
Main
Main folder. Material related to my books on synthetic data and generative AI. Also contains documents blending components from several folders, or covering topics spanning across multiple folders..
Stars: 66
This repository contains material related to the new book _Synthetic Data and Generative AI_ by the author, including code for NoGAN, DeepResampling, and NoGAN_Hellinger. NoGAN is a tabular data synthesizer that outperforms GenAI methods in terms of speed and results, utilizing state-of-the-art quality metrics. DeepResampling is a fast NoGAN based on resampling and Bayesian Models with hyperparameter auto-tuning. NoGAN_Hellinger combines NoGAN and DeepResampling with the Hellinger model evaluation metric.
README:
This repository features material related to content that spreads across multiple folders. For the time being, it is related to my new book Synthetic Data and Generative AI, available here, and published by Elsevier.
It also includes:
- NoGAN code, a tabular data synthesizer running 1000x faster than GenAI methods based on neural networks, and consistently delivering better results regardless of the evaluation metric (including state-of-the-art new quality metrics capturing a lot more than traditional distances), both on categorical and numerical features, or a mix of both. For details, see technical paper #29, available here.
- DeepResampling code, another fast NoGAN based on resampling and distribution-free Hierarchical Bayesian Models, with hyperparameter auto-tuning. For details, see technical paper #31, available here.
- NoGAN_Hellinger code (two scripts), with loss function replaced by the Hellinger model evaluation metric. A blend of NoGAN and DeepResampling. For details, see section 2.4 in the project textbook, here.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Main
Similar Open Source Tools

Main
This repository contains material related to the new book _Synthetic Data and Generative AI_ by the author, including code for NoGAN, DeepResampling, and NoGAN_Hellinger. NoGAN is a tabular data synthesizer that outperforms GenAI methods in terms of speed and results, utilizing state-of-the-art quality metrics. DeepResampling is a fast NoGAN based on resampling and Bayesian Models with hyperparameter auto-tuning. NoGAN_Hellinger combines NoGAN and DeepResampling with the Hellinger model evaluation metric.
matchem-llm
A public repository collecting links to state-of-the-art training sets, QA, benchmarks and other evaluations for various ML and LLM applications in materials science and chemistry. It includes datasets related to chemistry, materials, multimodal data, and knowledge graphs in the field. The repository aims to provide resources for training and evaluating machine learning models in the materials science and chemistry domains.
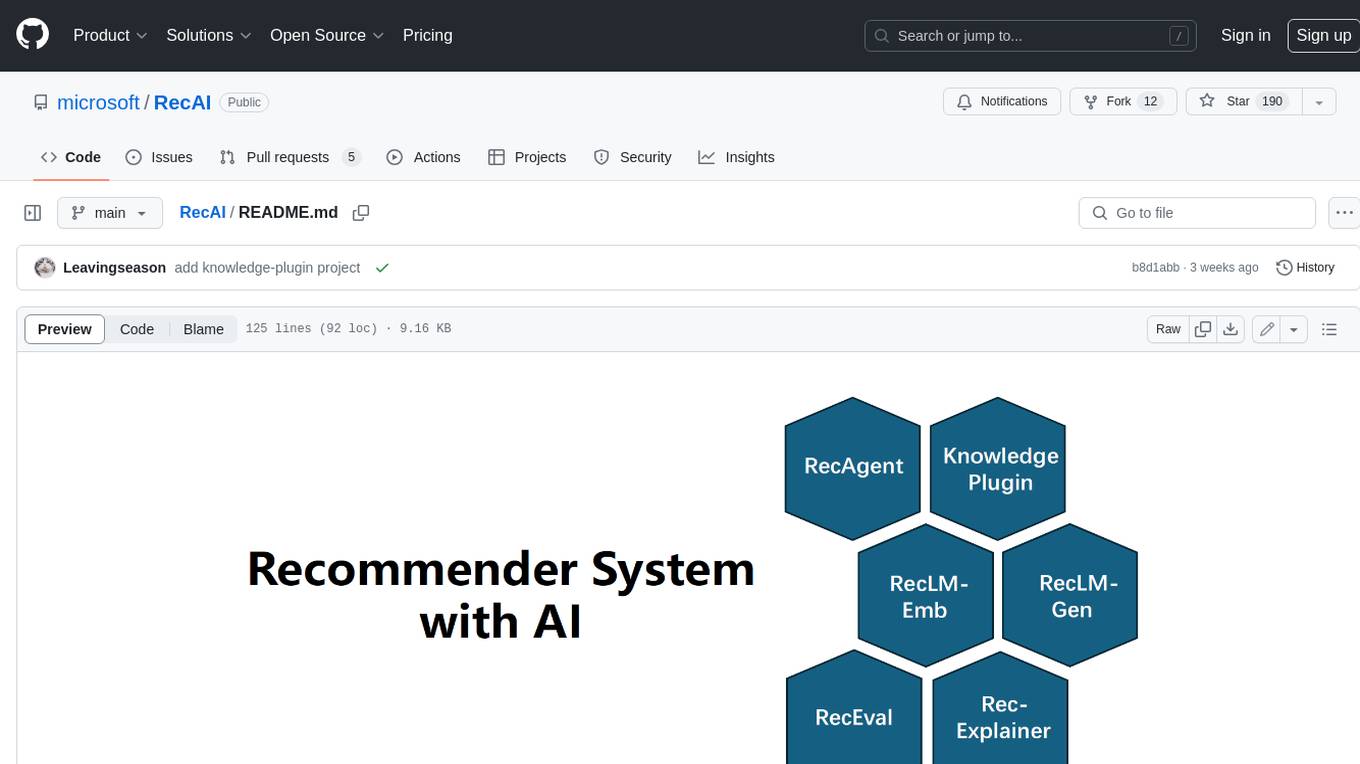
RecAI
RecAI is a project that explores the integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into recommender systems, addressing the challenges of interactivity, explainability, and controllability. It aims to bridge the gap between general-purpose LLMs and domain-specific recommender systems, providing a holistic perspective on the practical requirements of LLM4Rec. The project investigates various techniques, including Recommender AI agents, selective knowledge injection, fine-tuning language models, evaluation, and LLMs as model explainers, to create more sophisticated, interactive, and user-centric recommender systems.
public
This public repository contains API, tools, and packages for Datagrok, a web-based data analytics platform. It offers support for scientific domains, applications, connectors to web services, visualizations, file importing, scientific methods in R, Python, or Julia, file metadata extractors, custom predictive models, platform enhancements, and more. The open-source packages are free to use, with restrictions on server computational capacities for the public environment. Academic institutions can use Datagrok for research and education, benefiting from reproducible and scalable computations and data augmentation capabilities. Developers can contribute by creating visualizations, scientific methods, file editors, connectors to web services, and more.
miles-credit
CREDIT is an open software platform for training and deploying AI atmospheric prediction models. It offers fast models with flexible configuration options for input data and neural network architecture. The user-friendly interface enables quick setup and iteration. Developed by the MILES group and NSF National Center for Atmospheric Research, CREDIT combines advanced AI/ML with atmospheric science expertise. It provides a stable release with various models, training, and deployment options, with ongoing development. Detailed documentation is available for installation, training, deployment, config file interpretation, and API usage.
automatic-KG-creation-with-LLM
This repository presents a (semi-)automatic pipeline for Ontology and Knowledge Graph Construction using Large Language Models (LLMs) such as Mixtral 8x22B Instruct v0.1, GPT-4o, GPT-3.5, and Gemini. It explores the generation of Knowledge Graphs by formulating competency questions, developing ontologies, constructing KGs, and evaluating the results with minimal human involvement. The project showcases the creation of a KG on deep learning methodologies from scholarly publications. It includes components for data preprocessing, prompts for LLMs, datasets, and results from the selected LLMs.
ianvs
Ianvs is a distributed synergy AI benchmarking project incubated in KubeEdge SIG AI. It aims to test the performance of distributed synergy AI solutions following recognized standards, providing end-to-end benchmark toolkits, test environment management tools, test case control tools, and benchmark presentation tools. It also collaborates with other organizations to establish comprehensive benchmarks and related applications. The architecture includes critical components like Test Environment Manager, Test Case Controller, Generation Assistant, Simulation Controller, and Story Manager. Ianvs documentation covers quick start, guides, dataset descriptions, algorithms, user interfaces, stories, and roadmap.
lemonai
LemonAI is a versatile machine learning library designed to simplify the process of building and deploying AI models. It provides a wide range of tools and algorithms for data preprocessing, model training, and evaluation. With LemonAI, users can easily experiment with different machine learning techniques and optimize their models for various tasks. The library is well-documented and beginner-friendly, making it suitable for both novice and experienced data scientists. LemonAI aims to streamline the development of AI applications and empower users to create innovative solutions using state-of-the-art machine learning methods.
graph-llm-asynchow-plan
Graph-enhanced Large Language Models in Asynchronous Plan Reasoning is a repository containing code and datasets for the ICML-2024 paper. It includes naturalistic datasets, code for generating data, benchmarking experiments, and prototypical experiments. The repository also offers a train/test-split version of the dataset on huggingface. The paper focuses on utilizing large language models with graph enhancements for asynchronous plan reasoning.

awesome-generative-ai-guide
This repository serves as a comprehensive hub for updates on generative AI research, interview materials, notebooks, and more. It includes monthly best GenAI papers list, interview resources, free courses, and code repositories/notebooks for developing generative AI applications. The repository is regularly updated with the latest additions to keep users informed and engaged in the field of generative AI.
Java-AI-Book-Code
The Java-AI-Book-Code repository contains code examples for the 2020 edition of 'Practical Artificial Intelligence With Java'. It is a comprehensive update of the previous 2013 edition, featuring new content on deep learning, knowledge graphs, anomaly detection, linked data, genetic algorithms, search algorithms, and more. The repository serves as a valuable resource for Java developers interested in AI applications and provides practical implementations of various AI techniques and algorithms.
llm_recipes
This repository showcases the author's experiments with Large Language Models (LLMs) for text generation tasks. It includes dataset preparation, preprocessing, model fine-tuning using libraries such as Axolotl and HuggingFace, and model evaluation.
data-juicer
Data-Juicer is a one-stop data processing system to make data higher-quality, juicier, and more digestible for LLMs. It is a systematic & reusable library of 80+ core OPs, 20+ reusable config recipes, and 20+ feature-rich dedicated toolkits, designed to function independently of specific LLM datasets and processing pipelines. Data-Juicer allows detailed data analyses with an automated report generation feature for a deeper understanding of your dataset. Coupled with multi-dimension automatic evaluation capabilities, it supports a timely feedback loop at multiple stages in the LLM development process. Data-Juicer offers tens of pre-built data processing recipes for pre-training, fine-tuning, en, zh, and more scenarios. It provides a speedy data processing pipeline requiring less memory and CPU usage, optimized for maximum productivity. Data-Juicer is flexible & extensible, accommodating most types of data formats and allowing flexible combinations of OPs. It is designed for simplicity, with comprehensive documentation, easy start guides and demo configs, and intuitive configuration with simple adding/removing OPs from existing configs.
ai-algorithms
This repository is a work in progress that contains first-principle implementations of groundbreaking AI algorithms using various deep learning frameworks. Each implementation is accompanied by supporting research papers, aiming to provide comprehensive educational resources for understanding and implementing foundational AI algorithms from scratch.
llm-universe
This project is a tutorial on developing large model applications for novice developers. It aims to provide a comprehensive introduction to large model development, focusing on Alibaba Cloud servers and integrating personal knowledge assistant projects. The tutorial covers the following topics: 1. **Introduction to Large Models**: A simplified introduction for novice developers on what large models are, their characteristics, what LangChain is, and how to develop an LLM application. 2. **How to Call Large Model APIs**: This section introduces various methods for calling APIs of well-known domestic and foreign large model products, including calling native APIs, encapsulating them as LangChain LLMs, and encapsulating them as Fastapi calls. It also provides a unified encapsulation for various large model APIs, such as Baidu Wenxin, Xunfei Xinghuo, and Zh譜AI. 3. **Knowledge Base Construction**: Loading, processing, and vector database construction of different types of knowledge base documents. 4. **Building RAG Applications**: Integrating LLM into LangChain to build a retrieval question and answer chain, and deploying applications using Streamlit. 5. **Verification and Iteration**: How to implement verification and iteration in large model development, and common evaluation methods. The project consists of three main parts: 1. **Introduction to LLM Development**: A simplified version of V1 aims to help beginners get started with LLM development quickly and conveniently, understand the general process of LLM development, and build a simple demo. 2. **LLM Development Techniques**: More advanced LLM development techniques, including but not limited to: Prompt Engineering, processing of multiple types of source data, optimizing retrieval, recall ranking, Agent framework, etc. 3. **LLM Application Examples**: Introduce some successful open source cases, analyze the ideas, core concepts, and implementation frameworks of these application examples from the perspective of this course, and help beginners understand what kind of applications they can develop through LLM. Currently, the first part has been completed, and everyone is welcome to read and learn; the second and third parts are under creation. **Directory Structure Description**: requirements.txt: Installation dependencies in the official environment notebook: Notebook source code file docs: Markdown documentation file figures: Pictures data_base: Knowledge base source file used
For similar tasks

Main
This repository contains material related to the new book _Synthetic Data and Generative AI_ by the author, including code for NoGAN, DeepResampling, and NoGAN_Hellinger. NoGAN is a tabular data synthesizer that outperforms GenAI methods in terms of speed and results, utilizing state-of-the-art quality metrics. DeepResampling is a fast NoGAN based on resampling and Bayesian Models with hyperparameter auto-tuning. NoGAN_Hellinger combines NoGAN and DeepResampling with the Hellinger model evaluation metric.
qgate-model
QGate-Model is a machine learning meta-model with synthetic data, designed for MLOps and feature store. It is independent of machine learning solutions, with definitions in JSON and data in CSV/parquet formats. This meta-model is useful for comparing capabilities and functions of machine learning solutions, independently testing new versions of machine learning solutions, and conducting various types of tests (unit, sanity, smoke, system, regression, function, acceptance, performance, shadow, etc.). It can also be used for external test coverage when internal test coverage is not available or weak.
llm-datasets
LLM Datasets is a repository containing high-quality datasets, tools, and concepts for LLM fine-tuning. It provides datasets with characteristics like accuracy, diversity, and complexity to train large language models for various tasks. The repository includes datasets for general-purpose, math & logic, code, conversation & role-play, and agent & function calling domains. It also offers guidance on creating high-quality datasets through data deduplication, data quality assessment, data exploration, and data generation techniques.
LLM4IR-Survey
LLM4IR-Survey is a collection of papers related to large language models for information retrieval, organized according to the survey paper 'Large Language Models for Information Retrieval: A Survey'. It covers various aspects such as query rewriting, retrievers, rerankers, readers, search agents, and more, providing insights into the integration of large language models with information retrieval systems.
continuous-eval
Open-Source Evaluation for LLM Applications. `continuous-eval` is an open-source package created for granular and holistic evaluation of GenAI application pipelines. It offers modularized evaluation, a comprehensive metric library covering various LLM use cases, the ability to leverage user feedback in evaluation, and synthetic dataset generation for testing pipelines. Users can define their own metrics by extending the Metric class. The tool allows running evaluation on a pipeline defined with modules and corresponding metrics. Additionally, it provides synthetic data generation capabilities to create user interaction data for evaluation or training purposes.
eShopSupport
eShopSupport is a sample .NET application showcasing common use cases and development practices for building AI solutions in .NET, specifically Generative AI. It demonstrates a customer support application for an e-commerce website using a services-based architecture with .NET Aspire. The application includes support for text classification, sentiment analysis, text summarization, synthetic data generation, and chat bot interactions. It also showcases development practices such as developing solutions locally, evaluating AI responses, leveraging Python projects, and deploying applications to the Cloud.
Awesome-Knowledge-Distillation-of-LLMs
A collection of papers related to knowledge distillation of large language models (LLMs). The repository focuses on techniques to transfer advanced capabilities from proprietary LLMs to smaller models, compress open-source LLMs, and refine their performance. It covers various aspects of knowledge distillation, including algorithms, skill distillation, verticalization distillation in fields like law, medical & healthcare, finance, science, and miscellaneous domains. The repository provides a comprehensive overview of the research in the area of knowledge distillation of LLMs.
Kiln
Kiln is an intuitive tool for fine-tuning LLM models, generating synthetic data, and collaborating on datasets. It offers desktop apps for Windows, MacOS, and Linux, zero-code fine-tuning for various models, interactive data generation, and Git-based version control. Users can easily collaborate with QA, PM, and subject matter experts, generate auto-prompts, and work with a wide range of models and providers. The tool is open-source, privacy-first, and supports structured data tasks in JSON format. Kiln is free to use and helps build high-quality AI products with datasets, facilitates collaboration between technical and non-technical teams, allows comparison of models and techniques without code, ensures structured data integrity, and prioritizes user privacy.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
