imodels
Interpretable ML package 🔍 for concise, transparent, and accurate predictive modeling (sklearn-compatible).
Stars: 1432
Python package for concise, transparent, and accurate predictive modeling. All sklearn-compatible and easy to use. _For interpretability in NLP, check out our new package:imodelsX _
README:

Python package for concise, transparent, and accurate predictive modeling.
All sklearn-compatible and easy to use.
For interpretability in NLP, check out our new package: imodelsX
Modern machine-learning models are increasingly complex, often making them difficult to interpret. This package provides a simple interface for fitting and using state-of-the-art interpretable models, all compatible with scikit-learn. These models can often replace black-box models (e.g. random forests) with simpler models (e.g. rule lists) while improving interpretability and computational efficiency, all without sacrificing predictive accuracy! Simply import a classifier or regressor and use the fit and predict methods, same as standard scikit-learn models.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from imodels import get_clean_dataset, HSTreeClassifierCV # import any imodels model here
# prepare data (a sample clinical dataset)
X, y, feature_names = get_clean_dataset('csi_pecarn_pred')
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, random_state=42)
# fit the model
model = HSTreeClassifierCV(max_leaf_nodes=4) # initialize a tree model and specify only 4 leaf nodes
model.fit(X_train, y_train, feature_names=feature_names) # fit model
preds = model.predict(X_test) # discrete predictions: shape is (n_test, 1)
preds_proba = model.predict_proba(X_test) # predicted probabilities: shape is (n_test, n_classes)
print(model) # print the model------------------------------
Decision Tree with Hierarchical Shrinkage
Prediction is made by looking at the value in the appropriate leaf of the tree
------------------------------
|--- FocalNeuroFindings2 <= 0.50
| |--- HighriskDiving <= 0.50
| | |--- Torticollis2 <= 0.50
| | | |--- value: [0.10]
| | |--- Torticollis2 > 0.50
| | | |--- value: [0.30]
| |--- HighriskDiving > 0.50
| | |--- value: [0.68]
|--- FocalNeuroFindings2 > 0.50
| |--- value: [0.42]
Install with pip install imodels (see here for help).
🗂️ Docs 📄 Research paper 🔗 Reference code implementation
| Model | Reference | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Rulefit rule set | 🗂️, 📄, 🔗 | Fits a sparse linear model on rules extracted from decision trees |
| Skope rule set | 🗂️, 🔗 | Extracts rules from gradient-boosted trees, deduplicates them, then linearly combines them based on their OOB precision |
| Boosted rule set | 🗂️, 📄, 🔗 | Sequentially fits a set of rules with Adaboost |
| Slipper rule set | 🗂️, 📄 | Sequentially learns a set of rules with SLIPPER |
| Bayesian rule set | 🗂️, 📄, 🔗 | Finds concise rule set with Bayesian sampling (slow) |
| Optimal rule list | 🗂️, 📄, 🔗 | Fits rule list using global optimization for sparsity (CORELS) |
| Bayesian rule list | 🗂️, 📄, 🔗 | Fits compact rule list distribution with Bayesian sampling (slow) |
| Greedy rule list | 🗂️, 🔗 | Uses CART to fit a list (only a single path), rather than a tree |
| OneR rule list | 🗂️, 📄 | Fits rule list restricted to only one feature |
| Optimal rule tree | 🗂️, 📄, 🔗 | Fits succinct tree using global optimization for sparsity (GOSDT) |
| Greedy rule tree | 🗂️, 📄, 🔗 | Greedily fits tree using CART |
| C4.5 rule tree | 🗂️, 📄, 🔗 | Greedily fits tree using C4.5 |
| TAO rule tree | 🗂️, 📄 | Fits tree using alternating optimization |
| Iterative random forest |
🗂️, 📄, 🔗 | Repeatedly fit random forest, giving features with high importance a higher chance of being selected |
| Sparse integer linear model |
🗂️, 📄 | Sparse linear model with integer coefficients |
| Tree GAM | 🗂️, 📄, 🔗 | Generalized additive model fit with short boosted trees |
| Greedy treesums (FIGS) | 🗂️,ㅤ📄 | Sum of small trees with very few total rules (FIGS) |
| Hierarchical shrinkage wrapper |
🗂️, 📄 | Improve a decision tree, random forest, or gradient-boosting ensemble with ultra-fast, post-hoc regularization |
| RF+ (MDI+) | 🗂️, 📄 | Flexible random forest-based feature importance |
| Distillation wrapper |
🗂️ | Train a black-box model, then distill it into an interpretable model |
| AutoML wrapper | 🗂️ | Automatically fit and select an interpretable model |
| More models | ⌛ | (Coming soon!) Lightweight Rule Induction, MLRules, ... |
Demos are contained in the notebooks folder.
Quickstart demo
Shows how to fit, predict, and visualize with different interpretable modelsAutogluon demo
Fit/select an interpretable model automatically using Autogluon AutoMLQuickstart colab demo 
Shows how to fit, predict, and visualize with different interpretable models
Clinical decision rule notebook
Shows an example of usingimodels for deriving a clinical decision rule
Posthoc analysis
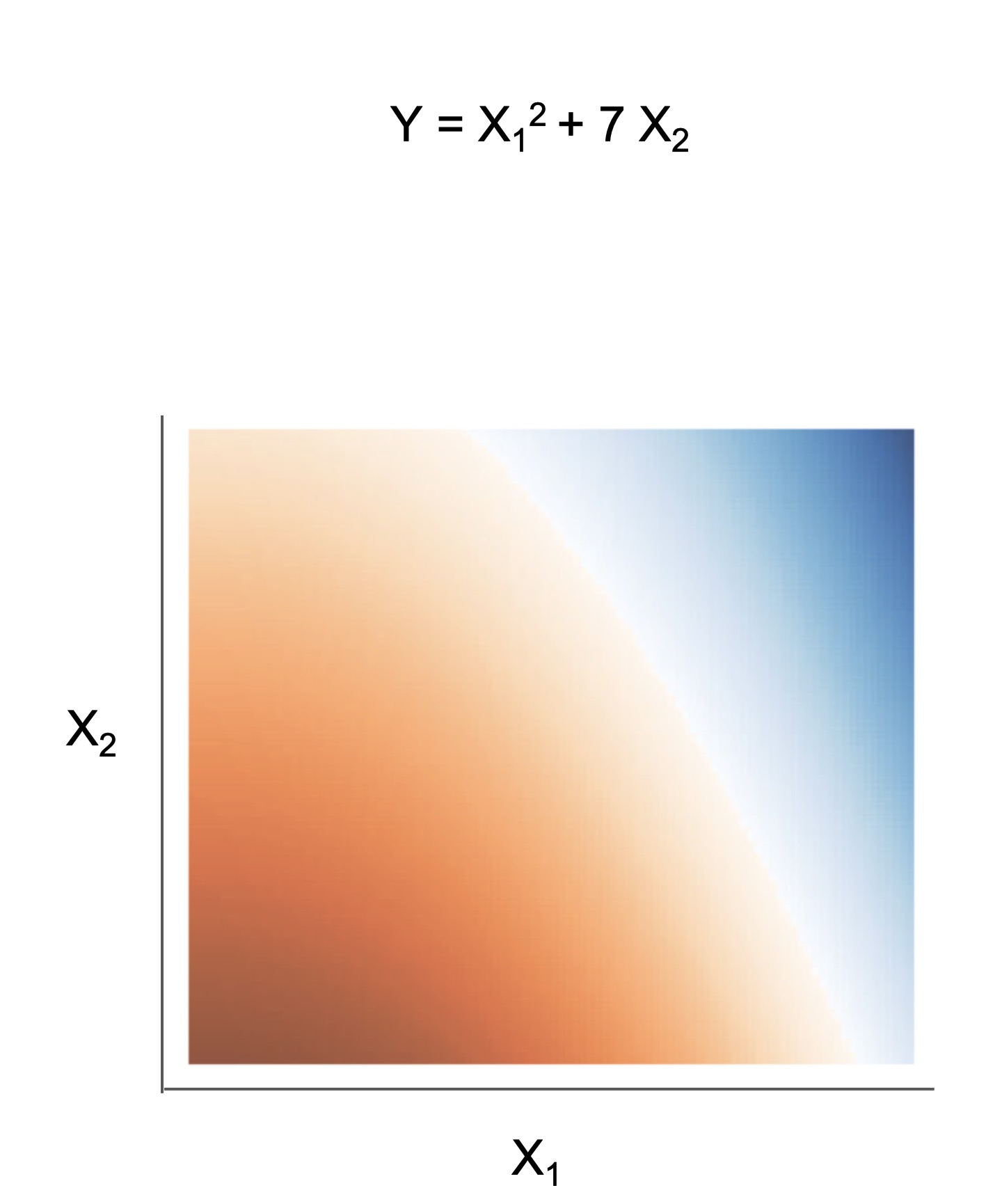
We also include some demos of posthoc analysis, which occurs after fitting models: posthoc.ipynb shows different simple analyses to interpret a trained model and uncertainty.ipynb contains basic code to get uncertainty estimates for a modelThe final form of the above models takes one of the following forms, which aim to be simultaneously simple to understand and highly predictive:
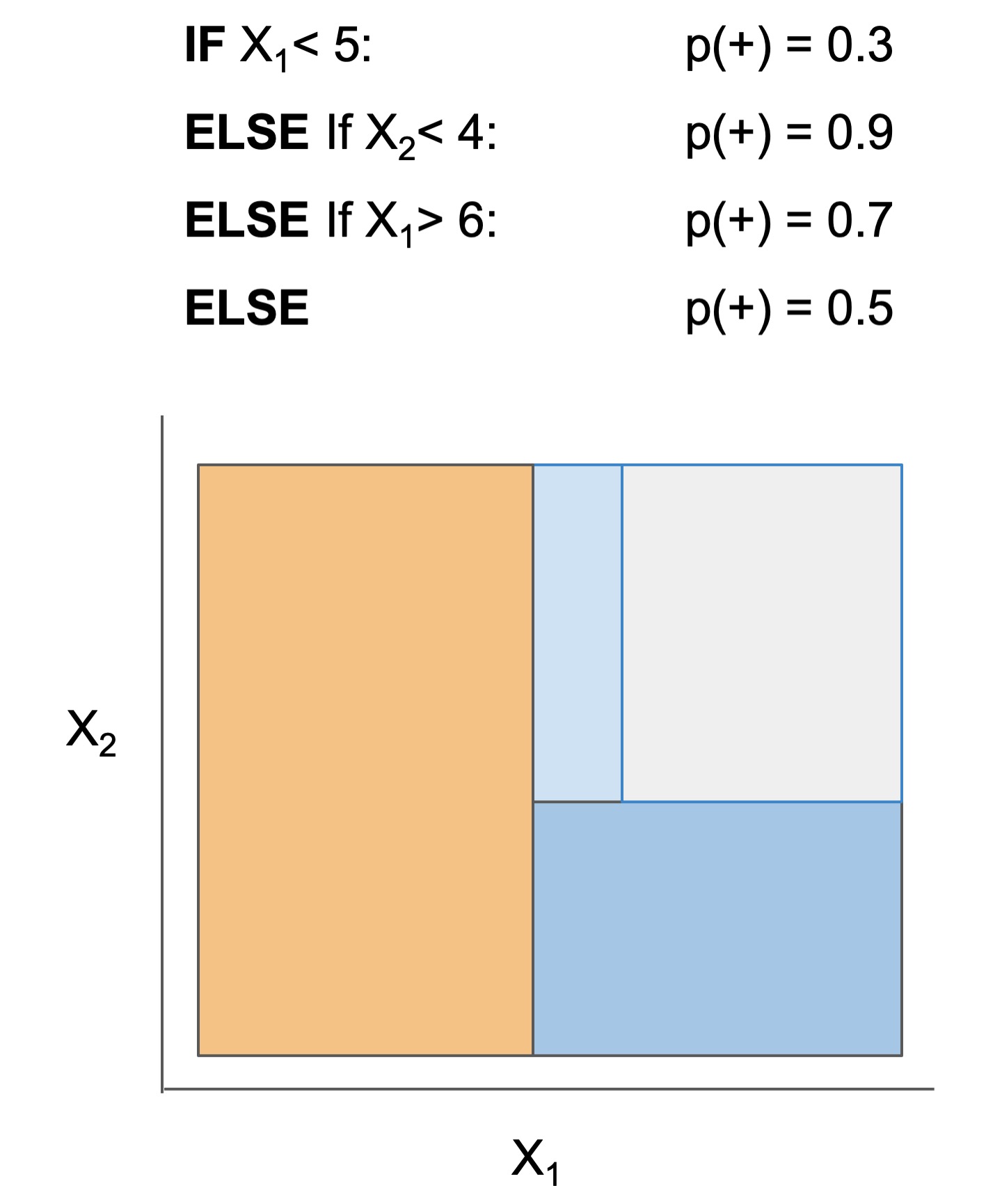
| Rule set | Rule list | Rule tree | Algebraic models |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
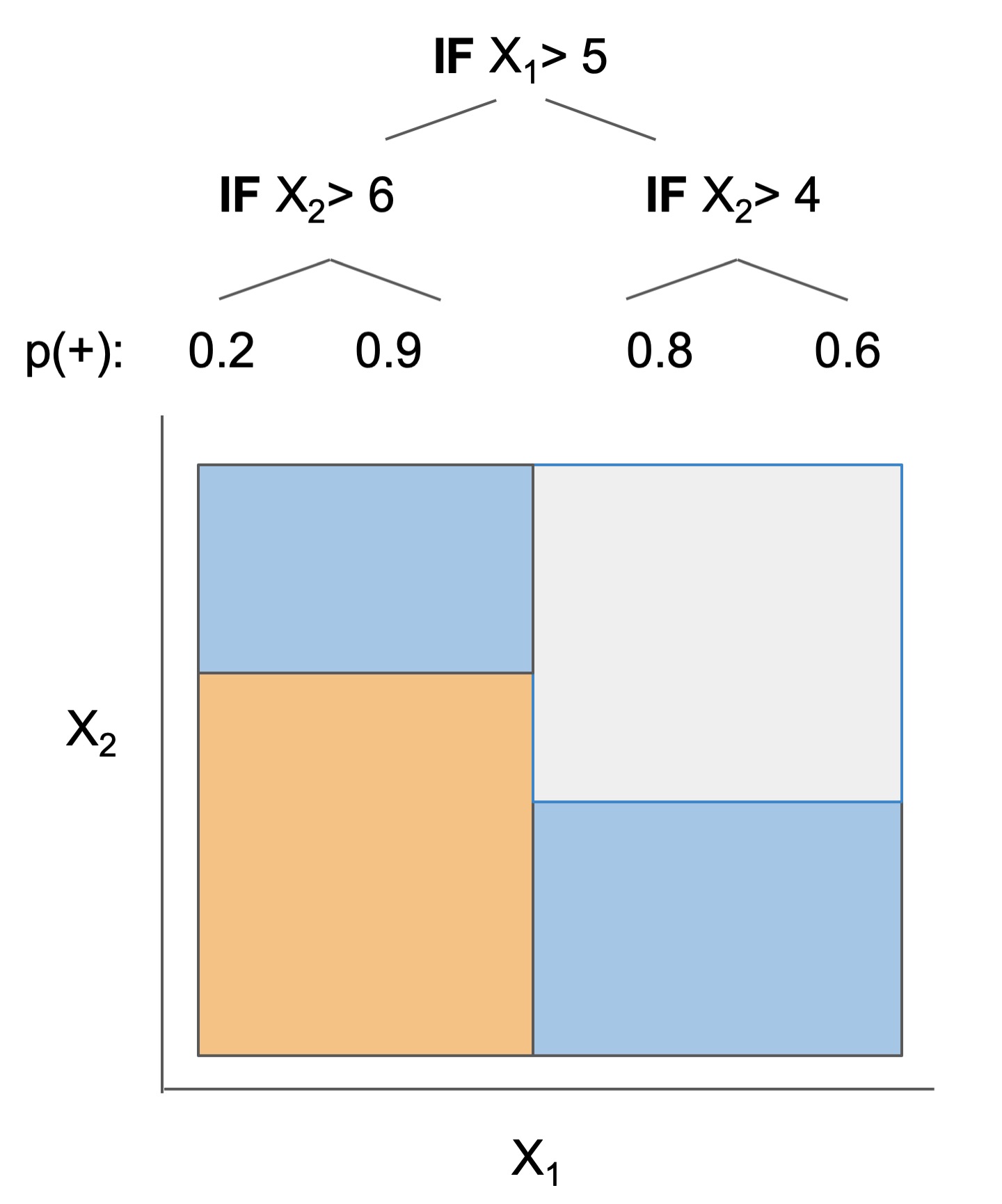 |
 |
Different models and algorithms vary not only in their final form but also in different choices made during modeling, such as how they generate, select, and postprocess rules:
| Rule candidate generation | Rule selection | Rule postprocessing |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
Ex. RuleFit vs. SkopeRules
RuleFit and SkopeRules differ only in the way they prune rules: RuleFit uses a linear model whereas SkopeRules heuristically deduplicates rules sharing overlap.Ex. Bayesian rule lists vs. greedy rule lists
Bayesian rule lists and greedy rule lists differ in how they select rules; bayesian rule lists perform a global optimization over possible rule lists while Greedy rule lists pick splits sequentially to maximize a given criterion.Ex. FPSkope vs. SkopeRules
FPSkope and SkopeRules differ only in the way they generate candidate rules: FPSkope uses FPgrowth whereas SkopeRules extracts rules from decision trees.Different models support different machine-learning tasks. Current support for different models is given below (each of these models can be imported directly from imodels (e.g. from imodels import RuleFitClassifier):
| Model | Binary classification | Regression | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rulefit rule set | RuleFitClassifier | RuleFitRegressor | |
| Skope rule set | SkopeRulesClassifier | ||
| Boosted rule set | BoostedRulesClassifier | BoostedRulesRegressor | |
| SLIPPER rule set | SlipperClassifier | ||
| Bayesian rule set | BayesianRuleSetClassifier | Fails for large problems | |
| Optimal rule list (CORELS) | OptimalRuleListClassifier | Requires corels, fails for large problems | |
| Bayesian rule list | BayesianRuleListClassifier | ||
| Greedy rule list | GreedyRuleListClassifier | ||
| OneR rule list | OneRClassifier | ||
| Optimal rule tree (GOSDT) | OptimalTreeClassifier | Requires gosdt, fails for large problems | |
| Greedy rule tree (CART) | GreedyTreeClassifier | GreedyTreeRegressor | |
| C4.5 rule tree | C45TreeClassifier | ||
| TAO rule tree | TaoTreeClassifier | TaoTreeRegressor | |
| Iterative random forest | IRFClassifier | Requires irf | |
| Sparse integer linear model | SLIMClassifier | SLIMRegressor | Requires extra dependencies for speed |
| Tree GAM | TreeGAMClassifier | TreeGAMRegressor | |
| Greedy tree sums (FIGS) | FIGSClassifier | FIGSRegressor | |
| Hierarchical shrinkage | HSTreeClassifierCV | HSTreeRegressorCV | Wraps any sklearn tree-based model |
| Distillation | DistilledRegressor | Wraps any sklearn-compatible models | |
| AutoML model | AutoInterpretableClassifier️ | AutoInterpretableRegressor️ |
Data-wrangling functions for working with popular tabular datasets (e.g. compas).
These functions, in conjunction with imodels-data and imodels-experiments, make it simple to download data and run experiments on new models.Explain classification errors with a simple posthoc function.
Fit an interpretable model to explain a previous model's errors (ex. in this notebook📓).Fast and effective discretizers for data preprocessing.
| Discretizer | Reference | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MDLP | 🗂️, 🔗, 📄 | Discretize using entropy minimization heuristic |
| Simple | 🗂️, 🔗 | Simple KBins discretization |
| Random Forest | 🗂️ | Discretize into bins based on random forest split popularity |
Rule-based utils for customizing models
The code here contains many useful and customizable functions for rule-based learning in the util folder. This includes functions / classes for rule deduplication, rule screening, and converting between trees, rulesets, and neural networks.After developing and playing with imodels, we developed a few new models to overcome limitations of existing interpretable models.
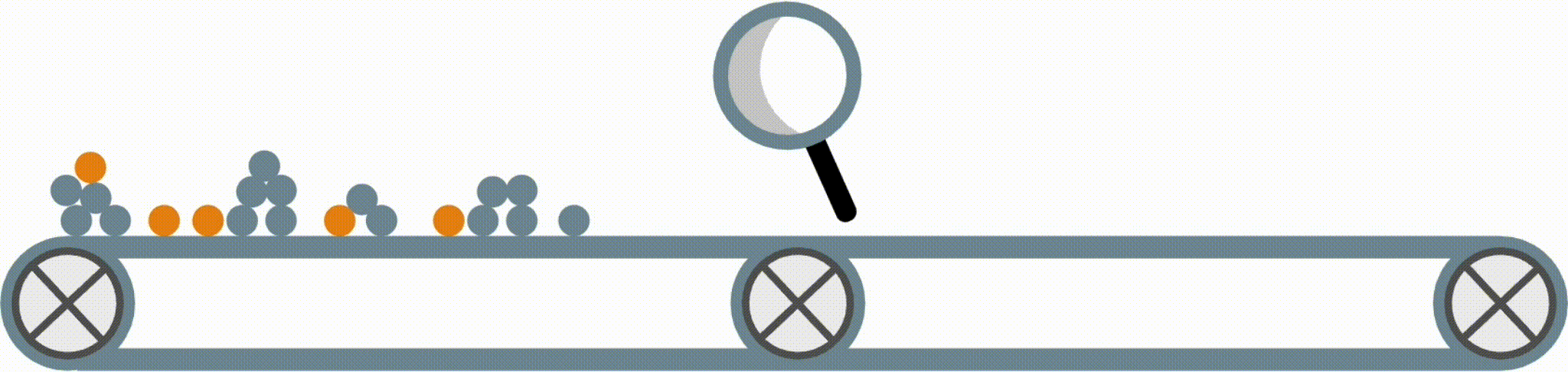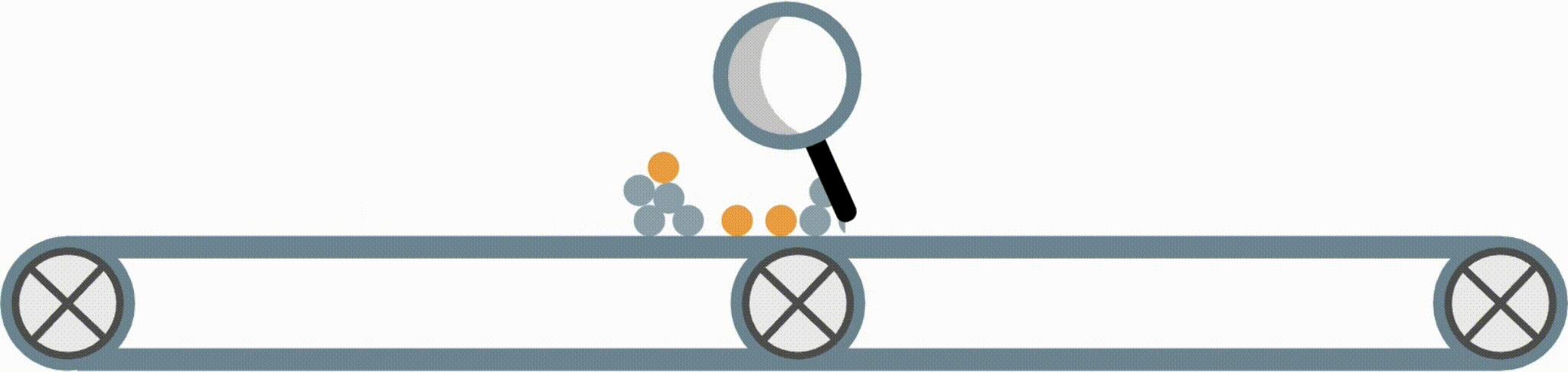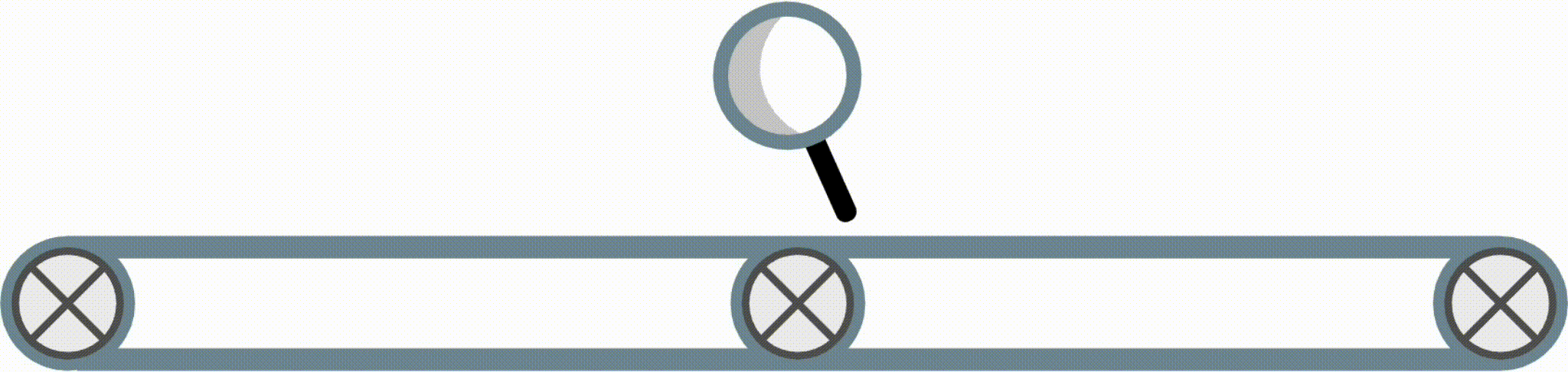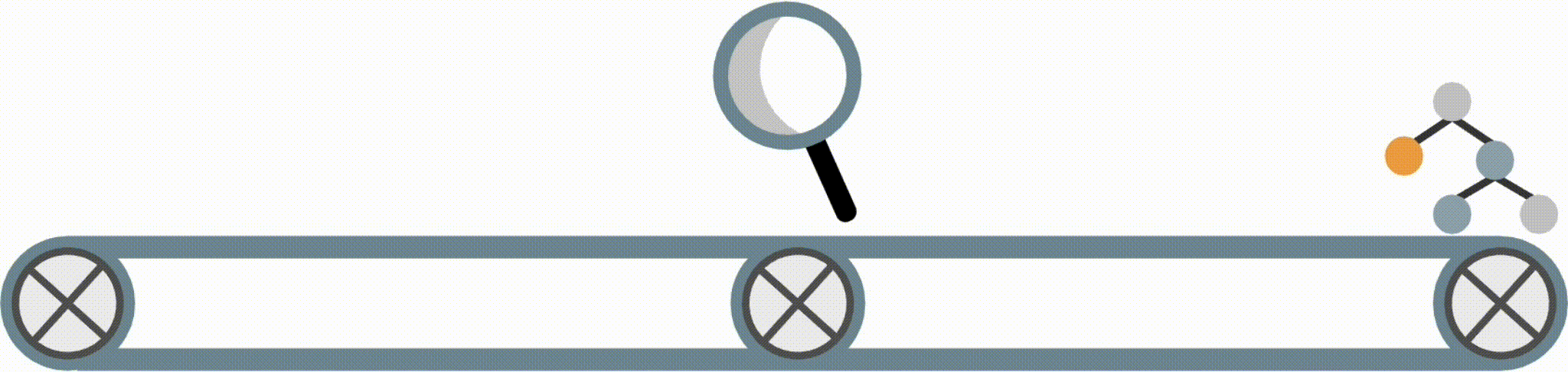
Fast Interpretable Greedy-Tree Sums (FIGS) is an algorithm for fitting concise rule-based models. Specifically, FIGS generalizes CART to simultaneously grow a flexible number of trees in a summation. The total number of splits across all the trees can be restricted by a pre-specified threshold, keeping the model interpretable. Experiments across a wide array of real-world datasets show that FIGS achieves state-of-the-art prediction performance when restricted to just a few splits (e.g. less than 20).
Example FIGS model. FIGS learns a sum of trees with a flexible number of trees; to make its prediction, it sums the result from each tree.
📄 Paper (ICML 2022), 🔗 Post, 📌 Citation
Hierarchical shrinkage is an extremely fast post-hoc regularization method which works on any decision tree (or tree-based ensemble, such as Random Forest). It does not modify the tree structure, and instead regularizes the tree by shrinking the prediction over each node towards the sample means of its ancestors (using a single regularization parameter). Experiments over a wide variety of datasets show that hierarchical shrinkage substantially increases the predictive performance of individual decision trees and decision-tree ensembles.
HS Example. HS applies post-hoc regularization to any decision tree by shrinking each node towards its parent.
MDI+ is a novel feature importance framework, which generalizes the popular mean decrease in impurity (MDI) importance score for random forests. At its core, MDI+ expands upon a recently discovered connection between linear regression and decision trees. In doing so, MDI+ enables practitioners to (1) tailor the feature importance computation to the data/problem structure and (2) incorporate additional features or knowledge to mitigate known biases of decision trees. In both real data case studies and extensive real-data-inspired simulations, MDI+ outperforms commonly used feature importance measures (e.g., MDI, permutation-based scores, and TreeSHAP) by substantional margins.
Readings
Reference implementations (also linked above)
The code here heavily derives from the wonderful work of previous projects. We seek to to extract out, unify, and maintain key parts of these projects.- pycorels - by @fingoldin and the original CORELS team
- sklearn-expertsys - by @tmadl and @kenben based on original code by Ben Letham
- rulefit - by @christophM
- skope-rules - by the skope-rules team (including @ngoix, @floriangardin, @datajms, Bibi Ndiaye, Ronan Gautier)
- boa - by @wangtongada
Related packages
- gplearn: symbolic regression/classification
- pysr: fast symbolic regression
- pygam: generative additive models
- interpretml: boosting-based gam
- h20 ai: gams + glms (and more)
- optbinning: data discretization / scoring models
Updates
- For updates, star the repo, see this related repo, or follow @csinva_
- Please make sure to give authors of original methods / base implementations appropriate credit!
- Contributing: pull requests very welcome!
Please cite the package if you use it in an academic work :)
@software{
imodels2021,
title = {imodels: a python package for fitting interpretable models},
journal = {Journal of Open Source Software},
publisher = {The Open Journal},
year = {2021},
author = {Singh, Chandan and Nasseri, Keyan and Tan, Yan Shuo and Tang, Tiffany and Yu, Bin},
volume = {6},
number = {61},
pages = {3192},
doi = {10.21105/joss.03192},
url = {https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03192},
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for imodels
Similar Open Source Tools

imodels
Python package for concise, transparent, and accurate predictive modeling. All sklearn-compatible and easy to use. _For interpretability in NLP, check out our new package:imodelsX _
LLM-PowerHouse-A-Curated-Guide-for-Large-Language-Models-with-Custom-Training-and-Inferencing
LLM-PowerHouse is a comprehensive and curated guide designed to empower developers, researchers, and enthusiasts to harness the true capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and build intelligent applications that push the boundaries of natural language understanding. This GitHub repository provides in-depth articles, codebase mastery, LLM PlayLab, and resources for cost analysis and network visualization. It covers various aspects of LLMs, including NLP, models, training, evaluation metrics, open LLMs, and more. The repository also includes a collection of code examples and tutorials to help users build and deploy LLM-based applications.
pytorch-grad-cam
This repository provides advanced AI explainability for PyTorch, offering state-of-the-art methods for Explainable AI in computer vision. It includes a comprehensive collection of Pixel Attribution methods for various tasks like Classification, Object Detection, Semantic Segmentation, and more. The package supports high performance with full batch image support and includes metrics for evaluating and tuning explanations. Users can visualize and interpret model predictions, making it suitable for both production and model development scenarios.
floneum
Floneum is a graph editor that makes it easy to develop your own AI workflows. It uses large language models (LLMs) to run AI models locally, without any external dependencies or even a GPU. This makes it easy to use LLMs with your own data, without worrying about privacy. Floneum also has a plugin system that allows you to improve the performance of LLMs and make them work better for your specific use case. Plugins can be used in any language that supports web assembly, and they can control the output of LLMs with a process similar to JSONformer or guidance.
SemanticFinder
SemanticFinder is a frontend-only live semantic search tool that calculates embeddings and cosine similarity client-side using transformers.js and SOTA embedding models from Huggingface. It allows users to search through large texts like books with pre-indexed examples, customize search parameters, and offers data privacy by keeping input text in the browser. The tool can be used for basic search tasks, analyzing texts for recurring themes, and has potential integrations with various applications like wikis, chat apps, and personal history search. It also provides options for building browser extensions and future ideas for further enhancements and integrations.
cambrian
Cambrian-1 is a fully open project focused on exploring multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) with a vision-centric approach. It offers competitive performance across various benchmarks with models at different parameter levels. The project includes training configurations, model weights, instruction tuning data, and evaluation details. Users can interact with Cambrian-1 through a Gradio web interface for inference. The project is inspired by LLaVA and incorporates contributions from Vicuna, LLaMA, and Yi. Cambrian-1 is licensed under Apache 2.0 and utilizes datasets and checkpoints subject to their respective original licenses.
TableLLM
TableLLM is a large language model designed for efficient tabular data manipulation tasks in real office scenarios. It can generate code solutions or direct text answers for tasks like insert, delete, update, query, merge, and chart operations on tables embedded in spreadsheets or documents. The model has been fine-tuned based on CodeLlama-7B and 13B, offering two scales: TableLLM-7B and TableLLM-13B. Evaluation results show its performance on benchmarks like WikiSQL, Spider, and self-created table operation benchmark. Users can use TableLLM for code and text generation tasks on tabular data.
Awesome-LLM-Large-Language-Models-Notes
Awesome-LLM-Large-Language-Models-Notes is a repository that provides a comprehensive collection of information on various Large Language Models (LLMs) classified by year, size, and name. It includes details on known LLM models, their papers, implementations, and specific characteristics. The repository also covers LLM models classified by architecture, must-read papers, blog articles, tutorials, and implementations from scratch. It serves as a valuable resource for individuals interested in understanding and working with LLMs in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP).
llm-datasets
LLM Datasets is a repository containing high-quality datasets, tools, and concepts for LLM fine-tuning. It provides datasets with characteristics like accuracy, diversity, and complexity to train large language models for various tasks. The repository includes datasets for general-purpose, math & logic, code, conversation & role-play, and agent & function calling domains. It also offers guidance on creating high-quality datasets through data deduplication, data quality assessment, data exploration, and data generation techniques.
DB-GPT-Hub
DB-GPT-Hub is an experimental project leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Text-to-SQL parsing. It includes stages like data collection, preprocessing, model selection, construction, and fine-tuning of model weights. The project aims to enhance Text-to-SQL capabilities, reduce model training costs, and enable developers to contribute to improving Text-to-SQL accuracy. The ultimate goal is to achieve automated question-answering based on databases, allowing users to execute complex database queries using natural language descriptions. The project has successfully integrated multiple large models and established a comprehensive workflow for data processing, SFT model training, prediction output, and evaluation.
recommenders
Recommenders is a project under the Linux Foundation of AI and Data that assists researchers, developers, and enthusiasts in prototyping, experimenting with, and bringing to production a range of classic and state-of-the-art recommendation systems. The repository contains examples and best practices for building recommendation systems, provided as Jupyter notebooks. It covers tasks such as preparing data, building models using various recommendation algorithms, evaluating algorithms, tuning hyperparameters, and operationalizing models in a production environment on Azure. The project provides utilities to support common tasks like loading datasets, evaluating model outputs, and splitting training/test data. It includes implementations of state-of-the-art algorithms for self-study and customization in applications.
fish-identification
Fishial.ai is a project focused on training and validating scripts for fish segmentation and classification models. It includes various scripts for automatic training with different loss functions, dataset manipulation, and model setup using Detectron2 API. The project also provides tools for converting classification models to TorchScript format and creating training datasets. The models available include MaskRCNN for fish segmentation and various versions of ResNet18 for fish classification with different class counts and features. The project aims to facilitate fish identification and analysis through machine learning techniques.
AgentGym
AgentGym is a framework designed to help the AI community evaluate and develop generally-capable Large Language Model-based agents. It features diverse interactive environments and tasks with real-time feedback and concurrency. The platform supports 14 environments across various domains like web navigating, text games, house-holding tasks, digital games, and more. AgentGym includes a trajectory set (AgentTraj) and a benchmark suite (AgentEval) to facilitate agent exploration and evaluation. The framework allows for agent self-evolution beyond existing data, showcasing comparable results to state-of-the-art models.
sqlcoder
Defog's SQLCoder is a family of state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) designed for converting natural language questions into SQL queries. It outperforms popular open-source models like gpt-4 and gpt-4-turbo on SQL generation tasks. SQLCoder has been trained on more than 20,000 human-curated questions based on 10 different schemas, and the model weights are licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0. Users can interact with SQLCoder through the 'transformers' library and run queries using the 'sqlcoder launch' command in the terminal. The tool has been tested on NVIDIA GPUs with more than 16GB VRAM and Apple Silicon devices with some limitations. SQLCoder offers a demo on their website and supports quantized versions of the model for consumer GPUs with sufficient memory.
cifar10-airbench
CIFAR-10 Airbench is a project offering fast and stable training baselines for CIFAR-10 dataset, facilitating machine learning research. It provides easily runnable PyTorch scripts for training neural networks with high accuracy levels. The methods used in this project aim to accelerate research on fundamental properties of deep learning. The project includes GPU-accelerated dataloader for custom experiments and trainings, and can be used for data selection and active learning experiments. The training methods provided are faster than standard ResNet training, offering improved performance for research projects.
For similar tasks

imodels
Python package for concise, transparent, and accurate predictive modeling. All sklearn-compatible and easy to use. _For interpretability in NLP, check out our new package:imodelsX _
vectordb-recipes
This repository contains examples, applications, starter code, & tutorials to help you kickstart your GenAI projects. * These are built using LanceDB, a free, open-source, serverless vectorDB that **requires no setup**. * It **integrates into python data ecosystem** so you can simply start using these in your existing data pipelines in pandas, arrow, pydantic etc. * LanceDB has **native Typescript SDK** using which you can **run vector search** in serverless functions! This repository is divided into 3 sections: - Examples - Get right into the code with minimal introduction, aimed at getting you from an idea to PoC within minutes! - Applications - Ready to use Python and web apps using applied LLMs, VectorDB and GenAI tools - Tutorials - A curated list of tutorials, blogs, Colabs and courses to get you started with GenAI in greater depth.
For similar jobs

lollms-webui
LoLLMs WebUI (Lord of Large Language Multimodal Systems: One tool to rule them all) is a user-friendly interface to access and utilize various LLM (Large Language Models) and other AI models for a wide range of tasks. With over 500 AI expert conditionings across diverse domains and more than 2500 fine tuned models over multiple domains, LoLLMs WebUI provides an immediate resource for any problem, from car repair to coding assistance, legal matters, medical diagnosis, entertainment, and more. The easy-to-use UI with light and dark mode options, integration with GitHub repository, support for different personalities, and features like thumb up/down rating, copy, edit, and remove messages, local database storage, search, export, and delete multiple discussions, make LoLLMs WebUI a powerful and versatile tool.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

minio
MinIO is a High Performance Object Storage released under GNU Affero General Public License v3.0. It is API compatible with Amazon S3 cloud storage service. Use MinIO to build high performance infrastructure for machine learning, analytics and application data workloads.

mage-ai
Mage is an open-source data pipeline tool for transforming and integrating data. It offers an easy developer experience, engineering best practices built-in, and data as a first-class citizen. Mage makes it easy to build, preview, and launch data pipelines, and provides observability and scaling capabilities. It supports data integrations, streaming pipelines, and dbt integration.

AiTreasureBox
AiTreasureBox is a versatile AI tool that provides a collection of pre-trained models and algorithms for various machine learning tasks. It simplifies the process of implementing AI solutions by offering ready-to-use components that can be easily integrated into projects. With AiTreasureBox, users can quickly prototype and deploy AI applications without the need for extensive knowledge in machine learning or deep learning. The tool covers a wide range of tasks such as image classification, text generation, sentiment analysis, object detection, and more. It is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to both beginners and experienced developers, making AI development more efficient and accessible to a wider audience.

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.

airbyte
Airbyte is an open-source data integration platform that makes it easy to move data from any source to any destination. With Airbyte, you can build and manage data pipelines without writing any code. Airbyte provides a library of pre-built connectors that make it easy to connect to popular data sources and destinations. You can also create your own connectors using Airbyte's no-code Connector Builder or low-code CDK. Airbyte is used by data engineers and analysts at companies of all sizes to build and manage their data pipelines.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.