rknn-llm
None
Stars: 368
RKLLM software stack is a toolkit designed to help users quickly deploy AI models to Rockchip chips. It consists of RKLLM-Toolkit for model conversion and quantization, RKLLM Runtime for deploying models on Rockchip NPU platform, and RKNPU kernel driver for hardware interaction. The toolkit supports RK3588 and RK3576 series chips and various models like TinyLLAMA, Qwen, Phi, ChatGLM3, Gemma, InternLM2, and MiniCPM. Users can download packages, docker images, examples, and docs from RKLLM_SDK. Additionally, RKNN-Toolkit2 SDK is available for deploying additional AI models.
README:
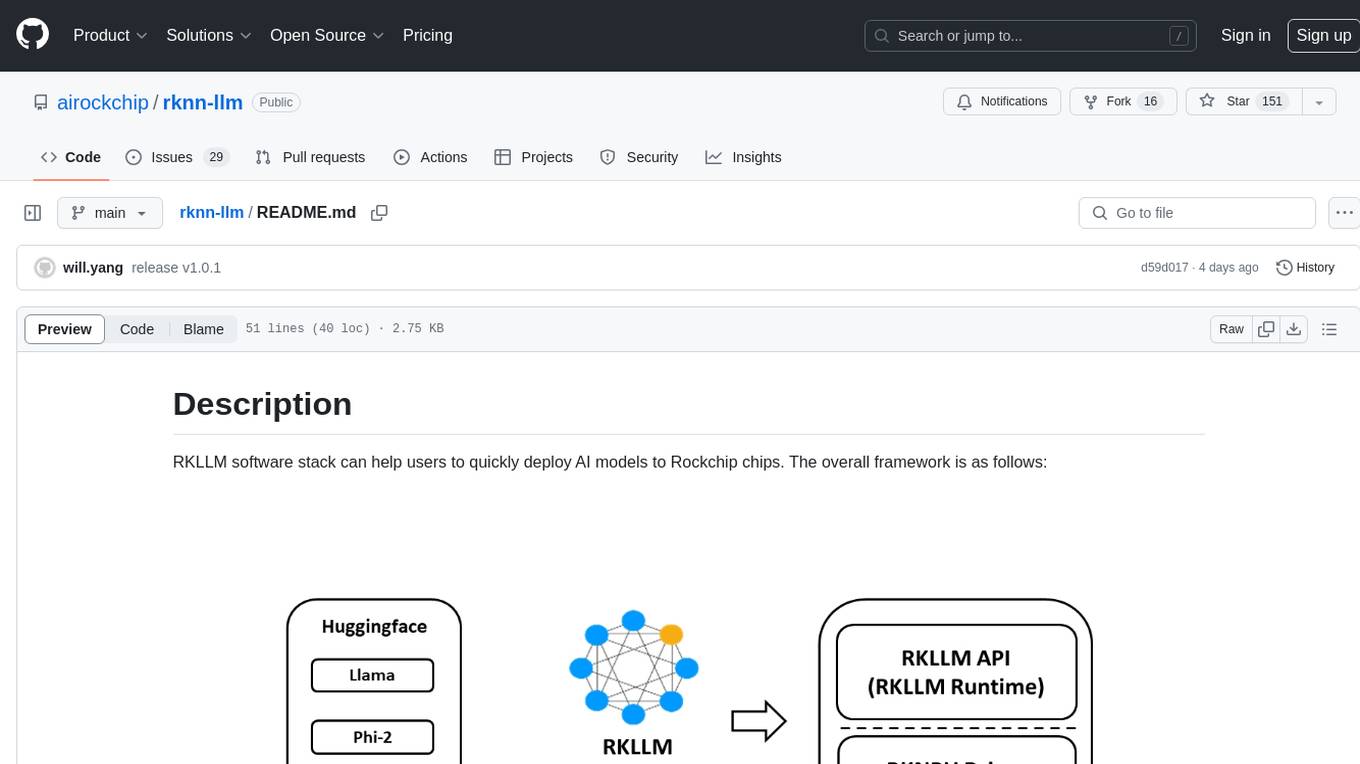
RKLLM software stack can help users to quickly deploy AI models to Rockchip chips. The overall framework is as follows:

In order to use RKNPU, users need to first run the RKLLM-Toolkit tool on the computer, convert the trained model into an RKLLM format model, and then inference on the development board using the RKLLM C API.
-
RKLLM-Toolkit is a software development kit for users to perform model conversionand quantization on PC.
-
RKLLM Runtime provides C/C++ programming interfaces for Rockchip NPU platform to help users deploy RKLLM models and accelerate the implementation of LLM applications.
-
RKNPU kernel driver is responsible for interacting with NPU hardware. It has been open source and can be found in the Rockchip kernel code.
- RK3588 Series
- RK3576 Series
- [x] LLAMA models
- [x] TinyLLAMA models
- [x] Qwen models
- [x] Phi models
- [x] ChatGLM3-6B
- [x] Gemma models
- [x] InternLM2 models
- [x] MiniCPM models
| model | dtype | seqlen | max_context | new_tokens | TTFT(ms) | Tokens/s | memory(G) | platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TinyLLAMA-1.1B | w4a16 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 345.00 | 21.10 | 0.77 | RK3576 |
| w4a16_g128 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 410.00 | 18.50 | 0.8 | RK3576 | |
| w8a8 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 140.46 | 24.21 | 1.25 | RK3588 | |
| w8a8_g512 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 195.00 | 20.08 | 1.29 | RK3588 | |
| Qwen2-1.5B | w4a16 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 512.00 | 14.40 | 1.75 | RK3576 |
| w4a16_g128 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 550.00 | 12.75 | 1.76 | RK3576 | |
| w8a8 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 206.00 | 16.46 | 2.47 | RK3588 | |
| w8a8_g128 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 725.00 | 7.00 | 2.65 | RK3588 | |
| Phi-3-3.8B | w4a16 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 975.00 | 6.60 | 2.16 | RK3576 |
| w4a16_g128 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 1180.00 | 5.85 | 2.23 | RK3576 | |
| w8a8 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 516.00 | 7.44 | 3.88 | RK3588 | |
| w8a8_g512 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 610.00 | 6.13 | 3.95 | RK3588 | |
| ChatGLM3-6B | w4a16 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 1168.00 | 4.62 | 3.86 | RK3576 |
| w4a16_g128 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 1582.56 | 3.82 | 3.96 | RK3576 | |
| w8a8 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 800.00 | 4.95 | 6.69 | RK3588 | |
| w8a8_g128 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 2190.00 | 2.70 | 7.18 | RK3588 | |
| Gemma2-2B | w4a16 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 628.00 | 8.00 | 3.63 | RK3576 |
| w4a16_g128 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 776.20 | 7.40 | 3.63 | RK3576 | |
| w8a8 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 342.29 | 9.67 | 4.84 | RK3588 | |
| w8a8_g128 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 1055.00 | 5.49 | 5.14 | RK3588 | |
| InternLM2-1.8B | w4a16 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 475.00 | 13.30 | 1.59 | RK3576 |
| w4a16_g128 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 572.00 | 11.95 | 1.62 | RK3576 | |
| w8a8 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 205.97 | 15.66 | 2.38 | RK3588 | |
| w8a8_g512 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 298.00 | 12.66 | 2.45 | RK3588 | |
| MiniCPM3-4B | w4a16 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 1397.00 | 4.80 | 2.7 | RK3576 |
| w4a16_g128 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 1645.00 | 4.39 | 2.8 | RK3576 | |
| w8a8 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 702.18 | 6.15 | 4.65 | RK3588 | |
| w8a8_g128 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 1691.00 | 3.42 | 5.06 | RK3588 | |
| llama3-8B | w4a16 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 1607.98 | 3.60 | 5.63 | RK3576 |
| w4a16_g128 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 2010.00 | 3.00 | 5.76 | RK3576 | |
| w8a8 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 1128.00 | 3.79 | 9.21 | RK3588 | |
| w8a8_g512 | 64 | 320 | 256 | 1281.35 | 3.05 | 9.45 | RK3588 |
- This performance data were collected based on the maximum CPU and NPU frequencies of each platform with version 1.1.0.
- The script for setting the frequencies is located in the scripts directory.
You can download the latest package, docker image, example, documentation, and platform-tool from RKLLM_SDK, fetch code: rkllm
-
The modifications in version 1.1 are significant, making it incompatible with older version models. Please use the latest toolchain for model conversion and inference.
-
The supported Python versions are:
-
Python 3.8
-
Python 3.10
-
-
Latest version: v1.1.1
If you want to deploy additional AI model, we have introduced a SDK called RKNN-Toolkit2. For details, please refer to:
https://github.com/airockchip/rknn-toolkit2
- Support group-wise quantization (w4a16 group sizes of 32/64/128, w8a8 group sizes of 128/256/512).
- Support joint inference with LoRA model loading
- Support storage and preloading of prompt cache.
- Support gguf model conversion (currently only support q4_0 and fp16).
- Optimize initialization, prefill, and decode time.
- Support four input types: prompt, embedding, token, and multimodal.
- Add PC-based simulation accuracy testing and inference interface support for rkllm-toolkit.
- Add gdq algorithm to improve 4-bit quantization accuracy.
- Add mixed quantization algorithm, supporting a combination of grouped and non-grouped quantization based on specified ratios.
- Add support for models such as Llama3, Gemma2, and MiniCPM3.
- Resolve catastrophic forgetting issue when the number of tokens exceeds max_context.
for older version, please refer CHANGELOG
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for rknn-llm
Similar Open Source Tools

rknn-llm
RKLLM software stack is a toolkit designed to help users quickly deploy AI models to Rockchip chips. It consists of RKLLM-Toolkit for model conversion and quantization, RKLLM Runtime for deploying models on Rockchip NPU platform, and RKNPU kernel driver for hardware interaction. The toolkit supports RK3588 and RK3576 series chips and various models like TinyLLAMA, Qwen, Phi, ChatGLM3, Gemma, InternLM2, and MiniCPM. Users can download packages, docker images, examples, and docs from RKLLM_SDK. Additionally, RKNN-Toolkit2 SDK is available for deploying additional AI models.

kumo-search
Kumo search is an end-to-end search engine framework that supports full-text search, inverted index, forward index, sorting, caching, hierarchical indexing, intervention system, feature collection, offline computation, storage system, and more. It runs on the EA (Elastic automic infrastructure architecture) platform, enabling engineering automation, service governance, real-time data, service degradation, and disaster recovery across multiple data centers and clusters. The framework aims to provide a ready-to-use search engine framework to help users quickly build their own search engines. Users can write business logic in Python using the AOT compiler in the project, which generates C++ code and binary dynamic libraries for rapid iteration of the search engine.
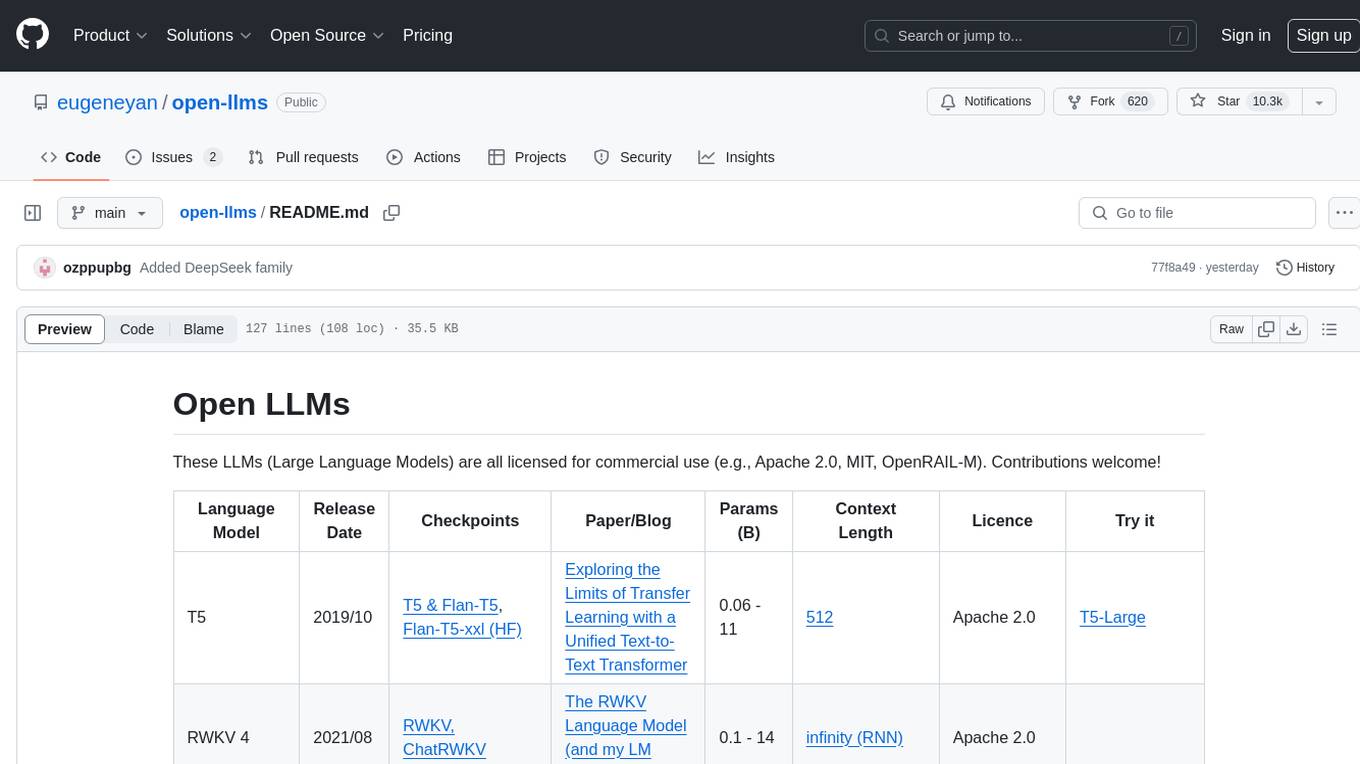
open-llms
Open LLMs is a repository containing various Large Language Models licensed for commercial use. It includes models like T5, GPT-NeoX, UL2, Bloom, Cerebras-GPT, Pythia, Dolly, and more. These models are designed for tasks such as transfer learning, language understanding, chatbot development, code generation, and more. The repository provides information on release dates, checkpoints, papers/blogs, parameters, context length, and licenses for each model. Contributions to the repository are welcome, and it serves as a resource for exploring the capabilities of different language models.
LLM-for-Healthcare
The repository 'LLM-for-Healthcare' provides a comprehensive survey of large language models (LLMs) for healthcare, covering data, technology, applications, and accountability and ethics. It includes information on various LLM models, training data, evaluation methods, and computation costs. The repository also discusses tasks such as NER, text classification, question answering, dialogue systems, and generation of medical reports from images in the healthcare domain.
so-vits-models
This repository collects various LLM, AI-related models, applications, and datasets, including LLM-Chat for dialogue models, LLMs for large models, so-vits-svc for sound-related models, stable-diffusion for image-related models, and virtual-digital-person for generating videos. It also provides resources for deep learning courses and overviews, AI competitions, and specific AI tasks such as text, image, voice, and video processing.
awesome-hosting
awesome-hosting is a curated list of hosting services sorted by minimal plan price. It includes various categories such as Web Services Platform, Backend-as-a-Service, Lambda, Node.js, Static site hosting, WordPress hosting, VPS providers, managed databases, GPU cloud services, and LLM/Inference API providers. Each category lists multiple service providers along with details on their minimal plan, trial options, free tier availability, open-source support, and specific features. The repository aims to help users find suitable hosting solutions based on their budget and requirements.
ai-reference-models
The Intel® AI Reference Models repository contains links to pre-trained models, sample scripts, best practices, and tutorials for popular open-source machine learning models optimized by Intel to run on Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors and Intel® Data Center GPUs. The purpose is to quickly replicate complete software environments showcasing the AI capabilities of Intel platforms. It includes optimizations for popular deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch, with additional plugins/extensions for improved performance. The repository is licensed under Apache License Version 2.0.
LLamaTuner
LLamaTuner is a repository for the Efficient Finetuning of Quantized LLMs project, focusing on building and sharing instruction-following Chinese baichuan-7b/LLaMA/Pythia/GLM model tuning methods. The project enables training on a single Nvidia RTX-2080TI and RTX-3090 for multi-round chatbot training. It utilizes bitsandbytes for quantization and is integrated with Huggingface's PEFT and transformers libraries. The repository supports various models, training approaches, and datasets for supervised fine-tuning, LoRA, QLoRA, and more. It also provides tools for data preprocessing and offers models in the Hugging Face model hub for inference and finetuning. The project is licensed under Apache 2.0 and acknowledges contributions from various open-source contributors.
Awesome-AgenticLLM-RL-Papers
This repository serves as the official source for the survey paper 'The Landscape of Agentic Reinforcement Learning for LLMs: A Survey'. It provides an extensive overview of various algorithms, methods, and frameworks related to Agentic RL, including detailed information on different families of algorithms, their key mechanisms, objectives, and links to relevant papers and resources. The repository covers a wide range of tasks such as Search & Research Agent, Code Agent, Mathematical Agent, GUI Agent, RL in Vision Agents, RL in Embodied Agents, and RL in Multi-Agent Systems. Additionally, it includes information on environments, frameworks, and methods suitable for different tasks related to Agentic RL and LLMs.
AIInfra
AIInfra is an open-source project focused on AI infrastructure, specifically targeting large models in distributed clusters, distributed architecture, distributed training, and algorithms related to large models. The project aims to explore and study system design in artificial intelligence and deep learning, with a focus on the hardware and software stack for building AI large model systems. It provides a comprehensive curriculum covering topics such as AI chip principles, communication and storage, AI clusters, large model training, and inference, as well as algorithms for large models. The course is designed for undergraduate and graduate students, as well as professionals working with AI large model systems, to gain a deep understanding of AI computer system architecture and design.
models
The Intel® AI Reference Models repository contains links to pre-trained models, sample scripts, best practices, and tutorials for popular open-source machine learning models optimized by Intel to run on Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors and Intel® Data Center GPUs. It aims to replicate the best-known performance of target model/dataset combinations in optimally-configured hardware environments. The repository will be deprecated upon the publication of v3.2.0 and will no longer be maintained or published.
ailia-models
The collection of pre-trained, state-of-the-art AI models. ailia SDK is a self-contained, cross-platform, high-speed inference SDK for AI. The ailia SDK provides a consistent C++ API across Windows, Mac, Linux, iOS, Android, Jetson, and Raspberry Pi platforms. It also supports Unity (C#), Python, Rust, Flutter(Dart) and JNI for efficient AI implementation. The ailia SDK makes extensive use of the GPU through Vulkan and Metal to enable accelerated computing. # Supported models 323 models as of April 8th, 2024

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.
PaddleScience
PaddleScience is a scientific computing suite developed based on the deep learning framework PaddlePaddle. It utilizes the learning ability of deep neural networks and the automatic (higher-order) differentiation mechanism of PaddlePaddle to solve problems in physics, chemistry, meteorology, and other fields. It supports three solving methods: physics mechanism-driven, data-driven, and mathematical fusion, and provides basic APIs and detailed documentation for users to use and further develop.
Github-Ranking-AI
This repository provides a list of the most starred and forked repositories on GitHub. It is updated automatically and includes information such as the project name, number of stars, number of forks, language, number of open issues, description, and last commit date. The repository is divided into two sections: LLM and chatGPT. The LLM section includes repositories related to large language models, while the chatGPT section includes repositories related to the chatGPT chatbot.
For similar tasks

rknn-llm
RKLLM software stack is a toolkit designed to help users quickly deploy AI models to Rockchip chips. It consists of RKLLM-Toolkit for model conversion and quantization, RKLLM Runtime for deploying models on Rockchip NPU platform, and RKNPU kernel driver for hardware interaction. The toolkit supports RK3588 and RK3576 series chips and various models like TinyLLAMA, Qwen, Phi, ChatGLM3, Gemma, InternLM2, and MiniCPM. Users can download packages, docker images, examples, and docs from RKLLM_SDK. Additionally, RKNN-Toolkit2 SDK is available for deploying additional AI models.
Ollama-Colab-Integration
Ollama Colab Integration V4 is a tool designed to enhance the interaction and management of large language models. It allows users to quantize models within their notebook environment, access a variety of models through a user-friendly interface, and manage public endpoints efficiently. The tool also provides features like LiteLLM proxy control, model insights, and customizable model file templating. Users can troubleshoot model loading issues, CPU fallback strategies, and manage VRAM and RAM effectively. Additionally, the tool offers functionalities for downloading model files from Hugging Face, model conversion with high precision, model quantization using Q and Kquants, and securely uploading converted models to Hugging Face.
LLMinator
LLMinator is a Gradio-based tool with an integrated chatbot designed to locally run and test Language Model Models (LLMs) directly from HuggingFace. It provides an easy-to-use interface made with Gradio, LangChain, and Torch, offering features such as context-aware streaming chatbot, inbuilt code syntax highlighting, loading any LLM repo from HuggingFace, support for both CPU and CUDA modes, enabling LLM inference with llama.cpp, and model conversion capabilities.

xFasterTransformer
xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for Large Language Models (LLMs) on the X86 platform, providing high performance and scalability for inference on mainstream LLM models. It offers C++ and Python APIs for easy integration, along with example codes and benchmark scripts. Users can prepare models in a different format, convert them, and use the APIs for tasks like encoding input prompts, generating token ids, and serving inference requests. The tool supports various data types and models, and can run in single or multi-rank modes using MPI. A web demo based on Gradio is available for popular LLM models like ChatGLM and Llama2. Benchmark scripts help evaluate model inference performance quickly, and MLServer enables serving with REST and gRPC interfaces.
ai-edge-torch
AI Edge Torch is a Python library that supports converting PyTorch models into a .tflite format for on-device applications on Android, iOS, and IoT devices. It offers broad CPU coverage with initial GPU and NPU support, closely integrating with PyTorch and providing good coverage of Core ATen operators. The library includes a PyTorch converter for model conversion and a Generative API for authoring mobile-optimized PyTorch Transformer models, enabling easy deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) on mobile devices.
BodhiApp
Bodhi App runs Open Source Large Language Models locally, exposing LLM inference capabilities as OpenAI API compatible REST APIs. It leverages llama.cpp for GGUF format models and huggingface.co ecosystem for model downloads. Users can run fine-tuned models for chat completions, create custom aliases, and convert Huggingface models to GGUF format. The CLI offers commands for environment configuration, model management, pulling files, serving API, and more.
lm.rs
lm.rs is a tool that allows users to run inference on Language Models locally on the CPU using Rust. It supports LLama3.2 1B and 3B models, with a WebUI also available. The tool provides benchmarks and download links for models and tokenizers, with recommendations for quantization options. Users can convert models from Google/Meta on huggingface using provided scripts. The tool can be compiled with cargo and run with various arguments for model weights, tokenizer, temperature, and more. Additionally, a backend for the WebUI can be compiled and run to connect via the web interface.
LiteRT
LiteRT is Google's open-source high-performance runtime for on-device AI, previously known as TensorFlow Lite. The repository is currently not intended for open-source development, but aims to evolve to allow direct building and contributions. LiteRT supports Python versions 3.9, 3.10, 3.11 on Linux and MacOS. It ensures compatibility with existing .tflite file extension and format, offering conversion tools and continued active development under the name LiteRT.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.