patchwork
Open-source framework to review and patch code using your preferred LLM.
Stars: 1300

PatchWork is an open-source framework designed for automating development tasks using large language models. It enables users to automate workflows such as PR reviews, bug fixing, security patching, and more through a self-hosted CLI agent and preferred LLMs. The framework consists of reusable atomic actions called Steps, customizable LLM prompts known as Prompt Templates, and LLM-assisted automations called Patchflows. Users can run Patchflows locally in their CLI/IDE or as part of CI/CD pipelines. PatchWork offers predefined patchflows like AutoFix, PRReview, GenerateREADME, DependencyUpgrade, and ResolveIssue, with the flexibility to create custom patchflows. Prompt templates are used to pass queries to LLMs and can be customized. Contributions to new patchflows, steps, and the core framework are encouraged, with chat assistants available to aid in the process. The roadmap includes expanding the patchflow library, introducing a debugger and validation module, supporting large-scale code embeddings, parallelization, fine-tuned models, and an open-source GUI. PatchWork is licensed under AGPL-3.0 terms, while custom patchflows and steps can be shared using the Apache-2.0 licensed patchwork template repository.
README:
Patchwork automates development gruntwork like PR reviews, bug fixing, security patching, and more using a self-hosted CLI agent and your preferred LLMs. Try the hosted version here.
- Steps: Reusable atomic actions like create PR, commit changes or call an LLM.
- Prompt Templates: Customizable LLM prompts optimized for a chore like library updates, code generation, issue analysis or vulnerability remediation.
- Patchflows: LLM-assisted automations such as PR reviews, code fixing, documentation etc. built by combining steps and prompts.
Patchflows can be run locally in your CLI and IDE, or as part of your CI/CD pipeline. There are several patchflows available out of the box, and you can always create your own.
Patchwork is available on PyPI and can be installed using pip:
pip install 'patchwork-cli[all]' --upgradeThe following optional dependency groups are available.
-
security: Installssemgrepanddepscanwithpip install 'patchwork-cli[security]'and is required for AutoFix and DependencyUpgrade patchflows. -
rag: Installschromadbwithpip install 'patchwork-cli[rag]'and is required for the ResolveIssue patchflow. -
notifications: Used by steps sending notifications, e.g. slack messages. -
all: installs everything. - Not specifying any dependency group (
pip install patchwork-cli) will install a core set of dependencies that are sufficient to run the GenerateDocstring, PRReview and GenerateREADME patchflows.
If you'd like to build from source using poetry, please see detailed documentation here .
The CLI runs Patchflows, as follows:
patchwork <PatchFlow> <?Arguments>
Where
-
Arguments: Allow for overriding default/optional attributes of the Patchflow in the format of
key=value. Ifkeydoes not have any value, it is considered a booleanTrueflag.
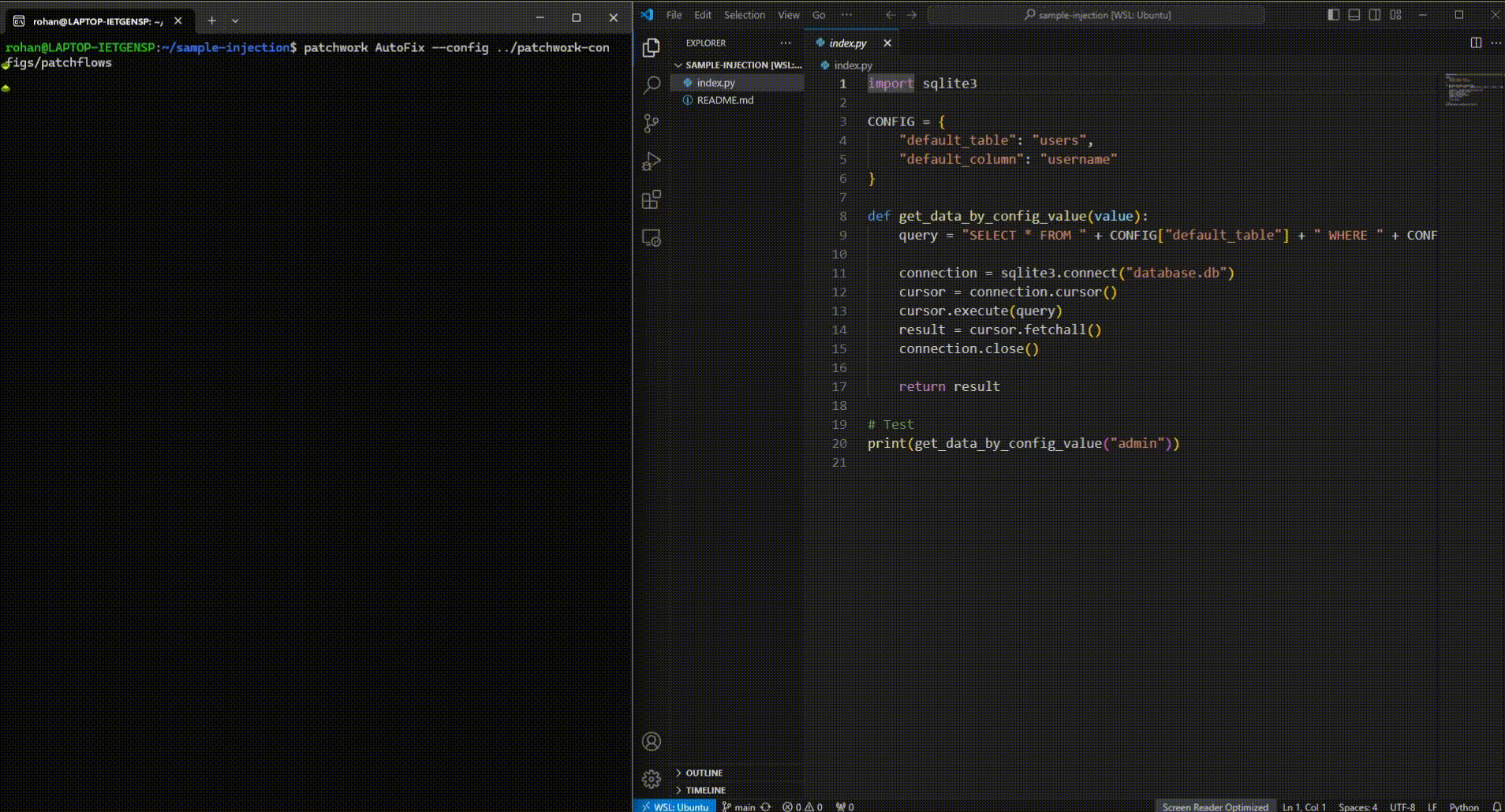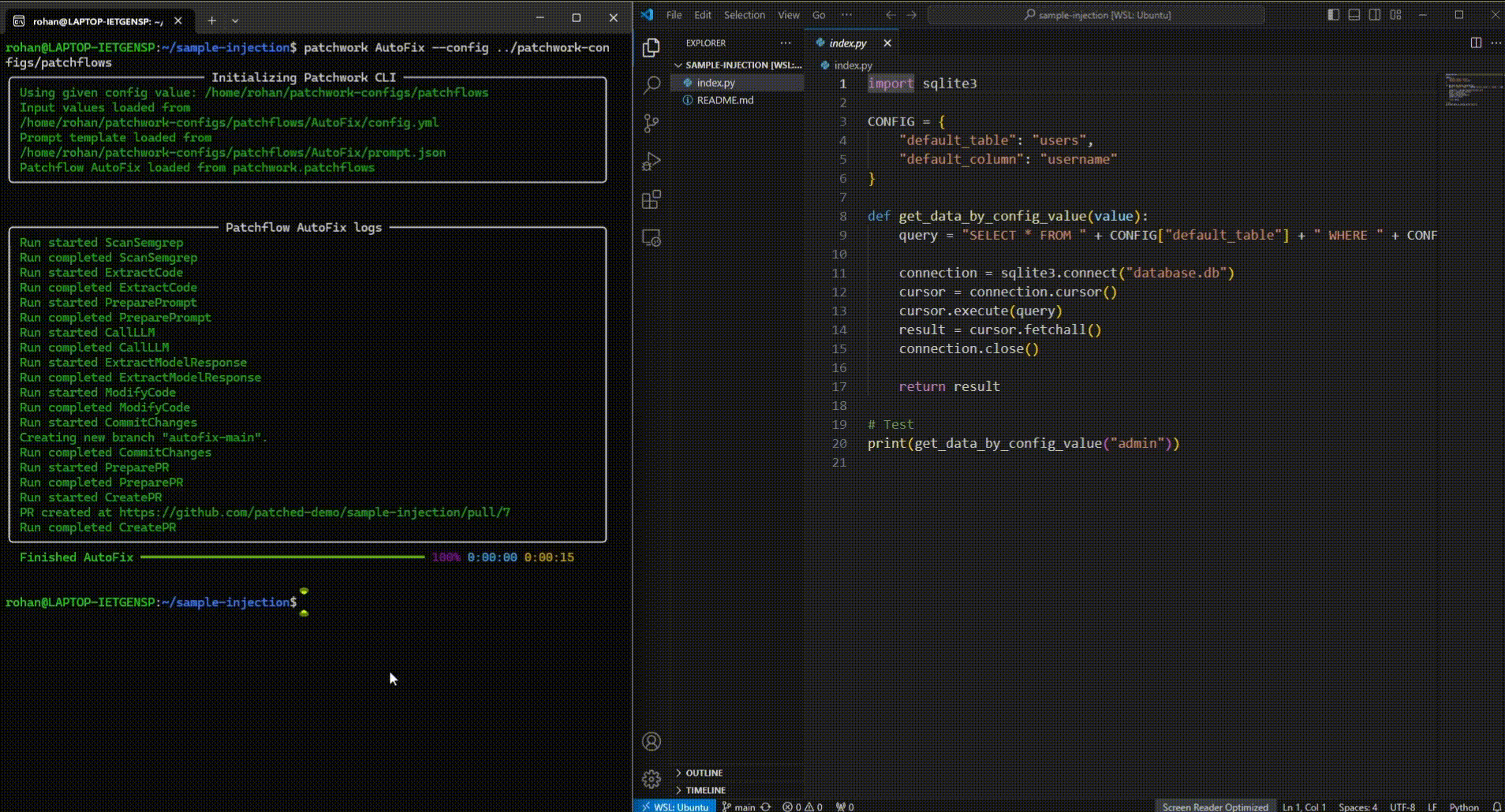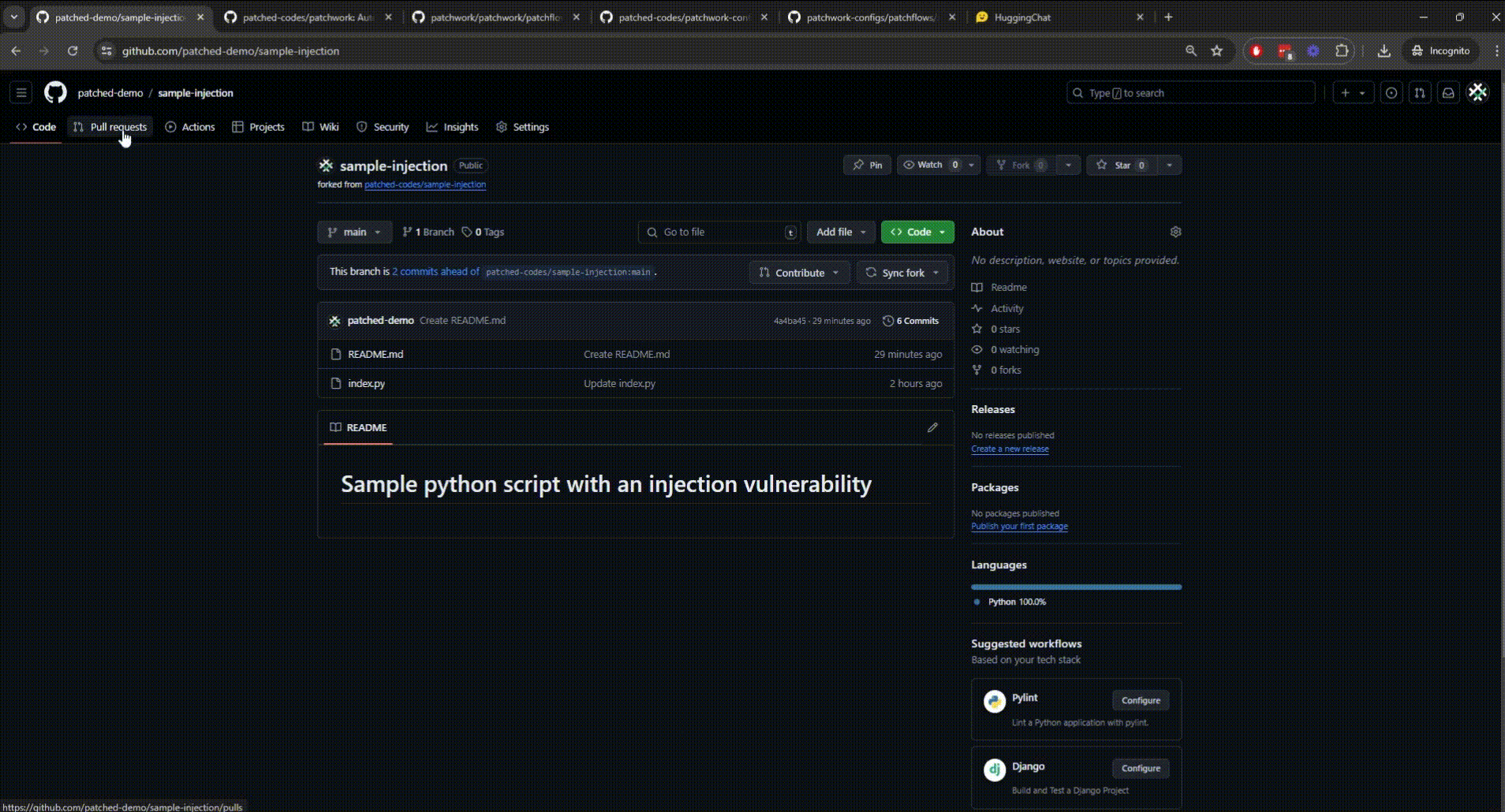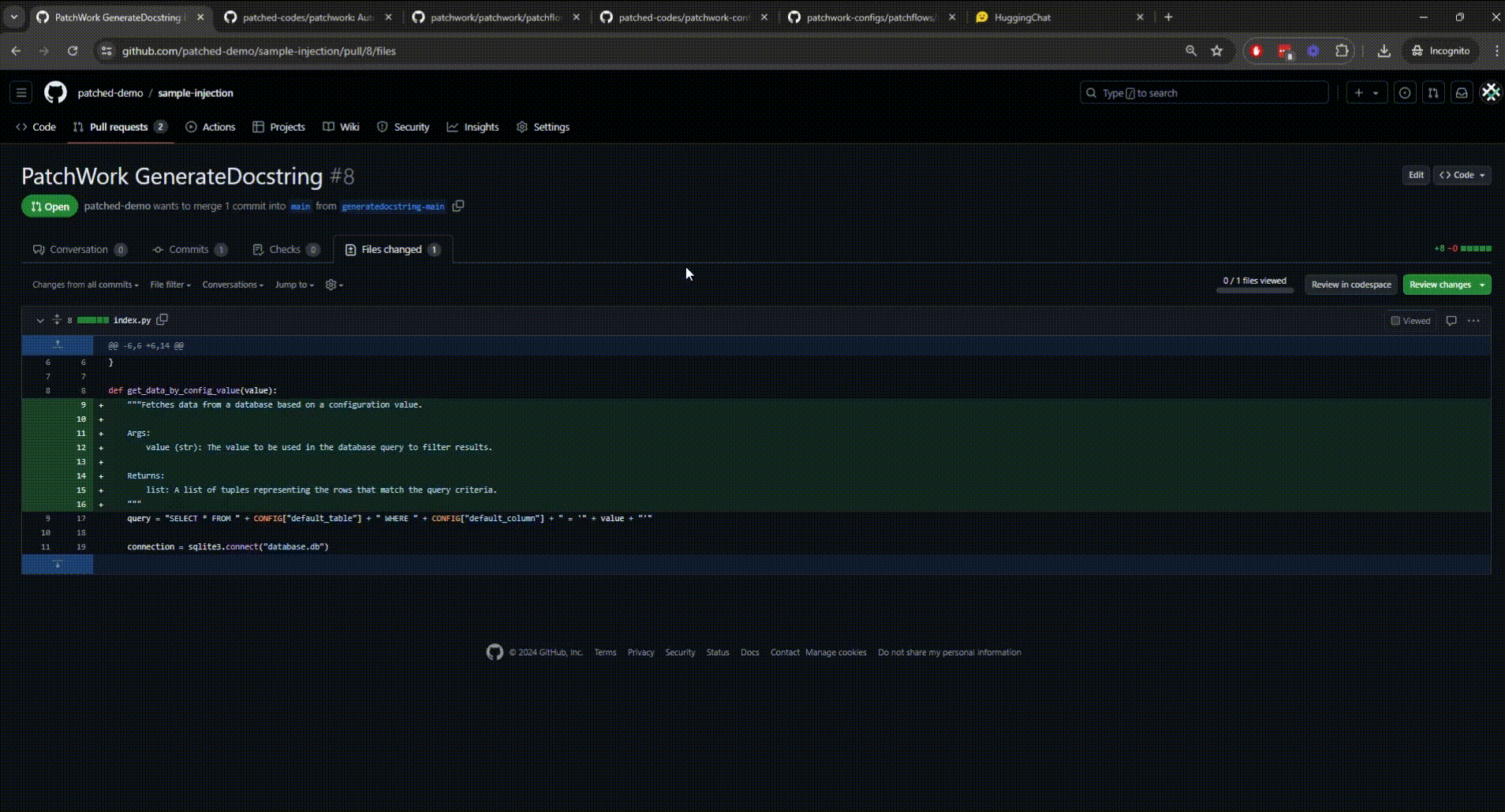
For an AutoFix patchflow which patches vulnerabilities based on a scan using Semgrep:
patchwork AutoFix openai_api_key=<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY> github_api_key=<YOUR_GITHUB_TOKEN>The above command defaults to patching code in the current directory by running Semgrep to identify the vulnerabilities. You can view the default.yml file for the list of configurations you can set to manage the AutoFix patchflow. For more details on how you can use a personal access token from GitHub on CLI, can read this.
You can replace the OpenAI key with a key from our managed service by signing in at https://app.patched.codes/signin and generating an API key from the integrations tab. You can then call the patchflow with the key as follows:
patchwork AutoFix patched_api_key=<YOUR_PATCHED_API_KEY> github_api_key=<YOUR_GITHUB_TOKEN>To use Google's models you can set the google_api_key and model, this is useful if you want to work with large contexts as the gemini-pro-1.5 model supports an input context length of 1 million tokens.
The patchwork-template repository contains the default configuration and prompts for all the patchflows. You can clone that repo and pass it as a flag to the CLI:
patchwork AutoFix --config /path/to/patchwork-configs/patchflowsPatchwork supports any OpenAI compatible endpoint, allowing use of any LLM from various providers like Groq, Together AI, or Hugging Face.
E.g. to use Llama 3.1 405B from Groq.com run:
patchwork AutoFix client_base_url=https://api.groq.com/openai/v1 openai_api_key=your_groq_key model=llama-3.1-405b-reasoning
You can also use a config file to do the same. To use Llama 3.1 405B from Hugging Face, create a config.yml file:
openai_api_key: your_hf_token
client_base_url: https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct-FP8/v1
model: Meta-Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct-FP8And run as:
patchwork AutoFix --config=/path/to/config.yml
This allows you to run local models via llama.cpp, ollama, vllm or tgi. For instance, you can run Llama 3.1 8B locally using llama_cpp.server:
python -m llama_cpp.server --hf_model_repo_id bullerwins/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-GGUF --model 'Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-Q4_K_M.gguf' --chat_format chatml
Then run your patchflow:
patchwork AutoFix client_base_url=http://localhost:8080/v1 openai_api_key=no_key_local_model
Patchwork comes with predefined patchflows, with more added over time. Sample patchflows include:
- GenerateDocstring: Generate docstrings for methods in your code.
- AutoFix: Generate and apply fixes to code vulnerabilities in a repository.
- PRReview: On PR creation, extract code diff, summarize changes, and comment on PR.
- GenerateREADME: Create a README markdown file for a given folder, to add documentation to your repository.
- DependencyUpgrade: Update your dependencies from vulnerable to fixed versions.
- ResolveIssue: Identify the files in your repository that need to be updated to resolve an issue (or bug) and create a PR to fix it.
Prompt templates are used by patchflows and passed as queries to LLMs. Templates contain prompts with placeholder variables enclosed by {{}} which are replaced by the data from the steps or inputs on every run.
Below is a sample prompt template:
{
"id": "diffreview_summary",
"prompts": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Summarize the following code change descriptions in 1 paragraph. {{diffreviews}}"
}
]
}Each patchflow comes with an optimized default prompt template. But you can specify your own using the prompt_template_file=/path/to/prompt/template/file option.
Contributions for new patchflows and steps, or to the core framework are welcome. Please look at open issues for details.
- To create a new patchflow, follow these instructions.
- To create a new step, follow these instructions.
We also provide a chat assistant to help you create new steps and patchflows easily.
- Patchwork Assistant on HuggingChat (based on Llama-3.1)
- Expand patchflow library and integration options
- Patchflow debugger and validation module
- Bug fixing and performance improvements
- Refactor code and documentation
- Support large-scale code embeddings in patchflows
- Support parallelization and branching
- Fine-tuned models that can be self-hosted
- Open-source GUI
Patchwork is licensed under AGPL-3.0 terms. However, custom patchflows and steps can be created and shared using the patchwork template repository which is licensed under Apache-2.0 terms.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for patchwork
Similar Open Source Tools

patchwork
PatchWork is an open-source framework designed for automating development tasks using large language models. It enables users to automate workflows such as PR reviews, bug fixing, security patching, and more through a self-hosted CLI agent and preferred LLMs. The framework consists of reusable atomic actions called Steps, customizable LLM prompts known as Prompt Templates, and LLM-assisted automations called Patchflows. Users can run Patchflows locally in their CLI/IDE or as part of CI/CD pipelines. PatchWork offers predefined patchflows like AutoFix, PRReview, GenerateREADME, DependencyUpgrade, and ResolveIssue, with the flexibility to create custom patchflows. Prompt templates are used to pass queries to LLMs and can be customized. Contributions to new patchflows, steps, and the core framework are encouraged, with chat assistants available to aid in the process. The roadmap includes expanding the patchflow library, introducing a debugger and validation module, supporting large-scale code embeddings, parallelization, fine-tuned models, and an open-source GUI. PatchWork is licensed under AGPL-3.0 terms, while custom patchflows and steps can be shared using the Apache-2.0 licensed patchwork template repository.
langmanus
LangManus is a community-driven AI automation framework that combines language models with specialized tools for tasks like web search, crawling, and Python code execution. It implements a hierarchical multi-agent system with agents like Coordinator, Planner, Supervisor, Researcher, Coder, Browser, and Reporter. The framework supports LLM integration, search and retrieval tools, Python integration, workflow management, and visualization. LangManus aims to give back to the open-source community and welcomes contributions in various forms.
RepoAgent
RepoAgent is an LLM-powered framework designed for repository-level code documentation generation. It automates the process of detecting changes in Git repositories, analyzing code structure through AST, identifying inter-object relationships, replacing Markdown content, and executing multi-threaded operations. The tool aims to assist developers in understanding and maintaining codebases by providing comprehensive documentation, ultimately improving efficiency and saving time.
code2prompt
Code2Prompt is a powerful command-line tool that generates comprehensive prompts from codebases, designed to streamline interactions between developers and Large Language Models (LLMs) for code analysis, documentation, and improvement tasks. It bridges the gap between codebases and LLMs by converting projects into AI-friendly prompts, enabling users to leverage AI for various software development tasks. The tool offers features like holistic codebase representation, intelligent source tree generation, customizable prompt templates, smart token management, Gitignore integration, flexible file handling, clipboard-ready output, multiple output options, and enhanced code readability.
gitingest
GitIngest is a tool that allows users to turn any Git repository into a prompt-friendly text ingest for LLMs. It provides easy code context by generating a text digest from a git repository URL or directory. The tool offers smart formatting for optimized output format for LLM prompts and provides statistics about file and directory structure, size of the extract, and token count. GitIngest can be used as a CLI tool on Linux and as a Python package for code integration. The tool is built using Tailwind CSS for frontend, FastAPI for backend framework, tiktoken for token estimation, and apianalytics.dev for simple analytics. Users can self-host GitIngest by building the Docker image and running the container. Contributions to the project are welcome, and the tool aims to be beginner-friendly for first-time contributors with a simple Python and HTML codebase.
sd-webui-agent-scheduler
AgentScheduler is an Automatic/Vladmandic Stable Diffusion Web UI extension designed to enhance image generation workflows. It allows users to enqueue prompts, settings, and controlnets, manage queued tasks, prioritize, pause, resume, and delete tasks, view generation results, and more. The extension offers hidden features like queuing checkpoints, editing queued tasks, and custom checkpoint selection. Users can access the functionality through HTTP APIs and API callbacks. Troubleshooting steps are provided for common errors. The extension is compatible with latest versions of A1111 and Vladmandic. It is licensed under Apache License 2.0.
atropos
Atropos is a robust and scalable framework for Reinforcement Learning Environments with Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides a flexible platform to accelerate LLM-based RL research across diverse interactive settings. Atropos supports multi-turn and asynchronous RL interactions, integrates with various inference APIs, offers a standardized training interface for experimenting with different RL algorithms, and allows for easy scalability by launching more environment instances. The framework manages diverse environment types concurrently for heterogeneous, multi-modal training.
SWELancer-Benchmark
SWE-Lancer is a benchmark repository containing datasets and code for the paper 'SWE-Lancer: Can Frontier LLMs Earn $1 Million from Real-World Freelance Software Engineering?'. It provides instructions for package management, building Docker images, configuring environment variables, and running evaluations. Users can use this tool to assess the performance of language models in real-world freelance software engineering tasks.
sage
Sage is a tool that allows users to chat with any codebase, providing a chat interface for code understanding and integration. It simplifies the process of learning how a codebase works by offering heavily documented answers sourced directly from the code. Users can set up Sage locally or on the cloud with minimal effort. The tool is designed to be easily customizable, allowing users to swap components of the pipeline and improve the algorithms powering code understanding and generation.
lexido
Lexido is an innovative assistant for the Linux command line, designed to boost your productivity and efficiency. Powered by Gemini Pro 1.0 and utilizing the free API, Lexido offers smart suggestions for commands based on your prompts and importantly your current environment. Whether you're installing software, managing files, or configuring system settings, Lexido streamlines the process, making it faster and more intuitive.
NeoGPT
NeoGPT is an AI assistant that transforms your local workspace into a powerhouse of productivity from your CLI. With features like code interpretation, multi-RAG support, vision models, and LLM integration, NeoGPT redefines how you work and create. It supports executing code seamlessly, multiple RAG techniques, vision models, and interacting with various language models. Users can run the CLI to start using NeoGPT and access features like Code Interpreter, building vector database, running Streamlit UI, and changing LLM models. The tool also offers magic commands for chat sessions, such as resetting chat history, saving conversations, exporting settings, and more. Join the NeoGPT community to experience a new era of efficiency and contribute to its evolution.
bedrock-claude-chat
This repository is a sample chatbot using the Anthropic company's LLM Claude, one of the foundational models provided by Amazon Bedrock for generative AI. It allows users to have basic conversations with the chatbot, personalize it with their own instructions and external knowledge, and analyze usage for each user/bot on the administrator dashboard. The chatbot supports various languages, including English, Japanese, Korean, Chinese, French, German, and Spanish. Deployment is straightforward and can be done via the command line or by using AWS CDK. The architecture is built on AWS managed services, eliminating the need for infrastructure management and ensuring scalability, reliability, and security.
safety-tooling
This repository, safety-tooling, is designed to be shared across various AI Safety projects. It provides an LLM API with a common interface for OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google models. The aim is to facilitate collaboration among AI Safety researchers, especially those with limited software engineering backgrounds, by offering a platform for contributing to a larger codebase. The repo can be used as a git submodule for easy collaboration and updates. It also supports pip installation for convenience. The repository includes features for installation, secrets management, linting, formatting, Redis configuration, testing, dependency management, inference, finetuning, API usage tracking, and various utilities for data processing and experimentation.
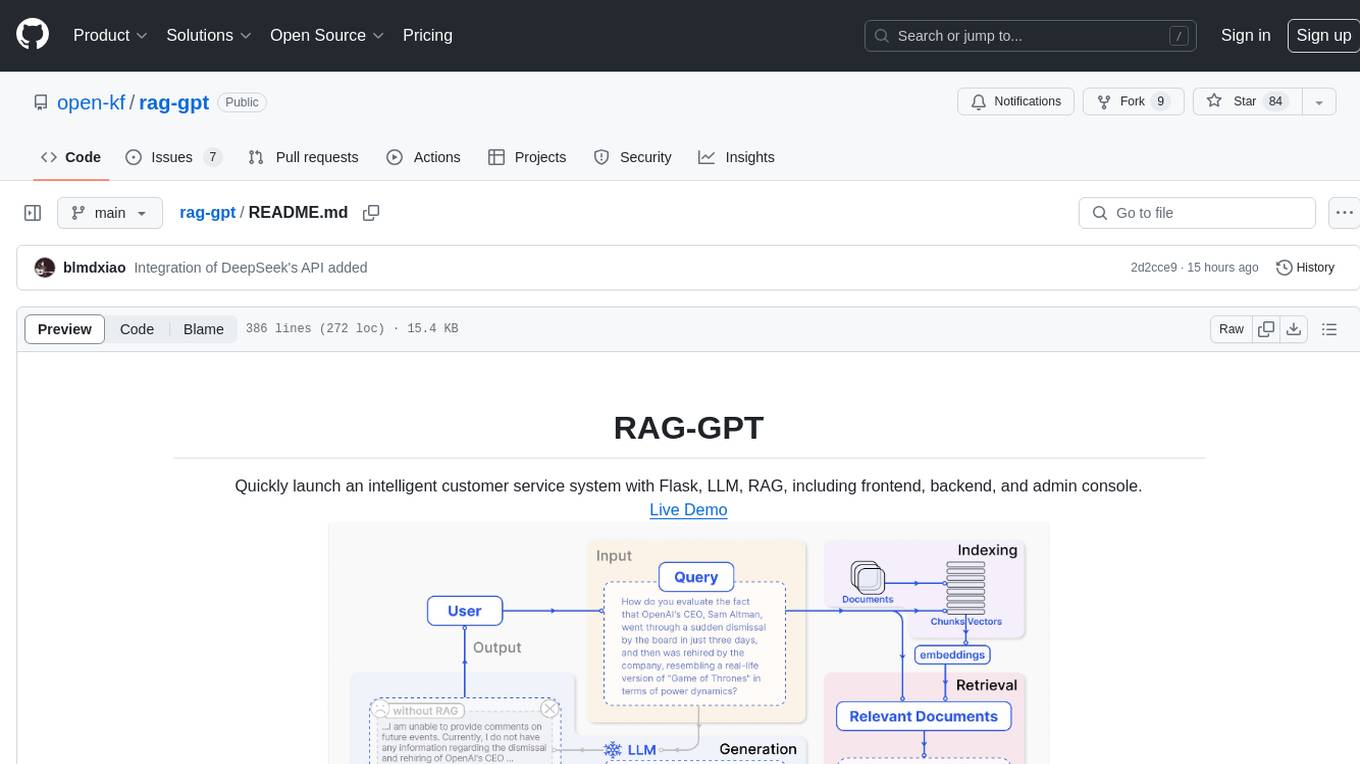
rag-gpt
RAG-GPT is a tool that allows users to quickly launch an intelligent customer service system with Flask, LLM, and RAG. It includes frontend, backend, and admin console components. The tool supports cloud-based and local LLMs, enables deployment of conversational service robots in minutes, integrates diverse knowledge bases, offers flexible configuration options, and features an attractive user interface.
wcgw
wcgw is a shell and coding agent designed for Claude and Chatgpt. It provides full shell access with no restrictions, desktop control on Claude for screen capture and control, interactive command handling, large file editing, and REPL support. Users can use wcgw to create, execute, and iterate on tasks, such as solving problems with Python, finding code instances, setting up projects, creating web apps, editing large files, and running server commands. Additionally, wcgw supports computer use on Docker containers for desktop control. The tool can be extended with a VS Code extension for pasting context on Claude app and integrates with Chatgpt for custom GPT interactions.
pipecat-flows
Pipecat Flows is a framework designed for building structured conversations in AI applications. It allows users to create both predefined conversation paths and dynamically generated flows, handling state management and LLM interactions. The framework includes a Python module for building conversation flows and a visual editor for designing and exporting flow configurations. Pipecat Flows is suitable for scenarios such as customer service scripts, intake forms, personalized experiences, and complex decision trees.
For similar tasks

patchwork
PatchWork is an open-source framework designed for automating development tasks using large language models. It enables users to automate workflows such as PR reviews, bug fixing, security patching, and more through a self-hosted CLI agent and preferred LLMs. The framework consists of reusable atomic actions called Steps, customizable LLM prompts known as Prompt Templates, and LLM-assisted automations called Patchflows. Users can run Patchflows locally in their CLI/IDE or as part of CI/CD pipelines. PatchWork offers predefined patchflows like AutoFix, PRReview, GenerateREADME, DependencyUpgrade, and ResolveIssue, with the flexibility to create custom patchflows. Prompt templates are used to pass queries to LLMs and can be customized. Contributions to new patchflows, steps, and the core framework are encouraged, with chat assistants available to aid in the process. The roadmap includes expanding the patchflow library, introducing a debugger and validation module, supporting large-scale code embeddings, parallelization, fine-tuned models, and an open-source GUI. PatchWork is licensed under AGPL-3.0 terms, while custom patchflows and steps can be shared using the Apache-2.0 licensed patchwork template repository.
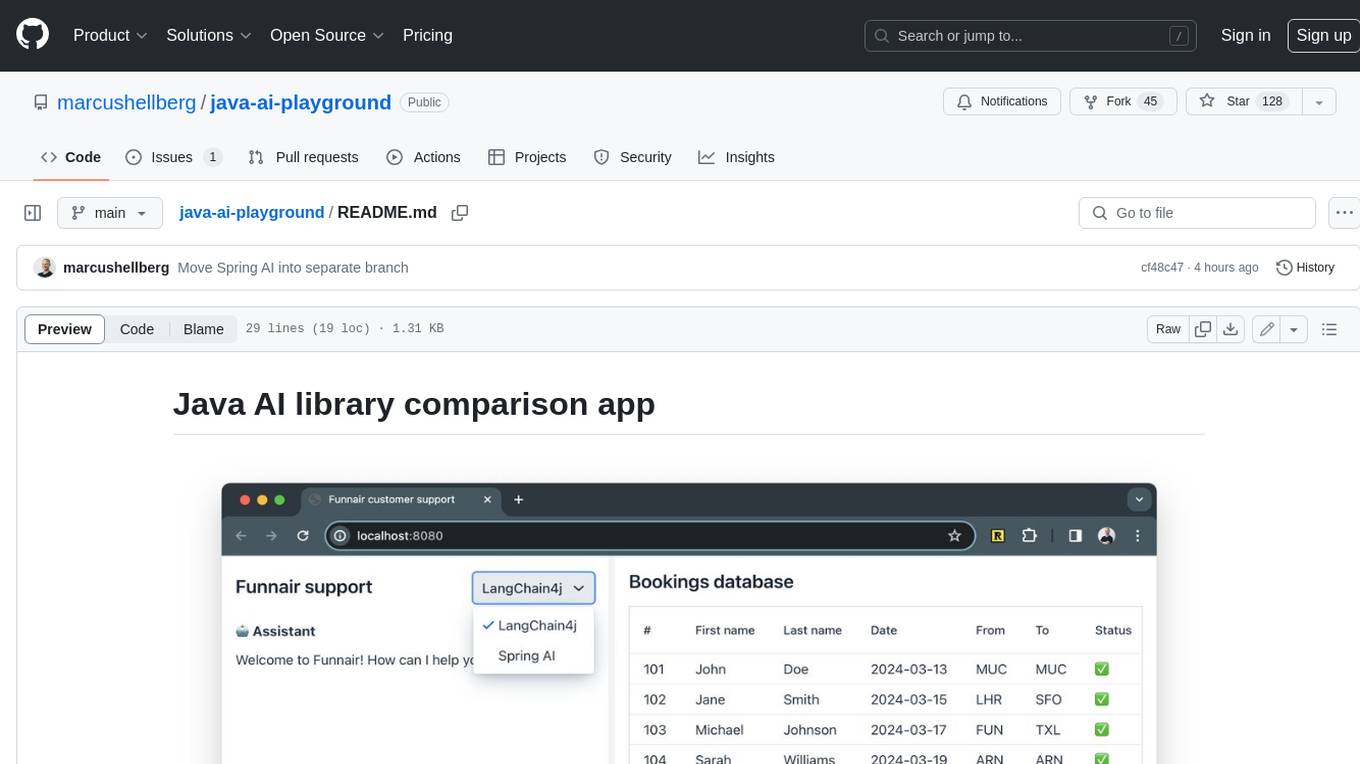
java-ai-playground
This AI-powered customer support application has access to terms and conditions (retrieval augmented generation, RAG), can access tools (Java methods) to perform actions, and uses an LLM to interact with the user. The application includes implementations for LangChain4j in the `main` branch and Spring AI in the `spring-ai` branch. The UI is built using Vaadin Hilla and the backend is built using Spring Boot.
robusta
Robusta is a tool designed to enhance Prometheus notifications for Kubernetes environments. It offers features such as smart grouping to reduce notification spam, AI investigation for alert analysis, alert enrichment with additional data like pod logs, self-healing capabilities for defining auto-remediation rules, advanced routing options, problem detection without PromQL, change-tracking for Kubernetes resources, auto-resolve functionality, and integration with various external systems like Slack, Teams, and Jira. Users can utilize Robusta with or without Prometheus, and it can be installed alongside existing Prometheus setups or as part of an all-in-one Kubernetes observability stack.
go-embeddings
This project provides API clients for fetching embeddings from various LLM providers. It includes implementations for OpenAI, Cohere, Google Vertex, VoyageAI, Ollama, and AWS Bedrock. Sample programs demonstrate how to use the client packages. The 'document' package offers text splitters inspired by Langchain framework. Environment variables are used to initialize API clients for each provider. Contributions are welcome.
software-agent-sdk
The OpenHands Software Agent SDK is a set of Python and REST APIs for building agents that work with code. It allows users to perform one-off tasks, routine maintenance tasks, and major tasks involving multiple agents. Agents can use the local machine or run in ephemeral workspaces like Docker or Kubernetes. The SDK can also be used to create new developer experiences, powering tools like the OpenHands CLI and OpenHands Cloud.
basilic
Basilic is a full-stack monorepo starter designed for teams developing Web3 and AI applications. It provides SDKs, public APIs, and multichain support to accelerate feature shipping. The starter includes AI-first development workflows, REST API with JWT authentication, SDK generation, Web3 and AI templates, design system, preconfigured development tools, security measures, multichain support, and TypeScript-first approach. It offers a technology stack covering AI, frontend, backend, Web3, and DevOps, along with various apps, packages, and scripts for setup, formatting, linting, testing, security, hooks, and miscellaneous tasks.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.