
brokk
Brokk brings code intelligence to AI
Stars: 64

Brokk is a code assistant designed to understand code semantically, allowing LLMs to work effectively on large codebases. It offers features like agentic search, summarizing related classes, parsing stack traces, adding source for usages, and autonomously fixing errors. Users can interact with Brokk through different panels and commands, enabling them to manipulate context, ask questions, search codebase, run shell commands, and more. Brokk helps with tasks like debugging regressions, exploring codebase, AI-powered refactoring, and working with dependencies. It is particularly useful for making complex, multi-file edits with o1pro.
README:
Brokk (the Norse god of the forge) is the first code assistant that understands code semantically, not just as chunks of text. Brokk is designed to allow LLMs to work effectively on large codebases that cannot be jammed entirely into working context.
Run using jbang (recommended):
- Install jbang
- Linux / Mac:
curl -Ls https://sh.jbang.dev | bash -s - app setup - Windows (Powershell):
iex "& { $(iwr https://ps.jbang.dev) } app setup" - Others: seehttps://www.jbang.dev/download/
- Linux / Mac:
- Run:
jbang run brokk@jbellis/brokk
You can also download the JAR from Releases and run it manually.
- Go to
File -> Edit Secret Keysto configure your preferred LLM. - Go to
File -> Open Projectto open your project.
Brokk will attempt to infer a build command and style guide for your project. You can edit these
in .brokk/project.properties and .brokk/style.md, respectively.
There is a Brokk Discord for questions and suggestions.
- Ridiculously good agentic search / code retrieval. Better than Claude Code, better than Sourcegraph, better than Augment Code. Here are Brokk's explanation of "how does bm25 search work?" in the DataStax Cassandra repo (a brand-new feature, not in anyone's training set), starting cold with no context, compared to Claude Code's (probably the second-best code RAG out there).
- Automatically determine the most-related classes to your working context and summarize them
- Parse a stacktrace and add source for all the methods to your context
- Add source for all the usages of a class, field, or method to your context
- Parse "anonymous" context pieces from external commands
- Build/lint your project and ask the LLM to fix errors autonomously
These allow some simple but powerful patterns:
- "Here is the diff for commit X, which introduced a regression. Here is the stacktrace of the error and the full source of the methods involved. Find the bug."
- "Here are the usages of Foo.bar. Is parameter zep always loaded from cache?"
When you start Brokk, you’ll see five main areas:
- Output: Displays the LLM or shell command output.
- History: A chronological list of your actions. Can undo changes to context as well as to your code.
- Command Input: Code, Ask, Search, and Run in Shell specify how your input is interpreted. Stop cancels the in-progress action.
- Context: Lists active code/text fragments in your current context, specifying whether they’re read-only or editable. Manipulated through right-click menu or top-level menu.
- Git: Log tab allows viewing diffs or adding them to context; Commit tab allows committing or stashing your changes
As you add context, Brokk will automatically include summaries of the most closely-related classes as determined by a graph analysis of your codebase. This helps the LLM avoid hallucinations when reasoning about your code. This is the "[Auto]" row that you see in the screenshot.
- Code: Tells the LLM you want code generation or modification.
- Ask: Ask a question referencing the current context.
- Search: Invokes a specialized agent that looks through your codebase for answers NOT in your current context.
- Run in Shell: Executes any shell command, streaming the output into the Output Panel.
- Stop: Cancels the currently running LLM or shell command.
- Edit, Read: Decide which files the LLM can modify (editable) or just look at (read-only).
- Summarize: Summarizes the specified classes (declarations and signatures, but no method bodies).
- Drop: Removes snippets you no longer want in context.
- Copy, Paste: Copy snippets to your clipboard or paste external text into Brokk’s context.
- Stacktraces get special treatment; they will be augmented with the source of referenced methods.
- URLs also get special treatment; their text will be retrieved and ingested
- Symbol Usage: Pick a symbol (class, field, or method) and automatically gather all references into a snippet.
- Call Graph To / Call Graph From: expands the call graph to or from the given function to the specified depth.
You can doubleclick on any context to preview it.
- Add relevant code or text to your context (choose Edit for modifiable files, Read for reference-only).
- Type instructions in the command box; use Code, Ask, Search, or Run in Shell as needed.
- Capture or incorporate external context using Run combined witn “Capture Text” or “Edit Files.”
- Use the History Panel to keep track, undo, or redo changes. Forget to commit and the LLM scribbled all over your code in the next request? No problem, Undo includes filesystem changes too.
Here are a few scenarios illustrating how Brokk helps with real-world tasks.
- Run
git bisectto identify the commit that caused a regression. - Load the commit and the files changed by that commit as editable context: run
git show [revision], thenCapture TextandEdit References. (You can also select the new context fragment in the context table and clickEdit Filesfrom there;Edit Referencesis a shortcut.) - Paste the stacktrace corresponding to the regression with ctrl-V or the Paste button.
- Tell the LLM: "This stacktrace is caused by a change in the attached diff. Look at the changes to see what could cause the problem, and fix it."
- You want to know how that BM25 search feature your colleague wrote works. Type "how does bm25 search work?" into the Instructions area and click Search.
- The Search output is automatically captured as context; if you want to make changes, select it and click
Edit Files.
- Invoke Symbol Usage on Project::getAnalyzerWrapper, and click Edit Files on the resulting usage context. This will make all files editable that include calls to that method.
- Add Project itself as editable. Brokk automatically includes a summary of AnalyzerWrapper in the auto-context.
- Type your instructions into the instructions area and click Code:
Replace Project.getAnalyzerWrapper with getAnalyzer() and getAnalyzerNonBlocking() that encapsulate aw.get and aw.getNonBlocking; update the callers appropriately.
Often you find yourself working with poorly documented dependencies that your LLM doesn't know enough about to use without hallucinating. Brokk can help!
Check out the source code and open it as a Brokk project. Then click on Summarize Fields
and use ** globbing to select everything. (Usually you will want to target e.g. src/main and not src/ to leave out test code.)
Brokk will summarize all the classes; now you can doubleclick on the context to make sure it's
what you wanted, then copy it and either paste it directly as context into Brokk as a one-off,
or save it as a file for re-use. In this example, I did this twice in the Gumtree library:
once for core/ and again for client/.
If you have a more targeted idea of what you need, you can also pick just those classes and
dial up the AutoContext size to get the surrounding infrastructure. Here I've left the Gumtree
client summary and let AutoContext=20 do its thing. This is 5x smaller than summarizing
all of core:
Brokk is particularly useful when making complex, multi-file edits with o1pro.
After setting up your session, use copy to pull all the content, including Brokk's prompts, into your clipboard.
Paste into o1pro and add your request at the bottom in the section. Then paste o1pro's response back into
Brokk and have it apply the edits with the Code action.
We are currently focused on making Brokk's Java support the best in the world. Other languages will follow.
- "Stop" button does not work reliably during search. This is caused by https://github.com/langchain4j/langchain4j/issues/2658
- Joern (the code intelligence engine) needs to run delombok before it can analyze anything. Delombok is extremely slow for anything but trivial projects, making Brokk a poor fit for large Lombok-using codebases.
- Brokk doesn't offer automatic running of tests (too much variance in what you might want it to do).
Instead, Brokk allows you to run arbitrary shell commands, and import those as context with "Capture Text"
or "Edit Files." You can easily run your tests this way and have Brokk work on the results. If you really
want Brokk to always run a test suite after making edits, you can change
buildCommandin.brokk/project.propertiesaccordingly. - There is some overlap between
Symbol UsageandCall Graph to Function; besides the former being just a single level deep in the call graph, Symbol Uage includes the entire source of each calling method while Call Graph to Function only includes one line per call.
Brokk uses sbt (Scala Build Tool) since it has a Scala component. To build Brokk,
- Install sbt (e.g. with sdkman)
- Run the sbt repl:
sbt - In the sbt repl, run individual commands:
run,clean,test,assembly, etc.
(You can run a single command without the repl with e.g. sbt run but sbt has a very high
startup overhead so using the repl is recommended.)
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for brokk
Similar Open Source Tools

brokk
Brokk is a code assistant designed to understand code semantically, allowing LLMs to work effectively on large codebases. It offers features like agentic search, summarizing related classes, parsing stack traces, adding source for usages, and autonomously fixing errors. Users can interact with Brokk through different panels and commands, enabling them to manipulate context, ask questions, search codebase, run shell commands, and more. Brokk helps with tasks like debugging regressions, exploring codebase, AI-powered refactoring, and working with dependencies. It is particularly useful for making complex, multi-file edits with o1pro.
lovelaice
Lovelaice is an AI-powered assistant for your terminal and editor. It can run bash commands, search the Internet, answer general and technical questions, complete text files, chat casually, execute code in various languages, and more. Lovelaice is configurable with API keys and LLM models, and can be used for a wide range of tasks requiring bash commands or coding assistance. It is designed to be versatile, interactive, and helpful for daily tasks and projects.
wtffmpeg
wtffmpeg is a command-line tool that uses a Large Language Model (LLM) to translate plain-English descriptions of video or audio tasks into actual, executable ffmpeg commands. It aims to streamline the process of generating ffmpeg commands by allowing users to describe what they want to do in natural language, review the generated command, optionally edit it, and then decide whether to run it. The tool provides an interactive REPL interface where users can input their commands, retain conversational context, and history, and control the level of interactivity. wtffmpeg is designed to assist users in efficiently working with ffmpeg commands, reducing the need to search for solutions, read lengthy explanations, and manually adjust commands.
claude.vim
Claude.vim is a Vim plugin that integrates Claude, an AI pair programmer, into your Vim workflow. It allows you to chat with Claude about what to build or how to debug problems, and Claude offers opinions, proposes modifications, or even writes code. The plugin provides a chat/instruction-centric interface optimized for human collaboration, with killer features like access to chat history and vimdiff interface. It can refactor code, modify or extend selected pieces of code, execute complex tasks by reading documentation, cloning git repositories, and more. Note that it is early alpha software and expected to rapidly evolve.
gpt-subtrans
GPT-Subtrans is an open-source subtitle translator that utilizes large language models (LLMs) as translation services. It supports translation between any language pairs that the language model supports. Note that GPT-Subtrans requires an active internet connection, as subtitles are sent to the provider's servers for translation, and their privacy policy applies.
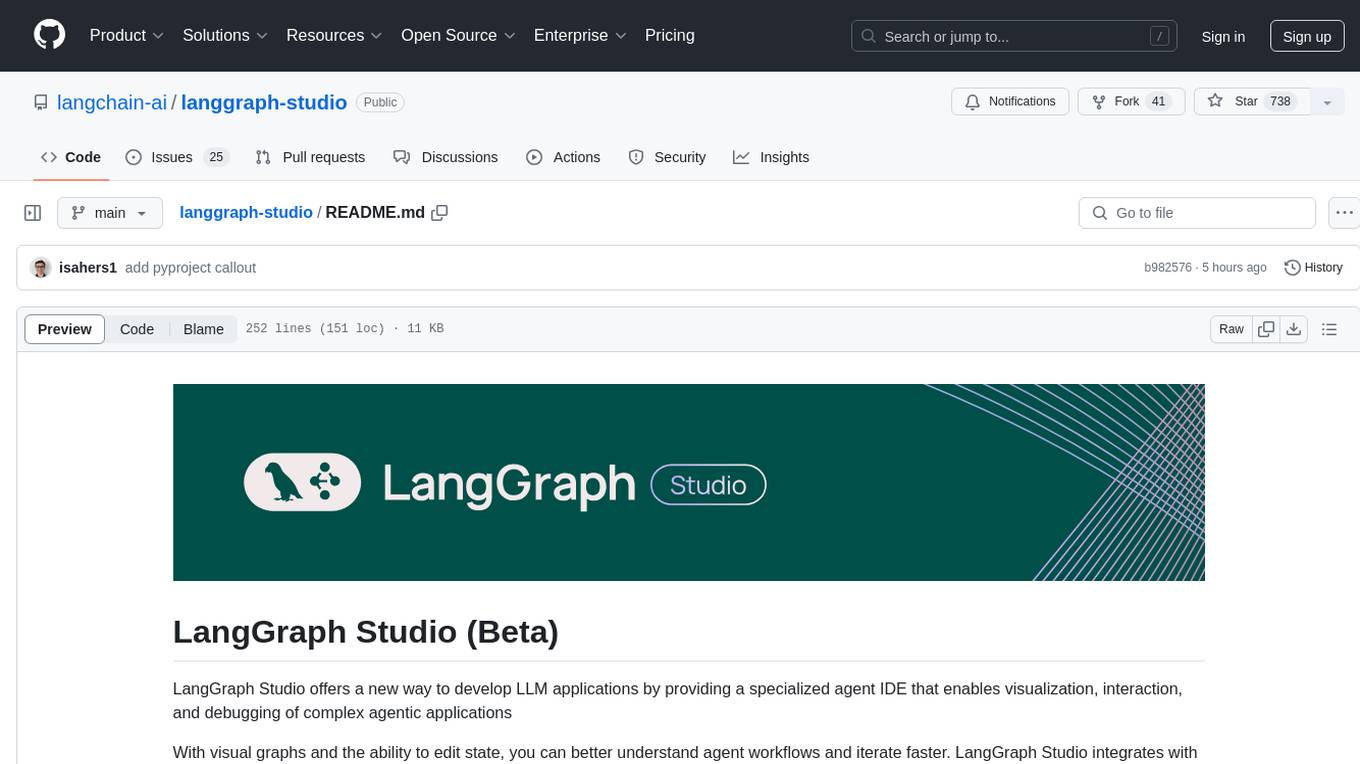
langgraph-studio
LangGraph Studio is a specialized agent IDE that enables visualization, interaction, and debugging of complex agentic applications. It offers visual graphs and state editing to better understand agent workflows and iterate faster. Users can collaborate with teammates using LangSmith to debug failure modes. The tool integrates with LangSmith and requires Docker installed. Users can create and edit threads, configure graph runs, add interrupts, and support human-in-the-loop workflows. LangGraph Studio allows interactive modification of project config and graph code, with live sync to the interactive graph for easier iteration on long-running agents.
roam-extension-live-ai-assistant
Live AI is an AI Assistant tailor-made for Roam, providing access to the latest LLMs directly in Roam blocks. Users can interact with AI to extend their thinking, explore their graph, and chat with structured responses. The tool leverages Roam's features to write prompts, query graph parts, and chat with content. Users can dictate, translate, transform, and enrich content easily. Live AI supports various tasks like audio and video analysis, PDF reading, image generation, and web search. The tool offers features like Chat panel, Live AI context menu, and Ask Your Graph agent for versatile usage. Users can control privacy levels, compare AI models, create custom prompts, and apply styles for response formatting. Security concerns are addressed by allowing users to control data sent to LLMs.
llm.c
LLM training in simple, pure C/CUDA. There is no need for 245MB of PyTorch or 107MB of cPython. For example, training GPT-2 (CPU, fp32) is ~1,000 lines of clean code in a single file. It compiles and runs instantly, and exactly matches the PyTorch reference implementation. I chose GPT-2 as the first working example because it is the grand-daddy of LLMs, the first time the modern stack was put together.
jaison-core
J.A.I.son is a Python project designed for generating responses using various components and applications. It requires specific plugins like STT, T2T, TTSG, and TTSC to function properly. Users can customize responses, voice, and configurations. The project provides a Discord bot, Twitch events and chat integration, and VTube Studio Animation Hotkeyer. It also offers features for managing conversation history, training AI models, and monitoring conversations.
ezkl
EZKL is a library and command-line tool for doing inference for deep learning models and other computational graphs in a zk-snark (ZKML). It enables the following workflow: 1. Define a computational graph, for instance a neural network (but really any arbitrary set of operations), as you would normally in pytorch or tensorflow. 2. Export the final graph of operations as an .onnx file and some sample inputs to a .json file. 3. Point ezkl to the .onnx and .json files to generate a ZK-SNARK circuit with which you can prove statements such as: > "I ran this publicly available neural network on some private data and it produced this output" > "I ran my private neural network on some public data and it produced this output" > "I correctly ran this publicly available neural network on some public data and it produced this output" In the backend we use the collaboratively-developed Halo2 as a proof system. The generated proofs can then be verified with much less computational resources, including on-chain (with the Ethereum Virtual Machine), in a browser, or on a device.
sorcery
Sorcery is a SillyTavern extension that allows AI characters to interact with the real world by executing user-defined scripts at specific events in the chat. It is easy to use and does not require a specially trained function calling model. Sorcery can be used to control smart home appliances, interact with virtual characters, and perform various tasks in the chat environment. It works by injecting instructions into the system prompt and intercepting markers to run associated scripts, providing a seamless user experience.
ai-rag-chat-evaluator
This repository contains scripts and tools for evaluating a chat app that uses the RAG architecture. It provides parameters to assess the quality and style of answers generated by the chat app, including system prompt, search parameters, and GPT model parameters. The tools facilitate running evaluations, with examples of evaluations on a sample chat app. The repo also offers guidance on cost estimation, setting up the project, deploying a GPT-4 model, generating ground truth data, running evaluations, and measuring the app's ability to say 'I don't know'. Users can customize evaluations, view results, and compare runs using provided tools.

wdoc
wdoc is a powerful Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system designed to summarize, search, and query documents across various file types. It aims to handle large volumes of diverse document types, making it ideal for researchers, students, and professionals dealing with extensive information sources. wdoc uses LangChain to process and analyze documents, supporting tens of thousands of documents simultaneously. The system includes features like high recall and specificity, support for various Language Model Models (LLMs), advanced RAG capabilities, advanced document summaries, and support for multiple tasks. It offers markdown-formatted answers and summaries, customizable embeddings, extensive documentation, scriptability, and runtime type checking. wdoc is suitable for power users seeking document querying capabilities and AI-powered document summaries.
ChatGPT-Telegram-Bot
The ChatGPT Telegram Bot is a powerful Telegram bot that utilizes various GPT models, including GPT3.5, GPT4, GPT4 Turbo, GPT4 Vision, DALL·E 3, Groq Mixtral-8x7b/LLaMA2-70b, and Claude2.1/Claude3 opus/sonnet API. It enables users to engage in efficient conversations and information searches on Telegram. The bot supports multiple AI models, online search with DuckDuckGo and Google, user-friendly interface, efficient message processing, document interaction, Markdown rendering, and convenient deployment options like Zeabur, Replit, and Docker. Users can set environment variables for configuration and deployment. The bot also provides Q&A functionality, supports model switching, and can be deployed in group chats with whitelisting. The project is open source under GPLv3 license.

Mapperatorinator
Mapperatorinator is a multi-model framework that uses spectrogram inputs to generate fully featured osu! beatmaps for all gamemodes and assist modding beatmaps. The project aims to automatically generate rankable quality osu! beatmaps from any song with a high degree of customizability. The tool is built upon osuT5 and osu-diffusion, utilizing GPU compute and instances on vast.ai for development. Users can responsibly use AI in their beatmaps with this tool, ensuring disclosure of AI usage. Installation instructions include cloning the repository, creating a virtual environment, and installing dependencies. The tool offers a Web GUI for user-friendly experience and a Command-Line Inference option for advanced configurations. Additionally, an Interactive CLI script is available for terminal-based workflow with guided setup. The tool provides generation tips and features MaiMod, an AI-driven modding tool for osu! beatmaps. Mapperatorinator tokenizes beatmaps, utilizes a model architecture based on HF Transformers Whisper model, and offers multitask training format for conditional generation. The tool ensures seamless long generation, refines coordinates with diffusion, and performs post-processing for improved beatmap quality. Super timing generator enhances timing accuracy, and LoRA fine-tuning allows adaptation to specific styles or gamemodes. The project acknowledges credits and related works in the osu! community.
blurt
Blurt is a Gnome shell extension that enables accurate speech-to-text input in Linux. It is based on the command line utility NoteWhispers and supports Gnome shell version 48. Users can transcribe speech using a local whisper.cpp installation or a whisper.cpp server. The extension allows for easy setup, start/stop of speech-to-text input with key bindings or icon click, and provides visual indicators during operation. It offers convenience by enabling speech input into any window that allows text input, with the transcribed text sent to the clipboard for easy pasting.
For similar tasks

brokk
Brokk is a code assistant designed to understand code semantically, allowing LLMs to work effectively on large codebases. It offers features like agentic search, summarizing related classes, parsing stack traces, adding source for usages, and autonomously fixing errors. Users can interact with Brokk through different panels and commands, enabling them to manipulate context, ask questions, search codebase, run shell commands, and more. Brokk helps with tasks like debugging regressions, exploring codebase, AI-powered refactoring, and working with dependencies. It is particularly useful for making complex, multi-file edits with o1pro.
chat-with-code
Chat-with-code is a codebase chatbot that enables users to interact with their codebase using the OpenAI Language Model. It provides a user-friendly chat interface where users can ask questions and interact with their code. The tool clones, chunks, and embeds the codebase, allowing for natural language interactions. It is designed to assist users in exploring and understanding their codebase more intuitively.
Devon
Devon is an open-source pair programmer tool designed to facilitate collaborative coding sessions. It provides features such as multi-file editing, codebase exploration, test writing, bug fixing, and architecture exploration. The tool supports Anthropic, OpenAI, and Groq APIs, with plans to add more models in the future. Devon is community-driven, with ongoing development goals including multi-model support, plugin system for tool builders, self-hostable Electron app, and setting SOTA on SWE-bench Lite. Users can contribute to the project by developing core functionality, conducting research on agent performance, providing feedback, and testing the tool.
sage
Sage is a tool that allows users to chat with any codebase, providing a chat interface for code understanding and integration. It simplifies the process of learning how a codebase works by offering heavily documented answers sourced directly from the code. Users can set up Sage locally or on the cloud with minimal effort. The tool is designed to be easily customizable, allowing users to swap components of the pipeline and improve the algorithms powering code understanding and generation.
agentsys
AgentSys is a modular runtime and orchestration system for AI agents, with 13 plugins, 42 agents, and 28 skills that compose into structured pipelines for software development. It handles task selection, branch management, code review, artifact cleanup, CI, PR comments, and deployment. The system runs on Claude Code, OpenCode, and Codex CLI, providing a functional software suite and runtime for AI agent orchestration.

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

sourcegraph
Sourcegraph is a code search and navigation tool that helps developers read, write, and fix code in large, complex codebases. It provides features such as code search across all repositories and branches, code intelligence for navigation and refactoring, and the ability to fix and refactor code across multiple repositories at once.
continue
Continue is an open-source autopilot for VS Code and JetBrains that allows you to code with any LLM. With Continue, you can ask coding questions, edit code in natural language, generate files from scratch, and more. Continue is easy to use and can help you save time and improve your coding skills.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.