awesome-rag
A curated list of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) in large language models
Stars: 94
Awesome RAG is a curated list of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) in large language models. It includes papers, surveys, general resources, lectures, talks, tutorials, workshops, tools, and other collections related to retrieval-augmented generation. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements, techniques, and applications in the field of RAG.
README:
A curated list of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) in large language models.
Suggest and discuss possible enhancements on the Potential Additions page.
Table of Content:
2024
-
Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models: A Survey
PaperCodearXiv -
Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Natural Language Processing: A Survey
PaperarXiv
2023
-
Benchmarking Large Language Models in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
PaperarXiv
2022
-
A Survey on Retrieval-Augmented Text Generation
PaperarXiv
2024
-
Learning to Retrieve In-Context Examples for Large Language Models
PaperCodeEACL -
Reliable, Adaptable, and Attributable Language Models with Retrieval
PaperarXiv
2023
-
Active Retrieval Augmented Generation
PaperCodeEMNLPArchitecture -
⭐ REPLUG: Retrieval-Augmented Black-Box Language Models
PaperarXivArchitecture -
Shall We Pretrain Autoregressive Language Models with Retrieval? A Comprehensive Study
PaperCodeEMNLP -
InstructRetro: Instruction Tuning post Retrieval-Augmented Pretraining
PaperCodearXiv -
Retrieve Anything To Augment Large Language Models
PaperCodearXiv -
Reimagining Retrieval Augmented Language Models for Answering Queries
PaperACL -
In-Context Retrieval-Augmented Language Models
PaperCodeTACLArchitecture -
Query Rewriting for Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models
PaperCodeEMNLP -
Pre-computed memory or on-the-fly encoding? A hybrid approach to retrieval augmentation makes the most of your compute
PaperPMLR -
Universal Information Extraction with Meta-Pretrained Self-Retrieval
PaperCodeACL -
RAVEN: In-Context Learning with Retrieval Augmented Encoder-Decoder Language Models
PaperarXiv -
Unlimiformer: Long-Range Transformers with Unlimited Length Input
PaperCodeNeurIPSArchitecture -
Nonparametric Masked Language Modeling
PaperCodeACLTraining
2022
-
Improving language models by retrieving from trillions of tokens
PaperBlogPMLRArchitecture -
⭐ Atlas: Few-shot Learning with Retrieval Augmented Language Models
PaperCodeBlogTrainingJMLR -
You can't pick your neighbors, or can you? When and how to rely on retrieval in the kNN-LM
PaperACLArchitecture -
Neuro-Symbolic Language Modeling with Automaton-augmented Retrieval
PaperCodeICMLArchitecture -
Training Language Models with Memory Augmentation
PaperEMNLPTraining -
Unsupervised Dense Information Retrieval with Contrastive Learning
PaperCodearXivTraining -
Teaching language models to support answers with verified quotes
PaperarXivApplication -
kNN-Prompt: Nearest Neighbor Zero-Shot Inference
PaperCodeEMNLPApplication
2021
-
Efficient Nearest Neighbor Language Models
PaperCodeEMNLPArchitecture -
Mention Memory: incorporating textual knowledge into Transformers through entity mention attention
PaperCodearXivArchitecture
2020
-
⭐ REALM: Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training
PaperCodeHuggingFacePMLRArchitecture -
Generalization through Memorization: Nearest Neighbor Language Models
PaperCodeICLRArchitecture -
Entities as Experts: Sparse Memory Access with Entity Supervision
PaperEMNLPArchitecture -
Dense Passage Retrieval for Open-Domain Question Answering
PaperCodeEMNLPTraining -
⭐ Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks
PaperHuggingFaceNeurIPS
2024
2023
-
Stanford CS25: V3 I Retrieval Augmented Language Models
Douwe Kiela (2023)Lecture
Video -
Building RAG-based LLM Applications for Production
Anyscale (2023)Tutorial
Blog -
Multi-Vector Retriever for RAG on tables, text, and images
LangChain (2023)Tutorial
Blog -
Retrieval-based Language Models and Applications
Asai et al. (2023)TutorialACL
WebsiteVideo -
Advanced RAG Techniques: an Illustrated Overview
Ivan Ilin (2023)Tutorial
Blog -
Retrieval Augmented Language Modeling
Melissa Dell (2023)Lecture
Video
2024
-
Towards Knowledgeable Language Models
Zoey Sha Li, Manling Li, Michael JQ Zhang, Eunsol Choi, Mor Geva, Peter Hase
@ACL2024, August 12-17
Website
-
LangChain
LangChain is a framework for developing applications powered by language models.
Website -
LlamaIndex
LlamaIndex is a simple, flexible data framework for connecting custom data sources to large language models.
Website -
Verba
Verba is an open-source application designed to offer an end-to-end, streamlined, and user-friendly interface for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) out of the box.
Website -
NEUM
Open-source RAG framework optimized for large-scale and real-time data.
Website -
Unstructured
Unstructured.io offers a powerful toolkit that handles the ingestion and data preprocessing step, allowing you to focus on the more exciting downstream steps in your machine learning pipeline. Unstructured has over a dozen data connectors that easily integrate with various data sources, including AWS S3, Discord, Slack, Wikipedia, and more.
Website
- Awesome LLM RAG
- Awesome RAG
- Awesome LLM with RAG
- RAG-Survey
- Awesome LLM Reader: A Repository of Retrieval-augmented LLMs
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for awesome-rag
Similar Open Source Tools

awesome-rag
Awesome RAG is a curated list of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) in large language models. It includes papers, surveys, general resources, lectures, talks, tutorials, workshops, tools, and other collections related to retrieval-augmented generation. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements, techniques, and applications in the field of RAG.
ort
Ort is an unofficial ONNX Runtime 1.17 wrapper for Rust based on the now inactive onnxruntime-rs. ONNX Runtime accelerates ML inference on both CPU and GPU.

oh-my-pi
oh-my-pi is an AI coding agent for the terminal, providing tools for interactive coding, AI-powered git commits, Python code execution, LSP integration, time-traveling streamed rules, interactive code review, task management, interactive questioning, custom TypeScript slash commands, universal config discovery, MCP & plugin system, web search & fetch, SSH tool, Cursor provider integration, multi-credential support, image generation, TUI overhaul, edit fuzzy matching, and more. It offers a modern terminal interface with smart session management, supports multiple AI providers, and includes various tools for coding, task management, code review, and interactive questioning.
human
AI-powered 3D Face Detection & Rotation Tracking, Face Description & Recognition, Body Pose Tracking, 3D Hand & Finger Tracking, Iris Analysis, Age & Gender & Emotion Prediction, Gaze Tracking, Gesture Recognition, Body Segmentation
code-graph-rag
Graph-Code is an accurate Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system that analyzes multi-language codebases using Tree-sitter. It builds comprehensive knowledge graphs, enabling natural language querying of codebase structure and relationships, along with editing capabilities. The system supports various languages, uses Tree-sitter for parsing, Memgraph for storage, and AI models for natural language to Cypher translation. It offers features like code snippet retrieval, advanced file editing, shell command execution, interactive code optimization, reference-guided optimization, dependency analysis, and more. The architecture consists of a multi-language parser and an interactive CLI for querying the knowledge graph.
mcp-svelte-docs
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) server providing authoritative Svelte 5 and SvelteKit definitions extracted directly from TypeScript declarations. Get precise syntax, parameters, and examples for all Svelte 5 concepts through a single, unified interface. The server offers a 'svelte_definition' tool that covers various Svelte 5 runes, modern features, event handling, migration guidance, TypeScript interfaces, and advanced patterns. It aims to provide up-to-date, type-safe, and comprehensive documentation for Svelte developers.

TrustEval-toolkit
TrustEval-toolkit is a dynamic and comprehensive framework for evaluating the trustworthiness of Generative Foundation Models (GenFMs) across dimensions such as safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and more. It offers features like dynamic dataset generation, multi-model compatibility, customizable metrics, metadata-driven pipelines, comprehensive evaluation dimensions, optimized inference, and detailed reports.
rust-genai
genai is a multi-AI providers library for Rust that aims to provide a common and ergonomic single API to various generative AI providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Cohere, Ollama, and Gemini. It focuses on standardizing chat completion APIs across major AI services, prioritizing ergonomics and commonality. The library initially focuses on text chat APIs and plans to expand to support images, function calling, and more in the future versions. Version 0.1.x will have breaking changes in patches, while version 0.2.x will follow semver more strictly. genai does not provide a full representation of a given AI provider but aims to simplify the differences at a lower layer for ease of use.
nanolang
NanoLang is a minimal, LLM-friendly programming language that transpiles to C for native performance. It features mandatory testing, unambiguous syntax, automatic memory management, LLM-powered autonomous optimization, dual notation for operators, static typing, C interop, and native performance. The language supports variables, functions with mandatory tests, control flow, structs, enums, generic types, and provides a clean, modern syntax optimized for both human readability and AI code generation.
9router
9Router is a free AI router tool designed to help developers maximize their AI subscriptions, auto-route to free and cheap AI models with smart fallback, and avoid hitting limits and wasting money. It offers features like real-time quota tracking, format translation between OpenAI, Claude, and Gemini, multi-account support, auto token refresh, custom model combinations, request logging, cloud sync, usage analytics, and flexible deployment options. The tool supports various providers like Claude Code, Codex, Gemini CLI, GitHub Copilot, GLM, MiniMax, iFlow, Qwen, and Kiro, and allows users to create combos for different scenarios. Users can connect to the tool via CLI tools like Cursor, Claude Code, Codex, OpenClaw, and Cline, and deploy it on VPS, Docker, or Cloudflare Workers.
mcp-ui
mcp-ui is a collection of SDKs that bring interactive web components to the Model Context Protocol (MCP). It allows servers to define reusable UI snippets, render them securely in the client, and react to their actions in the MCP host environment. The SDKs include @mcp-ui/server (TypeScript) for generating UI resources on the server, @mcp-ui/client (TypeScript) for rendering UI components on the client, and mcp_ui_server (Ruby) for generating UI resources in a Ruby environment. The project is an experimental community playground for MCP UI ideas, with rapid iteration and enhancements.

fit-framework
FIT Framework is a Java enterprise AI development framework that provides a multi-language function engine (FIT), a flow orchestration engine (WaterFlow), and a Java ecosystem alternative solution (FEL). It runs in native/Spring dual mode, supports plug-and-play and intelligent deployment, seamlessly unifying large models and business systems. FIT Core offers language-agnostic computation base with plugin hot-swapping and intelligent deployment. WaterFlow Engine breaks the dimensional barrier of BPM and reactive programming, enabling graphical orchestration and declarative API-driven logic composition. FEL revolutionizes LangChain for the Java ecosystem, encapsulating large models, knowledge bases, and toolchains to integrate AI capabilities into Java technology stack seamlessly. The framework emphasizes engineering practices with intelligent conventions to reduce boilerplate code and offers flexibility for deep customization in complex scenarios.
LLM-Tuning
LLM-Tuning is a collection of tools and resources for fine-tuning large language models (LLMs). It includes a library of pre-trained LoRA models, a set of tutorials and examples, and a community forum for discussion and support. LLM-Tuning makes it easy to fine-tune LLMs for a variety of tasks, including text classification, question answering, and dialogue generation. With LLM-Tuning, you can quickly and easily improve the performance of your LLMs on downstream tasks.
VimLM
VimLM is an AI-powered coding assistant for Vim that integrates AI for code generation, refactoring, and documentation directly into your Vim workflow. It offers native Vim integration with split-window responses and intuitive keybindings, offline first execution with MLX-compatible models, contextual awareness with seamless integration with codebase and external resources, conversational workflow for iterating on responses, project scaffolding for generating and deploying code blocks, and extensibility for creating custom LLM workflows with command chains.
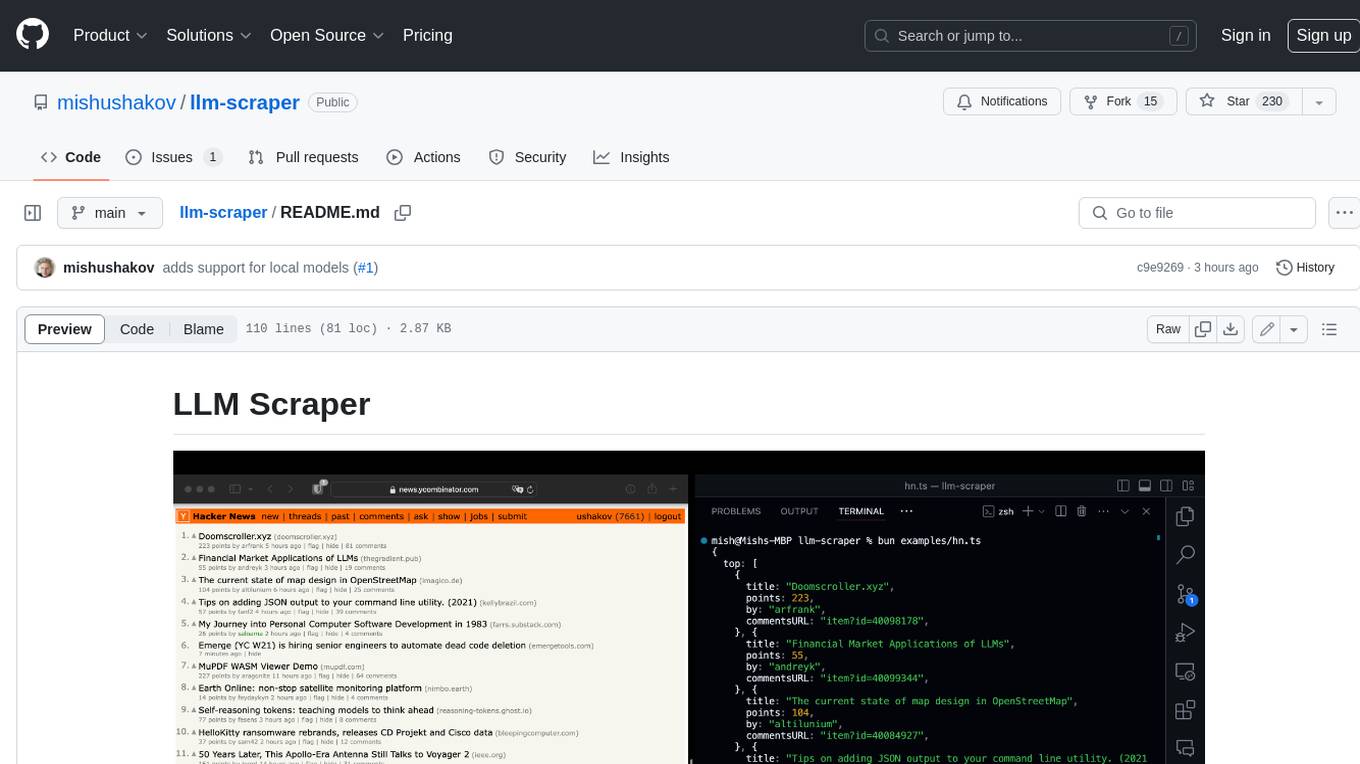
llm-scraper
LLM Scraper is a TypeScript library that allows you to convert any webpages into structured data using LLMs. It supports Local (GGUF), OpenAI, Groq chat models, and schemas defined with Zod. With full type-safety in TypeScript and based on the Playwright framework, it offers streaming when crawling multiple pages and supports four input modes: html, markdown, text, and image.
For similar tasks
basdonax-ai-rag
Basdonax AI RAG v1.0 is a repository that contains all the necessary resources to create your own AI-powered secretary using the RAG from Basdonax AI. It leverages open-source models from Meta and Microsoft, namely 'Llama3-7b' and 'Phi3-4b', allowing users to upload documents and make queries. This tool aims to simplify life for individuals by harnessing the power of AI. The installation process involves choosing between different data models based on GPU capabilities, setting up Docker, pulling the desired model, and customizing the assistant prompt file. Once installed, users can access the RAG through a local link and enjoy its functionalities.
TableLLM
TableLLM is a large language model designed for efficient tabular data manipulation tasks in real office scenarios. It can generate code solutions or direct text answers for tasks like insert, delete, update, query, merge, and chart operations on tables embedded in spreadsheets or documents. The model has been fine-tuned based on CodeLlama-7B and 13B, offering two scales: TableLLM-7B and TableLLM-13B. Evaluation results show its performance on benchmarks like WikiSQL, Spider, and self-created table operation benchmark. Users can use TableLLM for code and text generation tasks on tabular data.
awesome-agents
Awesome Agents is a curated list of open source AI agents designed for various tasks such as private interactions with documents, chat implementations, autonomous research, human-behavior simulation, code generation, HR queries, domain-specific research, and more. The agents leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) and other generative AI technologies to provide solutions for complex tasks and projects. The repository includes a diverse range of agents for different use cases, from conversational chatbots to AI coding engines, and from autonomous HR assistants to vision task solvers.
Lumi-AI
Lumi AI is a friendly AI sidekick with a human-like personality that offers features like file upload and analysis, web search, local chat storage, custom instructions, changeable conversational style, enhanced context retention, voice query input, and various tools. The project has been developed with contributions from a team of developers, designers, and testers, and is licensed under Apache 2.0 and MIT licenses.

awesome-rag
Awesome RAG is a curated list of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) in large language models. It includes papers, surveys, general resources, lectures, talks, tutorials, workshops, tools, and other collections related to retrieval-augmented generation. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements, techniques, and applications in the field of RAG.
ai2-scholarqa-lib
Ai2 Scholar QA is a system for answering scientific queries and literature review by gathering evidence from multiple documents across a corpus and synthesizing an organized report with evidence for each claim. It consists of a retrieval component and a three-step generator pipeline. The retrieval component fetches relevant evidence passages using the Semantic Scholar public API and reranks them. The generator pipeline includes quote extraction, planning and clustering, and summary generation. The system is powered by the ScholarQA class, which includes components like PaperFinder and MultiStepQAPipeline. It requires environment variables for Semantic Scholar API and LLMs, and can be run as local docker containers or embedded into another application as a Python package.
baibot
Baibot is a versatile chatbot framework designed to simplify the process of creating and deploying chatbots. It provides a user-friendly interface for building custom chatbots with various functionalities such as natural language processing, conversation flow management, and integration with external APIs. Baibot is highly customizable and can be easily extended to suit different use cases and industries. With Baibot, developers can quickly create intelligent chatbots that can interact with users in a seamless and engaging manner, enhancing user experience and automating customer support processes.
openclaw
OpenClaw is a personal AI assistant that runs on your own devices, answering you on various channels like WhatsApp, Telegram, Slack, Discord, and more. It can speak and listen on different platforms and render a live Canvas you control. The Gateway serves as the control plane, while the assistant is the main product. It provides a local, fast, and always-on single-user assistant experience. The preferred setup involves running the onboarding wizard in your terminal to guide you through setting up the gateway, workspace, channels, and skills. The tool supports various models and authentication methods, with a focus on security and privacy.
For similar jobs
responsible-ai-toolbox
Responsible AI Toolbox is a suite of tools providing model and data exploration and assessment interfaces and libraries for understanding AI systems. It empowers developers and stakeholders to develop and monitor AI responsibly, enabling better data-driven actions. The toolbox includes visualization widgets for model assessment, error analysis, interpretability, fairness assessment, and mitigations library. It also offers a JupyterLab extension for managing machine learning experiments and a library for measuring gender bias in NLP datasets.
LLMLingua
LLMLingua is a tool that utilizes a compact, well-trained language model to identify and remove non-essential tokens in prompts. This approach enables efficient inference with large language models, achieving up to 20x compression with minimal performance loss. The tool includes LLMLingua, LongLLMLingua, and LLMLingua-2, each offering different levels of prompt compression and performance improvements for tasks involving large language models.
llm-examples
Starter examples for building LLM apps with Streamlit. This repository showcases a growing collection of LLM minimum working examples, including a Chatbot, File Q&A, Chat with Internet search, LangChain Quickstart, LangChain PromptTemplate, and Chat with user feedback. Users can easily get their own OpenAI API key and set it as an environment variable in Streamlit apps to run the examples locally.

LMOps
LMOps is a research initiative focusing on fundamental research and technology for building AI products with foundation models, particularly enabling AI capabilities with Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI models. The project explores various aspects such as prompt optimization, longer context handling, LLM alignment, acceleration of LLMs, LLM customization, and understanding in-context learning. It also includes tools like Promptist for automatic prompt optimization, Structured Prompting for efficient long-sequence prompts consumption, and X-Prompt for extensible prompts beyond natural language. Additionally, LLMA accelerators are developed to speed up LLM inference by referencing and copying text spans from documents. The project aims to advance technologies that facilitate prompting language models and enhance the performance of LLMs in various scenarios.
awesome-tool-llm
This repository focuses on exploring tools that enhance the performance of language models for various tasks. It provides a structured list of literature relevant to tool-augmented language models, covering topics such as tool basics, tool use paradigm, scenarios, advanced methods, and evaluation. The repository includes papers, preprints, and books that discuss the use of tools in conjunction with language models for tasks like reasoning, question answering, mathematical calculations, accessing knowledge, interacting with the world, and handling non-textual modalities.
gaianet-node
GaiaNet-node is a tool that allows users to run their own GaiaNet node, enabling them to interact with an AI agent. The tool provides functionalities to install the default node software stack, initialize the node with model files and vector database files, start the node, stop the node, and update configurations. Users can use pre-set configurations or pass a custom URL for initialization. The tool is designed to facilitate communication with the AI agent and access node information via a browser. GaiaNet-node requires sudo privilege for installation but can also be installed without sudo privileges with specific commands.
llmops-duke-aipi
LLMOps Duke AIPI is a course focused on operationalizing Large Language Models, teaching methodologies for developing applications using software development best practices with large language models. The course covers various topics such as generative AI concepts, setting up development environments, interacting with large language models, using local large language models, applied solutions with LLMs, extensibility using plugins and functions, retrieval augmented generation, introduction to Python web frameworks for APIs, DevOps principles, deploying machine learning APIs, LLM platforms, and final presentations. Students will learn to build, share, and present portfolios using Github, YouTube, and Linkedin, as well as develop non-linear life-long learning skills. Prerequisites include basic Linux and programming skills, with coursework available in Python or Rust. Additional resources and references are provided for further learning and exploration.
Awesome-AISourceHub
Awesome-AISourceHub is a repository that collects high-quality information sources in the field of AI technology. It serves as a synchronized source of information to avoid information gaps and information silos. The repository aims to provide valuable resources for individuals such as AI book authors, enterprise decision-makers, and tool developers who frequently use Twitter to share insights and updates related to AI advancements. The platform emphasizes the importance of accessing information closer to the source for better quality content. Users can contribute their own high-quality information sources to the repository by following specific steps outlined in the contribution guidelines. The repository covers various platforms such as Twitter, public accounts, knowledge planets, podcasts, blogs, websites, YouTube channels, and more, offering a comprehensive collection of AI-related resources for individuals interested in staying updated with the latest trends and developments in the AI field.