
llm-datasets
High-quality datasets, tools, and concepts for LLM fine-tuning.
Stars: 2188
LLM Datasets is a repository containing high-quality datasets, tools, and concepts for LLM fine-tuning. It provides datasets with characteristics like accuracy, diversity, and complexity to train large language models for various tasks. The repository includes datasets for general-purpose, math & logic, code, conversation & role-play, and agent & function calling domains. It also offers guidance on creating high-quality datasets through data deduplication, data quality assessment, data exploration, and data generation techniques.
README:

𝕏 Follow me on X • 🤗 Hugging Face • 💻 Blog • 📙 Hands-on GNN
Curated list of datasets and tools for post-training.
Data is the most valuable asset in LLM development. When building a dataset, we target the three following characteristics:
- Accuracy: Samples should be factually correct and relevant to their corresponding instructions. This can involve using solvers for math and unit tests for code.
- Diversity: You want to cover as many use cases as possible to make sure you're never out of distribution. High diversity is essential as it leads to better generalization.
- Complexity: Answers should be both detailed (to maximize helpfulness) and include system 2 techniques like chain of thought (to force step-by-step reasoning).
Measuring accuracy is easy in most cases but near-impossible with open-ended, subjective questions. On the other hand, clustering datasets by topic is a good way of evaluating data mixture diversity. Finally, complexity can be assessed using other LLMs acting like judges.
Once a model has been pre-trained on a next-token prediction task, Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) is used to turn it into an assistant capable of answering questions and following instructions. These datasets contain pairs of instructions and outputs to train LLMs to understand conversational structure. Unless otherwise noted, all datasets listed here are under permissive licenses (Apache 2.0, MIT, CC-BY-4.0, etc.).
General-purpose datasets offer balanced mixtures of different types of data, including chat, code, and math. These datasets can be used to create general-purpose models that can handle various types of queries.
| Dataset | # | Authors | Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infinity-Instruct | 7.45M | BAAI | Aug 2024 | High-quality evolved samples based on a collection of open-source datasets. |
| WebInstructSub | 2.39M | Yue et al. | May 2024 | Instructions created by retrieving document from Common Crawl, extracting QA pairs, and refining them. See the MAmmoTH2 paper and full set (13.5M samples). |
| The-Tome | 1.75M | Arcee AI | Jul 2024 | Reranked and filtered collection of datasets with a focus on instruction following. See my 100k subset. |
| open-perfectblend | 1.42M | Xu et al., Labonne | Oct 2024 | Open reproduction of the dataset described in this paper. It's a solid general-purpose instruction dataset with chat, math, code, and instruction-following data. |
| smoltalk | 1.1M | Hugging Face | Nov 2024 | Mix of existing and new datasets used to train SmolLM2 with proper evaluations. |
| orca-agentinstruct-1M-v1 | 1.05M | Microsoft | Nov 2024 | Subset of the AgentInstruct dataset (~25 samples) designed for Orca-3-Mistral, using raw text publicly available on the web as seed data. |
| tulu3-sft-mixture | 939k | AI2 | Nov 2024 | (CC-BY-NC-4.0) SFT mixture used to train the Tulu 3. It uses public datasets and new synthetic versions, including persona-based answers for diversity. |
| Open-Platypus | 24.9k | Lee et al. | Sep 2023 | Collection of datasets that were deduplicated using Sentence Transformers (it contains an NC dataset). See Platypus paper. |
LLMs often struggle with mathematical reasoning and formal logic, which has led to the creation of specialized datasets. These datasets can include systematic thinking and step-by-step reasoning.
| Dataset | # | Authors | Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenMathInstruct-2 | 14M | Nvidia | Sep 2024 | Augmented samples from GSM8K and MATH (training set) using Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct. |
| NuminaMath-CoT | 859k | Jia Li et al. | July 2024 | Data used to win the first progress prize of the AI Math Olympiad. See the tool-integrated reasoning version here. |
| MetaMathQA | 395k | Yu et al. | Dec 2023 | Bootstrap mathematical questions by rewriting them from multiple perspectives. See MetaMath paper. |
| MathInstruct | 262k | Yue et al. | Sep 2023 | Compiled from 13 math rationale datasets, six of which are newly curated, and focuses on chain-of-thought and program-of-thought. |
| Orca-Math | 200k | Mitra et al. | Feb 2024 | Grade school math world problems generated using GPT4-Turbo. See Orca-Math paper. |
Code is another challenging domain for LLMs. Code datasets, containing diverse programming language examples, are used to fine-tune LLMs and enhance their ability to understand, generate, and analyze code.
| Dataset | # | Authors | Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| opc-sft-stage2 | 436k | Huang et al. | Nov 2024 | Dataset used in OpenCoder's Stage 2, based on four seed datasets. See OpenCoder paper. |
| CodeFeedback-Filtered-Instruction | 157k | Zheng et al. | Feb 2024 | Filtered version of Magicoder-OSS-Instruct, ShareGPT (Python), Magicoder-Evol-Instruct, and Evol-Instruct-Code. |
| Tested-143k-Python-Alpaca | 143k | Vezora | Mar 2024 | Collection of generated Python code that passed automatic tests to ensure high quality. |
| glaive-code-assistant | 136k | Glaive.ai | Sep 2023 | Synthetic data of problems and solutions with ~60% Python samples. Also see the v2 version. |
| Magicoder-Evol-Instruct-110K | 110k | Wei et al. | Nov 2023 | A decontaminated version of evol-codealpaca-v1. Decontamination is done in the same way as StarCoder (bigcode decontamination process). See Magicoder paper. |
| synthetic_tex_to_sql | 100k | Gretel.ai | Apr 2024 | Synthetic text-to-SQL samples (~23M tokens), covering diverse domains. |
| sql-create-context | 78.6k | b-mc2 | Apr 2023 | Cleansed and augmented version of the WikiSQL and Spider datasets. |
| Code-Feedback | 66.4k | Zheng et al. | Feb 2024 | Diverse Code Interpreter-like dataset with multi-turn dialogues and interleaved text and code responses. See OpenCodeInterpreter paper. |
| Open-Critic-GPT | 55.1k | Vezora | Jul 2024 | Use a local model to create, introduce, and identify bugs in code across multiple programming languages. |
| self-oss-instruct-sc2-exec-filter-50k | 50.7k | Lozhkov et al. | Apr 2024 | Created in three steps with seed functions from TheStack v1, self-instruction with StarCoder2, and self-validation. See the blog post. |
Instruction following corresponds to the ability to properly follow constraints in the user prompt, such as "write only two paragraphs", "write your answer in French", etc. Strong instruction-following capabilities is a must-have for modern LLMs.
| Dataset | # | Authors | Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AutoIF-instruct-61k-with-funcs | 61.5k | Diao et al. | Oct 2024 | Samples generated with this code and gpt-4o-mini, based on Qwen's AutoIF library. |
| ifeval-like-data | 56.3k | Argilla | Oct 2024 | Only use the "filtered" subset. Samples generated by Qwen2.5-72B and verified with lm-evaluation-harness. |
| tulu-3-sft-personas-instruction-following | 30k | AI2 | Nov 2024 | Synthetic samples created with personas, following the methodology introduced by Ge et al., 2024. |
Learning new languages "from scratch" is a pre-training task, but providing multilingual instruction samples is useful to boost performance in the languages of interest.
| Dataset | # | Authors | Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aya dataset | 204k | Singh et al. | Feb 2024 | Multilingual instruction fine-tuning dataset curated by an open-science community via Aya Annotation Platform. |
| M2Lingual | 175K | ServiceNow AI | June 2024 | Dataset spanning 70+ langauges and 20 NLP tasks generated from GPT-4 using task-based taxonomy guided evolutions. More details in M2Lingual paper. |
Function calling allows large language models (LLMs) to execute predefined functions with parameters inferred from user prompts, rather than generating standard text responses. This enables LLMs to seamlessly integrate with external systems, perform complex operations, and provide more accurate and contextually relevant responses.
| Dataset | # | Authors | Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| glaive-function-calling-v2 | 113k | Sahil Chaudhary | Sep 2023 | High-quality dataset with pairs of instructions and answers in different languages. See Locutusque/function-calling-chatml for a variant without conversation tags. |
| xlam-function-calling-60k | 60k | Salesforce | Jun 2024 | Samples created using a data generation pipeline designed to produce verifiable data for function-calling applications |
| Agent-FLAN | 34.4k | internlm | Mar 2024 | Mix of AgentInstruct, ToolBench, and ShareGPT datasets. |
| hermes-function-calling-v1 | 11.6k | Nous | Aug 2024 | Compilation of structured output and function calling data used in the Hermes 2 Pro series of models. |
| ToolACE | 11.3k | Liu et al. | Aug 2024 | Agentic pipeline self-evolution synthesis process to curate a comprehensive API pool |
Real-world conversations provide valuable insights into how people naturally interact with LLMs, helping us identify the most important use cases and understand typical usage patterns.
| Dataset | # | Authors | Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WildChat-1M | 1.04M | Zhao et al. | May 2023 | Real conversations between human users and GPT-3.5/4, including metadata. See the WildChat paper. |
| lmsys-chat-1m | 1M | LMSYS | Sep 2023 | Real-world conversations with 25 LLMs, collected from 210K unique IP addresses on the Vicuna demo and Chatbot Arena website from April to August 2023. |
| oasst2 | 135k | Köpf et al. | Dec 2023 | Human-generated conversations trees with multiple replies. See OASST1 paper. |
| ShareGPT52K | 90k | ShareGPT | Apr 2023 | Conversations scraped via the ShareGPT API before it was shut down. They include both user prompts and responses from GPT-3.5. |
| oasst1 | 84.4k | Köpf et al. | Mar 2023 | Human-generated assistant-style conversation corpus in 35 different languages. See OASST1 paper. |
Unlike instruction data, preference datasets consist of chosen and rejected answers. Preference alignment is used to align LLM's answers with human preferences to adopt the desired style and values.
| Dataset | # | Authors | Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skywork-Reward-Preference-80K-v0.2 | 77k | Skywork | 2024 | Preference pairs compiled from public sources like HelpSteer2, OffsetBias, WildGuard, and Magpie. |
| ultrafeedback-binarized-preferences-cleaned | 61.1k | Argilla | 2023 | Decontaminated version of the UltraChat dataset, scored by GPT-4 and binarized into "chosen" and "rejected" answers based on these scores. |
| Infinity-Preference | 59k | BAAI | Sep 2024 | Adjusts preference attribute weights per task using Infinity-Instruct's labeling system. Each instruction is accompanied by a preference pair sampled from Gemma-2-9B-IT. |
| Code-Preference-Pairs | 53k | Vezora | Jul 2024 | Pairs of code examples, where the chosen sample is correct and the rejected one contains a bug. |
| orpo-dpo-mix-40k | 44k | Argilla, Labonne | May 2024 | Combination of the following high-quality DPO datasets, mostly from Argilla. |
| chatbot_arena_conversations | 33k | LMSYS | Jul 2023 | Cleaned real conversations with pairwise human preferences collected on the Chatbot Arena from April to June 2023 |
| tulu-3-pref-personas-instruction-following | 19.9k | AI2 | Nov 2024 | Instruction following data in the form of chosen and rejected answers to teach the model to follow precise constraints. |
| Human-Like-DPO-Dataset | 10.9k | Weyaxi | May 2024 | Teach to output more human-like answers instead of the formal slop LLMS usually output. |
Tools listed in this section can help you evaluate, generate, and explore datasets. Start by aggregating available data from various sources (open-source or not) and applying filters like data deduplication and data quality. If the initial dataset is small or insufficient, consider synthetically generating additional data to fill the gap. Iteratively explore and refine the dataset by assessing model performance, identifying gaps, and collecting or generating data to address those shortcomings.
- Trafilatura: Python and command-line tool to gather text and metadata on the web. Used for the creation of RefinedWeb.
- Marker: Quickly convert PDFs to markdown text.
- Rule-based filtering: Remove samples based on a list of unwanted words, like refusals and "As an AI assistant" (example).
- Argilla: Platform that allows you to manually filter and annotate datasets in a collaborative way.
- judges: Small library of LLM judges with various classifiers and graders (early development).
- Distilabel: General-purpose framework that can generate and augment data (SFT, DPO) with techniques like UltraFeedback and DEITA.
- Augmentoolkit: Framework to convert raw text into datasets using open-source and closed-source models.
- Data Prep Kit: Framework for data preparation for both code and language, with modules in Python, Ray, and Spark, and a wide range of scale from laptops to data centers.
- Lilac: Tool for exploration, curation and quality control of datasets.
- Nomic Atlas: Interact with instructed data to find insights and store embeddings.
- text-clustering: A framework from Huggingface for clustering textual data.
- Autolabel: Automatically label data using popular language models.
Special thanks to geronimi73, Bytes-Explorer, euclaise, RishabhMaheshwary, and ParagEkbote for their PRs.
Please let me know if a dataset is not properly credited.
- Wei-Lin Chiang et al, "Vicuna: An Open-Source Chatbot Impressing GPT-4 with 90%* ChatGPT Quality," 2023.
- Yihan Cao et al, "Instruction Mining: When Data Mining Meets Large Language Model Finetuning," 2023.
- Subhabrata Mukherjee et al, "Orca: Progressive Learning from Complex Explanation Traces of GPT-4," 2023.
- Chunting Zhou et al, "LIMA: Less Is More for Alignment," 2023.
- Suriya Gunasekar et al, "Textbooks Are All You Need," 2023.
- Lichang Chen et al, "AlpaGasus: Training A Better Alpaca with Fewer Data," 2024.
- Zheng Cai et al, "InternLM2 Technical Report," 2024.
- Lifan Yuan et al, "Advancing LLM Reasoning Generalists with Preference Trees," 2024.
- Wei Liu et al, "What Makes Good Data for Alignment? A Comprehensive Study of Automatic Data Selection in Instruction Tuning," 2024.
- Xingyao Wang et al, "MINT: Evaluating LLMs in Multi-turn Interaction with Tools and Language Feedback," 2024.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llm-datasets
Similar Open Source Tools

llm-datasets
LLM Datasets is a repository containing high-quality datasets, tools, and concepts for LLM fine-tuning. It provides datasets with characteristics like accuracy, diversity, and complexity to train large language models for various tasks. The repository includes datasets for general-purpose, math & logic, code, conversation & role-play, and agent & function calling domains. It also offers guidance on creating high-quality datasets through data deduplication, data quality assessment, data exploration, and data generation techniques.
LLM-PowerHouse-A-Curated-Guide-for-Large-Language-Models-with-Custom-Training-and-Inferencing
LLM-PowerHouse is a comprehensive and curated guide designed to empower developers, researchers, and enthusiasts to harness the true capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and build intelligent applications that push the boundaries of natural language understanding. This GitHub repository provides in-depth articles, codebase mastery, LLM PlayLab, and resources for cost analysis and network visualization. It covers various aspects of LLMs, including NLP, models, training, evaluation metrics, open LLMs, and more. The repository also includes a collection of code examples and tutorials to help users build and deploy LLM-based applications.
Awesome-LLM-Large-Language-Models-Notes
Awesome-LLM-Large-Language-Models-Notes is a repository that provides a comprehensive collection of information on various Large Language Models (LLMs) classified by year, size, and name. It includes details on known LLM models, their papers, implementations, and specific characteristics. The repository also covers LLM models classified by architecture, must-read papers, blog articles, tutorials, and implementations from scratch. It serves as a valuable resource for individuals interested in understanding and working with LLMs in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP).
redis-ai-resources
A curated repository of code recipes, demos, and resources for basic and advanced Redis use cases in the AI ecosystem. It includes demos for ArxivChatGuru, Redis VSS, Vertex AI & Redis, Agentic RAG, ArXiv Search, and Product Search. Recipes cover topics like Getting started with RAG, Semantic Cache, Advanced RAG, and Recommendation systems. The repository also provides integrations/tools like RedisVL, AWS Bedrock, LangChain Python, LangChain JS, LlamaIndex, Semantic Kernel, RelevanceAI, and DocArray. Additional content includes blog posts, talks, reviews, and documentation related to Vector Similarity Search, AI-Powered Document Search, Vector Databases, Real-Time Product Recommendations, and more. Benchmarks compare Redis against other Vector Databases and ANN benchmarks. Documentation includes QuickStart guides, official literature for Vector Similarity Search, Redis-py client library docs, Redis Stack documentation, and Redis client list.
MathEval
MathEval is a benchmark designed for evaluating the mathematical capabilities of large models. It includes over 20 evaluation datasets covering various mathematical domains with more than 30,000 math problems. The goal is to assess the performance of large models across different difficulty levels and mathematical subfields. MathEval serves as a reliable reference for comparing mathematical abilities among large models and offers guidance on enhancing their mathematical capabilities in the future.
llm-compression-intelligence
This repository presents the findings of the paper "Compression Represents Intelligence Linearly". The study reveals a strong linear correlation between the intelligence of LLMs, as measured by benchmark scores, and their ability to compress external text corpora. Compression efficiency, derived from raw text corpora, serves as a reliable evaluation metric that is linearly associated with model capabilities. The repository includes the compression corpora used in the paper, code for computing compression efficiency, and data collection and processing pipelines.
COLD-Attack
COLD-Attack is a framework designed for controllable jailbreaks on large language models (LLMs). It formulates the controllable attack generation problem and utilizes the Energy-based Constrained Decoding with Langevin Dynamics (COLD) algorithm to automate the search of adversarial LLM attacks with control over fluency, stealthiness, sentiment, and left-right-coherence. The framework includes steps for energy function formulation, Langevin dynamics sampling, and decoding process to generate discrete text attacks. It offers diverse jailbreak scenarios such as fluent suffix attacks, paraphrase attacks, and attacks with left-right-coherence.
rubra
Rubra is a collection of open-weight large language models enhanced with tool-calling capability. It allows users to call user-defined external tools in a deterministic manner while reasoning and chatting, making it ideal for agentic use cases. The models are further post-trained to teach instruct-tuned models new skills and mitigate catastrophic forgetting. Rubra extends popular inferencing projects for easy use, enabling users to run the models easily.
dl_model_infer
This project is a c++ version of the AI reasoning library that supports the reasoning of tensorrt models. It provides accelerated deployment cases of deep learning CV popular models and supports dynamic-batch image processing, inference, decode, and NMS. The project has been updated with various models and provides tutorials for model exports. It also includes a producer-consumer inference model for specific tasks. The project directory includes implementations for model inference applications, backend reasoning classes, post-processing, pre-processing, and target detection and tracking. Speed tests have been conducted on various models, and onnx downloads are available for different models.
amber-train
Amber is the first model in the LLM360 family, an initiative for comprehensive and fully open-sourced LLMs. It is a 7B English language model with the LLaMA architecture. The model type is a language model with the same architecture as LLaMA-7B. It is licensed under Apache 2.0. The resources available include training code, data preparation, metrics, and fully processed Amber pretraining data. The model has been trained on various datasets like Arxiv, Book, C4, Refined-Web, StarCoder, StackExchange, and Wikipedia. The hyperparameters include a total of 6.7B parameters, hidden size of 4096, intermediate size of 11008, 32 attention heads, 32 hidden layers, RMSNorm ε of 1e^-6, max sequence length of 2048, and a vocabulary size of 32000.
recommenders
Recommenders is a project under the Linux Foundation of AI and Data that assists researchers, developers, and enthusiasts in prototyping, experimenting with, and bringing to production a range of classic and state-of-the-art recommendation systems. The repository contains examples and best practices for building recommendation systems, provided as Jupyter notebooks. It covers tasks such as preparing data, building models using various recommendation algorithms, evaluating algorithms, tuning hyperparameters, and operationalizing models in a production environment on Azure. The project provides utilities to support common tasks like loading datasets, evaluating model outputs, and splitting training/test data. It includes implementations of state-of-the-art algorithms for self-study and customization in applications.
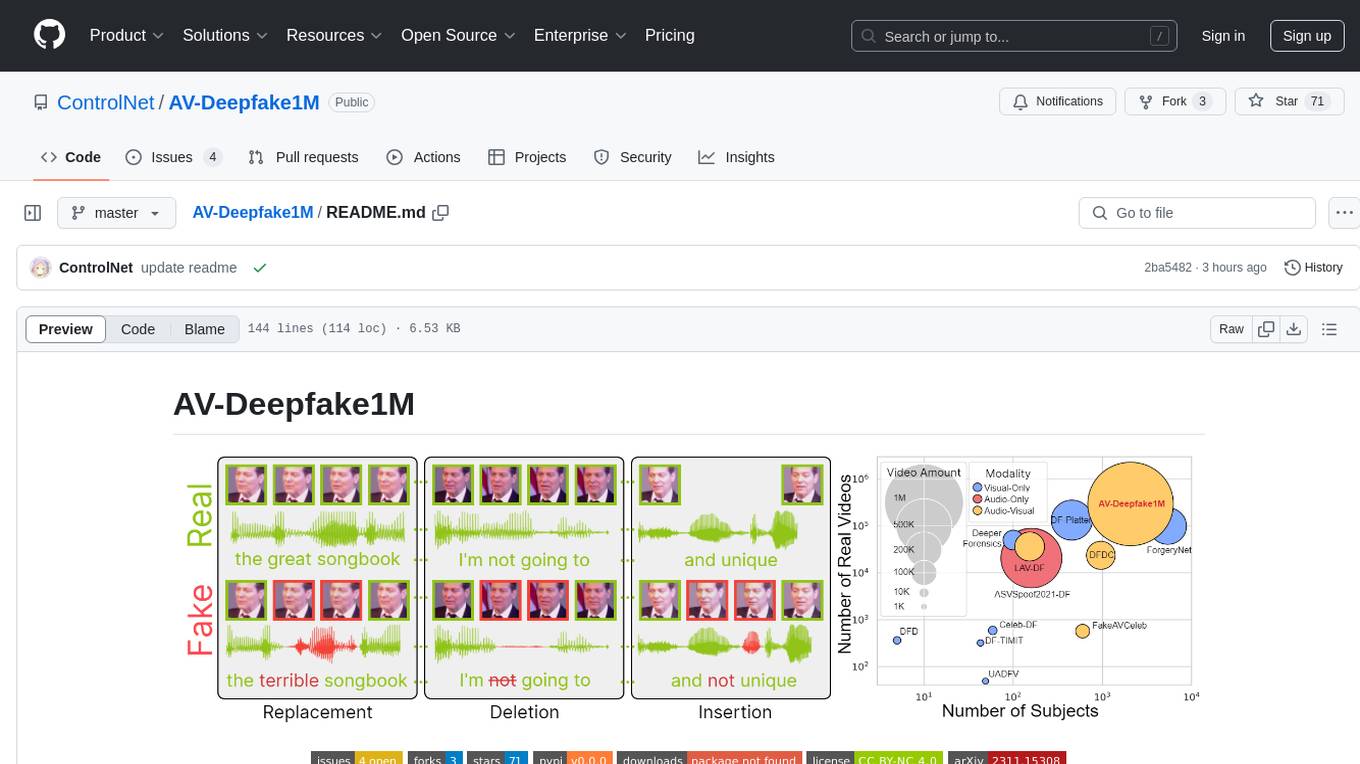
AV-Deepfake1M
The AV-Deepfake1M repository is the official repository for the paper AV-Deepfake1M: A Large-Scale LLM-Driven Audio-Visual Deepfake Dataset. It addresses the challenge of detecting and localizing deepfake audio-visual content by proposing a dataset containing video manipulations, audio manipulations, and audio-visual manipulations for over 2K subjects resulting in more than 1M videos. The dataset is crucial for developing next-generation deepfake localization methods.
imodels
Python package for concise, transparent, and accurate predictive modeling. All sklearn-compatible and easy to use. _For interpretability in NLP, check out our new package:imodelsX _
HighPerfLLMs2024
High Performance LLMs 2024 is a comprehensive course focused on building a high-performance Large Language Model (LLM) from scratch using Jax. The course covers various aspects such as training, inference, roofline analysis, compilation, sharding, profiling, and optimization techniques. Participants will gain a deep understanding of Jax and learn how to design high-performance computing systems that operate close to their physical limits.
GenAIExamples
This project provides a collective list of Generative AI (GenAI) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) examples such as chatbot with question and answering (ChatQnA), code generation (CodeGen), document summary (DocSum), etc.
my-best-resources
my-best-resources is a curated list of resources for web developers and designers, aimed at making their lives easier. It includes sections on design inspiration, ready-made components, stock images, artificial intelligence tools for various use cases, and other useful sources. The repository provides links and descriptions for each resource, offering a valuable collection of tools and assets for web development and design projects.
For similar tasks

llm-datasets
LLM Datasets is a repository containing high-quality datasets, tools, and concepts for LLM fine-tuning. It provides datasets with characteristics like accuracy, diversity, and complexity to train large language models for various tasks. The repository includes datasets for general-purpose, math & logic, code, conversation & role-play, and agent & function calling domains. It also offers guidance on creating high-quality datasets through data deduplication, data quality assessment, data exploration, and data generation techniques.

dolma
Dolma is a dataset and toolkit for curating large datasets for (pre)-training ML models. The dataset consists of 3 trillion tokens from a diverse mix of web content, academic publications, code, books, and encyclopedic materials. The toolkit provides high-performance, portable, and extensible tools for processing, tagging, and deduplicating documents. Key features of the toolkit include built-in taggers, fast deduplication, and cloud support.
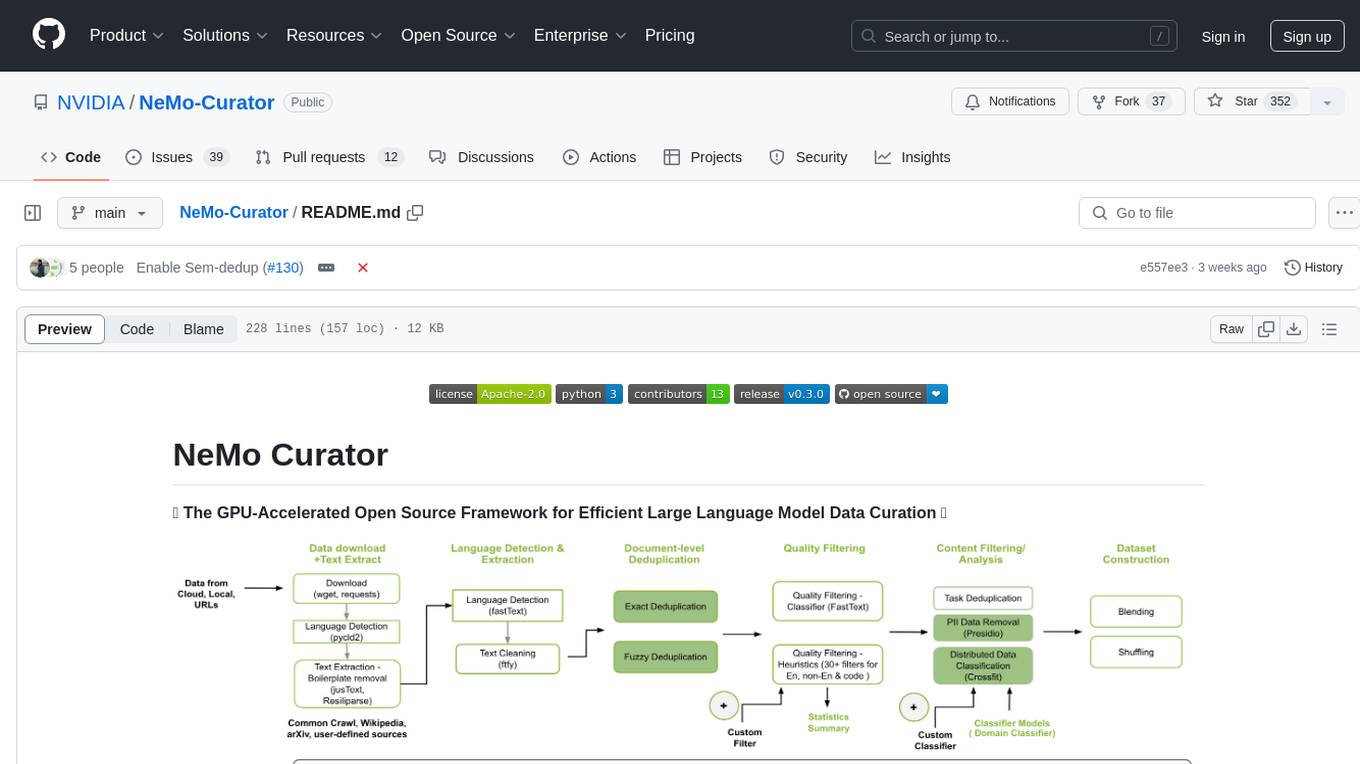
NeMo-Curator
NeMo Curator is a GPU-accelerated open-source framework designed for efficient large language model data curation. It provides scalable dataset preparation for tasks like foundation model pretraining, domain-adaptive pretraining, supervised fine-tuning, and parameter-efficient fine-tuning. The library leverages GPUs with Dask and RAPIDS to accelerate data curation, offering customizable and modular interfaces for pipeline expansion and model convergence. Key features include data download, text extraction, quality filtering, deduplication, downstream-task decontamination, distributed data classification, and PII redaction. NeMo Curator is suitable for curating high-quality datasets for large language model training.

pandas-ai
PandasAI is a Python library that makes it easy to ask questions to your data in natural language. It helps you to explore, clean, and analyze your data using generative AI.
supersonic
SuperSonic is a next-generation BI platform that integrates Chat BI (powered by LLM) and Headless BI (powered by semantic layer) paradigms. This integration ensures that Chat BI has access to the same curated and governed semantic data models as traditional BI. Furthermore, the implementation of both paradigms benefits from the integration: * Chat BI's Text2SQL gets augmented with context-retrieval from semantic models. * Headless BI's query interface gets extended with natural language API. SuperSonic provides a Chat BI interface that empowers users to query data using natural language and visualize the results with suitable charts. To enable such experience, the only thing necessary is to build logical semantic models (definition of metric/dimension/tag, along with their meaning and relationships) through a Headless BI interface. Meanwhile, SuperSonic is designed to be extensible and composable, allowing custom implementations to be added and configured with Java SPI. The integration of Chat BI and Headless BI has the potential to enhance the Text2SQL generation in two dimensions: 1. Incorporate data semantics (such as business terms, column values, etc.) into the prompt, enabling LLM to better understand the semantics and reduce hallucination. 2. Offload the generation of advanced SQL syntax (such as join, formula, etc.) from LLM to the semantic layer to reduce complexity. With these ideas in mind, we develop SuperSonic as a practical reference implementation and use it to power our real-world products. Additionally, to facilitate further development we decide to open source SuperSonic as an extensible framework.
DeepBI
DeepBI is an AI-native data analysis platform that leverages the power of large language models to explore, query, visualize, and share data from any data source. Users can use DeepBI to gain data insight and make data-driven decisions.

WrenAI
WrenAI is a data assistant tool that helps users get results and insights faster by asking questions in natural language, without writing SQL. It leverages Large Language Models (LLM) with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology to enhance comprehension of internal data. Key benefits include fast onboarding, secure design, and open-source availability. WrenAI consists of three core services: Wren UI (intuitive user interface), Wren AI Service (processes queries using a vector database), and Wren Engine (platform backbone). It is currently in alpha version, with new releases planned biweekly.
opendataeditor
The Open Data Editor (ODE) is a no-code application to explore, validate and publish data in a simple way. It is an open source project powered by the Frictionless Framework. The ODE is currently available for download and testing in beta.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.