
SimpleAICV_pytorch_training_examples
SimpleAICV:pytorch training and testing examples.
Stars: 429
SimpleAICV_pytorch_training_examples is a repository that provides simple training and testing examples for various computer vision tasks such as image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation, instance segmentation, knowledge distillation, contrastive learning, masked image modeling, OCR text detection, OCR text recognition, human matting, salient object detection, interactive segmentation, image inpainting, and diffusion model tasks. The repository includes support for multiple datasets and networks, along with instructions on how to prepare datasets, train and test models, and use gradio demos. It also offers pretrained models and experiment records for download from huggingface or Baidu-Netdisk. The repository requires specific environments and package installations to run effectively.
README:
- 📢 News!
- My column
- Introduction
- All task training results
- Environments
- Download my pretrained models and experiments records
- Prepare datasets
- How to train or test a model
- How to use gradio demo
- Reference
- Citation
- 2025/02/16: train light segment-anything model with bf16.
https://www.zhihu.com/column/c_1692623656205897728
This repository provides simple training and testing examples for following tasks:
| task | support dataset | support network |
|---|---|---|
| Image classification task | CIFAR100 ImageNet1K(ILSVRC2012) ImageNet21K(Winter 2021 release) |
Convformer DarkNet ResNet VAN ViT |
| Knowledge distillation task | ImageNet1K(ILSVRC2012) | DML loss(ResNet) KD loss(ResNet) |
| Masked image modeling task | ImageNet1K(ILSVRC2012) | MAE(ViT) |
| Object detection task | COCO2017 Objects365(v2,2020) VOC2007 and VOC2012 |
DETR DINO-DETR RetinaNet FCOS |
| Semantic segmentation task | ADE20K COCO2017 |
DeepLabv3+ |
| Instance segmentation task | COCO2017 | SOLOv2 YOLACT |
| Salient object detection task | combine dataset | pfan-segmentation |
| Human matting task | combine dataset | pfan-matting |
| OCR text detection task | combine dataset | DBNet |
| OCR text recognition task | combine dataset | CTC Model |
| Face detection task | combine dataset | RetinaFace |
| Face parsing task | FaceSynthetics CelebAMask-HQ |
pfan-face-parsing sapiens_face_parsing |
| Human parsing task | LIP CIHP |
pfan-human-parsing sapiens_human_parsing |
| Interactive segmentation task | combine dataset | SAM(segment-anything) light_sam light_sam_matting |
| Diffusion model task | CelebA-HQ CIFAR10 CIFAR100 FFHQ |
DDPM DDIM |
Most experiments were trained on 2-8 RTX4090D GPUs, pytorch2.3, ubuntu22.04.
See all task training results in results.md.
1、This repository only supports running on ubuntu(verison>=22.04 LTS).
2、This repository only support one node one gpu/one node multi gpus mode with pytorch DDP training.
3、Please make sure your Python environment version>=3.9 and pytorch version>=2.0.
4、If you want to use torch.complie() function,using pytorch2.0/2.2/2.3,don't use pytorch2.1.
Use pip or conda to install those Packages in your Python environment:
torch
torchvision
pillow
numpy
Cython
pycocotools
opencv-python
scipy
einops
scikit-image
pyclipper
shapely
imagesize
nltk
tqdm
yapf
onnx
onnxruntime
onnxsim
thop==0.1.1.post2209072238
gradio==3.50.0
transformers==4.41.2
open-clip-torch==2.24.0
If you want to use xformers,install xformers Packge from offical github repository:
https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers
If you want to use dino-detr model,install MultiScaleDeformableAttention Packge in your Python environment:
cd to simpleAICV/detection/compile_multiscale_deformable_attention,then run commands:
chmod +x make.sh
./make.sh
You can download all my pretrained models and experiments records/checkpoints from huggingface or Baidu-Netdisk.
If you only want to download all my pretrained models(model.state_dict()),you can download pretrained_models folder.
# huggingface
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/0.classification_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/1.distillation_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/2.masked_image_modeling_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/3.detection_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/4.semantic_segmentation_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/5.instance_segmentation_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/6.salient_object_detection_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/7.human_matting_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/8.ocr_text_detection_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/9.ocr_text_recognition_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/10.face_detection_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/11.face_parsing_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/12.human_parsing_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/13.interactive_segmentation_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/20.diffusion_model_training/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/zgcr654321/pretrained_models/tree/main
# Baidu-Netdisk
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1yhEwaZhrb2NZRpJ5eEqHBw
提取码:rgdo
Make sure the folder architecture as follows:
CIFAR10
|
|-----batches.meta unzip from cifar-10-python.tar.gz
|-----data_batch_1 unzip from cifar-10-python.tar.gz
|-----data_batch_2 unzip from cifar-10-python.tar.gz
|-----data_batch_3 unzip from cifar-10-python.tar.gz
|-----data_batch_4 unzip from cifar-10-python.tar.gz
|-----data_batch_5 unzip from cifar-10-python.tar.gz
|-----readme.html unzip from cifar-10-python.tar.gz
|-----test_batch unzip from cifar-10-python.tar.gz
Make sure the folder architecture as follows:
CIFAR100
|
|-----train unzip from cifar-100-python.tar.gz
|-----test unzip from cifar-100-python.tar.gz
|-----meta unzip from cifar-100-python.tar.gz
Make sure the folder architecture as follows:
ILSVRC2012
|
|-----train----1000 sub classes folders
|-----val------1000 sub classes folders
Please make sure the same class has same class folder name in train and val folders.
Make sure the folder architecture as follows:
ImageNet21K
|
|-----train-----------10450 sub classes folders
|-----val-------------10450 sub classes folders
|-----small_classes---10450 sub classes folders
|-----imagenet21k_miil_tree.pth
Please make sure the same class has same class folder name in train and val folders.
Make sure the folder architecture as follows:
ACCV2022
|
|-----train-------------5000 sub classes folders
|-----testa-------------60000 images
|-----accv2022_broken_list.json
Make sure the folder architecture as follows:
VOCdataset
| |----Annotations
| |----ImageSets
|----VOC2007------|----JPEGImages
| |----SegmentationClass
| |----SegmentationObject
|
| |----Annotations
| |----ImageSets
|----VOC2012------|----JPEGImages
| |----SegmentationClass
| |----SegmentationObject
Make sure the folder architecture as follows:
COCO2017
| |----captions_train2017.json
| |----captions_val2017.json
|--annotations---|----instances_train2017.json
| |----instances_val2017.json
| |----person_keypoints_train2017.json
| |----person_keypoints_val2017.json
|
| |----train2017
|----images------|----val2017
Make sure the folder architecture as follows:
SAMA-COCO
| |----sama_coco_train.json
| |----sama_coco_validation.json
|--annotations---|----train_labels.json
| |----validation_labels.json
| |----test_labels.json
| |----image_info_test2017.json
| |----image_info_test-dev2017.json
|
| |----train
|----images------|----validation
Make sure the folder architecture as follows:
objects365_2020
|
| |----zhiyuan_objv2_train.json
|--annotations---|----zhiyuan_objv2_val.json
| |----sample_2020.json
|
| |----train all train patch folders
|----images------|----val all val patch folders
|----test all test patch folders
Make sure the folder architecture as follows:
ADE20K
| |----training
|---images--------|----validation
| |----testing
|
| |----training
|---annotations---|----validation
Make sure the folder architecture as follows:
CelebA-HQ
| |----female
|---train---------|----male
|
| |----female
|---val-----------|----male
Make sure the folder architecture as follows:
FFHQ
|
|---images
|---ffhq-dataset-v1.json
|---ffhq-dataset-v2.json
If you want to train or test a model,you need enter a training experiment folder directory,then run train.sh or test.sh.
For example,you can enter in folder classification_training/imagenet/resnet50.
If you want to restart train this model,please delete checkpoints and log folders first,then run train.sh:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node=2 --master_addr 127.0.1.0 --master_port 10000 ../../../tools/train_classification_model.py --work-dir ./
if you want to test this model,you need have a pretrained model first,modify trained_model_path in test_config.py,then run test.sh:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node=1 --master_addr 127.0.1.0 --master_port 10000 ../../../tools/test_classification_model.py --work-dir ./
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES is used to specify the gpu ids for this training.Please make sure the number of nproc_per_node equal to the number of using gpu cards.Make sure master_addr/master_port are unique for each training.
Checkpoints/log folders are saved in your executing training/testing experiment folder directory.
Also, You can modify super parameters in train_config.py/test_config.py.
cd to gradio_demo,we have:
classification demo
detection demo
semantic_segmentation demo
instance_segmentation demo
salient_object_detection demo
human_matting demo
text_detection demo
text_recognition demo
face_detection demo
face_parsing demo
human_parsing demo
point target segment_anything demo
circle target segment_anything demo
For example,you can run detection gradio demo(please prepare trained model weight first and modify model weight load path):
python gradio_detect_single_image.py
https://github.com/facebookresearch/segment-anything
https://github.com/facebookresearch/sam2
If you find my work useful in your research, please consider citing:
@inproceedings{zgcr,
title={SimpleAICV-pytorch-training-examples},
author={zgcr},
year={2020-2024}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for SimpleAICV_pytorch_training_examples
Similar Open Source Tools

SimpleAICV_pytorch_training_examples
SimpleAICV_pytorch_training_examples is a repository that provides simple training and testing examples for various computer vision tasks such as image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation, instance segmentation, knowledge distillation, contrastive learning, masked image modeling, OCR text detection, OCR text recognition, human matting, salient object detection, interactive segmentation, image inpainting, and diffusion model tasks. The repository includes support for multiple datasets and networks, along with instructions on how to prepare datasets, train and test models, and use gradio demos. It also offers pretrained models and experiment records for download from huggingface or Baidu-Netdisk. The repository requires specific environments and package installations to run effectively.
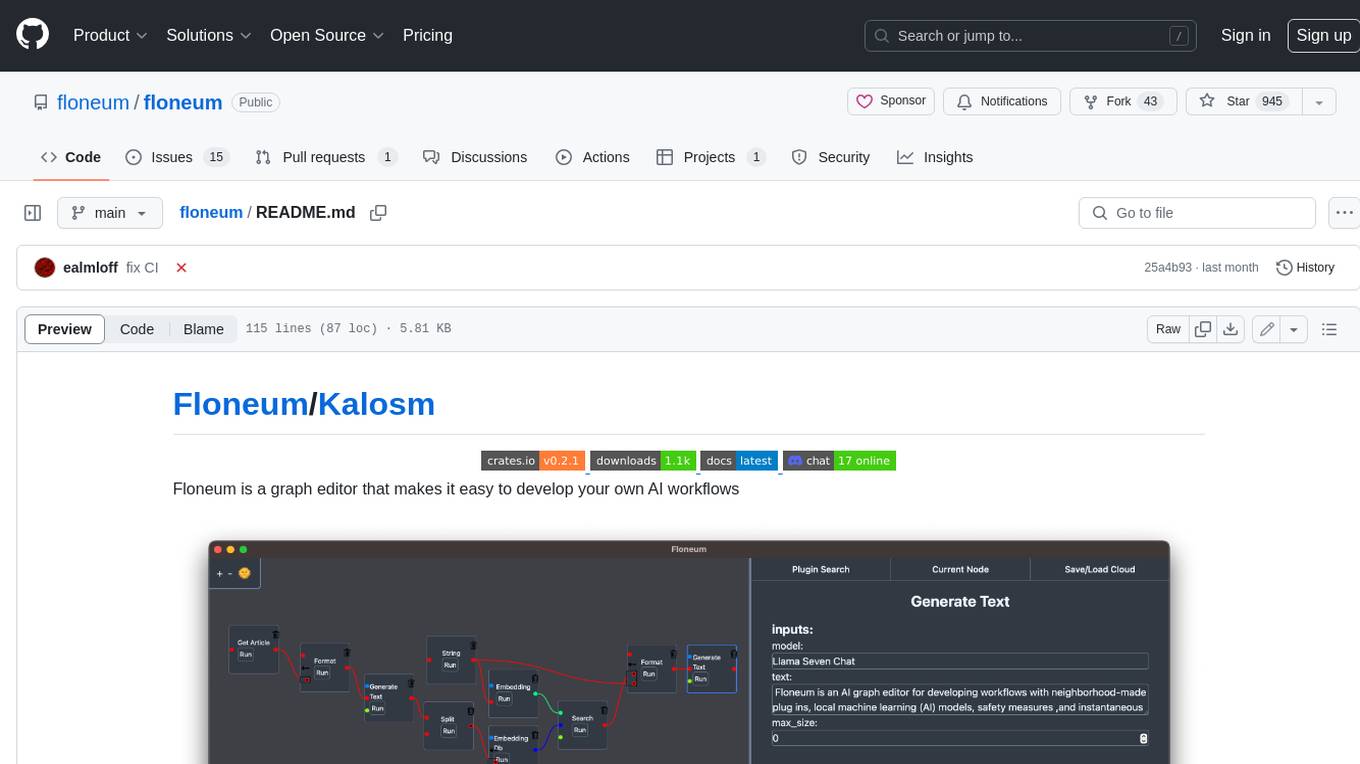
floneum
Floneum is a graph editor that makes it easy to develop your own AI workflows. It uses large language models (LLMs) to run AI models locally, without any external dependencies or even a GPU. This makes it easy to use LLMs with your own data, without worrying about privacy. Floneum also has a plugin system that allows you to improve the performance of LLMs and make them work better for your specific use case. Plugins can be used in any language that supports web assembly, and they can control the output of LLMs with a process similar to JSONformer or guidance.
llm-graph-builder
Knowledge Graph Builder App is a tool designed to convert PDF documents into a structured knowledge graph stored in Neo4j. It utilizes OpenAI's GPT/Diffbot LLM to extract nodes, relationships, and properties from PDF text content. Users can upload files from local machine or S3 bucket, choose LLM model, and create a knowledge graph. The app integrates with Neo4j for easy visualization and querying of extracted information.
TinyLLM
TinyLLM is a project that helps build a small locally hosted language model with a web interface using consumer-grade hardware. It supports multiple language models, builds a local OpenAI API web service, and serves a Chatbot web interface with customizable prompts. The project requires specific hardware and software configurations for optimal performance. Users can run a local language model using inference servers like vLLM, llama-cpp-python, and Ollama. The Chatbot feature allows users to interact with the language model through a web-based interface, supporting features like summarizing websites, displaying news headlines, stock prices, weather conditions, and using vector databases for queries.
gollama
Gollama is a delightful tool that brings Ollama, your offline conversational AI companion, directly into your terminal. It provides a fun and interactive way to generate responses from various models without needing internet connectivity. Whether you're brainstorming ideas, exploring creative writing, or just looking for inspiration, Gollama is here to assist you. The tool offers an interactive interface, customizable prompts, multiple models selection, and visual feedback to enhance user experience. It can be installed via different methods like downloading the latest release, using Go, running with Docker, or building from source. Users can interact with Gollama through various options like specifying a custom base URL, prompt, model, and enabling raw output mode. The tool supports different modes like interactive, piped, CLI with image, and TUI with image. Gollama relies on third-party packages like bubbletea, glamour, huh, and lipgloss. The roadmap includes implementing piped mode, support for extracting codeblocks, copying responses/codeblocks to clipboard, GitHub Actions for automated releases, and downloading models directly from Ollama using the rest API. Contributions are welcome, and the project is licensed under the MIT License.

zoonk
Zoonk is a web app designed for creating interactive courses using AI. Currently in early development stage, it is not yet ready for use but aims to be available for testing and contributions in the future. The project focuses on leveraging AI technology to enhance the learning experience by providing interactive course creation tools. Zoonk also conducts model evaluations on different prompts to improve its AI capabilities. The project has garnered support from various individuals who believe in its vision and potential.
thinc
Thinc is a lightweight deep learning library that offers an elegant, type-checked, functional-programming API for composing models, with support for layers defined in other frameworks such as PyTorch, TensorFlow and MXNet. You can use Thinc as an interface layer, a standalone toolkit or a flexible way to develop new models.
superduperdb
SuperDuperDB is a Python framework for integrating AI models, APIs, and vector search engines directly with your existing databases, including hosting of your own models, streaming inference and scalable model training/fine-tuning. Build, deploy and manage any AI application without the need for complex pipelines, infrastructure as well as specialized vector databases, and moving our data there, by integrating AI at your data's source: - Generative AI, LLMs, RAG, vector search - Standard machine learning use-cases (classification, segmentation, regression, forecasting recommendation etc.) - Custom AI use-cases involving specialized models - Even the most complex applications/workflows in which different models work together SuperDuperDB is **not** a database. Think `db = superduper(db)`: SuperDuperDB transforms your databases into an intelligent platform that allows you to leverage the full AI and Python ecosystem. A single development and deployment environment for all your AI applications in one place, fully scalable and easy to manage.

EvoAgentX
EvoAgentX is an open-source framework for building, evaluating, and evolving LLM-based agents or agentic workflows in an automated, modular, and goal-driven manner. It enables developers and researchers to move beyond static prompt chaining or manual workflow orchestration by introducing a self-evolving agent ecosystem. The framework includes features such as agent workflow autoconstruction, built-in evaluation, self-evolution engine, plug-and-play compatibility, comprehensive built-in tools, memory module support, and human-in-the-loop interactions.
clai
Clai is a command line context-feeder for AI tasks, supporting MCP client, vendor agnosticism, conversations, rate limit circumvention, profiles, and Unix-like functionality. Users can easily combine and tweak features for diverse use cases. Supported vendors include OpenAI, Anthropic, Mistral, Deepseek, Novita AI, Ollama, and Inception. Users need API keys for model access. Installation via 'go install' or setup script. 'clai help' provides guidance on usage. Glow can be installed for formatted markdown output.

FFAIVideo
FFAIVideo is a lightweight node.js project that utilizes popular AI LLM to intelligently generate short videos. It supports multiple AI LLM models such as OpenAI, Moonshot, Azure, g4f, Google Gemini, etc. Users can input text to automatically synthesize exciting video content with subtitles, background music, and customizable settings. The project integrates Microsoft Edge's online text-to-speech service for voice options and uses Pexels website for video resources. Installation of FFmpeg is essential for smooth operation. Inspired by MoneyPrinterTurbo, MoneyPrinter, and MsEdgeTTS, FFAIVideo is designed for front-end developers with minimal dependencies and simple usage.
vision-parse
Vision Parse is a tool that leverages Vision Language Models to parse PDF documents into beautifully formatted markdown content. It offers smart content extraction, content formatting, multi-LLM support, PDF document support, and local model hosting using Ollama. Users can easily convert PDFs to markdown with high precision and preserve document hierarchy and styling. The tool supports multiple Vision LLM providers like OpenAI, LLama, and Gemini for accuracy and speed, making document processing efficient and effortless.
airunner
AI Runner is a multi-modal AI interface that allows users to run open-source large language models and AI image generators on their own hardware. The tool provides features such as voice-based chatbot conversations, text-to-speech, speech-to-text, vision-to-text, text generation with large language models, image generation capabilities, image manipulation tools, utility functions, and more. It aims to provide a stable and user-friendly experience with security updates, a new UI, and a streamlined installation process. The application is designed to run offline on users' hardware without relying on a web server, offering a smooth and responsive user experience.
DB-GPT-Hub
DB-GPT-Hub is an experimental project leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Text-to-SQL parsing. It includes stages like data collection, preprocessing, model selection, construction, and fine-tuning of model weights. The project aims to enhance Text-to-SQL capabilities, reduce model training costs, and enable developers to contribute to improving Text-to-SQL accuracy. The ultimate goal is to achieve automated question-answering based on databases, allowing users to execute complex database queries using natural language descriptions. The project has successfully integrated multiple large models and established a comprehensive workflow for data processing, SFT model training, prediction output, and evaluation.
keras-llm-robot
The Keras-llm-robot Web UI project is an open-source tool designed for offline deployment and testing of various open-source models from the Hugging Face website. It allows users to combine multiple models through configuration to achieve functionalities like multimodal, RAG, Agent, and more. The project consists of three main interfaces: chat interface for language models, configuration interface for loading models, and tools & agent interface for auxiliary models. Users can interact with the language model through text, voice, and image inputs, and the tool supports features like model loading, quantization, fine-tuning, role-playing, code interpretation, speech recognition, image recognition, network search engine, and function calling.
pipeline
Pipeline is a Python library designed for constructing computational flows for AI/ML models. It supports both development and production environments, offering capabilities for inference, training, and finetuning. The library serves as an interface to Mystic, enabling the execution of pipelines at scale and on enterprise GPUs. Users can also utilize this SDK with Pipeline Core on a private hosted cluster. The syntax for defining AI/ML pipelines is reminiscent of sessions in Tensorflow v1 and Flows in Prefect.
For similar tasks

SimpleAICV_pytorch_training_examples
SimpleAICV_pytorch_training_examples is a repository that provides simple training and testing examples for various computer vision tasks such as image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation, instance segmentation, knowledge distillation, contrastive learning, masked image modeling, OCR text detection, OCR text recognition, human matting, salient object detection, interactive segmentation, image inpainting, and diffusion model tasks. The repository includes support for multiple datasets and networks, along with instructions on how to prepare datasets, train and test models, and use gradio demos. It also offers pretrained models and experiment records for download from huggingface or Baidu-Netdisk. The repository requires specific environments and package installations to run effectively.
MooER
MooER (摩耳) is an LLM-based speech recognition and translation model developed by Moore Threads. It allows users to transcribe speech into text (ASR) and translate speech into other languages (AST) in an end-to-end manner. The model was trained using 5K hours of data and is now also available with an 80K hours version. MooER is the first LLM-based speech model trained and inferred using domestic GPUs. The repository includes pretrained models, inference code, and a Gradio demo for a better user experience.
TPI-LLM
TPI-LLM (Tensor Parallelism Inference for Large Language Models) is a system designed to bring LLM functions to low-resource edge devices, addressing privacy concerns by enabling LLM inference on edge devices with limited resources. It leverages multiple edge devices for inference through tensor parallelism and a sliding window memory scheduler to minimize memory usage. TPI-LLM demonstrates significant improvements in TTFT and token latency compared to other models, and plans to support infinitely large models with low token latency in the future.
llm_recipes
This repository showcases the author's experiments with Large Language Models (LLMs) for text generation tasks. It includes dataset preparation, preprocessing, model fine-tuning using libraries such as Axolotl and HuggingFace, and model evaluation.
llm-leaderboard
Nejumi Leaderboard 3 is a comprehensive evaluation platform for large language models, assessing general language capabilities and alignment aspects. The evaluation framework includes metrics for language processing, translation, summarization, information extraction, reasoning, mathematical reasoning, entity extraction, knowledge/question answering, English, semantic analysis, syntactic analysis, alignment, ethics/moral, toxicity, bias, truthfulness, and robustness. The repository provides an implementation guide for environment setup, dataset preparation, configuration, model configurations, and chat template creation. Users can run evaluation processes using specified configuration files and log results to the Weights & Biases project.
OpenMusic
OpenMusic is a repository providing an implementation of QA-MDT, a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for music generation. The code integrates state-of-the-art models and offers training strategies for music generation. The repository includes implementations of AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. Users can train or fine-tune the model using different strategies and datasets. The model is well-pretrained and can be used for music generation tasks. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets, training the model, and performing inference. Contact information is provided for any questions or suggestions regarding the project.
llm-export
llm-export is a tool for exporting llm models to onnx and mnn formats. It has features such as passing onnxruntime correctness tests, optimizing the original code to support dynamic shapes, reducing constant parts, optimizing onnx models using OnnxSlim for performance improvement, and exporting lora weights to onnx and mnn formats. Users can clone the project locally, clone the desired LLM project locally, and use LLMExporter to export the model. The tool supports various export options like exporting the entire model as one onnx model, exporting model segments as multiple models, exporting model vocabulary to a text file, exporting specific model layers like Embedding and lm_head, testing the model with queries, validating onnx model consistency with onnxruntime, converting onnx models to mnn models, and more. Users can specify export paths, skip optimization steps, and merge lora weights before exporting.
Kolo
Kolo is a lightweight tool for fast and efficient data generation, fine-tuning, and testing of Large Language Models (LLMs) on your local machine. It simplifies the fine-tuning and data generation process, runs locally without the need for cloud-based services, and supports popular LLM toolkits. Kolo is built using tools like Unsloth, Torchtune, Llama.cpp, Ollama, Docker, and Open WebUI. It requires Windows 10 OS or higher, Nvidia GPU with CUDA 12.1 capability, and 8GB+ VRAM, and 16GB+ system RAM. Users can join the Discord group for issues or feedback. The tool provides easy setup, training data generation, and integration with major LLM frameworks.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.