
SlicerTotalSegmentator
Fully automatic total body segmentation in 3D Slicer using "TotalSegmentator" AI model
Stars: 167
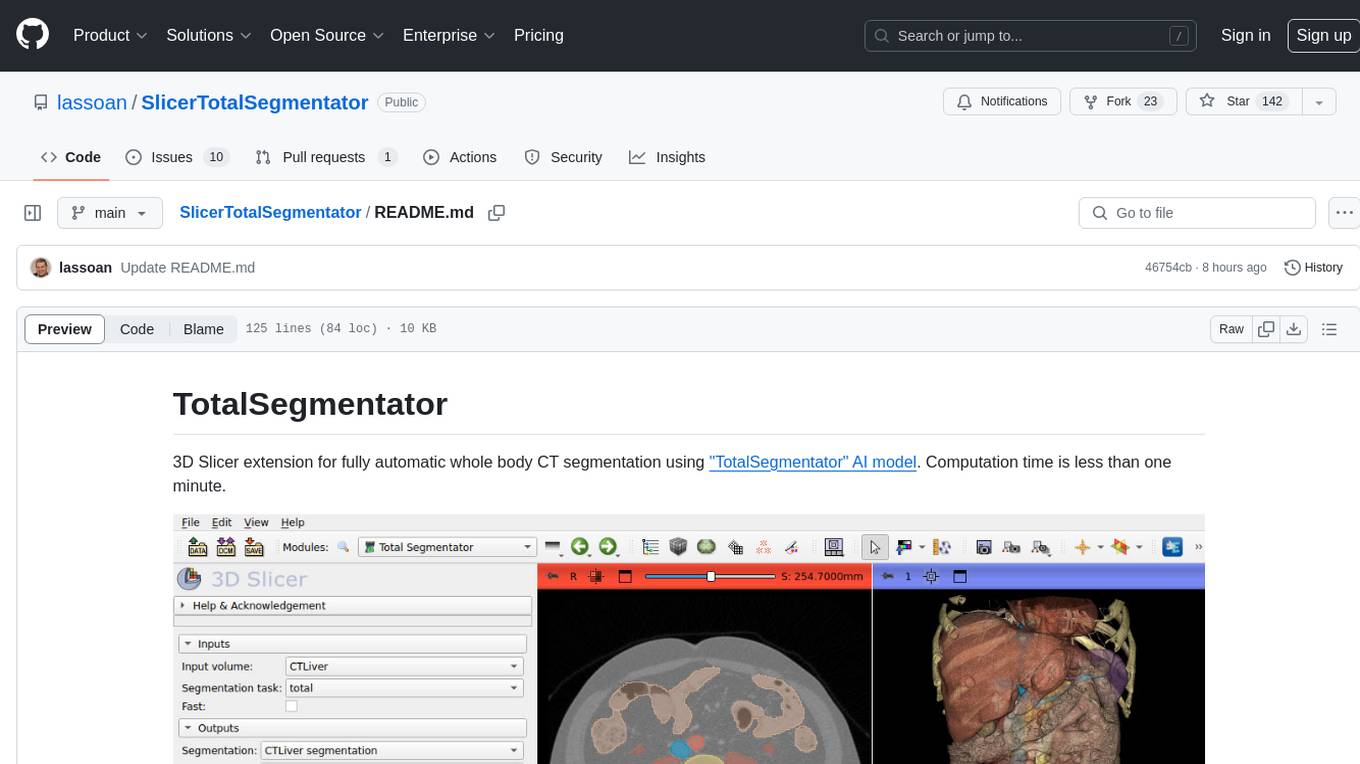
TotalSegmentator is a 3D Slicer extension designed for fully automatic whole body CT segmentation using the 'TotalSegmentator' AI model. The computation time is less than one minute, making it efficient for research purposes. Users can set up GPU acceleration for faster segmentation. The tool provides a user-friendly interface for loading CT images, creating segmentations, and displaying results in 3D. Troubleshooting steps are available for common issues such as failed computation, GPU errors, and inaccurate segmentations. Contributions to the extension are welcome, following 3D Slicer contribution guidelines.
README:
3D Slicer extension for fully automatic whole body CT segmentation using "TotalSegmentator" AI model. Computation time is less than one minute.
If you use the TotalSegmentator nn-Unet function from this software in your research, please cite:
Wasserthal J., Meyer M., , Hanns-Christian Breit H.C., Cyriac J., Shan Y., Segeroth, M.: TotalSegmentator: robust segmentation of 104 anatomical structures in CT images. https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.05868
- Setup your GPU driver (optional)
If you have a powerful GPU is available then a full-quality segmentation can be computed in a few minutes, instead of 40-50 minutes on the CPU. Therefore, it is recommended to set up GPU acceleration as described in this section.
- If a strong GPU with 7GB or more memory is available:
- On Windows:
- If using NVIDIA GPU: Make sure CUDA is installed. CUDA version must be one of those listed on pytorch website as "Compute platform" for your system. You can download CUDA from here.
- PyTorch does not officially support AMD GPUs for on Windows, therefore you need to use the CPU.
- On Linux:
- If using NVIDIA GPU: Make sure NVIDIA drivers are installed. If CUDA is installed then make sure CUDA version is one of those listed on pytorch website as "Compute platform" for your system. If CUDA is not installed then it will be set up automatically during installation (pytorch binary packages contain the appropriate CUDA version).
- If using AMD GPU: In theory, ROCm-compatible AMD GPUs should work, but this is not tested.
- On macOS: PyTorch does not officially support GPUs for macOS, therefore you need to use the CPU.
- On Windows:
- If suitable GPU is not available: Graphics driver updates or CUDA installation is not necessary, everything will still work, it will just take more time.
-
Install latest version of 3D Slicer
- Start 3D Slicer
- Go to
Sample Datamodule and loadCTA Abdomen (Panoramix)data set - Go to
TotalSegmentatormodule - Select
Input volume->Panoramix-cropped - Select
Segmentation->Create new segmentation - Click
Apply- When this module is used the first time:
- It needs to download and install PyTorch and TotalSegmentator Python packages and weights for the AI models. This can take 5-10 minutes and several GB disk space.
- You may get an error popup:
Failed to compute results ... Command ... 'pip', 'install' ... returned non-zero exit status 1. This may be normal, see what to do in Troubleshooting section
- Expected computation time:
- With CUDA-capable GPU: 20-30 seconds in fast mode, 40-50 seconds in full-resolution mode.
- Without GPU: 1 minute in fast mode, 40-50 minutes in full-resolution mode.
- When this module is used the first time:
- To display the segmentation in 3D: click the
Show 3Dbutton
- Inputs
- Input volume: input CT image
- Segmentation task: instead of the default "total" segmentation, a more specialized segmentation model can be chosen
- Fast: performs segmentation faster, but at lower resolution
- Outputs
- Segmentation: it will contain a brain segment, which specifies the brain region
- Show 3D: show/hide segments in 3D views
- Advanced:
- Use standard segment names: use names defined in standard terminology files from DCMQI (enabled by default). If disabled then TotalSegmentator identifiers will be used as segment names.
- Use latest development version: use latest development version from TotalSegmentator master branch during a forced reinstall.
- Force reinstall: force reinstallation of the AI engine - TotalSegmentator Python package. This may be needed if other modules compromise the installation.
- Import weights: When using TotalSegmentator, weights are often downloaded automatically. You can import any specialized or licensed weights you receive from the developer so that TotalSegmentator can find and use them.
- Get TotalSegmentator package information: retrieve installed version of the AI engine - TotalSegmentator Python package.
Problem: Error popup appears: Failed to compute results ... Command ... 'pip', 'install' ... returned non-zero exit status 1
Explanation: This happens because when the tool has to download and install PyTorch and other required Python packages.
Solution:
- The module instructs you to restart Slicer and try again if an error occurs. Please try this first.
- If this does not help then make sure you have enough memory space (physical RAM and virtual memory in total should be at least 32GB) and you have enough disk space (at least 20GB free disk space is required) and try again.
- If you still run into issues then report the problem on the 3D Slicer forum. In your forum post, include the full application log of the failed attempt (you can get the application log in menu: Help / Report a bug).
Problem: Error popup on the first run: Failed to compute results ... Command ... 'PythonSlicer', TotalSegmentator.exe ... returned non-zero exit status 120
Explanation: This typically happens when PyTorch is not installed correctly or your computer runs out of memory.
Solution:
- Check the message log (textbox under the Apply button). If you see a message like
RuntimeError: ... DefaultCPUAllocator: not enough memory: you tried to allocate ... bytes.then it means that your computer has not enough memory to process the input image. You can useCrop volumemodule to crop the your image to the relevant region and/or resample it (with using a scaling factor >1) until the memory usage drops low enough so that your computer can handle it. Alternatively, you can install more physical RAM or configure your operating system to use more virtual memory. - If the problem does not seem to be due to running out of memory then reinstall PyTorch as described in solution of
Segmentation fails while predictingissue.
Problem: Segmentation fails while predicting and the RuntimeError: CUDA out of memory. message is found in the message log (textbox under the Apply button).
Explanation: This means that a CUDA-capable GPU is available, but it is not powerful enough to be used by TotalSegmentator.
Solution: It is recommended to switch to use the CPU by the following steps:
- Go to
PyTorch Utilmodule, clickUninstall PyTorch. An error may be reported at the end of this step, as some PyTorch files are in use. ClickRestart the applicationbutton to unload all PyTorch files. - Go to
PyTorch Utilmodule, selectcpuasComputation backend, and clickInstall PyTorch.
If your GPU has more than 7GB memory and you still get this error then the error message might indicate that the PyTorch CUDA version does not match the CUDA version installed on the system. Reinstall PyTorch with the correct CUDA version by following the instructions given below for GPU is not found.
Problem: Segmentation fails while predicting and a message similar to this is found in the message log (textbox under the Apply button): numpy.core._exceptions._ArrayMemoryError: Unable to allocate 6.85 GiB for an array with shape (287, 233, 233, 118) and data type float32
Explanation: This means that your computer has ran out of memory (RAM) while performing the segmentation.
Solution: It is recommended to reduce the image size or increase avaialable memory size by one of the following options:
- A. Crop and/or resample the input image using
Crop volumemodule. Cropping the image to a smaller size will reduce memory need without decreasing the segmentation quality. Setting "Spacing scale" to value larger than 1 (for example 2 or 3) will preserve the extents of the image but small details may be lost (this should not be an issue when the object of interest is a large structure with a smooth surface). - B. Increase the available "virtual memory" (also known as "swap") size in your computer. On Windows and Linux, you can configure the virtual memory size in your system settings. On macOS, virtual memory is automatically allocated if there is sufficient free disk space. Increasing virtual memory size can avoid issues cause by short memory usage peaks, but can severely slow down the segmentation. To avoid slowdown, add more physical RAM to your computer.
- C. Upgrade your computer hardware. Add physical RAM to your computer, or if it is not upgradeable then get a new computer or rent a virtual machine from a cloud computing provider. If you have more physical RAM then you can process larger images without making the segmentation take significantly longer time.
Problem: Segmentation fails while predicting and the 'DummyFile' object has no attribute 'flush' message is found in the message log (textbox under the Apply button).
Explanation: This error message can be safely ignored (it is just a small bug in the implementation of the helper class that suppresses nnunet output). If segmentation failed then it is due to another error in the output.
Solution: Look for other messages in the output.
Problem: Your computer has a CUDA-capable GPU but TotalSegmentator reports that GPU is not available.
Explanation: CUDA may not be installed on the system or CUDA version in PyTorch does not match the system CUDA version.
Solution:
- Make sure that the the CUDA vesion installed on the system is one of those listed on pytorch website as "Compute platform" for your system. You can download CUDA from here.
- Go to
PyTorch Utilmodule, clickUninstall PyTorch. An error may be reported at the end of this step, as some PyTorch files are in use. ClickRestart the applicationbutton to unload all PyTorch files. - Go to
PyTorch Utilmodule, select theComputation backendthat matches the system CUDA version, and clickInstall PyTorch. The CUDA computational backend name has the formatcuNNN, where NNN corresponds to the CUDA major+minor version. For example, CUDA 11.7 backend name iscu117.
Problem: There is a big segment called face at the front of the head, which is not an accurate segmentation of the face.
Explanation: This segment is not designed to match the shape of an anatomical feature, but it designates the general area of the face. It can be used to remove features (for example by masking or blurring the image or clipping models) that might otherwise identify the individual subject. Removing these features makes it easier to share 3D data.
Model files are hosted on github.com or Zenodo.org and downloaded automatically when segmenting the first time. Institutional firewall or proxy servers may prevent access or the server may be temporarily overloaded, which may cause an error report similar to requests.exceptions.HTTPError: 404 Client Error: Not Found for url: https://zenodo.org/record/6802052/files/Task256_TotalSegmentator_3mm_1139subj.zip?download=1. Potential solutions:
- retry later when the server may be less overloaded
- talk to IT administrators or use a VPN to access the server
- download the file manually and unzip it in the
.totalsegmentatorfolder in the user's profile (for example inc:\Users\(yourusername)\.totalsegmentator\nnunet\results\Dataset291_TotalSegmentator_part1_organs_1559subj)
Contributions to this extensions are welcome. Please send a pull request with any suggested changes. 3D Slicer contribution guidelines apply.
Please post any questions to the Slicer Forum.
Developers of this extension are not associated with the developers of TotalSegmentator, just provide the convenient 3D Slicer based user interface.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for SlicerTotalSegmentator
Similar Open Source Tools

SlicerTotalSegmentator
TotalSegmentator is a 3D Slicer extension designed for fully automatic whole body CT segmentation using the 'TotalSegmentator' AI model. The computation time is less than one minute, making it efficient for research purposes. Users can set up GPU acceleration for faster segmentation. The tool provides a user-friendly interface for loading CT images, creating segmentations, and displaying results in 3D. Troubleshooting steps are available for common issues such as failed computation, GPU errors, and inaccurate segmentations. Contributions to the extension are welcome, following 3D Slicer contribution guidelines.
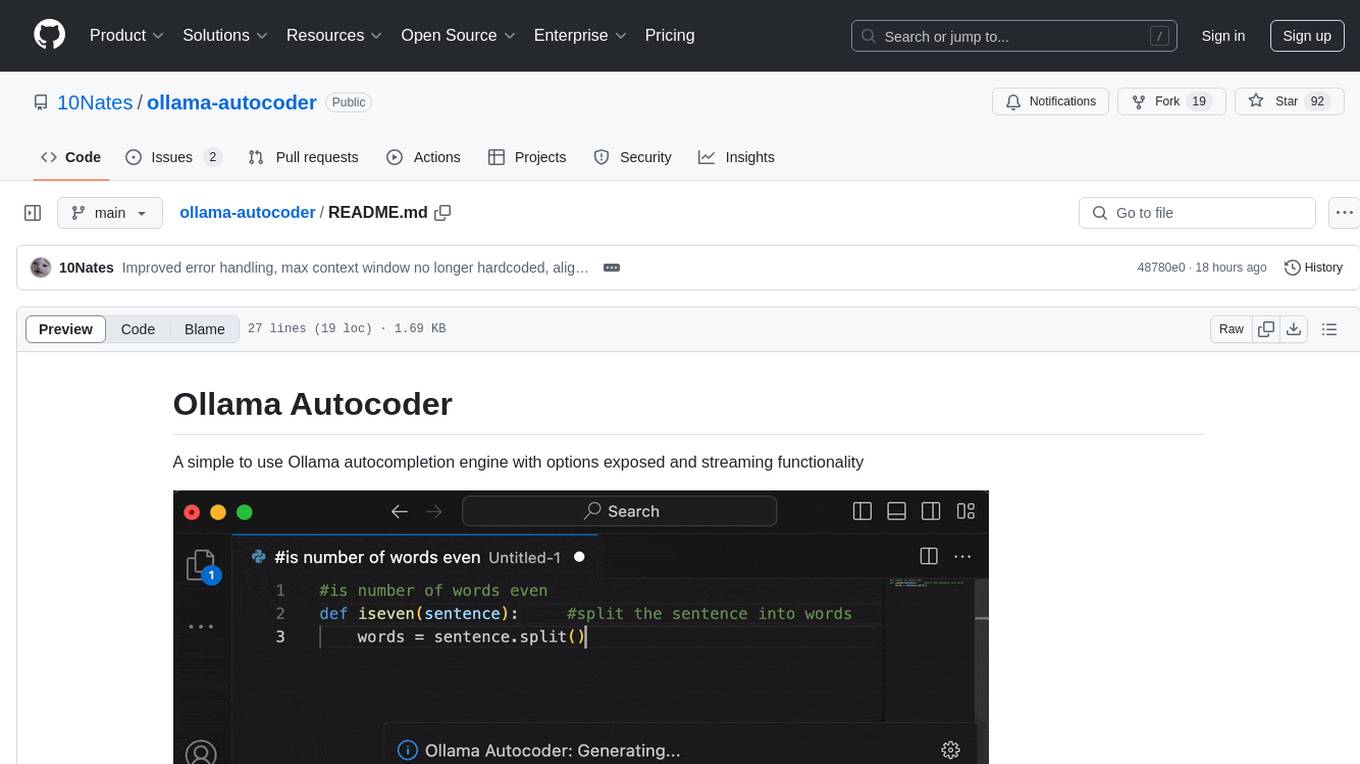
ollama-autocoder
Ollama Autocoder is a simple to use autocompletion engine that integrates with Ollama AI. It provides options for streaming functionality and requires specific settings for optimal performance. Users can easily generate text completions by pressing a key or using a command pallete. The tool is designed to work with Ollama API and a specified model, offering real-time generation of text suggestions.

airbroke
Airbroke is an open-source error catcher tool designed for modern web applications. It provides a PostgreSQL-based backend with an Airbrake-compatible HTTP collector endpoint and a React-based frontend for error management. The tool focuses on simplicity, maintaining a small database footprint even under heavy data ingestion. Users can ask AI about issues, replay HTTP exceptions, and save/manage bookmarks for important occurrences. Airbroke supports multiple OAuth providers for secure user authentication and offers occurrence charts for better insights into error occurrences. The tool can be deployed in various ways, including building from source, using Docker images, deploying on Vercel, Render.com, Kubernetes with Helm, or Docker Compose. It requires Node.js, PostgreSQL, and specific system resources for deployment.
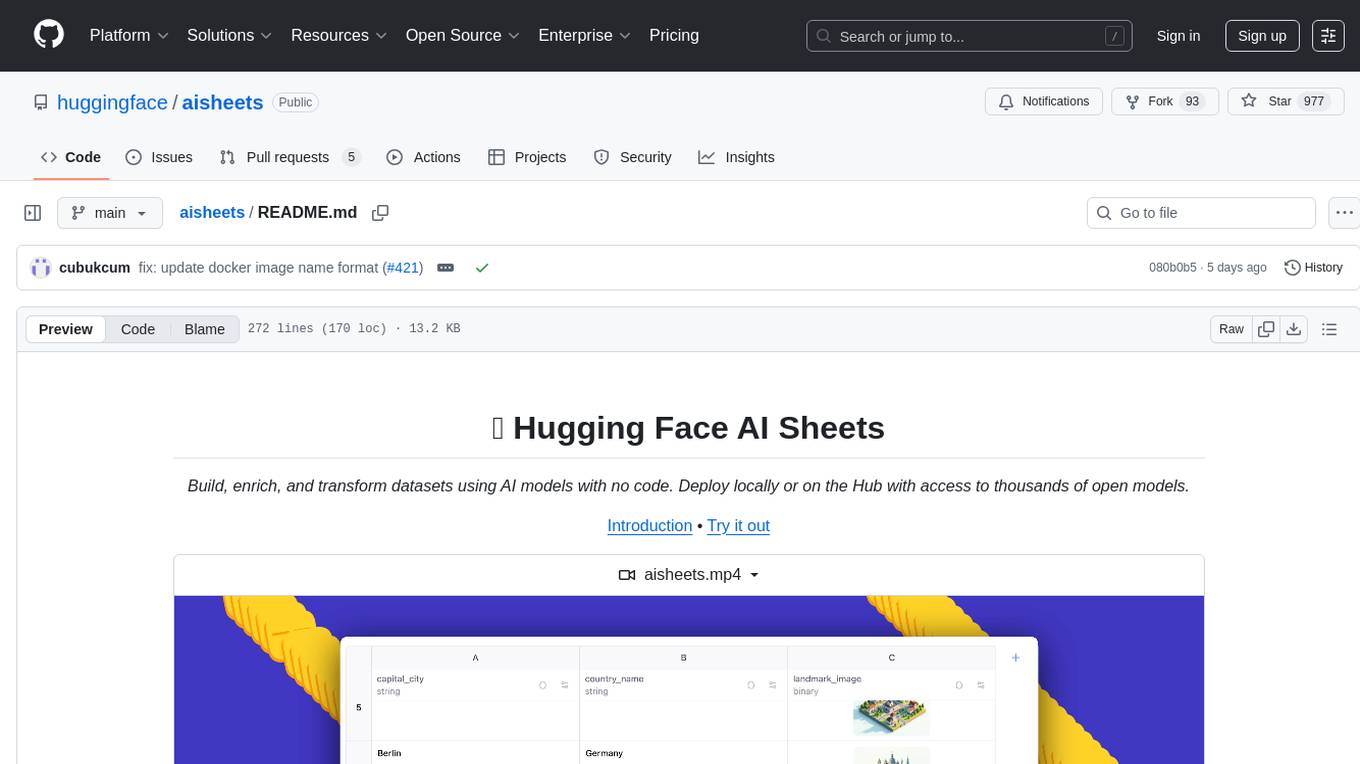
aisheets
Hugging Face AI Sheets is an open-source tool for building, enriching, and transforming datasets using AI models with no code. It can be deployed locally or on the Hub, providing access to thousands of open models. Users can easily generate datasets, run data generation scripts, and customize inference endpoints for text generation. The tool supports custom LLMs and offers advanced configuration options for authentication, inference, and miscellaneous settings. With AI Sheets, users can leverage the power of AI models without writing any code, making dataset management and transformation efficient and accessible.
gpt-subtrans
GPT-Subtrans is an open-source subtitle translator that utilizes large language models (LLMs) as translation services. It supports translation between any language pairs that the language model supports. Note that GPT-Subtrans requires an active internet connection, as subtitles are sent to the provider's servers for translation, and their privacy policy applies.
serena
Serena is a powerful coding agent that integrates with existing LLMs to provide essential semantic code retrieval and editing tools. It is free to use and does not require API keys or subscriptions. Serena can be used for coding tasks such as analyzing, planning, and editing code directly on your codebase. It supports various programming languages and offers semantic code analysis capabilities through language servers. Serena can be integrated with different LLMs using the model context protocol (MCP) or Agno framework. The tool provides a range of functionalities for code retrieval, editing, and execution, making it a versatile coding assistant for developers.
ultimate-rvc
Ultimate RVC is an extension of AiCoverGen, offering new features and improvements for generating audio content using RVC. It is designed for users looking to integrate singing functionality into AI assistants/chatbots/vtubers, create character voices for songs or books, and train voice models. The tool provides easy setup, voice conversion enhancements, TTS functionality, voice model training suite, caching system, UI improvements, and support for custom configurations. It is available for local and Google Colab use, with a PyPI package for easy access. The tool also offers CLI usage and customization through environment variables.
AirSane
AirSane is a SANE frontend and scanner server that supports Apple's AirScan protocol. It automatically detects scanners and publishes them through mDNS. Acquired images can be transferred in JPEG, PNG, and PDF/raster format. The tool is intended to be used with AirScan/eSCL clients such as Apple's Image Capture, sane-airscan on Linux, and the eSCL client built into Windows 10 and 11. It provides a simple web interface and encodes images on-the-fly to keep memory/storage demands low, making it suitable for devices like Raspberry Pi. Authentication and secure communication are supported in conjunction with a proxy server like nginx. AirSane has been reverse-engineered from Apple's AirScanScanner client communication protocol and offers a range of installation and configuration options for different operating systems.
llama-on-lambda
This project provides a proof of concept for deploying a scalable, serverless LLM Generative AI inference engine on AWS Lambda. It leverages the llama.cpp project to enable the usage of more accessible CPU and RAM configurations instead of limited and expensive GPU capabilities. By deploying a container with the llama.cpp converted models onto AWS Lambda, this project offers the advantages of scale, minimizing cost, and maximizing compute availability. The project includes AWS CDK code to create and deploy a Lambda function leveraging your model of choice, with a FastAPI frontend accessible from a Lambda URL. It is important to note that you will need ggml quantized versions of your model and model sizes under 6GB, as your inference RAM requirements cannot exceed 9GB or your Lambda function will fail.
llamafile
llamafile is a tool that enables users to distribute and run Large Language Models (LLMs) with a single file. It combines llama.cpp with Cosmopolitan Libc to create a framework that simplifies the complexity of LLMs into a single-file executable called a 'llamafile'. Users can run these executable files locally on most computers without the need for installation, making open LLMs more accessible to developers and end users. llamafile also provides example llamafiles for various LLM models, allowing users to try out different LLMs locally. The tool supports multiple CPU microarchitectures, CPU architectures, and operating systems, making it versatile and easy to use.
cluster-toolkit
Cluster Toolkit is an open-source software by Google Cloud for deploying AI/ML and HPC environments on Google Cloud. It allows easy deployment following best practices, with high customization and extensibility. The toolkit includes tutorials, examples, and documentation for various modules designed for AI/ML and HPC use cases.

brokk
Brokk is a code assistant designed to understand code semantically, allowing LLMs to work effectively on large codebases. It offers features like agentic search, summarizing related classes, parsing stack traces, adding source for usages, and autonomously fixing errors. Users can interact with Brokk through different panels and commands, enabling them to manipulate context, ask questions, search codebase, run shell commands, and more. Brokk helps with tasks like debugging regressions, exploring codebase, AI-powered refactoring, and working with dependencies. It is particularly useful for making complex, multi-file edits with o1pro.
llm-subtrans
LLM-Subtrans is an open source subtitle translator that utilizes LLMs as a translation service. It supports translating subtitles between any language pairs supported by the language model. The application offers multiple subtitle formats support through a pluggable system, including .srt, .ssa/.ass, and .vtt files. Users can choose to use the packaged release for easy usage or install from source for more control over the setup. The tool requires an active internet connection as subtitles are sent to translation service providers' servers for translation.
ChatGPT-Telegram-Bot
The ChatGPT Telegram Bot is a powerful Telegram bot that utilizes various GPT models, including GPT3.5, GPT4, GPT4 Turbo, GPT4 Vision, DALL·E 3, Groq Mixtral-8x7b/LLaMA2-70b, and Claude2.1/Claude3 opus/sonnet API. It enables users to engage in efficient conversations and information searches on Telegram. The bot supports multiple AI models, online search with DuckDuckGo and Google, user-friendly interface, efficient message processing, document interaction, Markdown rendering, and convenient deployment options like Zeabur, Replit, and Docker. Users can set environment variables for configuration and deployment. The bot also provides Q&A functionality, supports model switching, and can be deployed in group chats with whitelisting. The project is open source under GPLv3 license.
chronon
Chronon is a platform that simplifies and improves ML workflows by providing a central place to define features, ensuring point-in-time correctness for backfills, simplifying orchestration for batch and streaming pipelines, offering easy endpoints for feature fetching, and guaranteeing and measuring consistency. It offers benefits over other approaches by enabling the use of a broad set of data for training, handling large aggregations and other computationally intensive transformations, and abstracting away the infrastructure complexity of data plumbing.
lumigator
Lumigator is an open-source platform developed by Mozilla.ai to help users select the most suitable language model for their specific needs. It supports the evaluation of summarization tasks using sequence-to-sequence models such as BART and BERT, as well as causal models like GPT and Mistral. The platform aims to make model selection transparent, efficient, and empowering by providing a framework for comparing LLMs using task-specific metrics to evaluate how well a model fits a project's needs. Lumigator is in the early stages of development and plans to expand support to additional machine learning tasks and use cases in the future.
For similar tasks

SlicerTotalSegmentator
TotalSegmentator is a 3D Slicer extension designed for fully automatic whole body CT segmentation using the 'TotalSegmentator' AI model. The computation time is less than one minute, making it efficient for research purposes. Users can set up GPU acceleration for faster segmentation. The tool provides a user-friendly interface for loading CT images, creating segmentations, and displaying results in 3D. Troubleshooting steps are available for common issues such as failed computation, GPU errors, and inaccurate segmentations. Contributions to the extension are welcome, following 3D Slicer contribution guidelines.
For similar jobs
grand-challenge.org
Grand Challenge is a platform that provides access to large amounts of annotated training data, objective comparisons of state-of-the-art machine learning solutions, and clinical validation using real-world data. It assists researchers, data scientists, and clinicians in collaborating to develop robust machine learning solutions to problems in biomedical imaging.
Detection-and-Classification-of-Alzheimers-Disease
This tool is designed to detect and classify Alzheimer's Disease using Deep Learning and Machine Learning algorithms on an early basis, which is further optimized using the Crow Search Algorithm (CSA). Alzheimer's is a fatal disease, and early detection is crucial for patients to predetermine their condition and prevent its progression. By analyzing MRI scanned images using Artificial Intelligence technology, this tool can classify patients who may or may not develop AD in the future. The CSA algorithm, combined with ML algorithms, has proven to be the most effective approach for this purpose.
OpenCRISPR
OpenCRISPR is a set of free and open gene editing systems designed by Profluent Bio. The OpenCRISPR-1 protein maintains the prototypical architecture of a Type II Cas9 nuclease but is hundreds of mutations away from SpCas9 or any other known natural CRISPR-associated protein. You can view OpenCRISPR-1 as a drop-in replacement for many protocols that need a cas9-like protein with an NGG PAM and you can even use it with canonical SpCas9 gRNAs. OpenCRISPR-1 can be fused in a deactivated or nickase format for next generation gene editing techniques like base, prime, or epigenome editing.
AlphaFold3
AlphaFold3 is an implementation of the Alpha Fold 3 model in PyTorch for accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions. It includes modules for genetic diffusion and full model examples for forward pass computations. The tool allows users to generate random pair and single representations, operate on atomic coordinates, and perform structure predictions based on input tensors. The implementation also provides functionalities for training and evaluating the model.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.
hi-ml
The Microsoft Health Intelligence Machine Learning Toolbox is a repository that provides low-level and high-level building blocks for Machine Learning / AI researchers and practitioners. It simplifies and streamlines work on deep learning models for healthcare and life sciences by offering tested components such as data loaders, pre-processing tools, deep learning models, and cloud integration utilities. The repository includes two Python packages, 'hi-ml-azure' for helper functions in AzureML, 'hi-ml' for ML components, and 'hi-ml-cpath' for models and workflows related to histopathology images.

SlicerTotalSegmentator
TotalSegmentator is a 3D Slicer extension designed for fully automatic whole body CT segmentation using the 'TotalSegmentator' AI model. The computation time is less than one minute, making it efficient for research purposes. Users can set up GPU acceleration for faster segmentation. The tool provides a user-friendly interface for loading CT images, creating segmentations, and displaying results in 3D. Troubleshooting steps are available for common issues such as failed computation, GPU errors, and inaccurate segmentations. Contributions to the extension are welcome, following 3D Slicer contribution guidelines.
md-agent
MD-Agent is a LLM-agent based toolset for Molecular Dynamics. It uses Langchain and a collection of tools to set up and execute molecular dynamics simulations, particularly in OpenMM. The tool assists in environment setup, installation, and usage by providing detailed steps. It also requires API keys for certain functionalities, such as OpenAI and paper-qa for literature searches. Contributions to the project are welcome, with a detailed Contributor's Guide available for interested individuals.
