
Large-Language-Models-play-StarCraftII
TextStarCraft2,a pure language env which support llms play starcraft2
Stars: 152
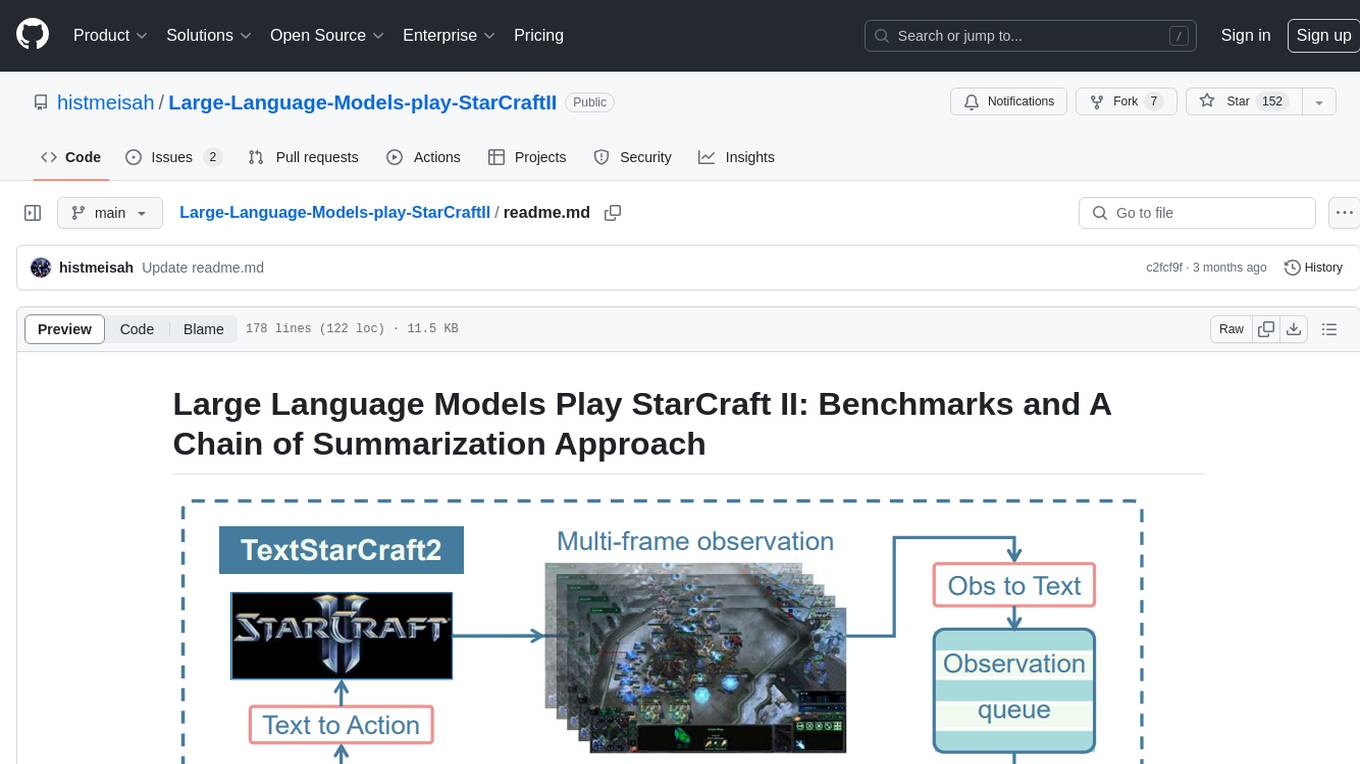
Large Language Models Play StarCraft II is a project that explores the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in playing the game StarCraft II. The project introduces TextStarCraft II, a textual environment for the game, and a Chain of Summarization method for analyzing game information and making strategic decisions. Through experiments, the project demonstrates that LLM agents can defeat the built-in AI at a challenging difficulty level. The project provides benchmarks and a summarization approach to enhance strategic planning and interpretability in StarCraft II gameplay.
README:
StarCraft II is a challenging benchmark for AI agents due to micro-level operations and macro-awareness. Previous works, such as Alphastar and SCC, achieve impressive performance on tackling StarCraft
II , however, still exhibit deficiencies in long-term strategic planning and strategy interpretability. Emerging large language model (LLM) agents, presents the immense potential in solving intricate tasks.
Motivated by this, we aim to validate the capabilities of LLMs on StarCraft II. We first develop textual StratCraft II environment, called TextStarCraft II. Secondly, we propose a Chain of Summarization method, including single-frame summarization for processing raw observations and multi-frame summarization for analyzing game information, providing command recommendations, and generating strategic decisions. Our experiment demonstrates that LLM agents are capable of defeating the built-in AI at the Harder(Lv5) difficulty level.
| Work | AlphaStar | SCC | HierNet-SC2 | AlphaStar Unplugged | ROA-Star | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | SL+RL+self-play | SL+RL+self-play | data-mining + RL | offline RL | SL+RL+self-play | prompt + Rule base script |
| Compute resource | 12000 CPU cores, 384 TPUs | Linear | 4 GPUs,48 CPU cores | not clear | 2x 64 v100 | 1 gpu,1 cpu(home computer) |
| Required replay | 971,000 | 4,638 | 608 | 20,000,000(20m) | 120938 | 0 |
| Best result(The greatest opponent ever to win) | Serral(One of the best progamer in the world) | Time(IEM2023 Champion) | build-in ai lv-10 | AlphaStar BC agent | hero(GSL Champion) | build-in ai lv-5 |
| Strategy Interpretability | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✔ |
| Expansibility(adapt to latest game version and other race ) | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✔ |
Our paper:
Large Language Models Play StarCraft II: Benchmarks and A Chain of Summarization Approach https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.11865
Our website:
Large Language Models Play StarCraft II: Benchmarks and A Chain of Summarization Approach
Our demo video:
Large Language Models Play StarCraft II: Benchmarks and A Chain of Summarization Approach
Comparing models using either the full CoS or CoS without CoT.
| Model | Method | Win Rate | PBR | RUR | APU | TR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Using Full CoS | ||||||
| GPT3.5-Turbo-16k | Full CoS | 5/10 | 0.0781 | 7875 | 0.7608 | 0.4476 |
| GPT4-Turbo | Full CoS | 3/6 | 0.0337 | 8306 | 0.7194 | 0.3452 |
| Gemini-Pro | Full CoS | 2/10 | 0.0318 | 9284 | 0.6611 | 0.3571 |
| GLM4 | Full CoS | 2/10 | 0.0327 | 3131 | 0.6644 | 0.2904 |
| Llama2 70B | Full CoS | / | / | / | / | / |
| Claude2.1 | Full CoS | 2/9 | 0.0219 | 10867 | 0.6599 | 0.4312 |
| Using CoS without CoT | ||||||
| Finetune-ChatGlm3 6b | CoS w/o CoT | 2/10 | 0.0528 | 30356 | 0.6547 | 0.1714 |
| Finetune-Qwen 1.8b | CoS w/o CoT | 6/10 | 0.0384 | 12826 | 0.7506 | 0.2095 |
| Finetune-Qwen 7b | CoS w/o CoT | 6/12 | 0.0421 | 12276 | 0.7234 | 0.3214 |
| Finetune-Llama2 7b | CoS w/o CoT | 0/12 | 0.0469 | 12295 | 0.5752 | 0.0853 |
| Prompt | LV1 | LV2 | LV3 | LV4 | LV5 | LV6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prompt1 | 7/8 | 6/9 | 2/8 | 1/8 | 0/8 | 0/8 |
| Prompt2 | 8/8 | 9/9 | 8/8 | 21/25 | 7/14 | 0/12 |
StatCraft II is a classic game developed by BLZ, and has some professional leagues such as IEM, WTL....You can download Battle.net from:https://us.shop.battle.net/en-us, or here:https://www.blizzard.com/zh-tw/
If you are Chinese, due to the Bobby Kotick, CN play cant own their sever again. So we must download StarCraft II by this video :video or you can search in the internet.
First , we should use StarCraft II Editor.exe to download the newest ladder map
when we open this, please log in your blz account and search the map which you want.
Then you should put maps to your StarCrafrt2 file in StarCraft II\Maps(If the 'Maps' file dont exist, please create it).
Or you can download maps in here:
- OS, We used Windows 11 to develop this demo, because BLZ didnt release the latest sc2 on liunx, so please run our repo on Windows OS!
-
python: python 3.10. -
cuda: cuda 12.1. -
torch: 2.1.0 -
openai: 0.27.9, very important. This is crucial as versions above 0.28 have altered API functionalities. Install all necessary packages withpip install -r requirements.txt.
-
burnysc2: This is our core package, offering an easy-to-use API for project development. Find more information here:Python-sc2 -
chromadb: We utilize the Chroma vector database. Due to package conflicts, install Chromadb first, followed by burnysc2. -
Huggingfaceandsentence-transformers: we used the embedding modelsentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v2, in our github version, it will automatically download. We also provide thereleasezip, you can just download and unzip that(with embedding model).
-
Agent vs Botai: You can test intest_the_env.py&multiprocess_test.py -
Human vs Agent: You can try in ourHuman_LLM_agent_test.py -
Agent vs Agent: You can try in our2agent_test.py
You can run test_the_env.py to try our agent. Here is some parameters you need to set.
-
player_race: Currently, onlyProtossis supported.ZergandTerranare under development. -
opposite_race: Typically set toZerg, butTerranandProtossare also compatible. -
difficulty: We offer 10 difficulty levels, ranging from Level 1 (VeryEasy) to Level 10 (CheatInsane). Note that these names differ from those in the StarCraft2 client, but the AI difficulty remains unchanged.
| Level | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLZ difficulty | VeryEasy | Easy | Medium | Hard | Harder | Very Hard | Elite | CheatVision | CheatMoney | CheatInsane |
| python-sc2 difficulty | VeryEasy | Easy | Medium | MediumHard | Hard | Harder | VeryHard | CheatVision | CheatMoney | CheatInsane |
-
replay_folder: Specify the folder for saving demo replays. -
LLM_model_name: We usedgpt-3.5-turbo-16kin our experiments. -
LLM_temperature: Set between 0 and 1 as per your preference. -
LLM_api_key: Your API key. -
LLM_api_base: Your API base URL.
Note: Using LLM to play StarCraft2 can take approximately 7 hours for a single game.
To save time, you can run multiple demos simultaneously using multiprocess_test.py. Configure the following parameter:
-
num_processes: The number of processes to spawn.
Other parameters are the same as in the Single Process setup.
In our experiments, we have added some more settings, but due to several reasons these settings will coming soon.
-
num_agents: This environment will supportLLM agentvsLLM agentorRL agent. -
env_type: This environment will support Text or MultiModal - 'player_race': This environment will support Zerg and Terran
-
opposite_type: This env will support some human designed botai.
If you want to use other llm to create your own llm agent, the following things you should to know.
-
LLM: In our repo, you should request llm fromChatBot_SingleTurnfunction inTextStarCraft2_2/LLM/gpt_test - 'L1_summarize': Our level-1 summarization method is here:
generate_summarize_L1inTextStarCraft2_2/summarize/L1_summarize.py -
L2_summarize: Our level-2 summarization method is here :L2_summaryinTextStarCraft2_2/summarize/gpt_test/L2_summarize.py -
action dict: The actions that llm agent can use. Here we can setTextStarCraft2_2/utils/action_info.py. You can add more actions for llm agent. -
action extractor: We can extract decisions byTextStarCraft2_2/utils/action_extractor.py
The core of our TextStarCraft II env is TextStarCraft2_2/env/bot. Here you can add more settings for environment. So if you want to realise Terran and Zerg bot, you can modify our code about this dictionary.
-
State: InProtoss_bot.py, the State of Env is generate fromget_informationfunction. This is what we saidObs to Text adaptor -
Action: InProtoss_bot.py, the Action space of Agent is designed by thesehandle_actionfunction. This is what we saidText to Action adaptor.
We have tested several LLMs in our experiments. The usage is in sc2_rl_agent/starcraftenv_test/LLM file
-
Online LLM:GPT3.5-tubor,GLM4,Gemini-pro,Claude2. -
Local LLM:GLM3,QWEN,QWEN1.5.
Our framework in TextStarCraft II extends traditional StarCraft II analytics to evaluate LLM agents’ strategies with metrics tailored for AI gameplay performance:
-
Win Rate: Reflects the agent's performance, calculated as the percentage of games won out of total games played.
-
Population Block Ratio (PBR): Indicates macro-management effectiveness, focusing on resource allocation and population growth. A higher PBR suggests less effective macro-strategy due to more time spent at population cap.
-
Resource Utilization Ratio (RUR): Measures how efficiently the agent manages resources throughout the game. Higher RUR indicates underutilization of resources.
-
Average Population Utilization (APU): Assesses efficiency in utilizing population capacity. Higher APU indicates better macro-management.
-
Technology Rate (TR): Evaluates the agent's use of the technology tree, showing the proportion of technologies and buildings completed. It reflects the agent’s technological advancement.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Large-Language-Models-play-StarCraftII
Similar Open Source Tools

Large-Language-Models-play-StarCraftII
Large Language Models Play StarCraft II is a project that explores the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in playing the game StarCraft II. The project introduces TextStarCraft II, a textual environment for the game, and a Chain of Summarization method for analyzing game information and making strategic decisions. Through experiments, the project demonstrates that LLM agents can defeat the built-in AI at a challenging difficulty level. The project provides benchmarks and a summarization approach to enhance strategic planning and interpretability in StarCraft II gameplay.
cambrian
Cambrian-1 is a fully open project focused on exploring multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) with a vision-centric approach. It offers competitive performance across various benchmarks with models at different parameter levels. The project includes training configurations, model weights, instruction tuning data, and evaluation details. Users can interact with Cambrian-1 through a Gradio web interface for inference. The project is inspired by LLaVA and incorporates contributions from Vicuna, LLaMA, and Yi. Cambrian-1 is licensed under Apache 2.0 and utilizes datasets and checkpoints subject to their respective original licenses.
AgentPoison
AgentPoison is a repository that provides the official PyTorch implementation of the paper 'AgentPoison: Red-teaming LLM Agents via Memory or Knowledge Base Backdoor Poisoning'. It offers tools for red-teaming LLM agents by poisoning memory or knowledge bases. The repository includes trigger optimization algorithms, agent experiments, and evaluation scripts for Agent-Driver, ReAct-StrategyQA, and EHRAgent. Users can fine-tune motion planners, inject queries with triggers, and evaluate red-teaming performance. The codebase supports multiple RAG embedders and provides a unified dataset access for all three agents.
AI-Toolbox
AI-Toolbox is a C++ library aimed at representing and solving common AI problems, with a focus on MDPs, POMDPs, and related algorithms. It provides an easy-to-use interface that is extensible to many problems while maintaining readable code. The toolbox includes tutorials for beginners in reinforcement learning and offers Python bindings for seamless integration. It features utilities for combinatorics, polytopes, linear programming, sampling, distributions, statistics, belief updating, data structures, logging, seeding, and more. Additionally, it supports bandit/normal games, single agent MDP/stochastic games, single agent POMDP, and factored/joint multi-agent scenarios.
optillm
optillm is an OpenAI API compatible optimizing inference proxy implementing state-of-the-art techniques to enhance accuracy and performance of LLMs, focusing on reasoning over coding, logical, and mathematical queries. By leveraging additional compute at inference time, it surpasses frontier models across diverse tasks.
llm-structured-output-benchmarks
Benchmark various LLM Structured Output frameworks like Instructor, Mirascope, Langchain, LlamaIndex, Fructose, Marvin, Outlines, LMFormatEnforcer, etc on tasks like multi-label classification, named entity recognition, synthetic data generation. The tool provides benchmark results, methodology, instructions to run the benchmark, add new data, and add a new framework. It also includes a roadmap for framework-related tasks, contribution guidelines, citation information, and feedback request.

skyvern
Skyvern automates browser-based workflows using LLMs and computer vision. It provides a simple API endpoint to fully automate manual workflows, replacing brittle or unreliable automation solutions. Traditional approaches to browser automations required writing custom scripts for websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions which would break whenever the website layouts changed. Instead of only relying on code-defined XPath interactions, Skyvern adds computer vision and LLMs to the mix to parse items in the viewport in real-time, create a plan for interaction and interact with them. This approach gives us a few advantages: 1. Skyvern can operate on websites it’s never seen before, as it’s able to map visual elements to actions necessary to complete a workflow, without any customized code 2. Skyvern is resistant to website layout changes, as there are no pre-determined XPaths or other selectors our system is looking for while trying to navigate 3. Skyvern leverages LLMs to reason through interactions to ensure we can cover complex situations. Examples include: 1. If you wanted to get an auto insurance quote from Geico, the answer to a common question “Were you eligible to drive at 18?” could be inferred from the driver receiving their license at age 16 2. If you were doing competitor analysis, it’s understanding that an Arnold Palmer 22 oz can at 7/11 is almost definitely the same product as a 23 oz can at Gopuff (even though the sizes are slightly different, which could be a rounding error!) Want to see examples of Skyvern in action? Jump to #real-world-examples-of- skyvern
AQLM
AQLM is the official PyTorch implementation for Extreme Compression of Large Language Models via Additive Quantization. It includes prequantized AQLM models without PV-Tuning and PV-Tuned models for LLaMA, Mistral, and Mixtral families. The repository provides inference examples, model details, and quantization setups. Users can run prequantized models using Google Colab examples, work with different model families, and install the necessary inference library. The repository also offers detailed instructions for quantization, fine-tuning, and model evaluation. AQLM quantization involves calibrating models for compression, and users can improve model accuracy through finetuning. Additionally, the repository includes information on preparing models for inference and contributing guidelines.
symbiotic-ai
Symbiotic AI is a tool that transforms any AI into a symbiotic agent by providing persistent memory, pattern recognition, and autonomous execution across sessions. It is not a chatbot but rather a co-pilot that resides in your filesystem. The system consists of four markdown files that define the agent's personality, user profile, agent operations, and current state. By updating these files, the agent gains insights and evolves based on real context about the user. Symbiotic AI challenges users, remembers information across sessions, takes actions such as writing code and researching, and evolves over time to provide personalized insights and advice.

vscode-unify-chat-provider
The 'vscode-unify-chat-provider' repository is a tool that integrates multiple LLM API providers into VS Code's GitHub Copilot Chat using the Language Model API. It offers free tier access to mainstream models, perfect compatibility with major LLM API formats, deep adaptation to API features, best performance with built-in parameters, out-of-the-box configuration, import/export support, great UX, and one-click use of various models. The tool simplifies model setup, migration, and configuration for users, providing a seamless experience within VS Code for utilizing different language models.
moatless-tools
Moatless Tools is a hobby project focused on experimenting with using Large Language Models (LLMs) to edit code in large existing codebases. The project aims to build tools that insert the right context into prompts and handle responses effectively. It utilizes an agentic loop functioning as a finite state machine to transition between states like Search, Identify, PlanToCode, ClarifyChange, and EditCode for code editing tasks.
LongLoRA
LongLoRA is a tool for efficient fine-tuning of long-context large language models. It includes LongAlpaca data with long QA data collected and short QA sampled, models from 7B to 70B with context length from 8k to 100k, and support for GPTNeoX models. The tool supports supervised fine-tuning, context extension, and improved LoRA fine-tuning. It provides pre-trained weights, fine-tuning instructions, evaluation methods, local and online demos, streaming inference, and data generation via Pdf2text. LongLoRA is licensed under Apache License 2.0, while data and weights are under CC-BY-NC 4.0 License for research use only.
ai-hands-on
A complete, hands-on guide to becoming an AI Engineer. This repository is designed to help you learn AI from first principles, build real neural networks, and understand modern LLM systems end-to-end. Progress through math, PyTorch, deep learning, transformers, RAG, and OCR with clean, intuitive Jupyter notebooks guiding you at every step. Suitable for beginners and engineers leveling up, providing clarity, structure, and intuition to build real AI systems.
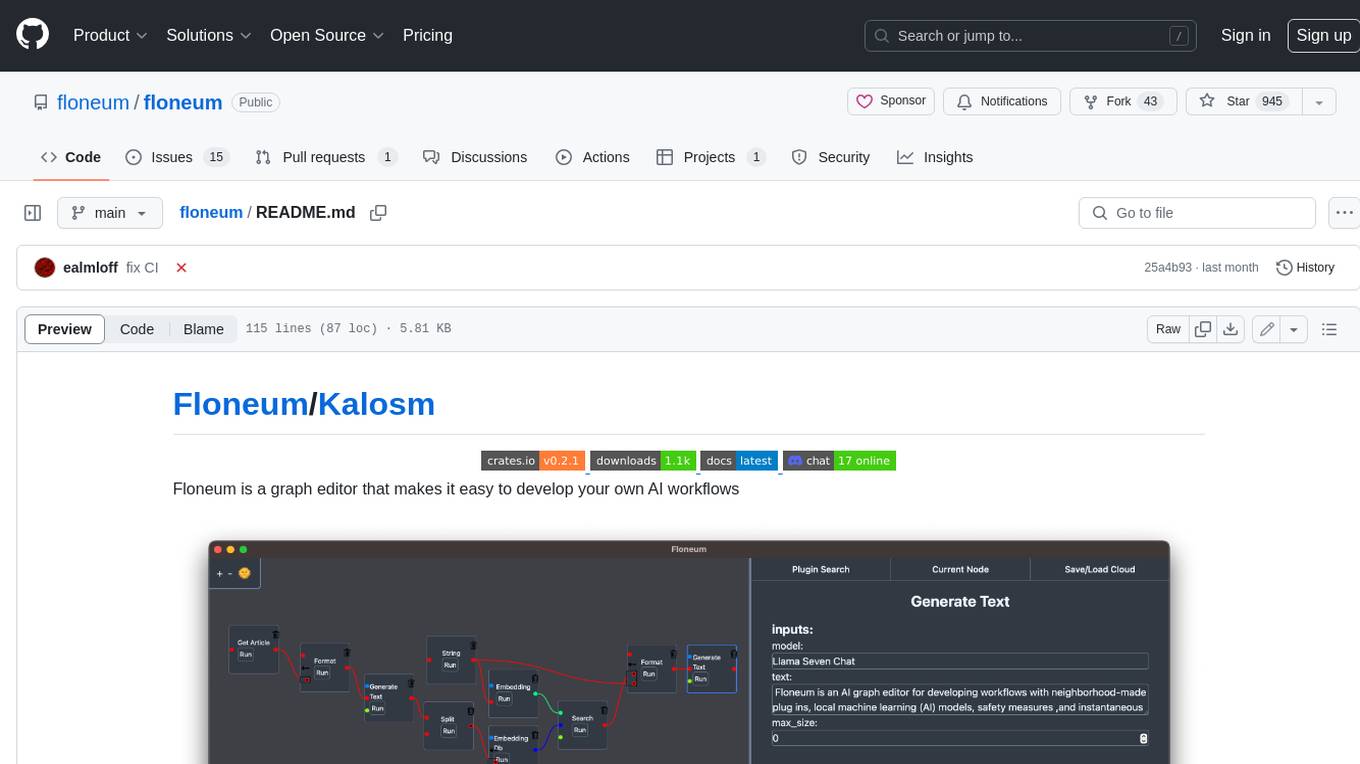
floneum
Floneum is a graph editor that makes it easy to develop your own AI workflows. It uses large language models (LLMs) to run AI models locally, without any external dependencies or even a GPU. This makes it easy to use LLMs with your own data, without worrying about privacy. Floneum also has a plugin system that allows you to improve the performance of LLMs and make them work better for your specific use case. Plugins can be used in any language that supports web assembly, and they can control the output of LLMs with a process similar to JSONformer or guidance.
RouterArena
RouterArena is an open evaluation platform and leaderboard for LLM routers, aiming to provide a standardized evaluation framework for assessing the performance of routers in terms of accuracy, cost, and other metrics. It offers diverse data coverage, comprehensive metrics, automated evaluation, and a live leaderboard to track router performance. Users can evaluate their routers by following setup steps, obtaining routing decisions, running LLM inference, and evaluating router performance. Contributions and collaborations are welcome, and users can submit their routers for evaluation to be included in the leaderboard.
AgentGym
AgentGym is a framework designed to help the AI community evaluate and develop generally-capable Large Language Model-based agents. It features diverse interactive environments and tasks with real-time feedback and concurrency. The platform supports 14 environments across various domains like web navigating, text games, house-holding tasks, digital games, and more. AgentGym includes a trajectory set (AgentTraj) and a benchmark suite (AgentEval) to facilitate agent exploration and evaluation. The framework allows for agent self-evolution beyond existing data, showcasing comparable results to state-of-the-art models.
For similar tasks

Large-Language-Models-play-StarCraftII
Large Language Models Play StarCraft II is a project that explores the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in playing the game StarCraft II. The project introduces TextStarCraft II, a textual environment for the game, and a Chain of Summarization method for analyzing game information and making strategic decisions. Through experiments, the project demonstrates that LLM agents can defeat the built-in AI at a challenging difficulty level. The project provides benchmarks and a summarization approach to enhance strategic planning and interpretability in StarCraft II gameplay.

balatrollm
BalatroLLM is a bot that utilizes Large Language Models (LLMs) to play Balatro, a popular roguelike poker deck-building game. The bot analyzes game states, makes strategic decisions, and executes actions through the BalatroBot API. It is designed to enhance the gaming experience by providing intelligent gameplay suggestions and actions based on sophisticated language models.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.