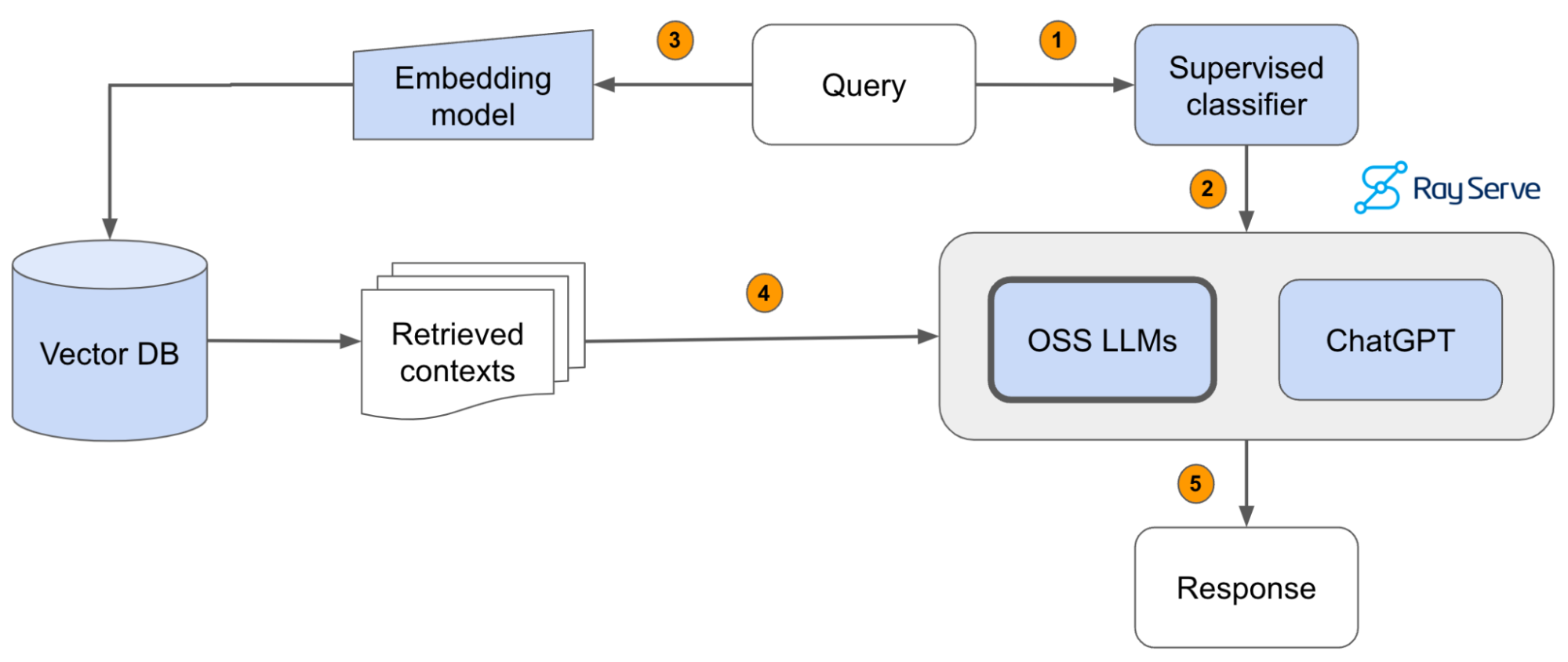
llm-applications
A comprehensive guide to building RAG-based LLM applications for production.
Stars: 1486
A comprehensive guide to building Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)-based LLM applications for production. This guide covers developing a RAG-based LLM application from scratch, scaling the major components, evaluating different configurations, implementing LLM hybrid routing, serving the application in a highly scalable and available manner, and sharing the impacts LLM applications have had on products.
README:
A comprehensive guide to building RAG-based LLM applications for production.
- Blog post: https://www.anyscale.com/blog/a-comprehensive-guide-for-building-rag-based-llm-applications-part-1
- GitHub repository: https://github.com/ray-project/llm-applications
- Interactive notebook: https://github.com/ray-project/llm-applications/blob/main/notebooks/rag.ipynb
- Anyscale Endpoints: https://endpoints.anyscale.com/
- Ray documentation: https://docs.ray.io/
In this guide, we will learn how to:
- 💻 Develop a retrieval augmented generation (RAG) based LLM application from scratch.
- 🚀 Scale the major components (load, chunk, embed, index, serve, etc.) in our application.
- ✅ Evaluate different configurations of our application to optimize for both per-component (ex. retrieval_score) and overall performance (quality_score).
- 🔀 Implement LLM hybrid routing approach to bridge the gap b/w OSS and closed LLMs.
- 📦 Serve the application in a highly scalable and available manner.
- 💥 Share the 1st order and 2nd order impacts LLM applications have had on our products.
We'll be using OpenAI to access ChatGPT models like gpt-3.5-turbo, gpt-4, etc. and Anyscale Endpoints to access OSS LLMs like Llama-2-70b. Be sure to create your accounts for both and have your credentials ready.
Local
You could run this on your local laptop but a we highly recommend using a setup with access to GPUs. You can set this up on your own or on [Anyscale](http://anyscale.com/).Anyscale
- Start a new Anyscale workspace on staging using an
g3.8xlargehead node, which has 2 GPUs and 32 CPUs. We can also add GPU worker nodes to run the workloads faster. If you're not on Anyscale, you can configure a similar instance on your cloud. - Use the
default_cluster_env_2.6.2_py39cluster environment. - Use the
us-west-2if you'd like to use the artifacts in our shared storage (source docs, vector DB dumps, etc.).
git clone https://github.com/ray-project/llm-applications.git .
git config --global user.name <GITHUB-USERNAME>
git config --global user.email <EMAIL-ADDRESS>Our data is already ready at /efs/shared_storage/goku/docs.ray.io/en/master/ (on Staging, us-east-1) but if you wanted to load it yourself, run this bash command (change /desired/output/directory, but make sure it's on the shared storage,
so that it's accessible to the workers)
git clone https://github.com/ray-project/llm-applications.git .Then set up the environment correctly by specifying the values in your .env file,
and installing the dependencies:
pip install --user -r requirements.txt
export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:$PWD
pre-commit install
pre-commit autoupdatetouch .env
# Add environment variables to .env
OPENAI_API_BASE="https://api.openai.com/v1"
OPENAI_API_KEY="" # https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys
ANYSCALE_API_BASE="https://api.endpoints.anyscale.com/v1"
ANYSCALE_API_KEY="" # https://app.endpoints.anyscale.com/credentials
DB_CONNECTION_STRING="dbname=postgres user=postgres host=localhost password=postgres"
source .envNow we're ready to go through the rag.ipynb interactive notebook to develop and serve our LLM application!
- If your team is investing heavily in developing LLM applications, reach out to us to learn more about how Ray and Anyscale can help you scale and productionize everything.
- Start serving (+fine-tuning) OSS LLMs with Anyscale Endpoints ($1/M tokens for
Llama-3-70b) and private endpoints available upon request (1M free tokens trial). - Learn more about how companies like OpenAI, Netflix, Pinterest, Verizon, Instacart and others leverage Ray and Anyscale for their AI workloads at the Ray Summit 2024 this Sept 18-20 in San Francisco.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llm-applications
Similar Open Source Tools

llm-applications
A comprehensive guide to building Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)-based LLM applications for production. This guide covers developing a RAG-based LLM application from scratch, scaling the major components, evaluating different configurations, implementing LLM hybrid routing, serving the application in a highly scalable and available manner, and sharing the impacts LLM applications have had on products.
BentoML
BentoML is an open-source model serving library for building performant and scalable AI applications with Python. It comes with everything you need for serving optimization, model packaging, and production deployment.
testzeus-hercules
Hercules is the world’s first open-source testing agent designed to handle the toughest testing tasks for modern web applications. It turns simple Gherkin steps into fully automated end-to-end tests, making testing simple, reliable, and efficient. Hercules adapts to various platforms like Salesforce and is suitable for CI/CD pipelines. It aims to democratize and disrupt test automation, making top-tier testing accessible to everyone. The tool is transparent, reliable, and community-driven, empowering teams to deliver better software. Hercules offers multiple ways to get started, including using PyPI package, Docker, or building and running from source code. It supports various AI models, provides detailed installation and usage instructions, and integrates with Nuclei for security testing and WCAG for accessibility testing. The tool is production-ready, open core, and open source, with plans for enhanced LLM support, advanced tooling, improved DOM distillation, community contributions, extensive documentation, and a bounty program.
AI-Scientist
The AI Scientist is a comprehensive system for fully automatic scientific discovery, enabling Foundation Models to perform research independently. It aims to tackle the grand challenge of developing agents capable of conducting scientific research and discovering new knowledge. The tool generates papers on various topics using Large Language Models (LLMs) and provides a platform for exploring new research ideas. Users can create their own templates for specific areas of study and run experiments to generate papers. However, caution is advised as the codebase executes LLM-written code, which may pose risks such as the use of potentially dangerous packages and web access.

doku
OpenLIT is an OpenTelemetry-native GenAI and LLM Application Observability tool. It's designed to make the integration process of observability into GenAI projects as easy as pie – literally, with just a single line of code. Whether you're working with popular LLM Libraries such as OpenAI and HuggingFace or leveraging vector databases like ChromaDB, OpenLIT ensures your applications are monitored seamlessly, providing critical insights to improve performance and reliability.
llm-engine
Scale's LLM Engine is an open-source Python library, CLI, and Helm chart that provides everything you need to serve and fine-tune foundation models, whether you use Scale's hosted infrastructure or do it in your own cloud infrastructure using Kubernetes.
draive
draive is an open-source Python library designed to simplify and accelerate the development of LLM-based applications. It offers abstract building blocks for connecting functionalities with large language models, flexible integration with various AI solutions, and a user-friendly framework for building scalable data processing pipelines. The library follows a function-oriented design, allowing users to represent complex programs as simple functions. It also provides tools for measuring and debugging functionalities, ensuring type safety and efficient asynchronous operations for modern Python apps.

guidellm
GuideLLM is a powerful tool for evaluating and optimizing the deployment of large language models (LLMs). By simulating real-world inference workloads, GuideLLM helps users gauge the performance, resource needs, and cost implications of deploying LLMs on various hardware configurations. This approach ensures efficient, scalable, and cost-effective LLM inference serving while maintaining high service quality. Key features include performance evaluation, resource optimization, cost estimation, and scalability testing.
OSWorld
OSWorld is a benchmarking tool designed to evaluate multimodal agents for open-ended tasks in real computer environments. It provides a platform for running experiments, setting up virtual machines, and interacting with the environment using Python scripts. Users can install the tool on their desktop or server, manage dependencies with Conda, and run benchmark tasks. The tool supports actions like executing commands, checking for specific results, and evaluating agent performance. OSWorld aims to facilitate research in AI by providing a standardized environment for testing and comparing different agent baselines.
llm-on-ray
LLM-on-Ray is a comprehensive solution for building, customizing, and deploying Large Language Models (LLMs). It simplifies complex processes into manageable steps by leveraging the power of Ray for distributed computing. The tool supports pretraining, finetuning, and serving LLMs across various hardware setups, incorporating industry and Intel optimizations for performance. It offers modular workflows with intuitive configurations, robust fault tolerance, and scalability. Additionally, it provides an Interactive Web UI for enhanced usability, including a chatbot application for testing and refining models.
agentok
Agentok Studio is a visual tool built for AutoGen, a cutting-edge agent framework from Microsoft and various contributors. It offers intuitive visual tools to simplify the construction and management of complex agent-based workflows. Users can create workflows visually as graphs, chat with agents, and share flow templates. The tool is designed to streamline the development process for creators and developers working on next-generation Multi-Agent Applications.
job-llm
ResumeFlow is an automated system utilizing Large Language Models (LLMs) to streamline the job application process. It aims to reduce human effort in various steps of job hunting by integrating LLM technology. Users can access ResumeFlow as a web tool, install it as a Python package, or download the source code. The project focuses on leveraging LLMs to automate tasks such as resume generation and refinement, making job applications smoother and more efficient.
kubeai
KubeAI is a highly scalable AI platform that runs on Kubernetes, serving as a drop-in replacement for OpenAI with API compatibility. It can operate OSS model servers like vLLM and Ollama, with zero dependencies and additional OSS addons included. Users can configure models via Kubernetes Custom Resources and interact with models through a chat UI. KubeAI supports serving various models like Llama v3.1, Gemma2, and Qwen2, and has plans for model caching, LoRA finetuning, and image generation.
autoarena
AutoArena is a tool designed to create leaderboards ranking Language Model outputs against one another using automated judge evaluation. It allows users to rank outputs from different LLMs, RAG setups, and prompts to find the best configuration of their system. Users can perform automated head-to-head evaluation using judges from various platforms like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Cohere. Additionally, users can define and run custom judges, connect to internal services, or implement bespoke logic. AutoArena enables users to run the application locally, providing full control over their environment and data.
merlinn
Merlinn is an open-source AI-powered on-call engineer that automatically jumps into incidents & alerts, providing useful insights and RCA in real time. It integrates with popular observability tools, lives inside Slack, offers an intuitive UX, and prioritizes security. Users can self-host Merlinn, use it for free, and benefit from automatic RCA, Slack integration, integrations with various tools, intuitive UX, and security features.
langdrive
LangDrive is an open-source AI library that simplifies training, deploying, and querying open-source large language models (LLMs) using private data. It supports data ingestion, fine-tuning, and deployment via a command-line interface, YAML file, or API, with a quick, easy setup. Users can build AI applications such as question/answering systems, chatbots, AI agents, and content generators. The library provides features like data connectors for ingestion, fine-tuning of LLMs, deployment to Hugging Face hub, inference querying, data utilities for CRUD operations, and APIs for model access. LangDrive is designed to streamline the process of working with LLMs and making AI development more accessible.
For similar tasks

llm-applications
A comprehensive guide to building Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)-based LLM applications for production. This guide covers developing a RAG-based LLM application from scratch, scaling the major components, evaluating different configurations, implementing LLM hybrid routing, serving the application in a highly scalable and available manner, and sharing the impacts LLM applications have had on products.
uptrain
UpTrain is an open-source unified platform to evaluate and improve Generative AI applications. We provide grades for 20+ preconfigured evaluations (covering language, code, embedding use cases), perform root cause analysis on failure cases and give insights on how to resolve them.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.