LLM-for-Healthcare
None
Stars: 96
The repository 'LLM-for-Healthcare' provides a comprehensive survey of large language models (LLMs) for healthcare, covering data, technology, applications, and accountability and ethics. It includes information on various LLM models, training data, evaluation methods, and computation costs. The repository also discusses tasks such as NER, text classification, question answering, dialogue systems, and generation of medical reports from images in the healthcare domain.
README:
A Survey of Large Language Models for Healthcare: from Data, Technology, and Applications to Accountability and Ethics
-
2023-05-31 update.new paper "Polaris: A Safety-focused LLM Constellation Architecture for Healthcare"
-
2023-05-31 update.new paper "Medical mT5: an open-source multilingual text-to-text LLM for the medical domain"
-
2023-05-31 update.new paper "Apollo: An Lightweight Multilingual Medical LLM towards Democratizing Medical AI to 6B People"
-
2023-05-31 update.new paper "LLM-CXR: INSTRUCTION-FINETUNED LLM FOR CXR IMAGE UNDERSTANDING AND GENERATION"
-
2023-05-31 update.new paper "Me LLaMA: Foundation large language models for medical applications"
-
2023-05-31 update.new paper "BioMistral: A collection of open-source pretrained large language models for medical domains"
-
2023-05-31 update.new paper "OncoGPT: A medical conversational model tailored with oncology domain expertise on a large language model Meta-AI (LLaMA)"
-
2023-03-17 update.new paper "Health-LLM: Personalized Retrieval-Augmented Disease Prediction System"
-
2023-03-17 update.new paper "HealAI: A Healthcare LLM for Effective Medical Documentation"
-
2023-03-17 update.new paper "BiMediX: Bilingual Medical Mixture of Experts LLM"
-
2023-03-17 update.new paper "JMLR: Joint Medical LLM and Retrieval Training for Enhancing Reasoning and Professional Question Answering Capability"
-
2023-03-17 update.new paper "MedChatZH: A tuning LLM for traditional Chinese medicine consultation"
-
2023-10-18 added new paper "Zhongjing: Enhancing the Chinese Medical Capabilities of Large Language Model through Expert Feedback and Real-world Multi-turn Dialogue".
-
2023-10-18 added new paper "Qilin-Med: Multi-stage Knowledge Injection Advanced Medical Large Language Model".
-
2023-10-9 We release the version 1 of the survey (https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.05694).
-
Introduction
-
What LLMs Can Do for Healthcare? From Fundamental Tasks to Advanced Applications
- NER and RE for Healthcare Alpacare
- Text Classification for Healthcare
- Semantic Textual Similarity for Healthcare
- Question Answering for Healthcare
- Dialogue System for Healthcare
- Generation of Medical Reports from Images
- Summary
-
From LMs to LLMs for Healthcare
- LMs for Healthcare
- LLMs for Healthcare
-
Train and Use LLM for Healthcare
- Pre-training Methods
- Masked Language Modeling
- Next Word Prediction
- Sequence-to-sequence MLM
- Replaced Token Detection
- Sentence Boundary Detection
- Next Sentence Prediction
- Sentence Order Prediction
-
Post-training Methods
- From predicting tokens to follow instructions: Instruction Fine-Tuning and Supervised Fine-tuning
- Reinforced Learning from Human Feedback
- From Human Feedback to AI Feedback
- Summary
-
Usage
- From Fine-tuning to In-context Learning
- From System 1 Deep Learning To System 2 Deep Learning: Chain-of-Thought
- AI Agents
- Summary
-
Parameters-, Memory-, and Compute-efficient Methods
- Parameters-efficient Methods
- Compute-efficient and Memory-efficient Methods
-
Useful Resources
- OpenBMB
- DeepSpeed Chat
- Training Data
- Summary
-
Evaluation Method
- General NLP tasks Evaluation
- Healthcare Evaluation
- Evaluation of Robustness, Bias, and Ethics
- Future Directions for Health Evaluation
- Summary
-
Improving Fairness, Accountability, Transparency, and Ethics
- Fairness
- Accountability
- Transparency
- Ethics
-
Future work and Conclusion
- Future Work
- Medical knowledge enhancement
- Integration with Healthcare process
- Effective Interaction with Patients and Doctors
- Hallucinations, Misunderstandings and Prompt Brittleness
-
Conclusion
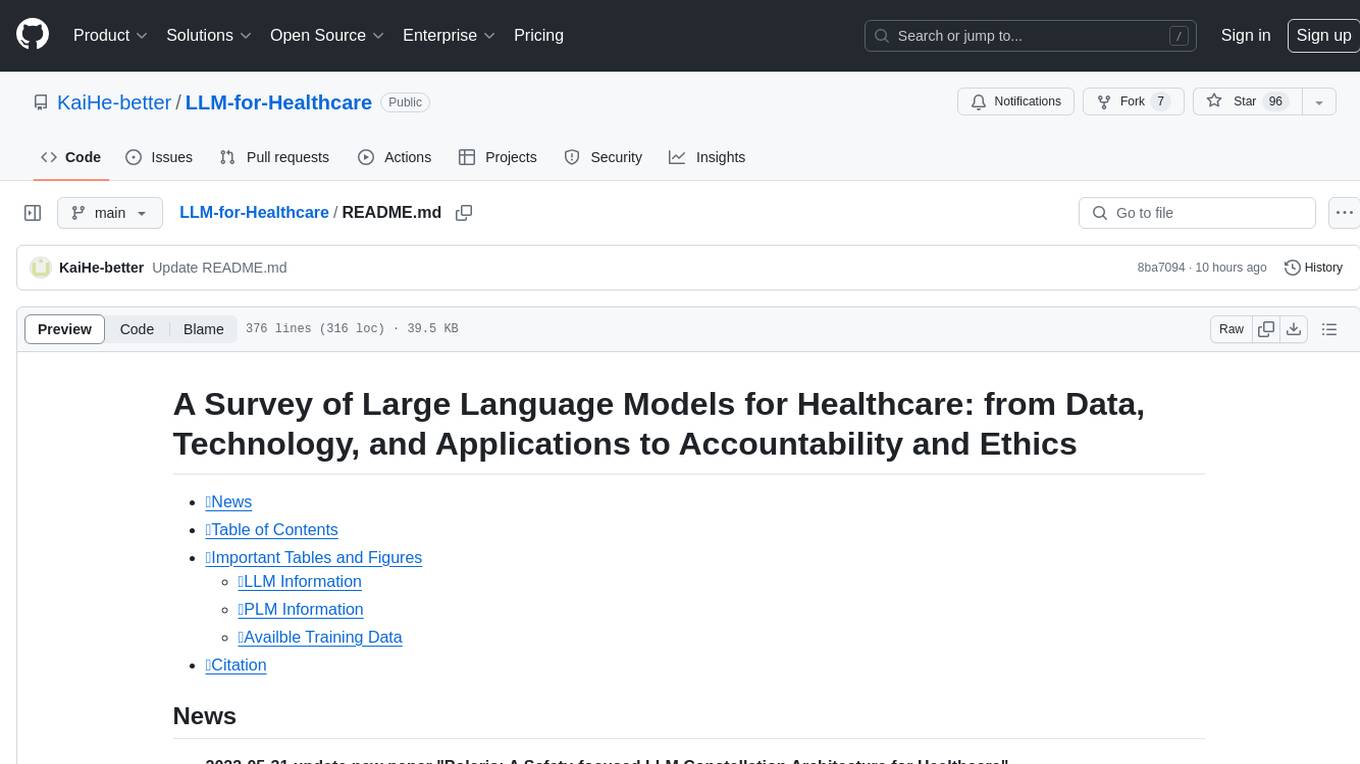
Fig. 2. The organizational framework for the content. Section III, Section IV, Section V are technology details, while Section II, Section VI and Section VI
are more valued for Healthcare professionals

| Model Name | Base | Para. (B) | Features | Date | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GatorTron | Transformer | 0.345, 3.9, 8.9 | Training from scratch | 06/2022 | https://github.com/uf-hobi-informatics-lab/GatorTron |
| Codex-Med | GPT-3.5 | 175 | CoT, Zero-shot | 07/2022 | https://github.com/vlievin/medical-reasoning |
| Galactica | Transformer | 1.3, 6.4, 30, 120 | Reasoning, Multidisciplinary | 11/2022 | https://galactica.org |
| Med-PaLM | Flan-PaLM/PaLM | 540 | CoT, Self-consistency | 12/2022 | - |
| GPT-4-Med | GPT-4 | - | no specialized prompt crafting | 03/2023 | - |
| DeID-GPT | GPT-4 | - | De-identifying | 03/2023 | https://github.com/yhydhx/ChatGPT-API |
| ChatDoctor | LLaMA | 7 | Retrieve online, external knowledge | 03/2023 | https://github.com/Kent0n-Li/ChatDoctor |
| DoctorGLM | ChatGLM | 6 | Extra prompt designer | 04/2023 | https://github.com/xionghonglin/DoctorGLM |
| MedAlpaca | LLaMA | 7, 13 | Adapt to Medicine | 04/2023 | https://github.com/kbressem/medAlpaca |
| BenTsao | LLaMA | 7 | Knowledge graph | 04/2023 | https://github.com/SCIR-HI/ Huatuo-Llama-Med-Chinese |
| PMC-LLaMA | LLaMA | 7 | Adapt to Medicine | 04/2023 | https://github.com/chaoyi-wu/PMC-LLaMA |
| Visual Med-Alpaca | LLaMA | 7 | multimodal generative model, Self-Instruct | 04/2023 | https://github.com/cambridgeltl/visual-med-alpaca |
| BianQue~ | ChatGLM | 6 | Chain of Questioning | 04/2023 | https://github.com/scutcyr/BianQue |
| Med-PaLM 2 | PaLM 2 | 340 | Ensemble refinement, CoT, Self-consistency | 05/2023 | - |
| GatorTronGPT | GPT-3 | 5, 20 | Training from scratch for medicine | 05/2023 | https://github.com/uf-hobi-informatics-lab/GatorTronGPT |
| HuatuoGPT | Bloomz | 7 | Reinforced learning from AI feedback | 05/2023 | https://github.com/FreedomIntelligence/HuatuoGPT |
| ClinicalGPT | BLOOM | 7 | multi-round dialogue consultations | 06/2023 | - |
| MedAGI | MiniGPT-4 | - | multimodal, AGI | 06/2023 | https://github.com/JoshuaChou2018/MedAGI |
| LLaVA-Med | LLaVA | 13 | multimodal, self-instruct, curriculum learning | 06/2023 | https://github.com/microsoft/LLaVA-Med |
| OphGLM | ChatGLM | 6 | multimodal, Ophthalmology LLM | 06/2023 | https://github.com/ML-AILab/OphGLM |
| SoulChat | ChatGLM | 6 | Mental Healthcare | 06/2023 | https://github.com/scutcyr/SoulChat |
| Med-Flamingo | Flamingo | 80B | multimodal, Few-Shot generative medical VQA | 07/2023 | https://github.com/snap-stanford/med-flamingo |
TABLE I BRIEF SUMMARIZATION OF EXISTING PLMS FOR HEALTHCARE.
| Model Name | Base | Para. (B) | Features | Date | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioBERT | BERT | 0.34 | Biomedical Adaption | 05/2019 | https://github.com/naver/biobert-pretrained |
| BlueBERT | BERT | 0.34 | Biomedical Benchmark | 06/2019 | https://github.com/ncbi-nlp/BLUE\_Benchmark |
| MIMIC-BERT | BERT | 0.34 | Clinical Concept Extraction | 08/2019 | - |
| BioFLAIR~ | BERT | 0.34 | Less Computationally Intensive | 08/2019 | https://github.com/zalandoresearch/flair |
| Bio-ELECTRA-small | ELECTRA | 0.03 | Training From Scratch | 03/2020 | - |
| AlphaBERT | BERT | 0.11 | Character-level | 04/2020 | https://github.com/wicebing/AlphaBERT.git |
| Spanish-bert | BERT | - | Spanish | 04/2020 | - |
| GreenCovidSQuADBERT | BERT | 0.34 | CPU-only, CORD-19 | 04/2020 | https://github.com/npoe/covid-qa |
| BEHRT | Transformer | - | Training From Scratch | 04/2020 | https://github.com/deepmedicine/BEHRT |
| BioMed-RoBERTa | RoBERTa | 0.11 | Biomedical Adaption | 05/2020 | https://github.com/allenai/dont-stop-pretraining |
| RadBERT~ | BERT | - | RadCore Radiology Reports | 05/2020 | - |
| CT-BERT~ | BERT | 0.34 | COVID-19 | 05/2020 | https://github.com/digitalepidemiologylab/covid-twitter-bert |
| French-BERT | BERT | 0.11 | French Language Models | 06/2020 | - |
| FS-/RAD-/GER-BERT | BERT | 0.11 | Chest Radiograph Reports | 07/2020 | https://github.com/fast-raidiology/bertfor-radiology |
| Japanese-BERT | BERT | 10.11 | Japanese Clinical Narrative | 07/2020 | ai-health.m.u-tokyo.ac.jp/home/research/uth-bert |
| MC-BERT | BERT | 0.11 | Chinese Biomedical Benchmark | 08/2020 | https://github.com/alibabaresearch/ChineseBLUE |
| BioALBERT-ner | ALBERT | 0.18 | Biomedical NER | 09/2020 | https://github.com/usmaann/BioALBERT |
| BioMegatron | Megatron | 1.2 | Training From Scratch | 10/2020 | https://github.com/NVIDIA/NeMo |
| CharacterBERT | BERT | 0.11 | Character-CNN module | 10/2020 | https://github.com/helboukkouri/character-bert |
| ClinicalBert | BERT | 0.11 | For Predicting Hospital Readmission | 11/2020 | https://github.com/kexinhuang12345/clinicalBERT |
| Clinical XLNet | XLNet | 0.11 | Temporal Information | 11/2020 | https://github.com/lindvalllab/clinicalXLNet |
| Bio-LM | RoBERTa | 0.34 | Biomedical Adaption | 11/2020 | https://github.com/facebookresearch/bio-lm |
| BioBERTpt | BERT | 0.11 | Portuguese Clinical | 11/2020 | https://github.com/HAILab-PUCPR/BioBERTpt |
| RoBERTa-MIMIC | RoBERTa | 0.11 | Clinical Concept Extraction | 12/2020 | https://github.com/uf-hobi-informatics-lab/ClinicalTransformerNER |
| Clinical KB-ALBERT | ALBERT | 0.03 | Introducing Medical KB | 12/2020 | https://github.com/noc-lab/clinical-kb-bert |
| CHMBERT | BERT | 0.11 | Chinese Medical, Cloud Computing | 01/2021 | - |
| PubMedBERT | BERT | 0.11 | Training From Scratch | 01/2021 | https://huggingface.co/microsoft/BiomedNLP-PubMedBERT-base-uncased-abstract-fulltext |
| ouBioBERT | BERT | 0.11 | Up-sampling, Amplified Vocabulary | 02/2021 | https://github.com/sy-wada/blue\_benchmark\_with\_transformers |
| BERT-EHR | BERT | - | Depression,Chronic Disease Prediction | 03/2021 | https://github.com/lanyexiaosa/brltm |
| AraBERT | BERT | 0.11 | Arabic Language | 03/2021 | https://github.com/aub-mind/araBERT |
| ABioNER | BERT | 0.11 | Arabic NER | 03/2021 | - |
| ELECTRAMed | ELECTRA | 0.11 | Biomedical Adaption | 04/2021 | https://github.com/gmpoli/electramed |
| KeBioLM | PubMedBERT | 0.11 | Introducing Medical KB | 04/2021 | https://github.com/GanjinZero/KeBioLM |
| SINA-BERT | BERT | 0.11 | Persian Language | 04/2021 | - |
| Med-BERT | BERT | 0.11 | Stay Length Prediction | 05/2021 | https://github.com/ZhiGroup/MedBERT |
| Galén | RoBERTa | 0.11 | Spanish Language | 05/2021 | https://github.com/guilopgar/ClinicalCodingTransformerES |
| SCIFIVE~ | T5 | 0.77 | Biomedical Text Generation | 05/2021 | https://github.com/justinphan3110/SciFive |
| BioELECTRA | ELECTRA | 0.34 | Training From Scratch | 06/2021 | https://github.com/kamalkraj/BioELECTRA |
| UmlsBERT | BERT | 0.11 | Introducing Medical KB | 06/2021 | https://github.com/gmichalo/UmlsBERT |
| MedGPT | GPT-2 | 1.5 | Temporal Modelling | 07/2021 | - |
| MentalBERT | BERT | 0.11 | Mental Healthcare | 10/2021 | https://huggingface.co/mental |
| CODER | mBERT | 0.34 | Cross-lingual, Introducing Medical KB | 02/2022 | https://github.com/GanjinZero/CODER |
| BioLinkBERT~ | BERT | 0.34 | PubMed with Citation Links | 03/2022 | https://github.com/michiyasunaga/LinkBERT |
| BioALBERT | ALBERT | 0.03 | Biomedical Adaption | 04/2022 | https://github.com/usmaann/BioALBERT |
| BioBART~ | BART | 0.4 | Biomedical NLG | 04/2022 | https://github.com/GanjinZero/BioBART |
| SAPBERT | BERT | 0.11 | Self-Alignment Pretraining | 10/2022 | https://github.com/cambridgeltl/sapbert |
| VPP | BART | 0.14 | Soft prompt, Biomedical NER | 03/2023 | https://github.com/KaiHe-better/VPP |
| KAD | BERT | - | Multimodal, Chest Radiology Images | 03/2023 | https://github.com/xiaoman-zhang/KAD |
TABLE II SUMMARIZATION OF TRAINING DATA AND EVALUATION TASKS FOR EXISTING PLMS FOR HEALTHCARE.
| Model Name | Method | Training Data | Eval task |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioBERT | FT | PubMed, PMC | Biomedical NER, RE, QA |
| BlueBert | FT | PubMed, MIMIC-III | BLUE |
| MIMIC-BERT | FT | MIMIC-III | Biomedical NER |
| BioFLAIR~ | FT | PubMed | Bio NER |
| Bio-ELECTRA-small | PT | PubMed | Biomedical NER |
| AlphaBERT | FT | Discharge diagnoses | Extractive Summarization Task |
| Spanish-bert | FT | Spanish | Spanish Clinical Case Corpus |
| GreenCovidSQuADBERT | FT | CORD19, PubMed, PMC | NER, QA |
| BEHRT | PT | CPRD, HES | Disease Prediction |
| BioMed-RoBERTa | FT | BIOMED | CHEMPROT, RCT |
| RadBERT~ | FT | Radiology Report Corpus | Report Coding, Summarization |
| CT-BERT~ | FT | Tweet | COVID-19 Text Classification |
| French-BERT | FT | French clinical documents | DEFT challenge |
| FS-/RAD-/GER-BERT | FT,PT | Unstructured radiology reports | Chest Radiograph Reports Classification |
| Japanese-BERT | FT | Japanese EHR | Symptoms Classification |
| MC-BERT | FT | Chinese EHR | Chinese Biomedical Evaluation benchmark |
| BioALBERT-ner | FT | PubMed, PMC | Biomedical NER |
| BioMegatron | PT | PubMed | biomedical NER, RE, QA |
| CharacterBERT | Bert | OpenWebText, MIMIC-III, PMC | Medical NER, NLI, RE, SS |
| ClinicalBert | FT | MIMIC-III | Hospital Readmission Prediction |
| Clinical XLNet | FT | MIMIC-III | PMV, Mortality |
| Bio-LM | FT | PubMed, PMC, MIMIC-III | 18 Biomedical NLP Tasks |
| BioBERTpt | FT | Private clinical notes, WMT16 | SemClinBr |
| RoBERTa-MIMIC | FT | i2b2 2010, 2012, n2c2 2018 | i2b2 2010, 2012, N2C2 2018 |
| Clinical KB-ALBERT | FT | MIMIC-III, UMLS | MedNLI, i2b2 2010, 2012 |
| CHMBERT | FT | Medical text data | Disease Prediction |
| PubMedBERT | PT | PubMed | BLURB |
| ouBioBERT | FT | PubMed, Wikipedia | BLUE |
| BERT-EHR | FT | General EHR | Myocardial Infarction, Breast Cancer, Liver Cirrhosis |
| AraBERT | PT | Arabic Wikipedia, OSIAN | Arabic SA, NER, QA |
| ABioNER | FT | Arabic scientific literature | Arabic NER |
| ELECTRAMed | FT | PubMed | Biomedical NER, RE, and QA |
| KeBioLM | FT | PubMed | BLURB |
| SINA-BERT | FT | Online Persian source | Persian QA, SA |
| Med-BERT | FT | General EHR | Disease prediction |
| Galén | FT | Private clinical cases | CodiEsp-D, CodiEsp-P, Cantemist-Coding tasks |
| SCIFIVE~ | T5 | PubMed, PMC | Biomedical NER, RE, NIL, QA |
| BioELECTRA | PT | PubMed, PMC | BLURB, BLUE |
| UmlsBERT | FT | MIMIC-III | MedNLI, i2b2 2006,2010, 2012, 2014 |
| MedGPT | FT | MIMIC-III, private EHRs | Disorder Prediction |
| MentalBERT | FT | Depression Stress, Suicide Detection, | |
| CODER | FT | UMLS | MCSM, Medical RE |
| BioLinkBERT~ | FT | PubMed | BLURB, USMLE |
| BioALBERT | FT | PubMed, PMC, MIMIC-III | 6 BioNLP Tasks |
| BioBART~ | FT | PubMed | Biomedical EL, NER, QA, Dialogue, Summarization |
| SAPBERT | FT | UMLS | MEL |
| VPP | FT | PubMed | Biomedical NER |
| KAD | FT | MIMIC-CXR | PadChest, ChestXray14, CheXpert and ChestX-Det10 |
| Data | Type | size | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIMIC-III | EHR | 58,976 hospital admissions for 38,597 patients | https://mimic.mit.edu/docs/iii/ |
| MIMIC-IV | EHR | covering a decade of admissions between 2008 and 2019 | https://mimic.mit.edu/docs/iv/ |
| CPRD | EHR | over 2,000 primary care practices and include 60 million patients | https://cprd.com/data |
| PubMed | Scientific Literature | 35M citations and abstracts of biomedical literature | https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/baseline/ |
| PMC | Scientific Literature | 8 million full-text article records | https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/pmc/oa_bulk |
| RCT | Scientific Literature | 4,528 abstract | https://github.com/bwallace/RCT-summarization-data |
| MS$\hat{~}$2 | Scientific Literature | 470,402 abstract | https://github.com/allenai/ms2/ |
| CDSR | Scientific Literature | 7,805 abstract | https://github.com/qiuweipku/Plain\_language\_summarization |
| SumPubMed | Scientific Literature | 33,772 abstract | https://github.com/vgupta123/sumpubmed |
| The Pile | Scientific Literature | 825 GB English text | https://pile.eleuther.ai/ |
| S2ORC | Scientific Literature | 63,709 abstract | https://github.com/jbshp/GenCompareSum |
| CORD-19 | Scientific Literature | 1M papers | https://github.com/allenai/cord19 |
| MeQSum | Medical Question Summarization | 1000 instances | https://github.com/abachaa/MeQSum |
| CHQ-Sum | Medical Question Summarization | 1507 instances | https://github.com/shwetanlp/Yahoo-CHQ-Summ |
| UMLS | Knowledge Base | 2M entities for 900K concepts | https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/index.html |
| COMETA | Web Data (social media) | 800K Reddit posts | https://github.com/cambridgeltl/cometa |
| MedDialog | Dialogue | 3.66 million conversations | https://github.com/UCSD-AI4H/COVID-Dialogue |
| CovidDialog | Dialogue | 603 consultations | https://github.com/UCSD-AI4H/COVID-Dialogue |
| Medical Flashcards | Dialogue | 33955 instances | https://github.com/kbressem/medalpaca |
| Wikidoc | Dialogue | 67704 instances | https://huggingface.co/datasets/medalpaca/medical\_meadow\_wikidoc |
| Wikidoc Patient Information | Dialogue | 5942 instances | https://huggingface.co/datasets/medalpaca/medical\_meadow\_wikidoc\_patient\_information |
| MEDIQA | Dialogue | 2208 instances | https://huggingface.co/datasets/medalpaca/medical\_meadow\_wikidoc\_patient\_information |
| CORD-19 | Dialogue | 1056660 instances | https://huggingface.co/datasets/medalpaca/medical\_meadow\_cord19 |
| MMMLU | Dialogue | 3787 instances | https://huggingface.co/datasets/medalpaca/medical\_meadow\_mmmlu |
| Pubmed Causal | Dialogue | 2446 instances | https://huggingface.co/datasets/medalpaca/medical\_meadow\_pubmed\_causal |
| ChatDoctor | Dialogue | 215000 instances | https://github.com/Kent0n-Li/ChatDoctor |
| Alpaca-EN-AN | English Instructions | 52K instructions | https://github.com/tatsu-lab/stanford\_alpaca/blob/main/alpaca\_data.json |
| Alpaca-CH-AN | Chinese Instructions | 52K instructions | https://github.com/Instruction-Tuning-with-GPT-4/GPT-4-LLM/tree/main/data |
| ShareGPT | Conversations | 61653 long conversations | https://huggingface.co/datasets/philschmid/sharegpt-raw |
| WebText | Web Data | 40 GB of text | https://commoncrawl.org/the-data/get-started/ |
| OpenWebText | Web Data | 38 GB of text | https://skylion007.github.io/OpenWebTextCorpus/ |
| Colossal Clean Crawled Corpus | Web Data | 806 GB of text | https://www.tensorflow.org/datasets/catalog/c4 |
| OpenI | EHR, Multimodel | 3.7 million images from about 1.2 million papers | https://openi.nlm.nih.gov/faq\#collection |
| U-Xray | Multimodel | 3,955 reports and 7,470 images | https://openi.nlm.nih.gov/ |
| ROCO | Multimodel | 81,000 radiology images and corresponding captions | https://github.com/razorx89/roco-dataset |
| MedICaT | Multimodel | 17,000 images includes captions | https://github.com/allenai/medicat |
| PMC-OA | Multimodel | 1.6M image-caption pairs | https://huggingface.co/datasets/axiong/pmc\_oa\_beta |
| CheXpert | Multimodel | 224,316 chest radiographs with associated reports | https://aimi.stanford.edu/chexpert-chest-x-rays |
| PadChest | Multimodel | 160,000 images with related text | http://bimcv.cipf.es/bimcv-projects/padchest/ |
| MIMIC-CXR | Multimodel | 227,835 imaging studies for 64,588 patients | https://mimic.mit.edu/docs/iv/modules/cxr/ |
| PMC-15M | Multimodel | 15 million Figure-caption | |
| pairs | https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.00915 | ||
| OpenPath | Multimodel | 208,414 pathology images related descriptions | https://laion.ai/blog/laion-5b/ |
TABLE VIII THE STATISTICS OF COMPUTATION COST FOR EXISTING HEALTHCARE LLM.
| Model Name | Total data size | epoch | Batch size | GPU type | GPU number | GPU time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Med-Alpaca | 54k data points | 3 | 128 | A100-80G | 4 | 2.51 hours |
| GatorTron | \textgreater 90 billion words | 10 | - | A100 | 992 | 6 days |
| Galactica | - | - | - | A100-80G | 128 | - |
| ChatDoctor | 100k conversations | 3 | 192 | A100 | 6 | 3 hours |
| DoctorGLM | 3.5G | 1 | 4 | A100-80G | 1 | 8 hours |
| PMC-LLaMA | 75B tokens | 5 | 128 | A100 | 8 | 7 days |
| Visual Med-Alpaca | 44.8MB* (without images) | - | 128 | A100-80G | 4 | 2.51 hours |
| BianQue 1.0 | 9 million samples | 1 | - | RTX 4090 | 8 | 16 days |
| GatorTronGPT | 277B tokens | 1,120/560 | A100-80G | 560 | 26 days | |
| HuatuoGPT | 226,042 instances | 3 | 128 | A100 | 8 | - |
| LLaVA-Med | 15 million figure-caption pairs | - | - | A100 | 8 | 15 hours |
| Med-Flamingo | 1.3M image-caption pairs | - | 400 | A100-80G | 8 | 6.75 days |
TABLE IX ESTIMATED FLOPS AND TRAINING TOKENS FOR DIFFERENT MODEL SIZES.
| Parameters | FLOPs | FLOPs (in Gopher unit) | Tokens |
|---|---|---|---|
| 400 Million | 1.92e+19 | 1/29, 968 | 8.0 Billion |
| 1 Billion | 1.21e+20 | 1/4, 761 | 20.2 Billion |
| 10 Billion | 1.23e+22 | 1/46 | 205.1 Billion |
| 67 Billion | 5.76e+23 | 1 | 1.5 Trillion |
| 175 Billion | 3.85e+24 | 6.7 | 3.7 Trillion |
| 280 Billion | 9.90e+24 | 17.2 | 5.9 Trillion |
| 520 Billion | 3.43e+25 | 59.5 | 11.0 Trillion |
| 1 Trillion | 1.27e+26 | 221.3 | 21.2 Trillion |
| 10 Trillion | 1.30e+28 | 22515.9 | 216.2 Trillion |
@misc{he2023survey,
title={A Survey of Large Language Models for Healthcare: from Data, Technology, and Applications to Accountability and Ethics},
author={Kai He and Rui Mao and Qika Lin and Yucheng Ruan and Xiang Lan and Mengling Feng and Erik Cambria},
year={2023},
eprint={2310.05694},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLM-for-Healthcare
Similar Open Source Tools

LLM-for-Healthcare
The repository 'LLM-for-Healthcare' provides a comprehensive survey of large language models (LLMs) for healthcare, covering data, technology, applications, and accountability and ethics. It includes information on various LLM models, training data, evaluation methods, and computation costs. The repository also discusses tasks such as NER, text classification, question answering, dialogue systems, and generation of medical reports from images in the healthcare domain.

kumo-search
Kumo search is an end-to-end search engine framework that supports full-text search, inverted index, forward index, sorting, caching, hierarchical indexing, intervention system, feature collection, offline computation, storage system, and more. It runs on the EA (Elastic automic infrastructure architecture) platform, enabling engineering automation, service governance, real-time data, service degradation, and disaster recovery across multiple data centers and clusters. The framework aims to provide a ready-to-use search engine framework to help users quickly build their own search engines. Users can write business logic in Python using the AOT compiler in the project, which generates C++ code and binary dynamic libraries for rapid iteration of the search engine.
Awesome-AgenticLLM-RL-Papers
This repository serves as the official source for the survey paper 'The Landscape of Agentic Reinforcement Learning for LLMs: A Survey'. It provides an extensive overview of various algorithms, methods, and frameworks related to Agentic RL, including detailed information on different families of algorithms, their key mechanisms, objectives, and links to relevant papers and resources. The repository covers a wide range of tasks such as Search & Research Agent, Code Agent, Mathematical Agent, GUI Agent, RL in Vision Agents, RL in Embodied Agents, and RL in Multi-Agent Systems. Additionally, it includes information on environments, frameworks, and methods suitable for different tasks related to Agentic RL and LLMs.
so-vits-models
This repository collects various LLM, AI-related models, applications, and datasets, including LLM-Chat for dialogue models, LLMs for large models, so-vits-svc for sound-related models, stable-diffusion for image-related models, and virtual-digital-person for generating videos. It also provides resources for deep learning courses and overviews, AI competitions, and specific AI tasks such as text, image, voice, and video processing.
Awesome-AGI
Awesome-AGI is a curated list of resources related to Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), including models, pipelines, applications, and concepts. It provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of AGI research and development, covering various aspects such as model training, fine-tuning, deployment, and applications in different domains. The repository also includes resources on prompt engineering, RLHF, LLM vocabulary expansion, long text generation, hallucination mitigation, controllability and safety, and text detection. It serves as a valuable resource for researchers, practitioners, and anyone interested in the field of AGI.
Awesome-LLM-Eval
Awesome-LLM-Eval: a curated list of tools, benchmarks, demos, papers for Large Language Models (like ChatGPT, LLaMA, GLM, Baichuan, etc) Evaluation on Language capabilities, Knowledge, Reasoning, Fairness and Safety.
PaddleScience
PaddleScience is a scientific computing suite developed based on the deep learning framework PaddlePaddle. It utilizes the learning ability of deep neural networks and the automatic (higher-order) differentiation mechanism of PaddlePaddle to solve problems in physics, chemistry, meteorology, and other fields. It supports three solving methods: physics mechanism-driven, data-driven, and mathematical fusion, and provides basic APIs and detailed documentation for users to use and further develop.
ML-AI-2-LT
ML-AI-2-LT is a repository that serves as a glossary for machine learning and deep learning concepts. It contains translations and explanations of various terms related to artificial intelligence, including definitions and notes. Users can contribute by filling issues for unclear concepts or by submitting pull requests with suggestions or additions. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive resource for understanding key terminology in the field of AI and machine learning.
Cool-GenAI-Fashion-Papers
Cool-GenAI-Fashion-Papers is a curated list of resources related to GenAI-Fashion, including papers, workshops, companies, and products. It covers a wide range of topics such as fashion design synthesis, outfit recommendation, fashion knowledge extraction, trend analysis, and more. The repository provides valuable insights and resources for researchers, industry professionals, and enthusiasts interested in the intersection of AI and fashion.
awesome-hosting
awesome-hosting is a curated list of hosting services sorted by minimal plan price. It includes various categories such as Web Services Platform, Backend-as-a-Service, Lambda, Node.js, Static site hosting, WordPress hosting, VPS providers, managed databases, GPU cloud services, and LLM/Inference API providers. Each category lists multiple service providers along with details on their minimal plan, trial options, free tier availability, open-source support, and specific features. The repository aims to help users find suitable hosting solutions based on their budget and requirements.
AIInfra
AIInfra is an open-source project focused on AI infrastructure, specifically targeting large models in distributed clusters, distributed architecture, distributed training, and algorithms related to large models. The project aims to explore and study system design in artificial intelligence and deep learning, with a focus on the hardware and software stack for building AI large model systems. It provides a comprehensive curriculum covering topics such as AI chip principles, communication and storage, AI clusters, large model training, and inference, as well as algorithms for large models. The course is designed for undergraduate and graduate students, as well as professionals working with AI large model systems, to gain a deep understanding of AI computer system architecture and design.
step_into_llm
The 'step_into_llm' repository is dedicated to the 昇思MindSpore technology open class, which focuses on exploring cutting-edge technologies, combining theory with practical applications, expert interpretations, open sharing, and empowering competitions. The repository contains course materials, including slides and code, for the ongoing second phase of the course. It covers various topics related to large language models (LLMs) such as Transformer, BERT, GPT, GPT2, and more. The course aims to guide developers interested in LLMs from theory to practical implementation, with a special emphasis on the development and application of large models.
LLM-Agent-Survey
Autonomous agents are designed to achieve specific objectives through self-guided instructions. With the emergence and growth of large language models (LLMs), there is a growing trend in utilizing LLMs as fundamental controllers for these autonomous agents. This repository conducts a comprehensive survey study on the construction, application, and evaluation of LLM-based autonomous agents. It explores essential components of AI agents, application domains in natural sciences, social sciences, and engineering, and evaluation strategies. The survey aims to be a resource for researchers and practitioners in this rapidly evolving field.
LLM-PlayLab
LLM-PlayLab is a repository containing various projects related to LLM (Large Language Models) fine-tuning, generative AI, time-series forecasting, and crash courses. It includes projects for text generation, sentiment analysis, data analysis, chat assistants, image captioning, and more. The repository offers a wide range of tools and resources for exploring and implementing advanced AI techniques.
For similar tasks

LLM-for-Healthcare
The repository 'LLM-for-Healthcare' provides a comprehensive survey of large language models (LLMs) for healthcare, covering data, technology, applications, and accountability and ethics. It includes information on various LLM models, training data, evaluation methods, and computation costs. The repository also discusses tasks such as NER, text classification, question answering, dialogue systems, and generation of medical reports from images in the healthcare domain.
MedicalGPT
MedicalGPT is a training medical GPT model with ChatGPT training pipeline, implement of Pretraining, Supervised Finetuning, RLHF(Reward Modeling and Reinforcement Learning) and DPO(Direct Preference Optimization).
Apollo
Apollo is a multilingual medical LLM that covers English, Chinese, French, Hindi, Spanish, Hindi, and Arabic. It is designed to democratize medical AI to 6B people. Apollo has achieved state-of-the-art results on a variety of medical NLP tasks, including question answering, medical dialogue generation, and medical text classification. Apollo is easy to use and can be integrated into a variety of applications, making it a valuable tool for healthcare professionals and researchers.
MING
MING is an open-sourced Chinese medical consultation model fine-tuned based on medical instructions. The main functions of the model are as follows: Medical Q&A: answering medical questions and analyzing cases. Intelligent consultation: giving diagnosis results and suggestions after multiple rounds of consultation.
Taiyi-LLM
Taiyi (太一) is a bilingual large language model fine-tuned for diverse biomedical tasks. It aims to facilitate communication between healthcare professionals and patients, provide medical information, and assist in diagnosis, biomedical knowledge discovery, drug development, and personalized healthcare solutions. The model is based on the Qwen-7B-base model and has been fine-tuned using rich bilingual instruction data. It covers tasks such as question answering, biomedical dialogue, medical report generation, biomedical information extraction, machine translation, title generation, text classification, and text semantic similarity. The project also provides standardized data formats, model training details, model inference guidelines, and overall performance metrics across various BioNLP tasks.
Medical_Image_Analysis
The Medical_Image_Analysis repository focuses on X-ray image-based medical report generation using large language models. It provides pre-trained models and benchmarks for CheXpert Plus dataset, context sample retrieval for X-ray report generation, and pre-training on high-definition X-ray images. The goal is to enhance diagnostic accuracy and reduce patient wait times by improving X-ray report generation through advanced AI techniques.
For similar jobs

LLM-for-Healthcare
The repository 'LLM-for-Healthcare' provides a comprehensive survey of large language models (LLMs) for healthcare, covering data, technology, applications, and accountability and ethics. It includes information on various LLM models, training data, evaluation methods, and computation costs. The repository also discusses tasks such as NER, text classification, question answering, dialogue systems, and generation of medical reports from images in the healthcare domain.
HuatuoGPT-II
HuatuoGPT2 is an innovative domain-adapted medical large language model that excels in medical knowledge and dialogue proficiency. It showcases state-of-the-art performance in various medical benchmarks, surpassing GPT-4 in expert evaluations and fresh medical licensing exams. The open-source release includes HuatuoGPT2 models in 7B, 13B, and 34B versions, training code for one-stage adaptation, partial pre-training and fine-tuning instructions, and evaluation methods for medical response capabilities and professional pharmacist exams. The tool aims to enhance LLM capabilities in the Chinese medical field through open-source principles.

Me-LLaMA
Me LLaMA introduces a suite of open-source medical Large Language Models (LLMs), including Me LLaMA 13B/70B and their chat-enhanced versions. Developed through innovative continual pre-training and instruction tuning, these models leverage a vast medical corpus comprising PubMed papers, medical guidelines, and general domain data. Me LLaMA sets new benchmarks on medical reasoning tasks, making it a significant asset for medical NLP applications and research. The models are intended for computational linguistics and medical research, not for clinical decision-making without validation and regulatory approval.
azure-health-data-and-ai-samples
The Azure Health Data and AI Samples Repo is a collection of sample apps and code to help users start with Azure Health Data and AI services, learn product usage, and speed up implementations. It includes samples for various health data workflows, such as data ingestion, analytics, machine learning, SMART on FHIR, patient services, FHIR service integration, Azure AD B2C access, DICOM service, MedTech service, and healthcare data solutions in Microsoft Fabric. These samples are simplified scenarios for testing purposes only.
HuatuoGPT-o1
HuatuoGPT-o1 is a medical language model designed for advanced medical reasoning. It can identify mistakes, explore alternative strategies, and refine answers. The model leverages verifiable medical problems and a specialized medical verifier to guide complex reasoning trajectories and enhance reasoning through reinforcement learning. The repository provides access to models, data, and code for HuatuoGPT-o1, allowing users to deploy the model for medical reasoning tasks.
aigt
AIGT is a repository containing scripts for deep learning in guided medical interventions, focusing on ultrasound imaging. It provides a complete workflow from formatting and annotations to real-time model deployment. Users can set up an Anaconda environment, run Slicer notebooks, acquire tracked ultrasound data, and process exported data for training. The repository includes tools for segmentation, image export, and annotation creation.

cyclops
Cyclops is a toolkit for facilitating research and deployment of ML models for healthcare. It provides a few high-level APIs namely: data - Create datasets for training, inference and evaluation. We use the popular 🤗 datasets to efficiently load and slice different modalities of data models - Use common model implementations using scikit-learn and PyTorch tasks - Use common ML task formulations such as binary classification or multi-label classification on tabular, time-series and image data evaluate - Evaluate models on clinical prediction tasks monitor - Detect dataset shift relevant for clinical use cases report - Create model report cards for clinical ML models
CareGPT
CareGPT is a medical large language model (LLM) that explores medical data, training, and deployment related research work. It integrates resources, open-source models, rich data, and efficient deployment methods. It supports various medical tasks, including patient diagnosis, medical dialogue, and medical knowledge integration. The model has been fine-tuned on diverse medical datasets to enhance its performance in the healthcare domain.