
TableLLM
TableLLM: Enabling Tabular Data Manipulation by LLMs in Real Office Usage Scenarios
Stars: 77
TableLLM is a large language model designed for efficient tabular data manipulation tasks in real office scenarios. It can generate code solutions or direct text answers for tasks like insert, delete, update, query, merge, and chart operations on tables embedded in spreadsheets or documents. The model has been fine-tuned based on CodeLlama-7B and 13B, offering two scales: TableLLM-7B and TableLLM-13B. Evaluation results show its performance on benchmarks like WikiSQL, Spider, and self-created table operation benchmark. Users can use TableLLM for code and text generation tasks on tabular data.
README:
| Paper | Homepage | Model | Training set | Platform |
We present TableLLM, a powerful large language model designed to handle tabular data manipulation tasks efficiently, whether they are embedded in spreadsheets or documents, meeting the demands of real office scenarios. The TableLLM series encompasses two distinct scales: TableLLM-7B and TableLLM-13B, which are fine-tuned based on CodeLlama-7B and 13B.
TableLLM generates either a code solution or a direct text answer to handle tabular data manipulation tasks based on different scenarios. Code generation is used for handling spreadsheet-embedded tabular data, which often involves the insert, delete, update, query, merge, and chart operations of tables. Text generation is used for handling document-embedded tabular data, which often involves the query operation of short tables.
[2024/06] 🔥 We open-source the frontend and backend for deploying TableLLM.
[2024/04] 📑 Our paper was published on arxiv.
[2024/03] 📊 We released training set.
[2024/02] 📦 We released TableLLM model, fine-tuning code, inference code, benchmarks, and evaluation scripts.
We evaluate the code solution generation ability of TableLLM on three benchmarks: WikiSQL, Spider and Self-created table operation benchmark. The text answer generation ability is tested on four benchmarks: WikiTableQuestion (WikiTQ), TAT-QA, FeTaQA and OTTQA. The evaluation result is shown below:
| Model | WikiTQ | TAT-QA | FeTaQA | OTTQA | WikiSQL | Spider | Self-created | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TaPEX | 38.5 | – | – | – | 83.9 | 15.0 | / | 45.8 |
| TaPas | 31.5 | – | – | – | 74.2 | 23.1 | / | 42.9 |
| TableLlama | 24.0 | 22.2 | 20.5 | 6.4 | 43.7 | 9.0 | / | 20.7 |
| GPT3.5 | 58.5 | 72.1 | 71.2 | 60.8 | 81.7 | 67.4 | 77.1 | 69.8 |
| GPT4 | 74.1 | 77.1 | 78.4 | 69.5 | 84.0 | 69.5 | 77.8 | 75.8 |
| Llama2-Chat (13B) | 48.8 | 49.6 | 67.7 | 61.5 | – | – | – | 56.9 |
| CodeLlama (13B) | 43.4 | 47.2 | 57.2 | 49.7 | 38.3 | 21.9 | 47.6 | 43.6 |
| Deepseek-Coder (33B) | 6.5 | 11.0 | 7.1 | 7.4 | 72.5 | 58.4 | 73.9 | 33.8 |
| StructGPT (GPT3.5) | 52.5 | 27.5 | 11.8 | 14.0 | 67.8 | 84.8 | / | 48.9 |
| Binder (GPT3.5) | 61.6 | 12.8 | 6.8 | 5.1 | 78.6 | 52.6 | / | 42.5 |
| DATER (GPT3.5) | 53.4 | 28.4 | 18.3 | 13.0 | 58.2 | 26.5 | / | 37.0 |
| TableLLM-7B (Ours) | 58.8 | 66.9 | 72.6 | 63.1 | 86.6 | 82.6 | 78.8 | 72.8 |
| TableLLM-13B (Ours) | 62.4 | 68.2 | 74.5 | 62.5 | 90.7 | 83.4 | 80.8 | 74.7 |
We use six public benchmarks and one self-created benchmark for evaluation. As the public benchmarks we used are modified to fit the application scenario of TableLLM, we provide a detailed description of these public benchmarks and self-created benchmarks below. You can obtain the original file of these benchmarks in benchmark folder.
- WikiTQ: Limit the table to a token count of less than 500 and randomly sample 633 instances.
- TAT-QA: Limit the table to a token count of less than 500 and randomly sample 800 instances.
- FeTaQA: Limit the table to a token count of less than 500 and randomly sample 753 instances.
- OTTQA: Limit the table to a token count of less than 500 and use all instances that meet this condition.
- WikiSQL: As the WikiSQL testset contains incorrect answers and ambiguous questions, we manually filter out 1000 records and construct a subset of the WikiSQL testset called wikisql-human-annotated.
- Spider: As TableLLM currently focuses on single-table queries, we filter out single-table questions in Spider dev ser and also remove questions whose answers are empty.
- Self-created: We create a new benchmark, including the insert, delete, update, query, merge, and chart operations of tables. For more details, please refer to the paper.
The prompts we used for generating code solutions and text answers are introduced below.
The prompt template for the insert, delete, update, query, and chart operations on a single table.
[INST]Below are the first few lines of a CSV file. You need to write a Python program to solve the provided question.
Header and first few lines of CSV file:
{csv_data}
Question: {question}[/INST]
The prompt template for the merge operation on two tables.
[INST]Below are the first few lines two CSV file. You need to write a Python program to solve the provided question.
Header and first few lines of CSV file 1:
{csv_data1}
Header and first few lines of CSV file 2:
{csv_data2}
Question: {question}[/INST]
The csv_data field is filled with the first few lines of your provided table file. Below is an example:
Sex,Length,Diameter,Height,Whole weight,Shucked weight,Viscera weight,Shell weight,Rings
M,0.455,0.365,0.095,0.514,0.2245,0.101,0.15,15
M,0.35,0.265,0.09,0.2255,0.0995,0.0485,0.07,7
F,0.53,0.42,0.135,0.677,0.2565,0.1415,0.21,9
M,0.44,0.365,0.125,0.516,0.2155,0.114,0.155,10
I,0.33,0.255,0.08,0.205,0.0895,0.0395,0.055,7
The prompt template for direct text answer generation on short tables.
[INST]Offer a thorough and accurate solution that directly addresses the Question outlined in the [Question].
### [Table Text]
{table_descriptions}
### [Table]
```
{table_in_csv}
```
### [Question]
{question}
### [Solution][INST/]
Install the requirements with pip:
pip install -r requirements.txt
The inference results of TableLLM are provided in inference/results folder. You can also obtain the inference result by yourself. The example commands of code and text generation are shown below:
cd inference
python inference.py --dataset wikisql --model_path TableLLM-13b
python inference.py --dataset wtq --model_path TableLLM-13b
The python code in evaluation folder is used for reproducing evaluation results. For code generation benchmarks, you can run the following command to reproduce the result of TableLLM-13b on WikiSQL:
cd evaluation/wikisql-eval
tar -zxvf csv_tables.tar.gz
python eval.py --infer_data ../../inference/results/TableLLM-13b/Infer_wikisql.jsonl
For text generation, as the CritiqueLLM we used has not been published yet, the judgement of CritiqueLLM is not reproducible. However, you can obtain the judgement result in inference/results folder and reproduce the results using the following command:
cd evaluation/text-eval
python get_sum_grade.py --grade_data ../../inference/results/TableLLM-13b/Grade_wtq.jsonl
You can use the code in deployment folder as the frontend and backend for deploying TableLLM.
Deploy TableLLM using vllm. Remember to modify the PORT and MODEL_PATH in the script and config.json.
cd deployment
bash scripts/deploy_tablellm.sh
Install mongodb and change the username and password to yours in config.json. Prepare the default tables and questions:
bash prepare_default.sh
Deploy the streamlit app:
streamlit run streamlit.py --server.port PORT
@article{zhang2024tablellm,
title={TableLLM: Enabling Tabular Data Manipulation by LLMs in Real Office Usage Scenarios},
author={Zhang, Xiaokang and Zhang, Jing and Ma, Zeyao and Li, Yang and Zhang, Bohan and Li, Guanlin and Yao, Zijun and Xu, Kangli and Zhou, Jinchang and Zhang-Li, Daniel and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.19318},
year={2024}
}
If you have any questions, we encourage you to either create Github issues or get in touch with us at [email protected], [email protected], or [email protected].
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for TableLLM
Similar Open Source Tools

TableLLM
TableLLM is a large language model designed for efficient tabular data manipulation tasks in real office scenarios. It can generate code solutions or direct text answers for tasks like insert, delete, update, query, merge, and chart operations on tables embedded in spreadsheets or documents. The model has been fine-tuned based on CodeLlama-7B and 13B, offering two scales: TableLLM-7B and TableLLM-13B. Evaluation results show its performance on benchmarks like WikiSQL, Spider, and self-created table operation benchmark. Users can use TableLLM for code and text generation tasks on tabular data.
cambrian
Cambrian-1 is a fully open project focused on exploring multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) with a vision-centric approach. It offers competitive performance across various benchmarks with models at different parameter levels. The project includes training configurations, model weights, instruction tuning data, and evaluation details. Users can interact with Cambrian-1 through a Gradio web interface for inference. The project is inspired by LLaVA and incorporates contributions from Vicuna, LLaMA, and Yi. Cambrian-1 is licensed under Apache 2.0 and utilizes datasets and checkpoints subject to their respective original licenses.
DB-GPT-Hub
DB-GPT-Hub is an experimental project leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Text-to-SQL parsing. It includes stages like data collection, preprocessing, model selection, construction, and fine-tuning of model weights. The project aims to enhance Text-to-SQL capabilities, reduce model training costs, and enable developers to contribute to improving Text-to-SQL accuracy. The ultimate goal is to achieve automated question-answering based on databases, allowing users to execute complex database queries using natural language descriptions. The project has successfully integrated multiple large models and established a comprehensive workflow for data processing, SFT model training, prediction output, and evaluation.
Cherry_LLM
Cherry Data Selection project introduces a self-guided methodology for LLMs to autonomously discern and select cherry samples from open-source datasets, minimizing manual curation and cost for instruction tuning. The project focuses on selecting impactful training samples ('cherry data') to enhance LLM instruction tuning by estimating instruction-following difficulty. The method involves phases like 'Learning from Brief Experience', 'Evaluating Based on Experience', and 'Retraining from Self-Guided Experience' to improve LLM performance.
cladder
CLadder is a repository containing the CLadder dataset for evaluating causal reasoning in language models. The dataset consists of yes/no questions in natural language that require statistical and causal inference to answer. It includes fields such as question_id, given_info, question, answer, reasoning, and metadata like query_type and rung. The dataset also provides prompts for evaluating language models and example questions with associated reasoning steps. Additionally, it offers dataset statistics, data variants, and code setup instructions for using the repository.
sqlcoder
Defog's SQLCoder is a family of state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) designed for converting natural language questions into SQL queries. It outperforms popular open-source models like gpt-4 and gpt-4-turbo on SQL generation tasks. SQLCoder has been trained on more than 20,000 human-curated questions based on 10 different schemas, and the model weights are licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0. Users can interact with SQLCoder through the 'transformers' library and run queries using the 'sqlcoder launch' command in the terminal. The tool has been tested on NVIDIA GPUs with more than 16GB VRAM and Apple Silicon devices with some limitations. SQLCoder offers a demo on their website and supports quantized versions of the model for consumer GPUs with sufficient memory.

CodeGeeX4
CodeGeeX4-ALL-9B is an open-source multilingual code generation model based on GLM-4-9B, offering enhanced code generation capabilities. It supports functions like code completion, code interpreter, web search, function call, and repository-level code Q&A. The model has competitive performance on benchmarks like BigCodeBench and NaturalCodeBench, outperforming larger models in terms of speed and performance.

Qwen
Qwen is a series of large language models developed by Alibaba DAMO Academy. It outperforms the baseline models of similar model sizes on a series of benchmark datasets, e.g., MMLU, C-Eval, GSM8K, MATH, HumanEval, MBPP, BBH, etc., which evaluate the models’ capabilities on natural language understanding, mathematic problem solving, coding, etc. Qwen models outperform the baseline models of similar model sizes on a series of benchmark datasets, e.g., MMLU, C-Eval, GSM8K, MATH, HumanEval, MBPP, BBH, etc., which evaluate the models’ capabilities on natural language understanding, mathematic problem solving, coding, etc. Qwen-72B achieves better performance than LLaMA2-70B on all tasks and outperforms GPT-3.5 on 7 out of 10 tasks.
RouterArena
RouterArena is an open evaluation platform and leaderboard for LLM routers, aiming to provide a standardized evaluation framework for assessing the performance of routers in terms of accuracy, cost, and other metrics. It offers diverse data coverage, comprehensive metrics, automated evaluation, and a live leaderboard to track router performance. Users can evaluate their routers by following setup steps, obtaining routing decisions, running LLM inference, and evaluating router performance. Contributions and collaborations are welcome, and users can submit their routers for evaluation to be included in the leaderboard.
llm-structured-output-benchmarks
Benchmark various LLM Structured Output frameworks like Instructor, Mirascope, Langchain, LlamaIndex, Fructose, Marvin, Outlines, LMFormatEnforcer, etc on tasks like multi-label classification, named entity recognition, synthetic data generation. The tool provides benchmark results, methodology, instructions to run the benchmark, add new data, and add a new framework. It also includes a roadmap for framework-related tasks, contribution guidelines, citation information, and feedback request.
optillm
optillm is an OpenAI API compatible optimizing inference proxy implementing state-of-the-art techniques to enhance accuracy and performance of LLMs, focusing on reasoning over coding, logical, and mathematical queries. By leveraging additional compute at inference time, it surpasses frontier models across diverse tasks.
AI-Toolbox
AI-Toolbox is a C++ library aimed at representing and solving common AI problems, with a focus on MDPs, POMDPs, and related algorithms. It provides an easy-to-use interface that is extensible to many problems while maintaining readable code. The toolbox includes tutorials for beginners in reinforcement learning and offers Python bindings for seamless integration. It features utilities for combinatorics, polytopes, linear programming, sampling, distributions, statistics, belief updating, data structures, logging, seeding, and more. Additionally, it supports bandit/normal games, single agent MDP/stochastic games, single agent POMDP, and factored/joint multi-agent scenarios.
AQLM
AQLM is the official PyTorch implementation for Extreme Compression of Large Language Models via Additive Quantization. It includes prequantized AQLM models without PV-Tuning and PV-Tuned models for LLaMA, Mistral, and Mixtral families. The repository provides inference examples, model details, and quantization setups. Users can run prequantized models using Google Colab examples, work with different model families, and install the necessary inference library. The repository also offers detailed instructions for quantization, fine-tuning, and model evaluation. AQLM quantization involves calibrating models for compression, and users can improve model accuracy through finetuning. Additionally, the repository includes information on preparing models for inference and contributing guidelines.
moatless-tools
Moatless Tools is a hobby project focused on experimenting with using Large Language Models (LLMs) to edit code in large existing codebases. The project aims to build tools that insert the right context into prompts and handle responses effectively. It utilizes an agentic loop functioning as a finite state machine to transition between states like Search, Identify, PlanToCode, ClarifyChange, and EditCode for code editing tasks.
rageval
Rageval is an evaluation tool for Retrieval-augmented Generation (RAG) methods. It helps evaluate RAG systems by performing tasks such as query rewriting, document ranking, information compression, evidence verification, answer generation, and result validation. The tool provides metrics for answer correctness and answer groundedness, along with benchmark results for ASQA and ALCE datasets. Users can install and use Rageval to assess the performance of RAG models in question-answering tasks.
SemanticFinder
SemanticFinder is a frontend-only live semantic search tool that calculates embeddings and cosine similarity client-side using transformers.js and SOTA embedding models from Huggingface. It allows users to search through large texts like books with pre-indexed examples, customize search parameters, and offers data privacy by keeping input text in the browser. The tool can be used for basic search tasks, analyzing texts for recurring themes, and has potential integrations with various applications like wikis, chat apps, and personal history search. It also provides options for building browser extensions and future ideas for further enhancements and integrations.
For similar tasks
basdonax-ai-rag
Basdonax AI RAG v1.0 is a repository that contains all the necessary resources to create your own AI-powered secretary using the RAG from Basdonax AI. It leverages open-source models from Meta and Microsoft, namely 'Llama3-7b' and 'Phi3-4b', allowing users to upload documents and make queries. This tool aims to simplify life for individuals by harnessing the power of AI. The installation process involves choosing between different data models based on GPU capabilities, setting up Docker, pulling the desired model, and customizing the assistant prompt file. Once installed, users can access the RAG through a local link and enjoy its functionalities.

TableLLM
TableLLM is a large language model designed for efficient tabular data manipulation tasks in real office scenarios. It can generate code solutions or direct text answers for tasks like insert, delete, update, query, merge, and chart operations on tables embedded in spreadsheets or documents. The model has been fine-tuned based on CodeLlama-7B and 13B, offering two scales: TableLLM-7B and TableLLM-13B. Evaluation results show its performance on benchmarks like WikiSQL, Spider, and self-created table operation benchmark. Users can use TableLLM for code and text generation tasks on tabular data.
awesome-agents
Awesome Agents is a curated list of open source AI agents designed for various tasks such as private interactions with documents, chat implementations, autonomous research, human-behavior simulation, code generation, HR queries, domain-specific research, and more. The agents leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) and other generative AI technologies to provide solutions for complex tasks and projects. The repository includes a diverse range of agents for different use cases, from conversational chatbots to AI coding engines, and from autonomous HR assistants to vision task solvers.
Lumi-AI
Lumi AI is a friendly AI sidekick with a human-like personality that offers features like file upload and analysis, web search, local chat storage, custom instructions, changeable conversational style, enhanced context retention, voice query input, and various tools. The project has been developed with contributions from a team of developers, designers, and testers, and is licensed under Apache 2.0 and MIT licenses.
awesome-rag
Awesome RAG is a curated list of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) in large language models. It includes papers, surveys, general resources, lectures, talks, tutorials, workshops, tools, and other collections related to retrieval-augmented generation. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements, techniques, and applications in the field of RAG.
ai2-scholarqa-lib
Ai2 Scholar QA is a system for answering scientific queries and literature review by gathering evidence from multiple documents across a corpus and synthesizing an organized report with evidence for each claim. It consists of a retrieval component and a three-step generator pipeline. The retrieval component fetches relevant evidence passages using the Semantic Scholar public API and reranks them. The generator pipeline includes quote extraction, planning and clustering, and summary generation. The system is powered by the ScholarQA class, which includes components like PaperFinder and MultiStepQAPipeline. It requires environment variables for Semantic Scholar API and LLMs, and can be run as local docker containers or embedded into another application as a Python package.
baibot
Baibot is a versatile chatbot framework designed to simplify the process of creating and deploying chatbots. It provides a user-friendly interface for building custom chatbots with various functionalities such as natural language processing, conversation flow management, and integration with external APIs. Baibot is highly customizable and can be easily extended to suit different use cases and industries. With Baibot, developers can quickly create intelligent chatbots that can interact with users in a seamless and engaging manner, enhancing user experience and automating customer support processes.
openclaw
OpenClaw is a personal AI assistant that runs on your own devices, answering you on various channels like WhatsApp, Telegram, Slack, Discord, and more. It can speak and listen on different platforms and render a live Canvas you control. The Gateway serves as the control plane, while the assistant is the main product. It provides a local, fast, and always-on single-user assistant experience. The preferred setup involves running the onboarding wizard in your terminal to guide you through setting up the gateway, workspace, channels, and skills. The tool supports various models and authentication methods, with a focus on security and privacy.
For similar jobs
databerry
Chaindesk is a no-code platform that allows users to easily set up a semantic search system for personal data without technical knowledge. It supports loading data from various sources such as raw text, web pages, files (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, PDF, Markdown, Plain Text), and upcoming support for web sites, Notion, and Airtable. The platform offers a user-friendly interface for managing datastores, querying data via a secure API endpoint, and auto-generating ChatGPT Plugins for each datastore. Chaindesk utilizes a Vector Database (Qdrant), Openai's text-embedding-ada-002 for embeddings, and has a chunk size of 1024 tokens. The technology stack includes Next.js, Joy UI, LangchainJS, PostgreSQL, Prisma, and Qdrant, inspired by the ChatGPT Retrieval Plugin.
OAD
OAD is a powerful open-source tool for analyzing and visualizing data. It provides a user-friendly interface for exploring datasets, generating insights, and creating interactive visualizations. With OAD, users can easily import data from various sources, clean and preprocess data, perform statistical analysis, and create customizable visualizations to communicate findings effectively. Whether you are a data scientist, analyst, or researcher, OAD can help you streamline your data analysis workflow and uncover valuable insights from your data.

sqlcoder
Defog's SQLCoder is a family of state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) designed for converting natural language questions into SQL queries. It outperforms popular open-source models like gpt-4 and gpt-4-turbo on SQL generation tasks. SQLCoder has been trained on more than 20,000 human-curated questions based on 10 different schemas, and the model weights are licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0. Users can interact with SQLCoder through the 'transformers' library and run queries using the 'sqlcoder launch' command in the terminal. The tool has been tested on NVIDIA GPUs with more than 16GB VRAM and Apple Silicon devices with some limitations. SQLCoder offers a demo on their website and supports quantized versions of the model for consumer GPUs with sufficient memory.

TableLLM
TableLLM is a large language model designed for efficient tabular data manipulation tasks in real office scenarios. It can generate code solutions or direct text answers for tasks like insert, delete, update, query, merge, and chart operations on tables embedded in spreadsheets or documents. The model has been fine-tuned based on CodeLlama-7B and 13B, offering two scales: TableLLM-7B and TableLLM-13B. Evaluation results show its performance on benchmarks like WikiSQL, Spider, and self-created table operation benchmark. Users can use TableLLM for code and text generation tasks on tabular data.
mlcraft
Synmetrix (prev. MLCraft) is an open source data engineering platform and semantic layer for centralized metrics management. It provides a complete framework for modeling, integrating, transforming, aggregating, and distributing metrics data at scale. Key features include data modeling and transformations, semantic layer for unified data model, scheduled reports and alerts, versioning, role-based access control, data exploration, caching, and collaboration on metrics modeling. Synmetrix leverages Cube (Cube.js) for flexible data models that consolidate metrics from various sources, enabling downstream distribution via a SQL API for integration into BI tools, reporting, dashboards, and data science. Use cases include data democratization, business intelligence, embedded analytics, and enhancing accuracy in data handling and queries. The tool speeds up data-driven workflows from metrics definition to consumption by combining data engineering best practices with self-service analytics capabilities.
data-scientist-roadmap2024
The Data Scientist Roadmap2024 provides a comprehensive guide to mastering essential tools for data science success. It includes programming languages, machine learning libraries, cloud platforms, and concepts categorized by difficulty. The roadmap covers a wide range of topics from programming languages to machine learning techniques, data visualization tools, and DevOps/MLOps tools. It also includes web development frameworks and specific concepts like supervised and unsupervised learning, NLP, deep learning, reinforcement learning, and statistics. Additionally, it delves into DevOps tools like Airflow and MLFlow, data visualization tools like Tableau and Matplotlib, and other topics such as ETL processes, optimization algorithms, and financial modeling.
VMind
VMind is an open-source solution for intelligent visualization, providing an intelligent chart component based on LLM by VisActor. It allows users to create chart narrative works with natural language interaction, edit charts through dialogue, and export narratives as videos or GIFs. The tool is easy to use, scalable, supports various chart types, and offers one-click export functionality. Users can customize chart styles, specify themes, and aggregate data using LLM models. VMind aims to enhance efficiency in creating data visualization works through dialogue-based editing and natural language interaction.
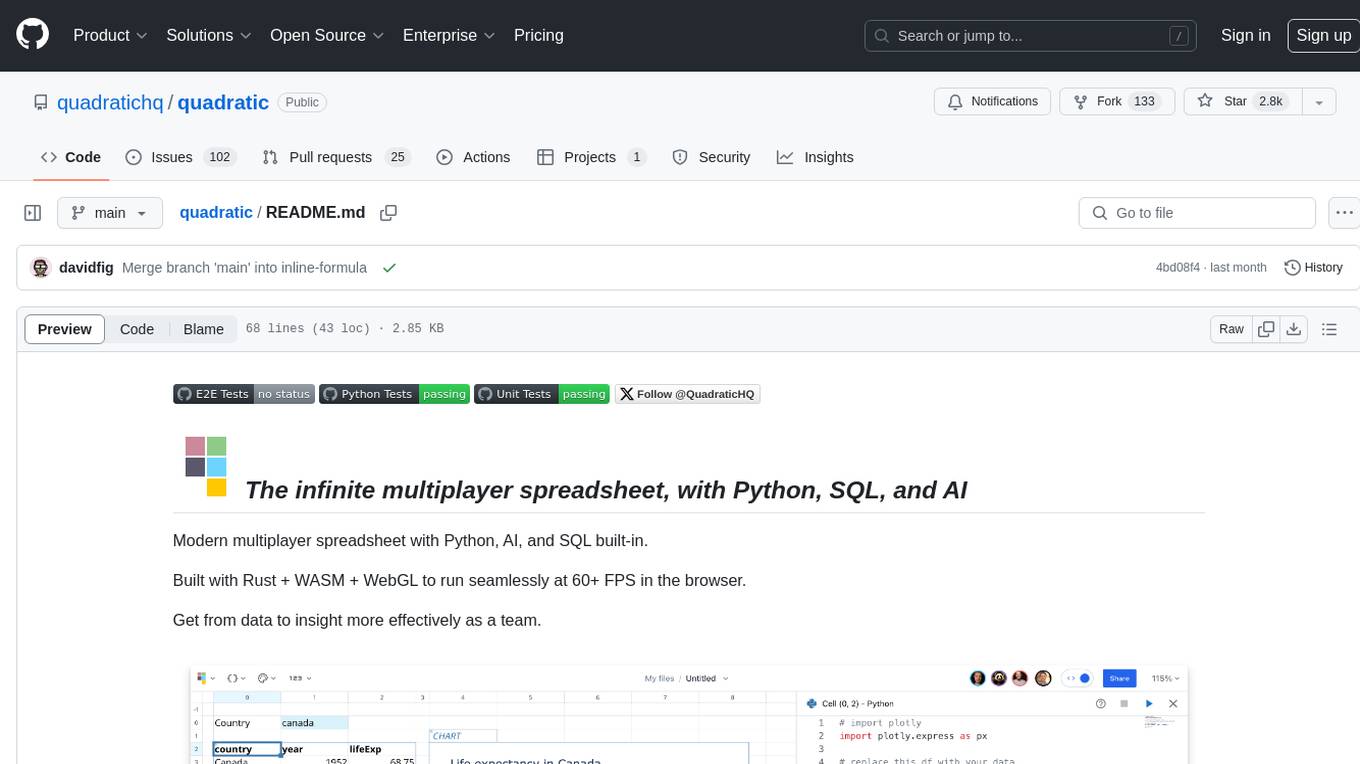
quadratic
Quadratic is a modern multiplayer spreadsheet application that integrates Python, AI, and SQL functionalities. It aims to streamline team collaboration and data analysis by enabling users to pull data from various sources and utilize popular data science tools. The application supports building dashboards, creating internal tools, mixing data from different sources, exploring data for insights, visualizing Python workflows, and facilitating collaboration between technical and non-technical team members. Quadratic is built with Rust + WASM + WebGL to ensure seamless performance in the browser, and it offers features like WebGL Grid, local file management, Python and Pandas support, Excel formula support, multiplayer capabilities, charts and graphs, and team support. The tool is currently in Beta with ongoing development for additional features like JS support, SQL database support, and AI auto-complete.
