
deepeval
The LLM Evaluation Framework
Stars: 13678

DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.
README:
Documentation | Metrics and Features | Getting Started | Integrations | DeepEval Platform
Deutsch | Español | français | 日本語 | 한국어 | Português | Русский | 中文
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework, for evaluating and testing large-language model systems. It is similar to Pytest but specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. DeepEval incorporates the latest research to evaluate LLM outputs based on metrics such as G-Eval, task completion, answer relevancy, hallucination, etc., which uses LLM-as-a-judge and other NLP models that run locally on your machine for evaluation.
Whether your LLM applications are AI agents, RAG pipelines, or chatbots, implemented via LangChain or OpenAI, DeepEval has you covered. With it, you can easily determine the optimal models, prompts, and architecture to improve your RAG pipeline, agentic workflows, prevent prompt drifting, or even transition from OpenAI to hosting your own Deepseek R1 with confidence.
[!IMPORTANT] Need a place for your DeepEval testing data to live 🏡❤️? Sign up to the DeepEval platform to compare iterations of your LLM app, generate & share testing reports, and more.
Want to talk LLM evaluation, need help picking metrics, or just to say hi? Come join our discord.
🥳 You can now share DeepEval's test results on the cloud directly on Confident AI
- Supports both end-to-end and component-level LLM evaluation.
- Large variety of ready-to-use LLM evaluation metrics (all with explanations) powered by ANY LLM of your choice, statistical methods, or NLP models that run locally on your machine:
- G-Eval
- DAG (deep acyclic graph)
-
RAG metrics:
- Answer Relevancy
- Faithfulness
- Contextual Recall
- Contextual Precision
- Contextual Relevancy
- RAGAS
-
Agentic metrics:
- Task Completion
- Tool Correctness
-
Others:
- Hallucination
- Summarization
- Bias
- Toxicity
-
Conversational metrics:
- Knowledge Retention
- Conversation Completeness
- Conversation Relevancy
- Role Adherence
- etc.
- Build your own custom metrics that are automatically integrated with DeepEval's ecosystem.
- Generate synthetic datasets for evaluation.
- Integrates seamlessly with ANY CI/CD environment.
-
Red team your LLM application for 40+ safety vulnerabilities in a few lines of code, including:
- Toxicity
- Bias
- SQL Injection
- etc., using advanced 10+ attack enhancement strategies such as prompt injections.
- Easily benchmark ANY LLM on popular LLM benchmarks in under 10 lines of code., which includes:
- MMLU
- HellaSwag
- DROP
- BIG-Bench Hard
- TruthfulQA
- HumanEval
- GSM8K
-
100% integrated with Confident AI for the full evaluation & observability lifecycle:
- Curate/annotate evaluation datasets on the cloud
- Benchmark LLM app using dataset, and compare with previous iterations to experiment which models/prompts works best
- Fine-tune metrics for custom results
- Debug evaluation results via LLM traces
- Monitor & evaluate LLM responses in product to improve datasets with real-world data
- Repeat until perfection
[!NOTE] DeepEval is available on Confident AI, an LLM evals platform for AI observability and quality. Create an account here.
- 🦄 LlamaIndex, to unit test RAG applications in CI/CD
- 🤗 Hugging Face, to enable real-time evaluations during LLM fine-tuning
Let's pretend your LLM application is a RAG based customer support chatbot; here's how DeepEval can help test what you've built.
Deepeval works with Python>=3.9+.
pip install -U deepeval
Using the deepeval platform will allow you to generate sharable testing reports on the cloud. It is free, takes no additional code to setup, and we highly recommend giving it a try.
To login, run:
deepeval login
Follow the instructions in the CLI to create an account, copy your API key, and paste it into the CLI. All test cases will automatically be logged (find more information on data privacy here).
Create a test file:
touch test_chatbot.pyOpen test_chatbot.py and write your first test case to run an end-to-end evaluation using DeepEval, which treats your LLM app as a black-box:
import pytest
from deepeval import assert_test
from deepeval.metrics import GEval
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCase, LLMTestCaseParams
def test_case():
correctness_metric = GEval(
name="Correctness",
criteria="Determine if the 'actual output' is correct based on the 'expected output'.",
evaluation_params=[LLMTestCaseParams.ACTUAL_OUTPUT, LLMTestCaseParams.EXPECTED_OUTPUT],
threshold=0.5
)
test_case = LLMTestCase(
input="What if these shoes don't fit?",
# Replace this with the actual output from your LLM application
actual_output="You have 30 days to get a full refund at no extra cost.",
expected_output="We offer a 30-day full refund at no extra costs.",
retrieval_context=["All customers are eligible for a 30 day full refund at no extra costs."]
)
assert_test(test_case, [correctness_metric])Set your OPENAI_API_KEY as an environment variable (you can also evaluate using your own custom model, for more details visit this part of our docs):
export OPENAI_API_KEY="..."
And finally, run test_chatbot.py in the CLI:
deepeval test run test_chatbot.py
Congratulations! Your test case should have passed ✅ Let's breakdown what happened.
- The variable
inputmimics a user input, andactual_outputis a placeholder for what your application's supposed to output based on this input. - The variable
expected_outputrepresents the ideal answer for a giveninput, andGEvalis a research-backed metric provided bydeepevalfor you to evaluate your LLM output's on any custom with human-like accuracy. - In this example, the metric
criteriais correctness of theactual_outputbased on the providedexpected_output. - All metric scores range from 0 - 1, which the
threshold=0.5threshold ultimately determines if your test have passed or not.
Read our documentation for more information on more options to run end-to-end evaluation, how to use additional metrics, create your own custom metrics, and tutorials on how to integrate with other tools like LangChain and LlamaIndex.
If you wish to evaluate individual components within your LLM app, you need to run component-level evals - a powerful way to evaluate any component within an LLM system.
Simply trace "components" such as LLM calls, retrievers, tool calls, and agents within your LLM application using the @observe decorator to apply metrics on a component-level. Tracing with deepeval is non-instrusive (learn more here) and helps you avoid rewriting your codebase just for evals:
from deepeval.tracing import observe, update_current_span
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCase
from deepeval.dataset import Golden
from deepeval.metrics import GEval
from deepeval import evaluate
correctness = GEval(name="Correctness", criteria="Determine if the 'actual output' is correct based on the 'expected output'.", evaluation_params=[LLMTestCaseParams.ACTUAL_OUTPUT, LLMTestCaseParams.EXPECTED_OUTPUT])
@observe(metrics=[correctness])
def inner_component():
# Component can be anything from an LLM call, retrieval, agent, tool use, etc.
update_current_span(test_case=LLMTestCase(input="...", actual_output="..."))
return
@observe
def llm_app(input: str):
inner_component()
return
evaluate(observed_callback=llm_app, goldens=[Golden(input="Hi!")])You can learn everything about component-level evaluations here.
Alternatively, you can evaluate without Pytest, which is more suited for a notebook environment.
from deepeval import evaluate
from deepeval.metrics import AnswerRelevancyMetric
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCase
answer_relevancy_metric = AnswerRelevancyMetric(threshold=0.7)
test_case = LLMTestCase(
input="What if these shoes don't fit?",
# Replace this with the actual output from your LLM application
actual_output="We offer a 30-day full refund at no extra costs.",
retrieval_context=["All customers are eligible for a 30 day full refund at no extra costs."]
)
evaluate([test_case], [answer_relevancy_metric])DeepEval is extremely modular, making it easy for anyone to use any of our metrics. Continuing from the previous example:
from deepeval.metrics import AnswerRelevancyMetric
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCase
answer_relevancy_metric = AnswerRelevancyMetric(threshold=0.7)
test_case = LLMTestCase(
input="What if these shoes don't fit?",
# Replace this with the actual output from your LLM application
actual_output="We offer a 30-day full refund at no extra costs.",
retrieval_context=["All customers are eligible for a 30 day full refund at no extra costs."]
)
answer_relevancy_metric.measure(test_case)
print(answer_relevancy_metric.score)
# All metrics also offer an explanation
print(answer_relevancy_metric.reason)Note that some metrics are for RAG pipelines, while others are for fine-tuning. Make sure to use our docs to pick the right one for your use case.
In DeepEval, a dataset is simply a collection of test cases. Here is how you can evaluate these in bulk:
import pytest
from deepeval import assert_test
from deepeval.dataset import EvaluationDataset, Golden
from deepeval.metrics import AnswerRelevancyMetric
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCase
dataset = EvaluationDataset(goldens=[Golden(input="What's the weather like today?")])
for golden in dataset.goldens:
test_case = LLMTestCase(
input=golden.input,
actual_output=your_llm_app(golden.input)
)
dataset.add_test_case(test_case)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"test_case",
dataset.test_cases,
)
def test_customer_chatbot(test_case: LLMTestCase):
answer_relevancy_metric = AnswerRelevancyMetric(threshold=0.5)
assert_test(test_case, [answer_relevancy_metric])# Run this in the CLI, you can also add an optional -n flag to run tests in parallel
deepeval test run test_<filename>.py -n 4Alternatively, although we recommend using deepeval test run, you can evaluate a dataset/test cases without using our Pytest integration:
from deepeval import evaluate
...
evaluate(dataset, [answer_relevancy_metric])
# or
dataset.evaluate([answer_relevancy_metric])DeepEval auto-loads .env.local then .env from the current working directory at import time.
Precedence: process env -> .env.local -> .env.
Opt out with DEEPEVAL_DISABLE_DOTENV=1.
cp .env.example .env.local
# then edit .env.local (ignored by git)DeepEval is available on Confident AI, an evals & observability platform that allows you to:
- Curate/annotate evaluation datasets on the cloud
- Benchmark LLM app using dataset, and compare with previous iterations to experiment which models/prompts works best
- Fine-tune metrics for custom results
- Debug evaluation results via LLM traces
- Monitor & evaluate LLM responses in product to improve datasets with real-world data
- Repeat until perfection
Everything on Confident AI, including how to use Confident is available here.
To begin, login from the CLI:
deepeval loginFollow the instructions to log in, create your account, and paste your API key into the CLI.
Now, run your test file again:
deepeval test run test_chatbot.pyYou should see a link displayed in the CLI once the test has finished running. Paste it into your browser to view the results!
Using .env.local or .env is optional. If they are missing, DeepEval uses your existing environment variables. When present, dotenv environment variables are auto-loaded at import time (unless you set DEEPEVAL_DISABLE_DOTENV=1).
Precedence: process env -> .env.local -> .env
cp .env.example .env.local
# then edit .env.local (ignored by git)Please read CONTRIBUTING.md for details on our code of conduct, and the process for submitting pull requests to us.
Features:
- [x] Integration with Confident AI
- [x] Implement G-Eval
- [x] Implement RAG metrics
- [x] Implement Conversational metrics
- [x] Evaluation Dataset Creation
- [x] Red-Teaming
- [ ] DAG custom metrics
- [ ] Guardrails
Built by the founders of Confident AI. Contact [email protected] for all enquiries.
DeepEval is licensed under Apache 2.0 - see the LICENSE.md file for details.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for deepeval
Similar Open Source Tools

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.
giskard
Giskard is an open-source Python library that automatically detects performance, bias & security issues in AI applications. The library covers LLM-based applications such as RAG agents, all the way to traditional ML models for tabular data.

Trace
Trace is a new AutoDiff-like tool for training AI systems end-to-end with general feedback. It generalizes the back-propagation algorithm by capturing and propagating an AI system's execution trace. Implemented as a PyTorch-like Python library, users can write Python code directly and use Trace primitives to optimize certain parts, similar to training neural networks.
llm-autoeval
LLM AutoEval is a tool that simplifies the process of evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) using a convenient Colab notebook. It automates the setup and execution of evaluations using RunPod, allowing users to customize evaluation parameters and generate summaries that can be uploaded to GitHub Gist for easy sharing and reference. LLM AutoEval supports various benchmark suites, including Nous, Lighteval, and Open LLM, enabling users to compare their results with existing models and leaderboards.
LLMBox
LLMBox is a comprehensive library designed for implementing Large Language Models (LLMs) with a focus on a unified training pipeline and comprehensive model evaluation. It serves as a one-stop solution for training and utilizing LLMs, offering flexibility and efficiency in both training and utilization stages. The library supports diverse training strategies, comprehensive datasets, tokenizer vocabulary merging, data construction strategies, parameter efficient fine-tuning, and efficient training methods. For utilization, LLMBox provides comprehensive evaluation on various datasets, in-context learning strategies, chain-of-thought evaluation, evaluation methods, prefix caching for faster inference, support for specific LLM models like vLLM and Flash Attention, and quantization options. The tool is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs for natural language processing tasks.
distilabel
Distilabel is a framework for synthetic data and AI feedback for AI engineers that require high-quality outputs, full data ownership, and overall efficiency. It helps you synthesize data and provide AI feedback to improve the quality of your AI models. With Distilabel, you can: * **Synthesize data:** Generate synthetic data to train your AI models. This can help you to overcome the challenges of data scarcity and bias. * **Provide AI feedback:** Get feedback from AI models on your data. This can help you to identify errors and improve the quality of your data. * **Improve your AI output quality:** By using Distilabel to synthesize data and provide AI feedback, you can improve the quality of your AI models and get better results.
evidently
Evidently is an open-source Python library designed for evaluating, testing, and monitoring machine learning (ML) and large language model (LLM) powered systems. It offers a wide range of functionalities, including working with tabular, text data, and embeddings, supporting predictive and generative systems, providing over 100 built-in metrics for data drift detection and LLM evaluation, allowing for custom metrics and tests, enabling both offline evaluations and live monitoring, and offering an open architecture for easy data export and integration with existing tools. Users can utilize Evidently for one-off evaluations using Reports or Test Suites in Python, or opt for real-time monitoring through the Dashboard service.

zenml
ZenML is an extensible, open-source MLOps framework for creating portable, production-ready machine learning pipelines. By decoupling infrastructure from code, ZenML enables developers across your organization to collaborate more effectively as they develop to production.
premsql
PremSQL is an open-source library designed to help developers create secure, fully local Text-to-SQL solutions using small language models. It provides essential tools for building and deploying end-to-end Text-to-SQL pipelines with customizable components, ideal for secure, autonomous AI-powered data analysis. The library offers features like Local-First approach, Customizable Datasets, Robust Executors and Evaluators, Advanced Generators, Error Handling and Self-Correction, Fine-Tuning Support, and End-to-End Pipelines. Users can fine-tune models, generate SQL queries from natural language inputs, handle errors, and evaluate model performance against predefined metrics. PremSQL is extendible for customization and private data usage.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
Easy-Translate
Easy-Translate is a script designed for translating large text files with a single command. It supports various models like M2M100, NLLB200, SeamlessM4T, LLaMA, and Bloom. The tool is beginner-friendly and offers seamless and customizable features for advanced users. It allows acceleration on CPU, multi-CPU, GPU, multi-GPU, and TPU, with support for different precisions and decoding strategies. Easy-Translate also provides an evaluation script for translations. Built on HuggingFace's Transformers and Accelerate library, it supports prompt usage and loading huge models efficiently.
sec-parser
The `sec-parser` project simplifies extracting meaningful information from SEC EDGAR HTML documents by organizing them into semantic elements and a tree structure. It helps in parsing SEC filings for financial and regulatory analysis, analytics and data science, AI and machine learning, causal AI, and large language models. The tool is especially beneficial for AI, ML, and LLM applications by streamlining data pre-processing and feature extraction.
bigcodebench
BigCodeBench is an easy-to-use benchmark for code generation with practical and challenging programming tasks. It aims to evaluate the true programming capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in a more realistic setting. The benchmark is designed for HumanEval-like function-level code generation tasks, but with much more complex instructions and diverse function calls. BigCodeBench focuses on the evaluation of LLM4Code with diverse function calls and complex instructions, providing precise evaluation & ranking and pre-generated samples to accelerate code intelligence research. It inherits the design of the EvalPlus framework but differs in terms of execution environment and test evaluation.
CogAgent
CogAgent is an advanced intelligent agent model designed for automating operations on graphical interfaces across various computing devices. It supports platforms like Windows, macOS, and Android, enabling users to issue commands, capture device screenshots, and perform automated operations. The model requires a minimum of 29GB of GPU memory for inference at BF16 precision and offers capabilities for executing tasks like sending Christmas greetings and sending emails. Users can interact with the model by providing task descriptions, platform specifications, and desired output formats.

axar
AXAR AI is a lightweight framework designed for building production-ready agentic applications using TypeScript. It aims to simplify the process of creating robust, production-grade LLM-powered apps by focusing on familiar coding practices without unnecessary abstractions or steep learning curves. The framework provides structured, typed inputs and outputs, familiar and intuitive patterns like dependency injection and decorators, explicit control over agent behavior, real-time logging and monitoring tools, minimalistic design with little overhead, model agnostic compatibility with various AI models, and streamed outputs for fast and accurate results. AXAR AI is ideal for developers working on real-world AI applications who want a tool that gets out of the way and allows them to focus on shipping reliable software.
TileRT
TileRT is a project designed to serve large language models (LLMs) in ultra-low-latency scenarios. It aims to push the latency limits of LLMs without compromising model size or quality, enabling models with hundreds of billions of parameters to achieve millisecond-level time per output token. TileRT prioritizes responsiveness for applications like high-frequency trading, interactive AI, real-time decision-making, long-running agents, and AI-assisted coding. It introduces a tile-level runtime engine that dynamically reschedules computation, I/O, and communication across multiple devices to minimize idle time and improve hardware utilization. The project is actively evolving, with compiler techniques gradually shared with the community through TileLang and TileScale.
For similar tasks

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.
bench
Bench is a tool for evaluating LLMs for production use cases. It provides a standardized workflow for LLM evaluation with a common interface across tasks and use cases. Bench can be used to test whether open source LLMs can do as well as the top closed-source LLM API providers on specific data, and to translate the rankings on LLM leaderboards and benchmarks into scores that are relevant for actual use cases.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

llm-autoeval
LLM AutoEval is a tool that simplifies the process of evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) using a convenient Colab notebook. It automates the setup and execution of evaluations using RunPod, allowing users to customize evaluation parameters and generate summaries that can be uploaded to GitHub Gist for easy sharing and reference. LLM AutoEval supports various benchmark suites, including Nous, Lighteval, and Open LLM, enabling users to compare their results with existing models and leaderboards.

moonshot
Moonshot is a simple and modular tool developed by the AI Verify Foundation to evaluate Language Model Models (LLMs) and LLM applications. It brings Benchmarking and Red-Teaming together to assist AI developers, compliance teams, and AI system owners in assessing LLM performance. Moonshot can be accessed through various interfaces including User-friendly Web UI, Interactive Command Line Interface, and seamless integration into MLOps workflows via Library APIs or Web APIs. It offers features like benchmarking LLMs from popular model providers, running relevant tests, creating custom cookbooks and recipes, and automating Red Teaming to identify vulnerabilities in AI systems.

llm_client
llm_client is a Rust interface designed for Local Large Language Models (LLMs) that offers automated build support for CPU, CUDA, MacOS, easy model presets, and a novel cascading prompt workflow for controlled generation. It provides a breadth of configuration options and API support for various OpenAI compatible APIs. The tool is primarily focused on deterministic signals from probabilistic LLM vibes, enabling specialized workflows for specific tasks and reproducible outcomes.
LLM-Synthetic-Data
LLM-Synthetic-Data is a repository focused on real-time, fine-grained LLM-Synthetic-Data generation. It includes methods, surveys, and application areas related to synthetic data for language models. The repository covers topics like pre-training, instruction tuning, model collapse, LLM benchmarking, evaluation, and distillation. It also explores application areas such as mathematical reasoning, code generation, text-to-SQL, alignment, reward modeling, long context, weak-to-strong generalization, agent and tool use, vision and language, factuality, federated learning, generative design, and safety.
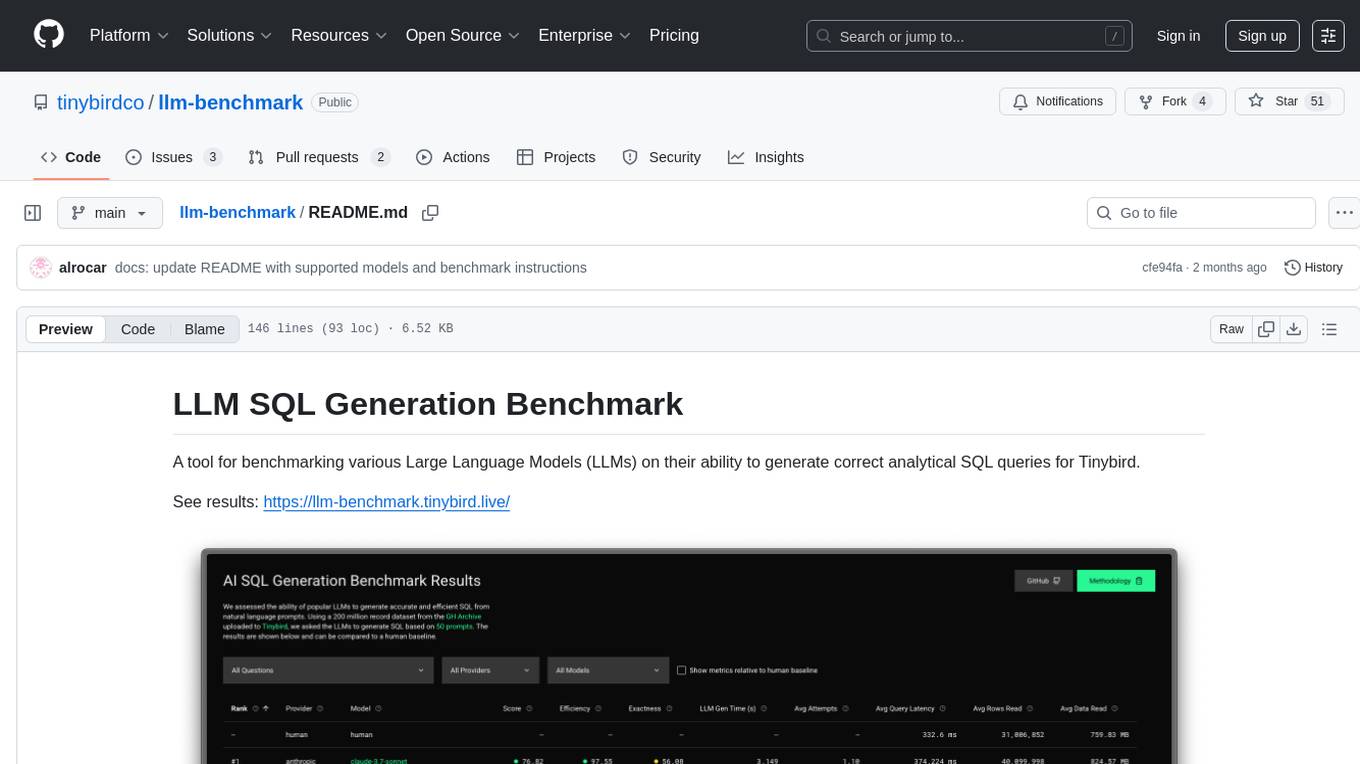
llm-benchmark
LLM SQL Generation Benchmark is a tool for evaluating different Large Language Models (LLMs) on their ability to generate accurate analytical SQL queries for Tinybird. It measures SQL query correctness, execution success, performance metrics, error handling, and recovery. The benchmark includes an automated retry mechanism for error correction. It supports various providers and models through OpenRouter and can be extended to other models. The benchmark is based on a GitHub dataset with 200M rows, where each LLM must produce SQL from 50 natural language prompts. Results are stored in JSON files and presented in a web application. Users can benchmark new models by following provided instructions.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.




