
llm_recipes
A set of scripts and notebooks on LLM finetunning and dataset creation
Stars: 90
This repository showcases the author's experiments with Large Language Models (LLMs) for text generation tasks. It includes dataset preparation, preprocessing, model fine-tuning using libraries such as Axolotl and HuggingFace, and model evaluation.
README:
This repo contains my own exploration of the LLM world right now. I am interested mostly in fine-tuning LMs for text generation tasks. This implies:
- Dataset preparation and preprocessing
- Model fine-tuning with libraries like Axolotl, HuggingFace, etc.
- Model evaluation
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llm_recipes
Similar Open Source Tools

llm_recipes
This repository showcases the author's experiments with Large Language Models (LLMs) for text generation tasks. It includes dataset preparation, preprocessing, model fine-tuning using libraries such as Axolotl and HuggingFace, and model evaluation.
awesome-VLLMs
This repository contains a collection of pre-trained Very Large Language Models (VLLMs) that can be used for various natural language processing tasks. The models are fine-tuned on large text corpora and can be easily integrated into existing NLP pipelines for tasks such as text generation, sentiment analysis, and language translation. The repository also provides code examples and tutorials to help users get started with using these powerful language models in their projects.
llms-from-scratch-rs
This project provides Rust code that follows the text 'Build An LLM From Scratch' by Sebastian Raschka. It translates PyTorch code into Rust using the Candle crate, aiming to build a GPT-style LLM. Users can clone the repo, run examples/exercises, and access the same datasets as in the book. The project includes chapters on understanding large language models, working with text data, coding attention mechanisms, implementing a GPT model, pretraining unlabeled data, fine-tuning for classification, and fine-tuning to follow instructions.
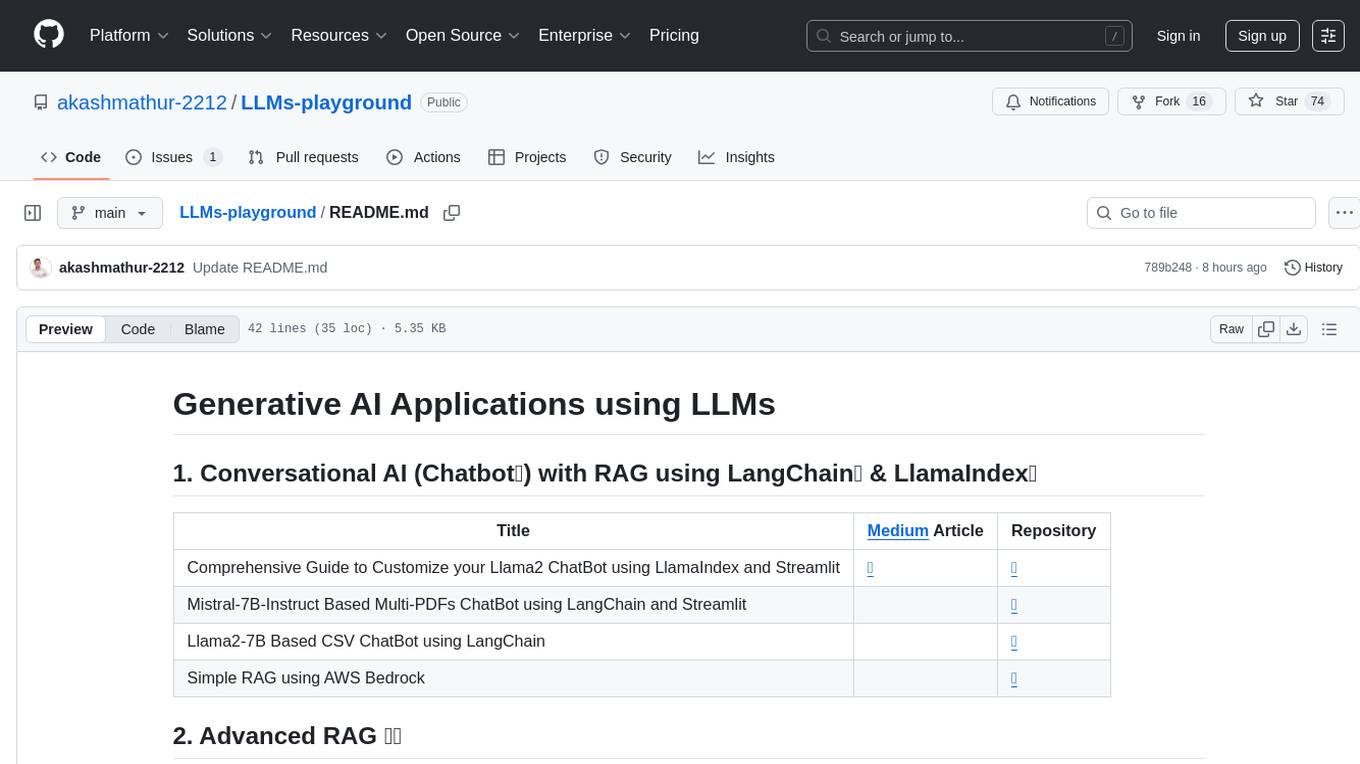
LLMs-playground
LLMs-playground is a repository containing code examples and tutorials for learning and experimenting with Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides a hands-on approach to understanding how LLMs work and how to fine-tune them for specific tasks. The repository covers various LLM architectures, pre-training techniques, and fine-tuning strategies, making it a valuable resource for researchers, students, and practitioners interested in natural language processing and machine learning. By exploring the code and following the tutorials, users can gain practical insights into working with LLMs and apply their knowledge to real-world projects.
graph-llm-asynchow-plan
Graph-enhanced Large Language Models in Asynchronous Plan Reasoning is a repository containing code and datasets for the ICML-2024 paper. It includes naturalistic datasets, code for generating data, benchmarking experiments, and prototypical experiments. The repository also offers a train/test-split version of the dataset on huggingface. The paper focuses on utilizing large language models with graph enhancements for asynchronous plan reasoning.
Main
This repository contains material related to the new book _Synthetic Data and Generative AI_ by the author, including code for NoGAN, DeepResampling, and NoGAN_Hellinger. NoGAN is a tabular data synthesizer that outperforms GenAI methods in terms of speed and results, utilizing state-of-the-art quality metrics. DeepResampling is a fast NoGAN based on resampling and Bayesian Models with hyperparameter auto-tuning. NoGAN_Hellinger combines NoGAN and DeepResampling with the Hellinger model evaluation metric.
awesome-LLM-resources
This repository is a curated list of resources for learning and working with Large Language Models (LLMs). It includes a collection of articles, tutorials, tools, datasets, and research papers related to LLMs such as GPT-3, BERT, and Transformer models. Whether you are a researcher, developer, or enthusiast interested in natural language processing and artificial intelligence, this repository provides valuable resources to help you understand, implement, and experiment with LLMs.
ai-tutor-rag-system
The AI Tutor RAG System repository contains Jupyter notebooks supporting the RAG course, focusing on enhancing AI models with retrieval-based methods. It covers foundational and advanced concepts in retrieval-augmented generation, including data retrieval techniques, model integration with retrieval systems, and practical applications of RAG in real-world scenarios.
intro-llm.github.io
Large Language Models (LLM) are language models built by deep neural networks containing hundreds of billions of weights, trained on a large amount of unlabeled text using self-supervised learning methods. Since 2018, companies and research institutions including Google, OpenAI, Meta, Baidu, and Huawei have released various models such as BERT, GPT, etc., which have performed well in almost all natural language processing tasks. Starting in 2021, large models have shown explosive growth, especially after the release of ChatGPT in November 2022, attracting worldwide attention. Users can interact with systems using natural language to achieve various tasks from understanding to generation, including question answering, classification, summarization, translation, and chat. Large language models demonstrate powerful knowledge of the world and understanding of language. This repository introduces the basic theory of large language models including language models, distributed model training, and reinforcement learning, and uses the Deepspeed-Chat framework as an example to introduce the implementation of large language models and ChatGPT-like systems.
Awesome-RAG
Awesome-RAG is a repository that lists recent developments in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for large language models (LLM). It includes accepted papers, evaluation datasets, latest news, and papers from various conferences like NIPS, EMNLP, ACL, ICML, and ICLR. The repository is continuously updated and aims to build a general framework for RAG. Researchers are encouraged to submit pull requests to update information in their papers. The repository covers a wide range of topics related to RAG, including knowledge-enhanced generation, contrastive reasoning, self-alignment, mobile agents, and more.
LLM-Fine-Tuning
This GitHub repository contains examples of fine-tuning open source large language models. It showcases the process of fine-tuning and quantizing large language models using efficient techniques like Lora and QLora. The repository serves as a practical guide for individuals looking to optimize the performance of language models through fine-tuning.
Langchain-Projects-LLM
Langchain-Projects-LLM is a repository containing various projects utilizing Large Language Models such as GPT and LLAMA from HuggingFace and OpenAI. Users need the OpenAI API to run these models.
amazon-sagemaker-generativeai
Repository for training and deploying Generative AI models, including text-text, text-to-image generation, prompt engineering playground and chain of thought examples using SageMaker Studio. The tool provides a platform for users to experiment with generative AI techniques, enabling them to create text and image outputs based on input data. It offers a range of functionalities for training and deploying models, as well as exploring different generative AI applications.
LLM-Project
LLM-Project is a machine learning model for sentiment analysis. It is designed to analyze text data and classify it into positive, negative, or neutral sentiments. The model uses natural language processing techniques to extract features from the text and train a classifier to make predictions. LLM-Project is suitable for researchers, developers, and data scientists who are working on sentiment analysis tasks. It provides a pre-trained model that can be easily integrated into existing projects or used for experimentation and research purposes. The codebase is well-documented and easy to understand, making it accessible to users with varying levels of expertise in machine learning and natural language processing.
PaddleNLP
PaddleNLP is an easy-to-use and high-performance NLP library. It aggregates high-quality pre-trained models in the industry and provides out-of-the-box development experience, covering a model library for multiple NLP scenarios with industry practice examples to meet developers' flexible customization needs.
DelhiLM
DelhiLM is a natural language processing tool for building and training language models. It provides a user-friendly interface for text processing tasks such as tokenization, lemmatization, and language model training. With DelhiLM, users can easily preprocess text data and train custom language models for various NLP applications. The tool supports different languages and allows for fine-tuning pre-trained models to suit specific needs. DelhiLM is designed to be flexible, efficient, and easy to use for both beginners and experienced NLP practitioners.
For similar tasks

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.
promptfoo
Promptfoo is a tool for testing and evaluating LLM output quality. With promptfoo, you can build reliable prompts, models, and RAGs with benchmarks specific to your use-case, speed up evaluations with caching, concurrency, and live reloading, score outputs automatically by defining metrics, use as a CLI, library, or in CI/CD, and use OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure, Google, HuggingFace, open-source models like Llama, or integrate custom API providers for any LLM API.
vespa
Vespa is a platform that performs operations such as selecting a subset of data in a large corpus, evaluating machine-learned models over the selected data, organizing and aggregating it, and returning it, typically in less than 100 milliseconds, all while the data corpus is continuously changing. It has been in development for many years and is used on a number of large internet services and apps which serve hundreds of thousands of queries from Vespa per second.
python-aiplatform
The Vertex AI SDK for Python is a library that provides a convenient way to use the Vertex AI API. It offers a high-level interface for creating and managing Vertex AI resources, such as datasets, models, and endpoints. The SDK also provides support for training and deploying custom models, as well as using AutoML models. With the Vertex AI SDK for Python, you can quickly and easily build and deploy machine learning models on Vertex AI.
ScandEval
ScandEval is a framework for evaluating pretrained language models on mono- or multilingual language tasks. It provides a unified interface for benchmarking models on a variety of tasks, including sentiment analysis, question answering, and machine translation. ScandEval is designed to be easy to use and extensible, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners alike.
opencompass
OpenCompass is a one-stop platform for large model evaluation, aiming to provide a fair, open, and reproducible benchmark for large model evaluation. Its main features include: * Comprehensive support for models and datasets: Pre-support for 20+ HuggingFace and API models, a model evaluation scheme of 70+ datasets with about 400,000 questions, comprehensively evaluating the capabilities of the models in five dimensions. * Efficient distributed evaluation: One line command to implement task division and distributed evaluation, completing the full evaluation of billion-scale models in just a few hours. * Diversified evaluation paradigms: Support for zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought evaluations, combined with standard or dialogue-type prompt templates, to easily stimulate the maximum performance of various models. * Modular design with high extensibility: Want to add new models or datasets, customize an advanced task division strategy, or even support a new cluster management system? Everything about OpenCompass can be easily expanded! * Experiment management and reporting mechanism: Use config files to fully record each experiment, and support real-time reporting of results.
flower
Flower is a framework for building federated learning systems. It is designed to be customizable, extensible, framework-agnostic, and understandable. Flower can be used with any machine learning framework, for example, PyTorch, TensorFlow, Hugging Face Transformers, PyTorch Lightning, scikit-learn, JAX, TFLite, MONAI, fastai, MLX, XGBoost, Pandas for federated analytics, or even raw NumPy for users who enjoy computing gradients by hand.
thinc
Thinc is a lightweight deep learning library that offers an elegant, type-checked, functional-programming API for composing models, with support for layers defined in other frameworks such as PyTorch, TensorFlow and MXNet. You can use Thinc as an interface layer, a standalone toolkit or a flexible way to develop new models.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.