
REINVENT4
AI molecular design tool for de novo design, scaffold hopping, R-group replacement, linker design and molecule optimization.
Stars: 447
REINVENT is a molecular design tool for de novo design, scaffold hopping, R-group replacement, linker design, molecule optimization, and other small molecule design tasks. It uses a Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithm to generate optimized molecules compliant with a user-defined property profile defined as a multi-component score. Transfer Learning (TL) can be used to create or pre-train a model that generates molecules closer to a set of input molecules.
README:
REINVENT is a molecular design tool for de novo design, scaffold hopping, R-group replacement, linker design, molecule optimization, and other small molecule design tasks. REINVENT uses a Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithm to generate optimized molecules compliant with a user defined property profile defined as a multi-component score. Transfer Learning (TL) can be used to create or pre-train a model that generates molecules closer to a set of input molecules.
A paper describing the software has been published as Open Access in the Journal of Cheminformatics: Reinvent 4: Modern AI–driven generative molecule design. See AUTHORS.md for references to previous papers.
REINVENT is being developed on Linux and supports both GPU and CPU. The Linux version is fully validated. REINVENT on Windows and MacOSX supports both GPU and CPU but is only partially tested on these platforms and therefore support is limited.
The code is written in Python 3 (>= 3.10). The list of dependencies can be found in the repository (see also Installation below).
A GPU is not strictly necessary but strongly recommended for performance reasons especially for transfer learning and model training. Reinforcement learning (RL) requires the computation of scores where most scoring components run on the CPU. Thus, a GPU is less important for RL (depending on how much time is spent on the CPU).
Note that if no GPU is installed in your computer the code will run on the CPU automatically. REINVENT supports NVIDIA GPUs and also some AMD GPUs. For most design tasks a memory of about 8 GiB for both CPU main memory and GPU memory is sufficient.
- Clone this Git repository.
- Install a compatible version of Python, for example with Conda (other virtual environments like Docker, pyenv, or the system package manager work too).
conda create --name reinvent4 python=3.10 conda activate reinvent4
- Change directory to the repository and install the dependencies from the lockfile:
pip install -r requirements-linux-64.lock
-
Optional: if you want to use AMD GPUs on Linux you would need to install the ROCm PyTorch version manually after installation of the dependencies in point 3, e.g.
pip install torch==2.2.1 torchvision==0.17.1 torchaudio==2.2.1 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/rocm5.7
-
Optional: use requirements file
requirements-macOS.lockfor MacOSX.
-
Optional: if you want to use AMD GPUs on Linux you would need to install the ROCm PyTorch version manually after installation of the dependencies in point 3, e.g.
- Install the tool. The dependencies were already installed in the previous step, so there is no need to install them again (flag `--no-deps). If you want to install in editable mode (changes to the code are automatically available), add -e before the dot.
pip install --no-deps . - Test the tool. The installer has added a script
reinventto your PATH.reinvent --help
REINVENT is a command line tool and works principally as follows
reinvent -l sampling.log sampling.tomlThis writes logging information to the file sampling.log. If you wish to write
this to the screen, leave out the -l sampling.log part. sampling.toml is the
configuration file. The main user format is TOML as it tends to be more
use friendly. JSON can be used too, add -f json, but a specialised editor is
recommended as the format is very sensitive to minor changes.
Sample configuration files for all run modes are
located in configs/toml in the repository and file paths in these files would need to be
adjusted to your local installation. In particular, ready made prior models are
located in priors and you would choose a model and the
appropriate run mode depending on the research problem you are trying to address.
There is additional information in configs/toml in several *.md files with
instructions on how to configure the TOML file. Internal priors can be referenced with a
dot notation (see reinvent/prior_registry.py).
Basic instructions can be found in the comments in the config examples in configs/toml.
Notebooks are provided in the notebooks/ directory. Please note that we
provide the notebooks in jupytext "light script" format. To work with the light
scripts you will need to install jupytext. A few other packages will come in handy too.
pip install jupytext mols2grid seabornThe Python files in notebooks/ can then be converted to a notebook e.g.
jupytext -o Reinvent_demo.ipynb Reinvent_demo.pyUpdate the lock files with pip-tools (please, do not edit the files manually):
pip-compile --extra-index-url=https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121 --extra-index-url=https://pypi.anaconda.org/OpenEye/simple --resolver=backtracking pyproject.tomlTo update a single package, use pip-compile --upgrade-package somepackage
(see the documentation for pip-tools).
The scoring subsystem uses a simple plugin mechanism (Python native namespace packages). If you wish to write your own plugin, follow the instructions below. There is no need to touch any of the REINVENT code. The public repository contains a contrib directory with some useful examples.
- Create
/top/dir/somewhere/reinvent\_plugins/componentswhere/top/dir/somewhereis a convenient location for you. - Do not place a
__init__.pyin eitherreinvent_pluginsorcomponentsas this would break the mechanism. It is fine to create normal packages withincomponentsas long as you import those correctly. - Place a file whose name starts with
comp_*intoreinvent_plugins/components. Files with different names will be ignored i.e. not imported. The directory will be searched recursively so structure your code as needed but directory/package names must be unique. - Tag the scoring component class(es) in that file with the @add_tag decorator. More than one component class can be added to the same comp_ file. See existing code.
- Tag at most one dataclass for parameters in the same file, see existing code. This is optional.
- Set or add
/top/dir/somewhereto thePYTHONPATHenvironment variable or use any other mechanism to extendsys.path. - The scoring component should now automatically be picked up by REINVENT.
This is primarily for developers and admins/users who wish to ensure that the
installation works. The information here is not relevant to the practical use
of REINVENT. Please refer to Basic Usage for instructions on how to use the
reinvent command.
The REINVENT project uses the pytest framework for its tests. Before you run
them you first have to create a configuration file for the tests.
In the project directory, create a config.json file in the configs/ directory.
You can use the example config example.config.json as a base. Make sure that
you set MAIN_TEST_PATH to a non-existent directory. That is where temporary
files will be written during the tests. If it is set to an existing directory,
that directory will be removed once the tests have finished.
Some tests require a proprietary OpenEye license. You have to set up a few
things to make the tests read your license. The simple way is to just set the
OE_LICENSE environment variable to the path of the file containing the
license.
Once you have a configuration and your license can be read, you can run the tests.
$ pytest tests --json /path/to/config.json --device cuda
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for REINVENT4
Similar Open Source Tools

REINVENT4
REINVENT is a molecular design tool for de novo design, scaffold hopping, R-group replacement, linker design, molecule optimization, and other small molecule design tasks. It uses a Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithm to generate optimized molecules compliant with a user-defined property profile defined as a multi-component score. Transfer Learning (TL) can be used to create or pre-train a model that generates molecules closer to a set of input molecules.
gpt-subtrans
GPT-Subtrans is an open-source subtitle translator that utilizes large language models (LLMs) as translation services. It supports translation between any language pairs that the language model supports. Note that GPT-Subtrans requires an active internet connection, as subtitles are sent to the provider's servers for translation, and their privacy policy applies.
llm-subtrans
LLM-Subtrans is an open source subtitle translator that utilizes LLMs as a translation service. It supports translating subtitles between any language pairs supported by the language model. The application offers multiple subtitle formats support through a pluggable system, including .srt, .ssa/.ass, and .vtt files. Users can choose to use the packaged release for easy usage or install from source for more control over the setup. The tool requires an active internet connection as subtitles are sent to translation service providers' servers for translation.

Mapperatorinator
Mapperatorinator is a multi-model framework that uses spectrogram inputs to generate fully featured osu! beatmaps for all gamemodes and assist modding beatmaps. The project aims to automatically generate rankable quality osu! beatmaps from any song with a high degree of customizability. The tool is built upon osuT5 and osu-diffusion, utilizing GPU compute and instances on vast.ai for development. Users can responsibly use AI in their beatmaps with this tool, ensuring disclosure of AI usage. Installation instructions include cloning the repository, creating a virtual environment, and installing dependencies. The tool offers a Web GUI for user-friendly experience and a Command-Line Inference option for advanced configurations. Additionally, an Interactive CLI script is available for terminal-based workflow with guided setup. The tool provides generation tips and features MaiMod, an AI-driven modding tool for osu! beatmaps. Mapperatorinator tokenizes beatmaps, utilizes a model architecture based on HF Transformers Whisper model, and offers multitask training format for conditional generation. The tool ensures seamless long generation, refines coordinates with diffusion, and performs post-processing for improved beatmap quality. Super timing generator enhances timing accuracy, and LoRA fine-tuning allows adaptation to specific styles or gamemodes. The project acknowledges credits and related works in the osu! community.
aisheets
Hugging Face AI Sheets is an open-source tool for building, enriching, and transforming datasets using AI models with no code. It can be deployed locally or on the Hub, providing access to thousands of open models. Users can easily generate datasets, run data generation scripts, and customize inference endpoints for text generation. The tool supports custom LLMs and offers advanced configuration options for authentication, inference, and miscellaneous settings. With AI Sheets, users can leverage the power of AI models without writing any code, making dataset management and transformation efficient and accessible.
ultimate-rvc
Ultimate RVC is an extension of AiCoverGen, offering new features and improvements for generating audio content using RVC. It is designed for users looking to integrate singing functionality into AI assistants/chatbots/vtubers, create character voices for songs or books, and train voice models. The tool provides easy setup, voice conversion enhancements, TTS functionality, voice model training suite, caching system, UI improvements, and support for custom configurations. It is available for local and Google Colab use, with a PyPI package for easy access. The tool also offers CLI usage and customization through environment variables.
dockershrink
Dockershrink is an AI-powered Commandline Tool designed to help reduce the size of Docker images. It combines traditional Rule-based analysis with Generative AI techniques to optimize Image configurations. The tool supports NodeJS applications and aims to save costs on storage, data transfer, and build times while increasing developer productivity. By automatically applying advanced optimization techniques, Dockershrink simplifies the process for engineers and organizations, resulting in significant savings and efficiency improvements.
nx_open
The `nx_open` repository contains open-source components for the Network Optix Meta Platform, used to build products like Nx Witness Video Management System. It includes source code, specifications, and a Desktop Client. The repository is licensed under Mozilla Public License 2.0. Users can build the Desktop Client and customize it using a zip file. The build environment supports Windows, Linux, and macOS platforms with specific prerequisites. The repository provides scripts for building, signing executable files, and running the Desktop Client. Compatibility with VMS Server versions is crucial, and automatic VMS updates are disabled for the open-source Desktop Client.
tutor-gpt
Tutor-GPT is an LLM powered learning companion developed by Plastic Labs. It dynamically reasons about your learning needs and updates its own prompts to best serve you. It is an expansive learning companion that uses theory of mind experiments to provide personalized learning experiences. The project is split into different modules for backend logic, including core logic, discord bot implementation, FastAPI API interface, NextJS web front end, common utilities, and SQL scripts for setting up local supabase. Tutor-GPT is powered by Honcho to build robust user representations and create personalized experiences for each user. Users can run their own instance of the bot by following the provided instructions.
Open-LLM-VTuber
Open-LLM-VTuber is a project in early stages of development that allows users to interact with Large Language Models (LLM) using voice commands and receive responses through a Live2D talking face. The project aims to provide a minimum viable prototype for offline use on macOS, Linux, and Windows, with features like long-term memory using MemGPT, customizable LLM backends, speech recognition, and text-to-speech providers. Users can configure the project to chat with LLMs, choose different backend services, and utilize Live2D models for visual representation. The project supports perpetual chat, offline operation, and GPU acceleration on macOS, addressing limitations of existing solutions on macOS.
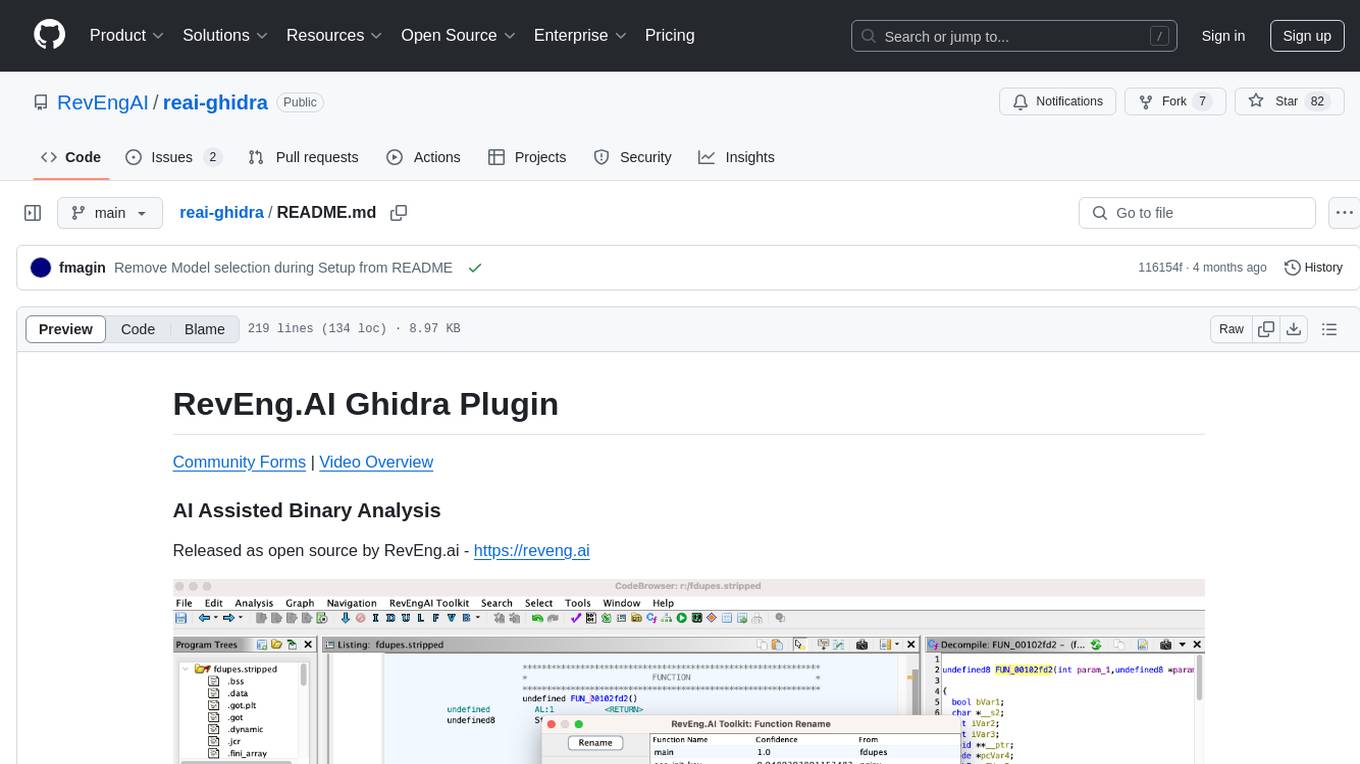
reai-ghidra
The RevEng.AI Ghidra Plugin by RevEng.ai allows users to interact with their API within Ghidra for Binary Code Similarity analysis to aid in Reverse Engineering stripped binaries. Users can upload binaries, rename functions above a confidence threshold, and view similar functions for a selected function.
jaison-core
J.A.I.son is a Python project designed for generating responses using various components and applications. It requires specific plugins like STT, T2T, TTSG, and TTSC to function properly. Users can customize responses, voice, and configurations. The project provides a Discord bot, Twitch events and chat integration, and VTube Studio Animation Hotkeyer. It also offers features for managing conversation history, training AI models, and monitoring conversations.
StableSwarmUI
StableSwarmUI is a modular Stable Diffusion web user interface that emphasizes making power tools easily accessible, high performance, and extensible. It is designed to be a one-stop-shop for all things Stable Diffusion, providing a wide range of features and capabilities to enhance the user experience.
ezkl
EZKL is a library and command-line tool for doing inference for deep learning models and other computational graphs in a zk-snark (ZKML). It enables the following workflow: 1. Define a computational graph, for instance a neural network (but really any arbitrary set of operations), as you would normally in pytorch or tensorflow. 2. Export the final graph of operations as an .onnx file and some sample inputs to a .json file. 3. Point ezkl to the .onnx and .json files to generate a ZK-SNARK circuit with which you can prove statements such as: > "I ran this publicly available neural network on some private data and it produced this output" > "I ran my private neural network on some public data and it produced this output" > "I correctly ran this publicly available neural network on some public data and it produced this output" In the backend we use the collaboratively-developed Halo2 as a proof system. The generated proofs can then be verified with much less computational resources, including on-chain (with the Ethereum Virtual Machine), in a browser, or on a device.
openui
OpenUI is a tool designed to simplify the process of building UI components by allowing users to describe UI using their imagination and see it rendered live. It supports converting HTML to React, Svelte, Web Components, etc. The tool is open source and aims to make UI development fun, fast, and flexible. It integrates with various AI services like OpenAI, Groq, Gemini, Anthropic, Cohere, and Mistral, providing users with the flexibility to use different models. OpenUI also supports LiteLLM for connecting to various LLM services and allows users to create custom proxy configs. The tool can be run locally using Docker or Python, and it offers a development environment for quick setup and testing.
aiarena-web
aiarena-web is a website designed for running the aiarena.net infrastructure. It consists of different modules such as core functionality, web API endpoints, frontend templates, and a module for linking users to their Patreon accounts. The website serves as a platform for obtaining new matches, reporting results, featuring match replays, and connecting with Patreon supporters. The project is licensed under GPLv3 in 2019.
For similar tasks

REINVENT4
REINVENT is a molecular design tool for de novo design, scaffold hopping, R-group replacement, linker design, molecule optimization, and other small molecule design tasks. It uses a Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithm to generate optimized molecules compliant with a user-defined property profile defined as a multi-component score. Transfer Learning (TL) can be used to create or pre-train a model that generates molecules closer to a set of input molecules.
Generative_AI_For_Science
Generative AI for Science is a comprehensive, hands-on guide for researchers, students, and practitioners who want to apply cutting-edge AI techniques to scientific discovery. The book bridges the gap between AI/ML expertise and domain science, providing practical implementations across chemistry, biology, physics, geoscience, and beyond. It covers key AI architectures like Transformers, Diffusion Models, VAEs, and GNNs, and teaches how to apply generative models to problems in climate science, drug discovery, genomics, materials science, and more. The book also emphasizes best practices around ethics, reproducibility, and deployment, helping readers develop the intuition to know when and how to apply AI to scientific research.
ai4chem_course
The AI4Chemistry course is a hands-on course focusing on Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Chemistry. It covers topics such as Python programming, machine learning, cheminformatics toolkits, data science, deep learning for chemistry, and advanced AI topics. The course includes exercises using Google Colab and covers supervised and unsupervised machine learning, property prediction models, Bayesian optimization, and more. The course is created by the LIAC team and references open-source community examples. It aims to be accessible to learners with varying levels of experience in Python and ML.
For similar jobs

REINVENT4
REINVENT is a molecular design tool for de novo design, scaffold hopping, R-group replacement, linker design, molecule optimization, and other small molecule design tasks. It uses a Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithm to generate optimized molecules compliant with a user-defined property profile defined as a multi-component score. Transfer Learning (TL) can be used to create or pre-train a model that generates molecules closer to a set of input molecules.