
clearml-fractional-gpu
ClearML Fractional GPU - Run multiple containers on the same GPU with driver level memory limitation ✨ and compute time-slicing
Stars: 56
ClearML Fractional GPU is a tool designed to optimize GPU resource utilization by allowing multiple containers to run on the same GPU with driver-level memory limitation and compute time-slicing. It supports CUDA 11.x & CUDA 12.x, preventing greedy processes from grabbing the entire GPU memory. The tool offers options like Dynamic GPU Slicing, Container-based Memory Limits, and Kubernetes-based Static MIG Slicing to enhance hardware utilization and workload performance for AI development.
README:
Run multiple containers on the same GPU with driver level memory limitation ✨ and compute time-slicing 🎊
🌟 Leave a star to support the project! 🌟
Sharing high-end GPUs or even prosumer & consumer GPUs between multiple users is the most cost-effective
way to accelerate AI development. Unfortunately, until now the
only existing solution applied for MIG/Slicing high-end GPUs (A100+) and required Kubernetes,
🔥 🎉 Welcome To Container Based Fractional GPU For Any Nvidia Card! 🎉 🔥
We present pre-packaged containers supporting CUDA 11.x & CUDA 12.x with pre-built hard memory limitation! This means multiple containers can be launched on the same GPU, ensuring one user cannot allocate the entire host GPU memory! (No more greedy processes grabbing the entire GPU memory! Finally we have a driver level hard limiting memory option).
ClearML offers several options to optimize GPU resource utilization by partitioning GPUs:
- Dynamic GPU Slicing: On-demand GPU slicing per task for both MIG and non-MIG devices (available under the ClearML Enterprise plan):
- Container-based Memory Limits (this repository): Use pre-packaged containers with built-in memory limits to run multiple containers on the same GPU (available as part of the ClearML open source offering).
- Kubernetes-based Static MIG Slicing: Set up Kubernetes support for NVIDIA MIG (Multi-Instance GPU) to define GPU fractions for specific workloads (available as part of the ClearML open source offering).
With these options, ClearML enables running AI workloads with optimized hardware utilization and workload performance. This repository covers container-based fractional GPUs. For more information on ClearML's fractional GPU offerings, see the ClearML documentation.
Pick the container that works for you and launch it:
docker run -it --gpus 0 --ipc=host --pid=host clearml/fractional-gpu:u22-cu12.3-8gb bashTo verify fraction GPU memory limit is working correctly, run inside the container:
nvidia-smiHere is an example output from A100 GPU:
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 545.23.08 Driver Version: 545.23.08 CUDA Version: 12.3 |
|-----------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M | Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap | Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|=========================================+======================+======================|
| 0 A100-PCIE-40GB Off | 00000000:01:00.0 Off | N/A |
| 32% 33C P0 66W / 250W | 0MiB / 8128MiB | 3% Default |
| | | Disabled |
+-----------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: |
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
| ID ID Usage |
|=======================================================================================|
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Memory Limit | CUDA Ver | Ubuntu Ver | Docker Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 GiB | 12.3 | 22.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u22-cu12.3-12gb |
| 12 GiB | 12.3 | 20.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u20-cu12.3-12gb |
| 12 GiB | 11.7 | 22.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u22-cu11.7-12gb |
| 12 GiB | 11.1 | 20.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u20-cu11.1-12gb |
| 8 GiB | 12.3 | 22.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u22-cu12.3-8gb |
| 8 GiB | 12.3 | 20.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u20-cu12.3-8gb |
| 8 GiB | 11.7 | 22.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u22-cu11.7-8gb |
| 8 GiB | 11.1 | 20.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u20-cu11.1-8gb |
| 4 GiB | 12.3 | 22.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u22-cu12.3-4gb |
| 4 GiB | 12.3 | 20.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u20-cu12.3-4gb |
| 4 GiB | 11.7 | 22.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u22-cu11.7-4gb |
| 4 GiB | 11.1 | 20.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u20-cu11.1-4gb |
| 2 GiB | 12.3 | 22.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u22-cu12.3-2gb |
| 2 GiB | 12.3 | 20.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u20-cu12.3-2gb |
| 2 GiB | 11.7 | 22.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u22-cu11.7-2gb |
| 2 GiB | 11.1 | 20.04 | clearml/fractional-gpu:u20-cu11.1-2gb |
[!IMPORTANT]
You must execute the container with
--pid=host!
[!NOTE]
--pid=hostis required to allow the driver to differentiate between the container's processes and other host processes when limiting memory / utilization usage
[!TIP]
ClearML-Agent users add
[--pid=host]to youragent.extra_docker_argumentssection in your config file
Build your own containers and inherit form the original containers.
You can find a few examples here.
Fractional GPU containers can be used on bare-metal executions as well as Kubernetes PODs. Yes! By using one of the Fractional GPU containers you can limit the memory consumption of your Job/Pod and easily share GPUs without fearing they will memory crash one another!
Here's a simple Kubernetes POD template:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: train-pod
labels:
app: trainme
spec:
hostPID: true
containers:
- name: train-container
image: clearml/fractional-gpu:u22-cu12.3-8gb
command: ['python3', '-c', 'print(f"Free GPU Memory: (free, global) {torch.cuda.mem_get_info()}")'][!IMPORTANT]
You must execute the pod with
hostPID: true!
[!NOTE]
hostPID: trueis required to allow the driver to differentiate between the pod's processes and other host processes when limiting memory / utilization usage
The containers support Nvidia drivers <= 545.x.x.
We will keep updating & supporting new drivers as they continue to be released
Supported GPUs: RTX series 10, 20, 30, 40, A series, and Data-Center P100, A100, A10/A40, L40/s, H100
Limitations: Windows Host machines are currently not supported. If this is important for you, leave a request in the Issues section
-
Q: Will running
nvidia-smiinside the container report the local processes GPU consumption?
A: Yes,nvidia-smiis communicating directly with the low-level drivers and reports both accurate container GPU memory as well as the container local memory limitation.
Notice GPU utilization will be the global (i.e. host side) GPU utilization and not the specific local container GPU utilization. -
Q: How do I make sure my Python / Pytorch / Tensorflow are actually memory limited?
A: For PyTorch you can run:
import torch
print(f'Free GPU Memory: (free, global) {torch.cuda.mem_get_info()}')Numba example:
from numba import cuda
print(f'Free GPU Memory: {cuda.current_context().get_memory_info()}')-
Q: Can the limitation be broken by a user?
A: We are sure a malicious user will find a way. It was never our intention to protect against malicious users.
If you have a malicious user with access to your machines, fractional GPUs are not your number 1 problem 😃 -
Q: How can I programmatically detect the memory limitation?
A: You can check the OS environment variableGPU_MEM_LIMIT_GB.
Notice that changing it will not remove or reduce the limitation. -
Q: Is running the container with
--pid=hostsecure / safe?
A: It should be both secure and safe. The main caveat from a security perspective is that a container process can see any command line running on the host system. If a process command line contains a "secret" then yes, this might become a potential data leak. Notice that passing "secrets" in the command line is ill-advised, and hence we do not consider it a security risk. That said if security is key, the enterprise edition (see below) eliminate the need to run withpid-hostand thus fully secure. -
Q: Can you run the container without
--pid=host?
A: You can! But you will have to use the enterprise version of the clearml-fractional-gpu container (otherwise the memory limit is applied system wide instead of container wide). If this feature is important for you, please contact ClearML sales & support.
The license to use ClearML is granted for research or development purposes only. ClearML may be used for educational, personal, or internal commercial use.
An expanded Commercial license for use within a product or service is available as part of the ClearML Scale or Enterprise solution.
ClearML offers enterprise and commercial license adding many additional features on top of fractional GPUs, these include orchestration, priority queues, quota management, compute cluster dashboard, dataset management & experiment management, as well as enterprise grade security and support. Learn more about ClearML Orchestration or talk to us directly at ClearML sales.
Tell everyone about it! #ClearMLFractionalGPU
Join our Slack Channel
Tell us when things are not working, and help us debug it on the Issues Page
This product is brought to you by the ClearML team with ❤️
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for clearml-fractional-gpu
Similar Open Source Tools

clearml-fractional-gpu
ClearML Fractional GPU is a tool designed to optimize GPU resource utilization by allowing multiple containers to run on the same GPU with driver-level memory limitation and compute time-slicing. It supports CUDA 11.x & CUDA 12.x, preventing greedy processes from grabbing the entire GPU memory. The tool offers options like Dynamic GPU Slicing, Container-based Memory Limits, and Kubernetes-based Static MIG Slicing to enhance hardware utilization and workload performance for AI development.
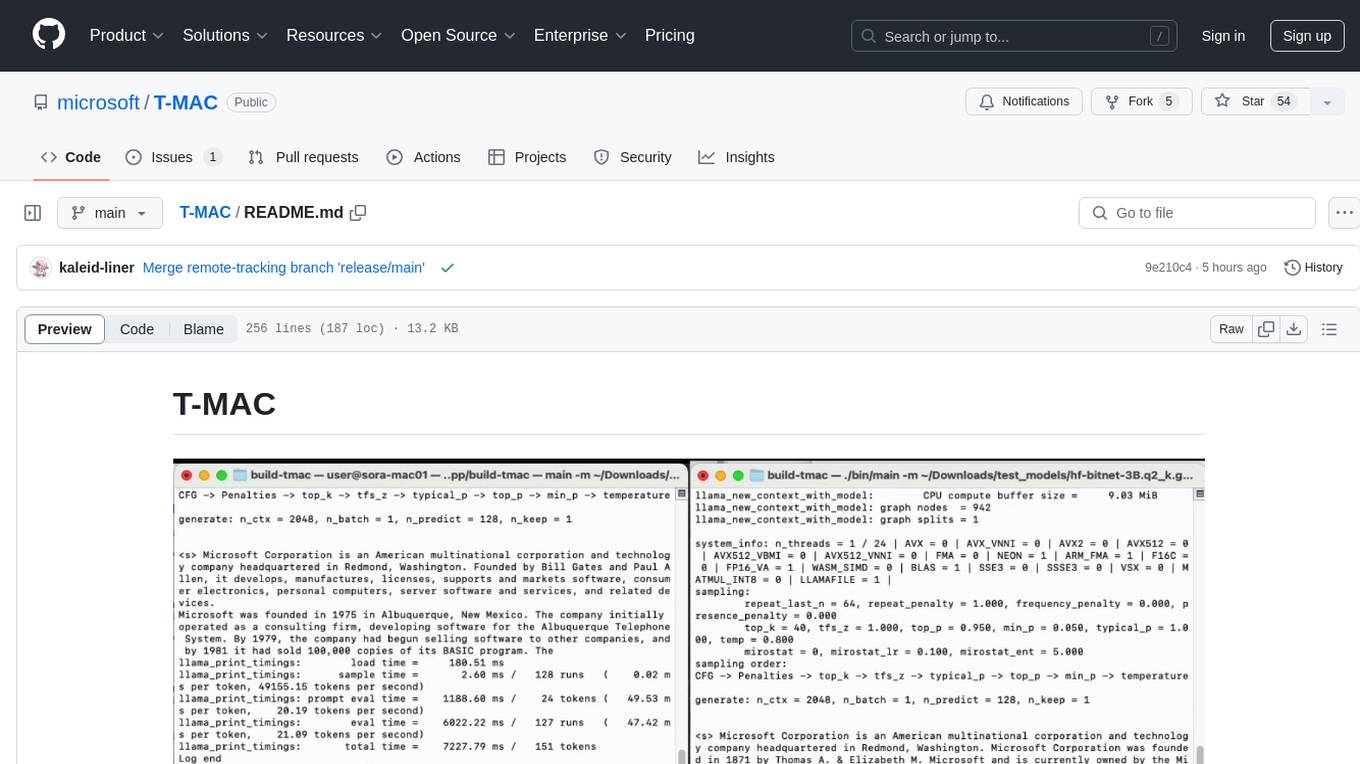
T-MAC
T-MAC is a kernel library that directly supports mixed-precision matrix multiplication without the need for dequantization by utilizing lookup tables. It aims to boost low-bit LLM inference on CPUs by offering support for various low-bit models. T-MAC achieves significant speedup compared to SOTA CPU low-bit framework (llama.cpp) and can even perform well on lower-end devices like Raspberry Pi 5. The tool demonstrates superior performance over existing low-bit GEMM kernels on CPU, reduces power consumption, and provides energy savings. It achieves comparable performance to CUDA GPU on certain tasks while delivering considerable power and energy savings. T-MAC's method involves using lookup tables to support mpGEMM and employs key techniques like precomputing partial sums, shift and accumulate operations, and utilizing tbl/pshuf instructions for fast table lookup.
zo2
ZO2 (Zeroth-Order Offloading) is an innovative framework designed to enhance the fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs) using zeroth-order (ZO) optimization techniques and advanced offloading technologies. It is tailored for setups with limited GPU memory, enabling the fine-tuning of models with over 175 billion parameters on single GPUs with as little as 18GB of memory. ZO2 optimizes CPU offloading, incorporates dynamic scheduling, and has the capability to handle very large models efficiently without extra time costs or accuracy losses.

Qwen
Qwen is a series of large language models developed by Alibaba DAMO Academy. It outperforms the baseline models of similar model sizes on a series of benchmark datasets, e.g., MMLU, C-Eval, GSM8K, MATH, HumanEval, MBPP, BBH, etc., which evaluate the models’ capabilities on natural language understanding, mathematic problem solving, coding, etc. Qwen models outperform the baseline models of similar model sizes on a series of benchmark datasets, e.g., MMLU, C-Eval, GSM8K, MATH, HumanEval, MBPP, BBH, etc., which evaluate the models’ capabilities on natural language understanding, mathematic problem solving, coding, etc. Qwen-72B achieves better performance than LLaMA2-70B on all tasks and outperforms GPT-3.5 on 7 out of 10 tasks.
FlexFlow
FlexFlow Serve is an open-source compiler and distributed system for **low latency**, **high performance** LLM serving. FlexFlow Serve outperforms existing systems by 1.3-2.0x for single-node, multi-GPU inference and by 1.4-2.4x for multi-node, multi-GPU inference.
text-embeddings-inference
Text Embeddings Inference (TEI) is a toolkit for deploying and serving open source text embeddings and sequence classification models. TEI enables high-performance extraction for popular models like FlagEmbedding, Ember, GTE, and E5. It implements features such as no model graph compilation step, Metal support for local execution on Macs, small docker images with fast boot times, token-based dynamic batching, optimized transformers code for inference using Flash Attention, Candle, and cuBLASLt, Safetensors weight loading, and production-ready features like distributed tracing with Open Telemetry and Prometheus metrics.
exllamav2
ExLlamaV2 is an inference library designed for running local LLMs on modern consumer GPUs. The library supports paged attention via Flash Attention 2.5.7+, offers a new dynamic generator with features like dynamic batching, smart prompt caching, and K/V cache deduplication. It also provides an API for local or remote inference using TabbyAPI, with extended features like HF model downloading and support for HF Jinja2 chat templates. ExLlamaV2 aims to optimize performance and speed across different GPU models, with potential future optimizations and variations in speeds. The tool can be integrated with TabbyAPI for OpenAI-style web API compatibility and supports a standalone web UI called ExUI for single-user interaction with chat and notebook modes. ExLlamaV2 also offers support for text-generation-webui and lollms-webui through specific loaders and bindings.
exllamav2
ExLlamaV2 is an inference library for running local LLMs on modern consumer GPUs. It is a faster, better, and more versatile codebase than its predecessor, ExLlamaV1, with support for a new quant format called EXL2. EXL2 is based on the same optimization method as GPTQ and supports 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8-bit quantization. It allows for mixing quantization levels within a model to achieve any average bitrate between 2 and 8 bits per weight. ExLlamaV2 can be installed from source, from a release with prebuilt extension, or from PyPI. It supports integration with TabbyAPI, ExUI, text-generation-webui, and lollms-webui. Key features of ExLlamaV2 include: - Faster and better kernels - Cleaner and more versatile codebase - Support for EXL2 quantization format - Integration with various web UIs and APIs - Community support on Discord
AQLM
AQLM is the official PyTorch implementation for Extreme Compression of Large Language Models via Additive Quantization. It includes prequantized AQLM models without PV-Tuning and PV-Tuned models for LLaMA, Mistral, and Mixtral families. The repository provides inference examples, model details, and quantization setups. Users can run prequantized models using Google Colab examples, work with different model families, and install the necessary inference library. The repository also offers detailed instructions for quantization, fine-tuning, and model evaluation. AQLM quantization involves calibrating models for compression, and users can improve model accuracy through finetuning. Additionally, the repository includes information on preparing models for inference and contributing guidelines.
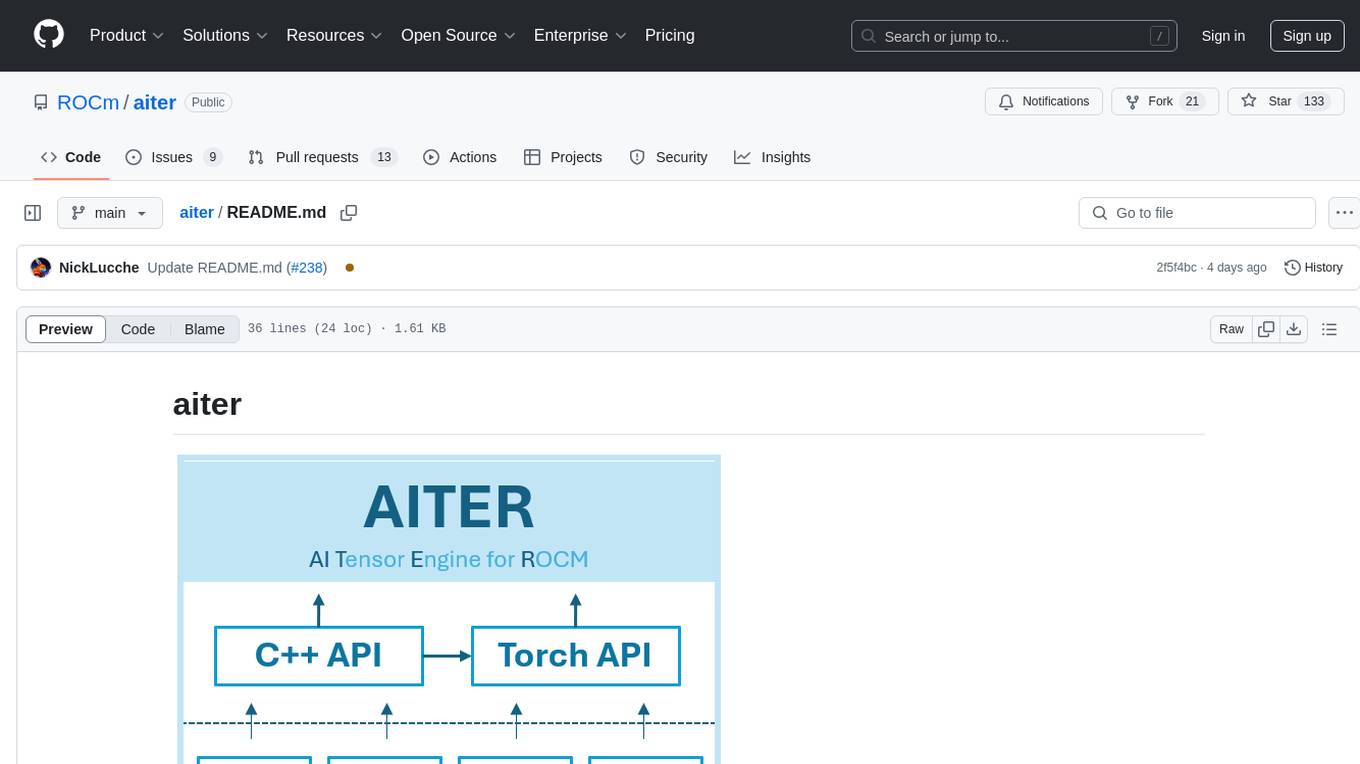
aiter
AITER is AMD’s centralized repository that supports various high performance AI operators for AI workloads acceleration. It serves as a unified platform for customer operator-level requests, catering to different customer needs. Developers can focus on operators and customers can integrate this collection into their own frameworks. Features include C++ and Python level APIs, kernels from triton/ck/asm, support for inference, training, GEMM, and communication kernels for workarounds in any kernel-framework combination for any architecture limitation.
r2ai
r2ai is a tool designed to run a language model locally without internet access. It can be used to entertain users or assist in answering questions related to radare2 or reverse engineering. The tool allows users to prompt the language model, index large codebases, slurp file contents, embed the output of an r2 command, define different system-level assistant roles, set environment variables, and more. It is accessible as an r2lang-python plugin and can be scripted from various languages. Users can use different models, adjust query templates dynamically, load multiple models, and make them communicate with each other.
llama-coder
Llama Coder is a self-hosted Github Copilot replacement for VS Code that provides autocomplete using Ollama and Codellama. It works best with Mac M1/M2/M3 or RTX 4090, offering features like fast performance, no telemetry or tracking, and compatibility with any coding language. Users can install Ollama locally or on a dedicated machine for remote usage. The tool supports different models like stable-code and codellama with varying RAM/VRAM requirements, allowing users to optimize performance based on their hardware. Troubleshooting tips and a changelog are also provided for user convenience.
cambrian
Cambrian-1 is a fully open project focused on exploring multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) with a vision-centric approach. It offers competitive performance across various benchmarks with models at different parameter levels. The project includes training configurations, model weights, instruction tuning data, and evaluation details. Users can interact with Cambrian-1 through a Gradio web interface for inference. The project is inspired by LLaVA and incorporates contributions from Vicuna, LLaMA, and Yi. Cambrian-1 is licensed under Apache 2.0 and utilizes datasets and checkpoints subject to their respective original licenses.
tts-generation-webui
TTS Generation WebUI is a comprehensive tool that provides a user-friendly interface for text-to-speech and voice cloning tasks. It integrates various AI models such as Bark, MusicGen, AudioGen, Tortoise, RVC, Vocos, Demucs, SeamlessM4T, and MAGNeT. The tool offers one-click installers, Google Colab demo, videos for guidance, and extra voices for Bark. Users can generate audio outputs, manage models, caches, and system space for AI projects. The project is open-source and emphasizes ethical and responsible use of AI technology.
open-chatgpt
Open-ChatGPT is an open-source library that enables users to train a hyper-personalized ChatGPT-like AI model using their own data with minimal computational resources. It provides an end-to-end training framework for ChatGPT-like models, supporting distributed training and offloading for extremely large models. The project implements RLHF (Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback) powered by transformer library and DeepSpeed, allowing users to create high-quality ChatGPT-style models. Open-ChatGPT is designed to be user-friendly and efficient, aiming to empower users to develop their own conversational AI models easily.
LLamaSharp
LLamaSharp is a cross-platform library to run 🦙LLaMA/LLaVA model (and others) on your local device. Based on llama.cpp, inference with LLamaSharp is efficient on both CPU and GPU. With the higher-level APIs and RAG support, it's convenient to deploy LLM (Large Language Model) in your application with LLamaSharp.
For similar tasks

clearml-fractional-gpu
ClearML Fractional GPU is a tool designed to optimize GPU resource utilization by allowing multiple containers to run on the same GPU with driver-level memory limitation and compute time-slicing. It supports CUDA 11.x & CUDA 12.x, preventing greedy processes from grabbing the entire GPU memory. The tool offers options like Dynamic GPU Slicing, Container-based Memory Limits, and Kubernetes-based Static MIG Slicing to enhance hardware utilization and workload performance for AI development.

tensor-fusion
Tensor Fusion is a state-of-the-art GPU virtualization and pooling solution designed to optimize GPU cluster utilization. It offers features like fractional virtual GPU, remote GPU sharing, GPU-first scheduling, GPU oversubscription, GPU pooling, monitoring, live migration, and more. The tool aims to enhance GPU utilization efficiency and streamline AI infrastructure management for organizations.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
