
HuatuoGPT-o1
Medical o1, Towards medical complex reasoning with LLMs
Stars: 480
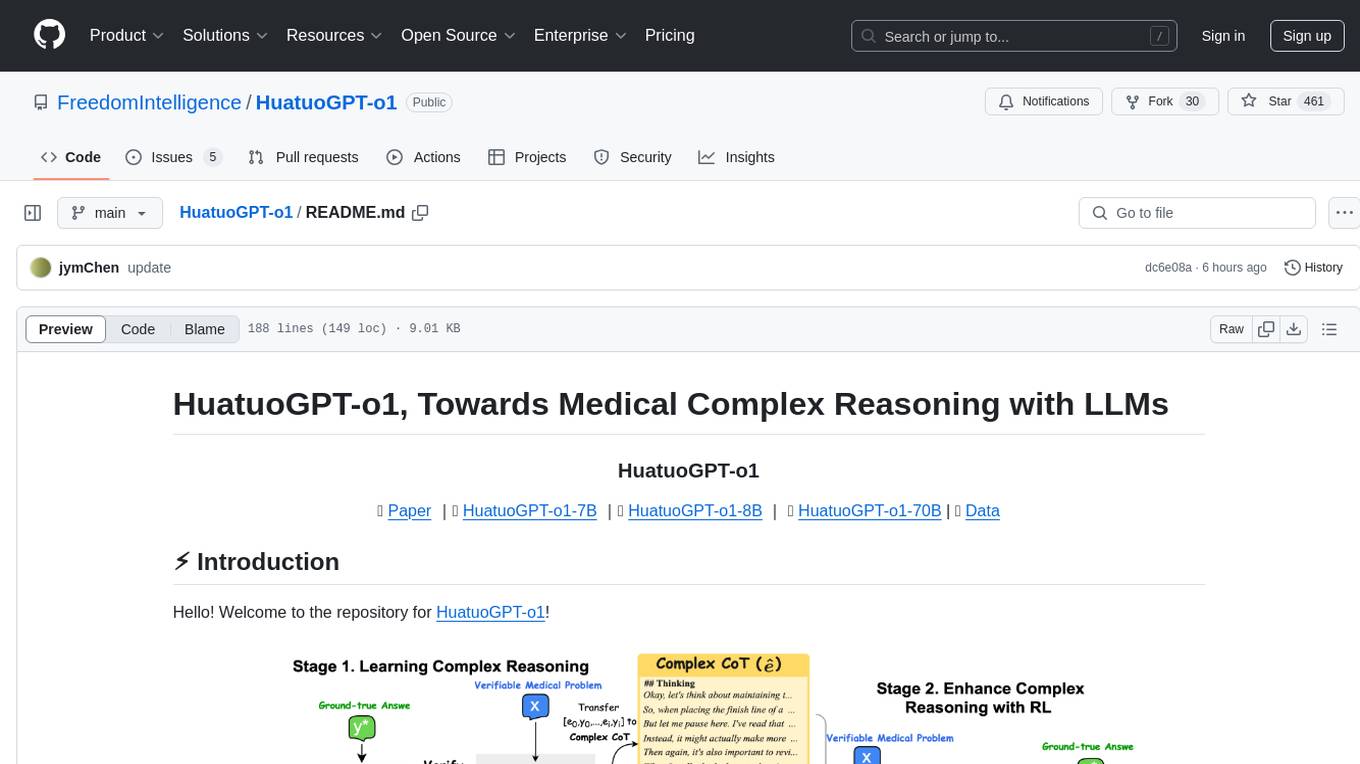
HuatuoGPT-o1 is a medical language model designed for advanced medical reasoning. It can identify mistakes, explore alternative strategies, and refine answers. The model leverages verifiable medical problems and a specialized medical verifier to guide complex reasoning trajectories and enhance reasoning through reinforcement learning. The repository provides access to models, data, and code for HuatuoGPT-o1, allowing users to deploy the model for medical reasoning tasks.
README:
📃 Paper |🤗 HuatuoGPT-o1-7B |🤗 HuatuoGPT-o1-8B | 🤗 HuatuoGPT-o1-70B | 📚 Data
Hello! Welcome to the repository for HuatuoGPT-o1!
HuatuoGPT-o1 is a medical LLM designed for advanced medical reasoning. It can identify mistakes, explore alternative strategies, and refine its answers. By leveraging verifiable medical problems and a specialized medical verifier, it advances reasoning through:
- Using the verifier to guide the search for a complex reasoning trajectory for fine-tuning LLMs.
- Applying reinforcement learning (PPO) with verifier-based rewards to enhance complex reasoning further.
We open-sourced our models, data, and code here.
- Model Access
| Backbone | Supported Languages | Link | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HuatuoGPT-o1-8B | LLaMA-3.1-8B | English | HF Link |
| HuatuoGPT-o1-70B | LLaMA-3.1-70B | English | HF Link |
| HuatuoGPT-o1-7B | Qwen2.5-7B | English & Chinese | HF Link |
| HuatuoGPT-o1-72B | Qwen2.5-72B | English & Chinese | HF Link |
- Deploy
HuatuoGPT-o1 can be used just like Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct. You can deploy it with tools like vllm or Sglang, or perform direct inference:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("FreedomIntelligence/HuatuoGPT-o1-8B",torch_dtype="auto",device_map="auto")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("FreedomIntelligence/HuatuoGPT-o1-8B")
input_text = "How to stop a cough?"
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": input_text}]
inputs = tokenizer(tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False,add_generation_prompt=True
), return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=2048)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))HuatuoGPT-o1 adopts a thinks-before-it-answers approach, with outputs formatted as:
## Thinking
[Reasoning process]
## Final Response
[Output]
- Data Access
| Data | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Verifiable Problems | Open-ended medical problems sourced from challenging medical exams, paired with ground-truth answers. | Link |
| SFT Data in Stage 1 | Fine-tuning data generated using GPT-4o, including complex chains of thought (Complex CoT) and output (Response). | Link |
- Data Construction
We provide scripts to construct verifiable problems and searching reasoning paths.
1. Constructing Verifiable Problems from Multi-choice Questions.
python construct_verifiable_medical_problems.py --data_path data/demo_data.json --filter_data --model_name gpt-4o --api_key [your api key]2. Searching Complex Reasoning Paths for SFT
python search_for_complex_reasoning_path.py --data_path data/demo_data.json --efficient_search True --max_search_attempts 1 --max_search_depth 2 --model_name gpt-4o --api_key [your api key]- Stage 1: Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT)
Fine-tune the model on an 8-GPU setup:
accelerate launch --config_file ./configs/deepspeed_zero3.yaml \
--num_processes 8 \
--num_machines 1 \
--machine_rank 0 \
--deepspeed_multinode_launcher standard SFT_stage1.py \
--model_path [meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct] \
--data_path [FreedomIntelligence/medical-o1-reasoning-SFT] - Stage 2: Reinforcement Learning (RL)
We provide a simple PPO script using the trl library. Below is an example for training an 8B model with PPO on an 8-GPU A100 machine. Ensure you first download our medical verifier as the reward model.
accelerate launch \
--num_processes 8 \
--num_machines 1 \
--machine_rank 0 \
--config_file ./configs/deepspeed_zero3.yaml \
--deepspeed_multinode_launcher standard RL_stage2.py \
--model_name_or_path [FreedomIntelligence/HuatuoGPT-o1-8B] \
--reward_model_path [FreedomIntelligence/medical_o1_verifier_3B] \
--value_model_path [meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct] \
--dataset_name [FreedomIntelligence/medical-o1-verifiable-problem]\
--response_length 1300 \
--temperature 0.5 \
--local_rollout_forward_batch_size 8 \
--num_ppo_epochs 3 \
--num_mini_batches 1 \
--total_episodes 20000 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 1 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps 16 \
--bf16 True \
--output_dir ./ckpts \
--save_strategy steps \
--save_step 20 \
--save_total_limit 1 \
--eval_strategy steps \
--eval_steps 20 \
--kl_coef 0.03 \
--learning_rate 5e-7 \
--warmup_ratio 0.05 \
--gradient_checkpointing True \
--dataloader_num_workers 4 \
--run_name ppo_medical_o1_8B \
--num_sample_generations -1 \
--report_to wandb- You first need to install Sglang. After installation, deploy the model you want to test using Sglang with the following command:
log_num=0
model_name="FreedomIntelligence/HuatuoGPT-o1-8B" # Path to the model you are deploying
port=28${log_num}35
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python -m sglang.launch_server --model-path $model_name --port $port --mem-fraction-static 0.8 --dp 1 --tp 1 > sglang${log_num}.log 2>&1 &- Wait for the model to be deployed. After deployment, you can run the following code for evaluation. We use prompts that allow the model to respond freely. We find that the extracted results are consistently reliable and broadly cover the intended scope. You can also set the
--strict_promptoption to use stricter prompts for more precise answer extraction.
python evaluation/eval.py --model_name $model_name --eval_file evaluation/data/eval_data.json --port $port - After completing the evaluation, run the following code to stop the Sglang service and release GPU memory.
bash evaluation/kill_sglang_server.shThe evaluation code above can be used to test most models supported by Sglang.
Explore our HuatuoGPT series:
- HuatuoGPT: Taming Language Models to Be a Doctor
- HuatuoGPT-II: One-stage Training for Medical Adaptation of LLMs
- HuatuoGPT-Vision: Injecting Medical Visual Knowledge into Multimodal LLMs at Scale
- CoD (Chain-of-Diagnosis): Towards an Interpretable Medical Agent using Chain of Diagnosis
- HuatuoGPT-o1: Towards Medical Complex Reasoning with LLMs
@misc{chen2024huatuogpto1medicalcomplexreasoning,
title={HuatuoGPT-o1, Towards Medical Complex Reasoning with LLMs},
author={Junying Chen and Zhenyang Cai and Ke Ji and Xidong Wang and Wanlong Liu and Rongsheng Wang and Jianye Hou and Benyou Wang},
year={2024},
eprint={2412.18925},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.18925},
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for HuatuoGPT-o1
Similar Open Source Tools

HuatuoGPT-o1
HuatuoGPT-o1 is a medical language model designed for advanced medical reasoning. It can identify mistakes, explore alternative strategies, and refine answers. The model leverages verifiable medical problems and a specialized medical verifier to guide complex reasoning trajectories and enhance reasoning through reinforcement learning. The repository provides access to models, data, and code for HuatuoGPT-o1, allowing users to deploy the model for medical reasoning tasks.
evalchemy
Evalchemy is a unified and easy-to-use toolkit for evaluating language models, focusing on post-trained models. It integrates multiple existing benchmarks such as RepoBench, AlpacaEval, and ZeroEval. Key features include unified installation, parallel evaluation, simplified usage, and results management. Users can run various benchmarks with a consistent command-line interface and track results locally or integrate with a database for systematic tracking and leaderboard submission.
TempCompass
TempCompass is a benchmark designed to evaluate the temporal perception ability of Video LLMs. It encompasses a diverse set of temporal aspects and task formats to comprehensively assess the capability of Video LLMs in understanding videos. The benchmark includes conflicting videos to prevent models from relying on single-frame bias and language priors. Users can clone the repository, install required packages, prepare data, run inference using examples like Video-LLaVA and Gemini, and evaluate the performance of their models across different tasks such as Multi-Choice QA, Yes/No QA, Caption Matching, and Caption Generation.

deepfabric
DeepFabric is a CLI tool and SDK designed for researchers and developers to generate high-quality synthetic datasets at scale using large language models. It leverages a graph and tree-based architecture to create diverse and domain-specific datasets while minimizing redundancy. The tool supports generating Chain of Thought datasets for step-by-step reasoning tasks and offers multi-provider support for using different language models. DeepFabric also allows for automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub and uses YAML configuration files for flexibility in dataset generation.
awesome-slash
Automate the entire development workflow beyond coding. awesome-slash provides production-ready skills, agents, and commands for managing tasks, branches, reviews, CI, and deployments. It automates the entire workflow, including task exploration, planning, implementation, review, and shipping. The tool includes 11 plugins, 40 agents, 26 skills, and 26k lines of lib code, with 3,357 tests and support for 3 platforms. It works with Claude Code, OpenCode, and Codex CLI, offering specialized capabilities through skills and agents.
agentscope
AgentScope is a multi-agent platform designed to empower developers to build multi-agent applications with large-scale models. It features three high-level capabilities: Easy-to-Use, High Robustness, and Actor-Based Distribution. AgentScope provides a list of `ModelWrapper` to support both local model services and third-party model APIs, including OpenAI API, DashScope API, Gemini API, and ollama. It also enables developers to rapidly deploy local model services using libraries such as ollama (CPU inference), Flask + Transformers, Flask + ModelScope, FastChat, and vllm. AgentScope supports various services, including Web Search, Data Query, Retrieval, Code Execution, File Operation, and Text Processing. Example applications include Conversation, Game, and Distribution. AgentScope is released under Apache License 2.0 and welcomes contributions.
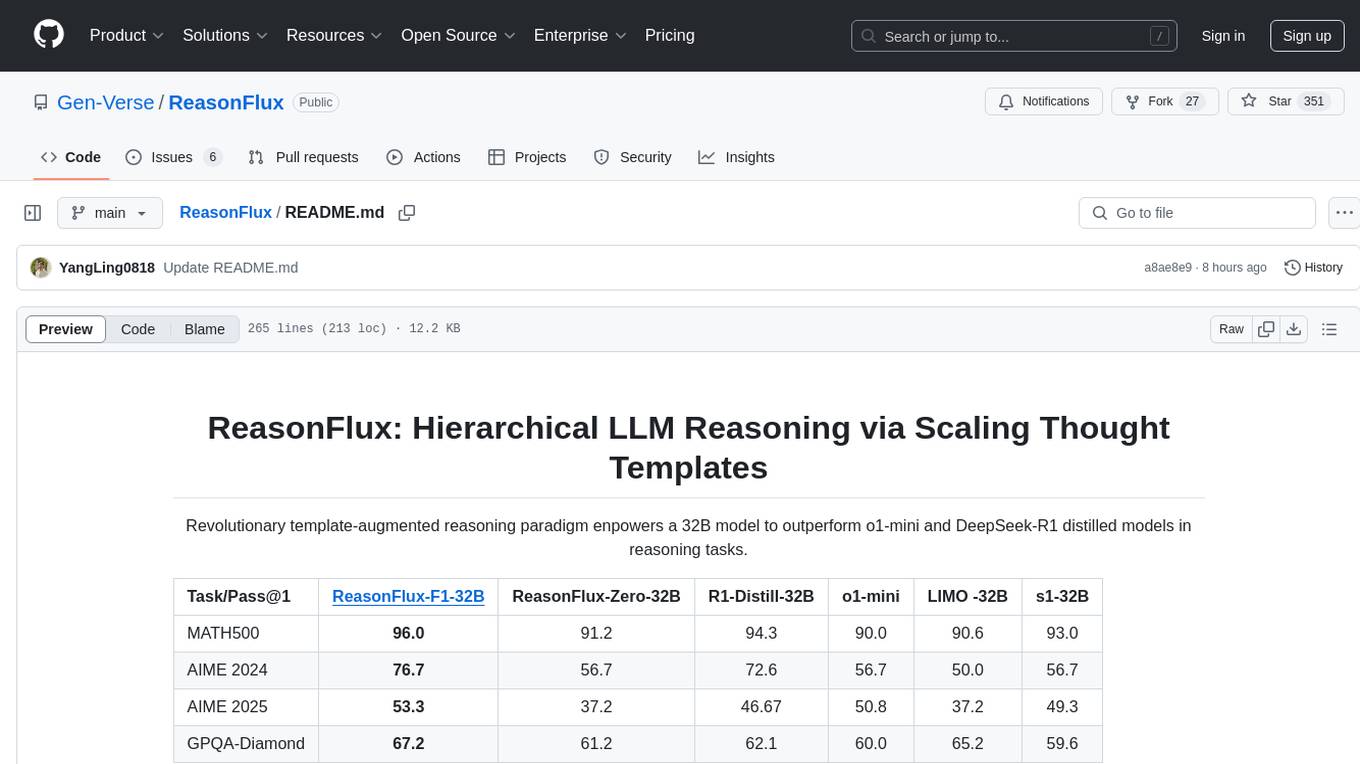
ReasonFlux
ReasonFlux is a revolutionary template-augmented reasoning paradigm that empowers a 32B model to outperform other models in reasoning tasks. The repository provides official resources for the paper 'ReasonFlux: Hierarchical LLM Reasoning via Scaling Thought Templates', including the latest released model ReasonFlux-F1-32B. It includes updates, dataset links, model zoo, getting started guide, training instructions, evaluation details, inference examples, performance comparisons, reasoning examples, preliminary work references, and citation information.
LongLoRA
LongLoRA is a tool for efficient fine-tuning of long-context large language models. It includes LongAlpaca data with long QA data collected and short QA sampled, models from 7B to 70B with context length from 8k to 100k, and support for GPTNeoX models. The tool supports supervised fine-tuning, context extension, and improved LoRA fine-tuning. It provides pre-trained weights, fine-tuning instructions, evaluation methods, local and online demos, streaming inference, and data generation via Pdf2text. LongLoRA is licensed under Apache License 2.0, while data and weights are under CC-BY-NC 4.0 License for research use only.
Cherry_LLM
Cherry Data Selection project introduces a self-guided methodology for LLMs to autonomously discern and select cherry samples from open-source datasets, minimizing manual curation and cost for instruction tuning. The project focuses on selecting impactful training samples ('cherry data') to enhance LLM instruction tuning by estimating instruction-following difficulty. The method involves phases like 'Learning from Brief Experience', 'Evaluating Based on Experience', and 'Retraining from Self-Guided Experience' to improve LLM performance.
Evaluator
NeMo Evaluator SDK is an open-source platform for robust, reproducible, and scalable evaluation of Large Language Models. It enables running hundreds of benchmarks across popular evaluation harnesses against any OpenAI-compatible model API. The platform ensures auditable and trustworthy results by executing evaluations in open-source Docker containers. NeMo Evaluator SDK is built on four core principles: Reproducibility by Default, Scale Anywhere, State-of-the-Art Benchmarking, and Extensible and Customizable.
bumblecore
BumbleCore is a hands-on large language model training framework that allows complete control over every training detail. It provides manual training loop, customizable model architecture, and support for mainstream open-source models. The framework follows core principles of transparency, flexibility, and efficiency. BumbleCore is suitable for deep learning researchers, algorithm engineers, learners, and enterprise teams looking for customization and control over model training processes.
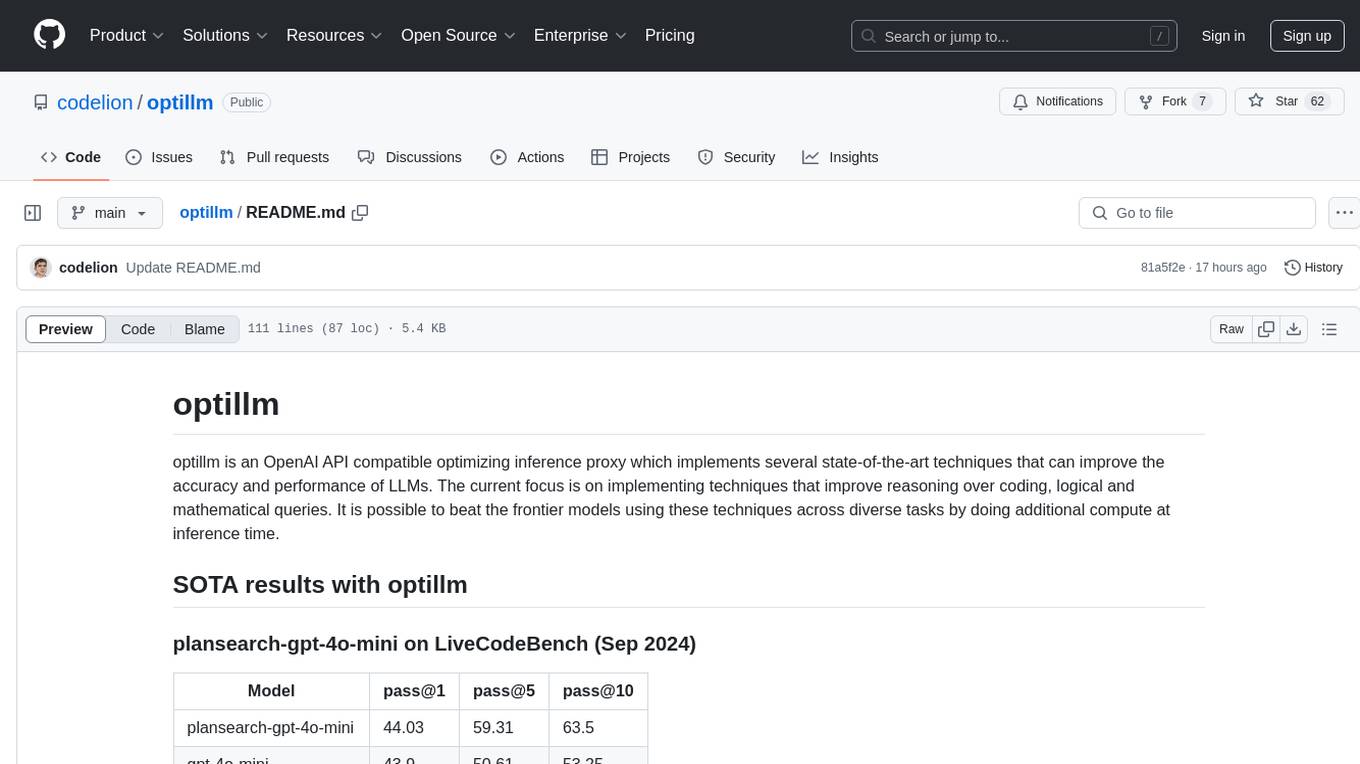
optillm
optillm is an OpenAI API compatible optimizing inference proxy implementing state-of-the-art techniques to enhance accuracy and performance of LLMs, focusing on reasoning over coding, logical, and mathematical queries. By leveraging additional compute at inference time, it surpasses frontier models across diverse tasks.
AgentDoG
AgentDoG is a risk-aware evaluation and guarding framework for autonomous agents that focuses on trajectory-level risk assessment. It analyzes the full execution trace of tool-using agents to detect risks that emerge mid-trajectory. It provides trajectory-level monitoring, taxonomy-guided diagnosis, flexible use cases, and state-of-the-art performance. The framework includes a safety taxonomy for agentic systems, a methodology for task definition, data synthesis and collection, training, and performance highlights. It also offers deployment examples, agentic XAI attribution framework, and repository structure. Customization options are available, and the project is licensed under Apache 2.0.
pollinations
pollinations.ai is an open-source generative AI platform based in Berlin, empowering community projects with accessible text, image, video, and audio generation APIs. It offers a unified API endpoint for various AI generation needs, including text, images, audio, and video. The platform provides features like image generation using models such as Flux, GPT Image, Seedream, and Kontext, video generation with Seedance and Veo, and audio generation with text-to-speech and speech-to-text capabilities. Users can access the platform through a web interface or API, and authentication is managed through API keys. The platform is community-driven, transparent, and ethical, aiming to make AI technology open, accessible, and interconnected while fostering innovation and responsible development.

llm4ad
LLM4AD is an open-source Python-based platform leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automatic Algorithm Design (AD). It provides unified interfaces for methods, tasks, and LLMs, along with features like evaluation acceleration, secure evaluation, logs, GUI support, and more. The platform was originally developed for optimization tasks but is versatile enough to be used in other areas such as machine learning, science discovery, game theory, and engineering design. It offers various search methods and algorithm design tasks across different domains. LLM4AD supports remote LLM API, local HuggingFace LLM deployment, and custom LLM interfaces. The project is licensed under the MIT License and welcomes contributions, collaborations, and issue reports.
BitBLAS
BitBLAS is a library for mixed-precision BLAS operations on GPUs, for example, the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ mixed-precision matrix multiplication where $C_{cdtype}[M, N] = A_{adtype}[M, K] \times W_{wdtype}[N, K]$. BitBLAS aims to support efficient mixed-precision DNN model deployment, especially the $W_{wdtype}A_{adtype}$ quantization in large language models (LLMs), for example, the $W_{UINT4}A_{FP16}$ in GPTQ, the $W_{INT2}A_{FP16}$ in BitDistiller, the $W_{INT2}A_{INT8}$ in BitNet-b1.58. BitBLAS is based on techniques from our accepted submission at OSDI'24.
For similar tasks
Detection-and-Classification-of-Alzheimers-Disease
This tool is designed to detect and classify Alzheimer's Disease using Deep Learning and Machine Learning algorithms on an early basis, which is further optimized using the Crow Search Algorithm (CSA). Alzheimer's is a fatal disease, and early detection is crucial for patients to predetermine their condition and prevent its progression. By analyzing MRI scanned images using Artificial Intelligence technology, this tool can classify patients who may or may not develop AD in the future. The CSA algorithm, combined with ML algorithms, has proven to be the most effective approach for this purpose.
MedLLMsPracticalGuide
This repository serves as a practical guide for Medical Large Language Models (Medical LLMs) and provides resources, surveys, and tools for building, fine-tuning, and utilizing LLMs in the medical domain. It covers a wide range of topics including pre-training, fine-tuning, downstream biomedical tasks, clinical applications, challenges, future directions, and more. The repository aims to provide insights into the opportunities and challenges of LLMs in medicine and serve as a practical resource for constructing effective medical LLMs.

AMIE-pytorch
Implementation of the general framework for AMIE, from the paper Towards Conversational Diagnostic AI, out of Google Deepmind. This repository provides a Pytorch implementation of the AMIE framework, aimed at enabling conversational diagnostic AI. It is a work in progress and welcomes collaboration from individuals with a background in deep learning and an interest in medical applications.

HuatuoGPT-o1
HuatuoGPT-o1 is a medical language model designed for advanced medical reasoning. It can identify mistakes, explore alternative strategies, and refine answers. The model leverages verifiable medical problems and a specialized medical verifier to guide complex reasoning trajectories and enhance reasoning through reinforcement learning. The repository provides access to models, data, and code for HuatuoGPT-o1, allowing users to deploy the model for medical reasoning tasks.
minions
Minions is a communication protocol that enables small on-device models to collaborate with frontier models in the cloud. By only reading long contexts locally, it reduces cloud costs with minimal or no quality degradation. The repository provides a demonstration of the protocol.
MING
MING is an open-sourced Chinese medical consultation model fine-tuned based on medical instructions. The main functions of the model are as follows: Medical Q&A: answering medical questions and analyzing cases. Intelligent consultation: giving diagnosis results and suggestions after multiple rounds of consultation.
IvyGPT
IvyGPT is a medical large language model that aims to generate the most realistic doctor consultation effects. It has been fine-tuned on high-quality medical Q&A data and trained using human feedback reinforcement learning. The project features full-process training on medical Q&A LLM, multiple fine-tuning methods support, efficient dataset creation tools, and a dataset of over 300,000 high-quality doctor-patient dialogues for training.
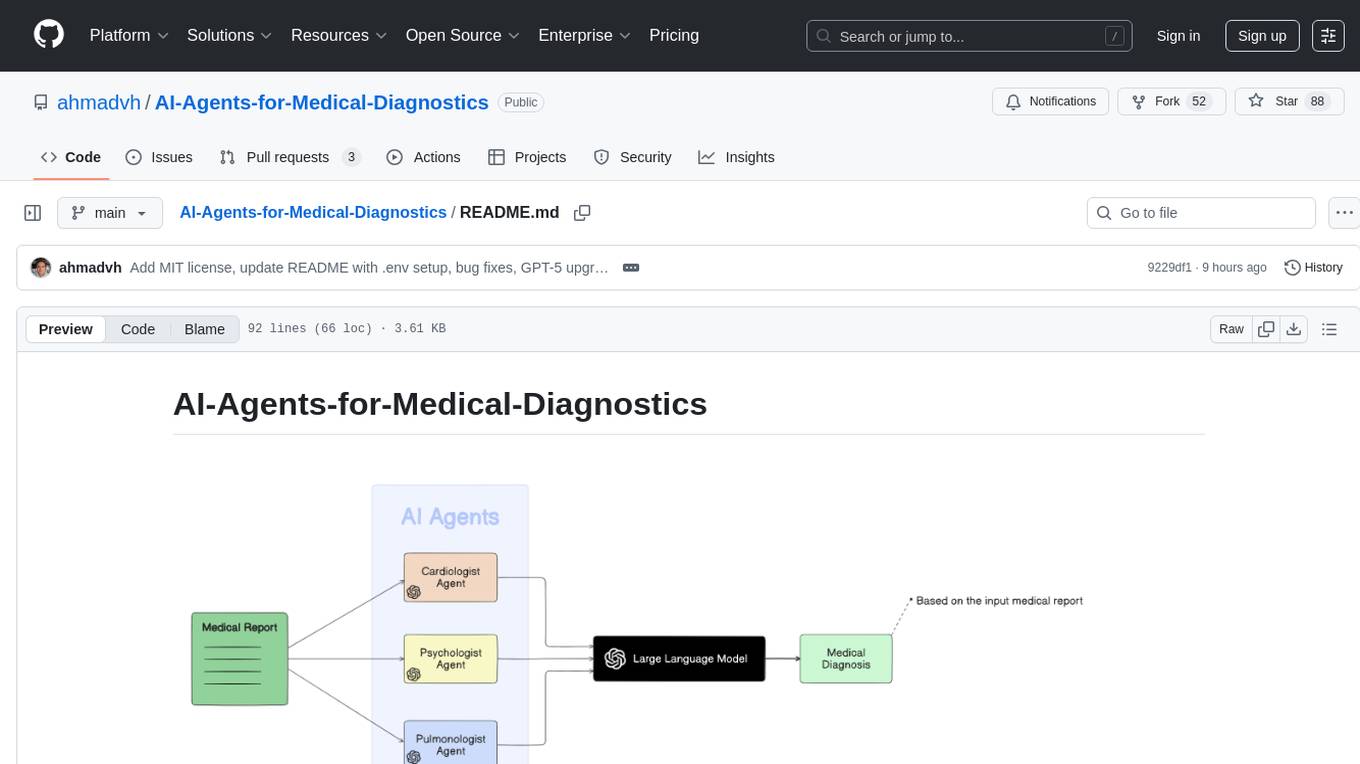
AI-Agents-for-Medical-Diagnostics
AI Agents for Medical Diagnostics is a repository containing a collection of machine learning models and algorithms designed to assist in medical diagnosis. The tools provided in this repository are specifically tailored for analyzing medical data and making predictions related to various health conditions. By leveraging the power of artificial intelligence, these agents aim to improve the accuracy and efficiency of diagnostic processes in the medical field. Researchers, healthcare professionals, and data scientists can benefit from the resources available in this repository to develop innovative solutions for diagnosing illnesses and predicting patient outcomes.
For similar jobs

HuatuoGPT-o1
HuatuoGPT-o1 is a medical language model designed for advanced medical reasoning. It can identify mistakes, explore alternative strategies, and refine answers. The model leverages verifiable medical problems and a specialized medical verifier to guide complex reasoning trajectories and enhance reasoning through reinforcement learning. The repository provides access to models, data, and code for HuatuoGPT-o1, allowing users to deploy the model for medical reasoning tasks.
LLM-for-Healthcare
The repository 'LLM-for-Healthcare' provides a comprehensive survey of large language models (LLMs) for healthcare, covering data, technology, applications, and accountability and ethics. It includes information on various LLM models, training data, evaluation methods, and computation costs. The repository also discusses tasks such as NER, text classification, question answering, dialogue systems, and generation of medical reports from images in the healthcare domain.
HuatuoGPT-II
HuatuoGPT2 is an innovative domain-adapted medical large language model that excels in medical knowledge and dialogue proficiency. It showcases state-of-the-art performance in various medical benchmarks, surpassing GPT-4 in expert evaluations and fresh medical licensing exams. The open-source release includes HuatuoGPT2 models in 7B, 13B, and 34B versions, training code for one-stage adaptation, partial pre-training and fine-tuning instructions, and evaluation methods for medical response capabilities and professional pharmacist exams. The tool aims to enhance LLM capabilities in the Chinese medical field through open-source principles.
azure-health-data-and-ai-samples
The Azure Health Data and AI Samples Repo is a collection of sample apps and code to help users start with Azure Health Data and AI services, learn product usage, and speed up implementations. It includes samples for various health data workflows, such as data ingestion, analytics, machine learning, SMART on FHIR, patient services, FHIR service integration, Azure AD B2C access, DICOM service, MedTech service, and healthcare data solutions in Microsoft Fabric. These samples are simplified scenarios for testing purposes only.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.

MedLLMsPracticalGuide
This repository serves as a practical guide for Medical Large Language Models (Medical LLMs) and provides resources, surveys, and tools for building, fine-tuning, and utilizing LLMs in the medical domain. It covers a wide range of topics including pre-training, fine-tuning, downstream biomedical tasks, clinical applications, challenges, future directions, and more. The repository aims to provide insights into the opportunities and challenges of LLMs in medicine and serve as a practical resource for constructing effective medical LLMs.
hi-ml
The Microsoft Health Intelligence Machine Learning Toolbox is a repository that provides low-level and high-level building blocks for Machine Learning / AI researchers and practitioners. It simplifies and streamlines work on deep learning models for healthcare and life sciences by offering tested components such as data loaders, pre-processing tools, deep learning models, and cloud integration utilities. The repository includes two Python packages, 'hi-ml-azure' for helper functions in AzureML, 'hi-ml' for ML components, and 'hi-ml-cpath' for models and workflows related to histopathology images.
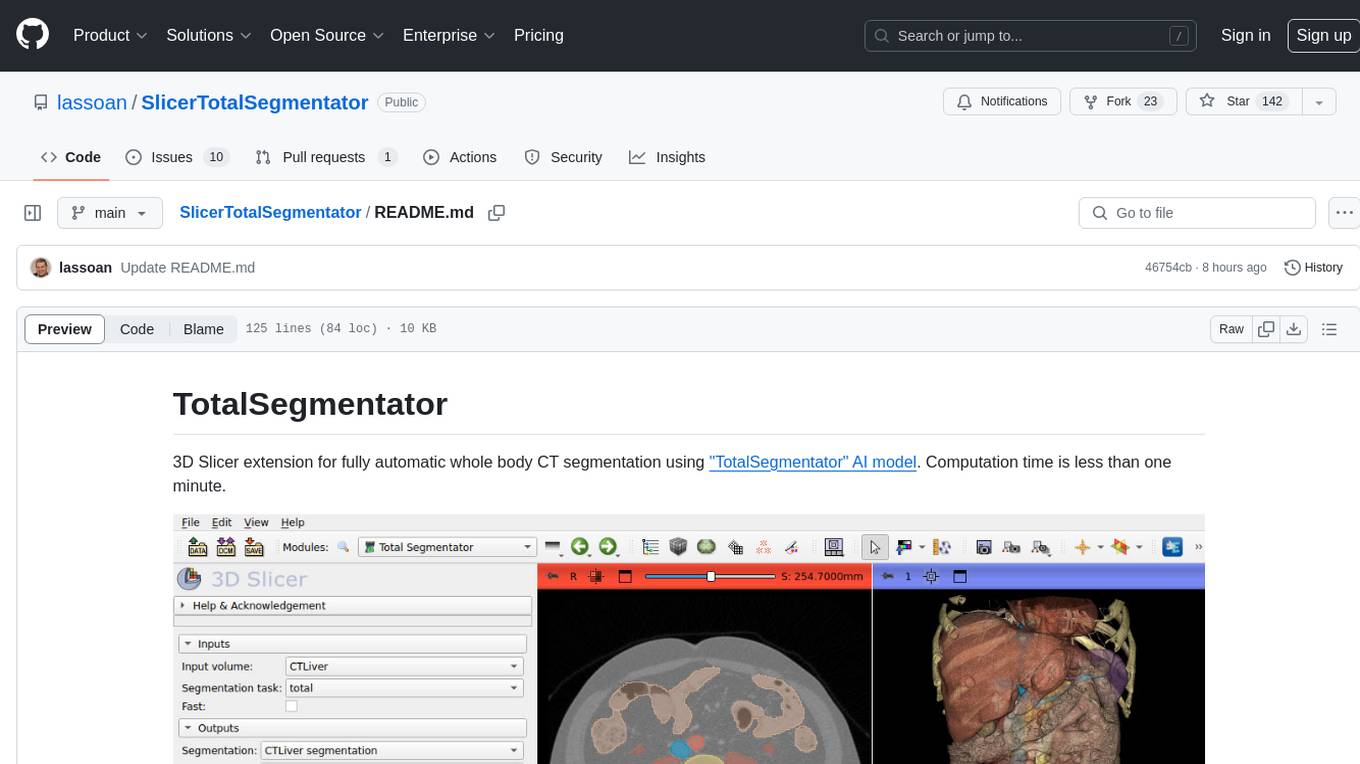
SlicerTotalSegmentator
TotalSegmentator is a 3D Slicer extension designed for fully automatic whole body CT segmentation using the 'TotalSegmentator' AI model. The computation time is less than one minute, making it efficient for research purposes. Users can set up GPU acceleration for faster segmentation. The tool provides a user-friendly interface for loading CT images, creating segmentations, and displaying results in 3D. Troubleshooting steps are available for common issues such as failed computation, GPU errors, and inaccurate segmentations. Contributions to the extension are welcome, following 3D Slicer contribution guidelines.
