. It offers broad CPU coverage with initial GPU and NPU support, closely integrating with PyTorch and providing good coverage of Core ATen operators. The library includes a PyTorch converter for model conversion and a Generative API for authoring mobile-optimized PyTorch Transformer models, enabling easy deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) on mobile devices.
BodhiApp
Bodhi App runs Open Source Large Language Models locally, exposing LLM inference capabilities as OpenAI API compatible REST APIs. It leverages llama.cpp for GGUF format models and huggingface.co ecosystem for model downloads. Users can run fine-tuned models for chat completions, create custom aliases, and convert Huggingface models to GGUF format. The CLI offers commands for environment configuration, model management, pulling files, serving API, and more.
lm.rs
lm.rs is a tool that allows users to run inference on Language Models locally on the CPU using Rust. It supports LLama3.2 1B and 3B models, with a WebUI also available. The tool provides benchmarks and download links for models and tokenizers, with recommendations for quantization options. Users can convert models from Google/Meta on huggingface using provided scripts. The tool can be compiled with cargo and run with various arguments for model weights, tokenizer, temperature, and more. Additionally, a backend for the WebUI can be compiled and run to connect via the web interface.
LiteRT
LiteRT is Google's open-source high-performance runtime for on-device AI, previously known as TensorFlow Lite. The repository is currently not intended for open-source development, but aims to evolve to allow direct building and contributions. LiteRT supports Python versions 3.9, 3.10, 3.11 on Linux and MacOS. It ensures compatibility with existing .tflite file extension and format, offering conversion tools and continued active development under the name LiteRT.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

