responsible-ai-toolbox
Responsible AI Toolbox is a suite of tools providing model and data exploration and assessment user interfaces and libraries that enable a better understanding of AI systems. These interfaces and libraries empower developers and stakeholders of AI systems to develop and monitor AI more responsibly, and take better data-driven actions.
Stars: 1275
Responsible AI Toolbox is a suite of tools providing model and data exploration and assessment interfaces and libraries for understanding AI systems. It empowers developers and stakeholders to develop and monitor AI responsibly, enabling better data-driven actions. The toolbox includes visualization widgets for model assessment, error analysis, interpretability, fairness assessment, and mitigations library. It also offers a JupyterLab extension for managing machine learning experiments and a library for measuring gender bias in NLP datasets.
README:
Responsible AI is an approach to assessing, developing, and deploying AI systems in a safe, trustworthy, and ethical manner, and take responsible decisions and actions.
Responsible AI Toolbox is a suite of tools providing a collection of model and data exploration and assessment user interfaces and libraries that enable a better understanding of AI systems. These interfaces and libraries empower developers and stakeholders of AI systems to develop and monitor AI more responsibly, and take better data-driven actions.
The Toolbox consists of three repositories:
| Repository | Tools Covered |
|---|---|
| Responsible-AI-Toolbox Repository (Here) | This repository contains four visualization widgets for model assessment and decision making: 1. Responsible AI dashboard, a single pane of glass bringing together several mature Responsible AI tools from the toolbox for a holistic responsible assessment and debugging of models and making informed business decisions. With this dashboard, you can identify model errors, diagnose why those errors are happening, and mitigate them. Moreover, the causal decision-making capabilities provide actionable insights to your stakeholders and customers. 2. Error Analysis dashboard, for identifying model errors and discovering cohorts of data for which the model underperforms. 3. Interpretability dashboard, for understanding model predictions. This dashboard is powered by InterpretML. 4. Fairness dashboard, for understanding model’s fairness issues using various group-fairness metrics across sensitive features and cohorts. This dashboard is powered by Fairlearn. |
| Responsible-AI-Toolbox-Mitigations Repository | The Responsible AI Mitigations Library helps AI practitioners explore different measurements and mitigation steps that may be most appropriate when the model underperforms for a given data cohort. The library currently has two modules: 1. DataProcessing, which offers mitigation techniques for improving model performance for specific cohorts. 2. DataBalanceAnalysis, which provides metrics for diagnosing errors that originate from data imbalance either on class labels or feature values. 3. Cohort: provides classes for handling and managing cohorts, which allows the creation of custom pipelines for each cohort in an easy and intuitive interface. The module also provides techniques for learning different decoupled estimators (models) for different cohorts and combining them in a way that optimizes different definitions of group fairness. |
| Responsible-AI-Tracker Repository | Responsible AI Toolbox Tracker is a JupyterLab extension for managing, tracking, and comparing results of machine learning experiments for model improvement. Using this extension, users can view models, code, and visualization artifacts within the same framework enabling therefore fast model iteration and evaluation processes. Main functionalities include: 1. Managing and linking model improvement artifacts 2. Disaggregated model evaluation and comparisons 3. Integration with the Responsible AI Mitigations library 4. Integration with mlflow |
| Responsible-AI-Toolbox-GenBit Repository | The Responsible AI Gender Bias (GenBit) Library helps AI practitioners measure gender bias in Natural Language Processing (NLP) datasets. The main goal of GenBit is to analyze your text corpora and compute metrics that give insights into the gender bias present in a corpus. |
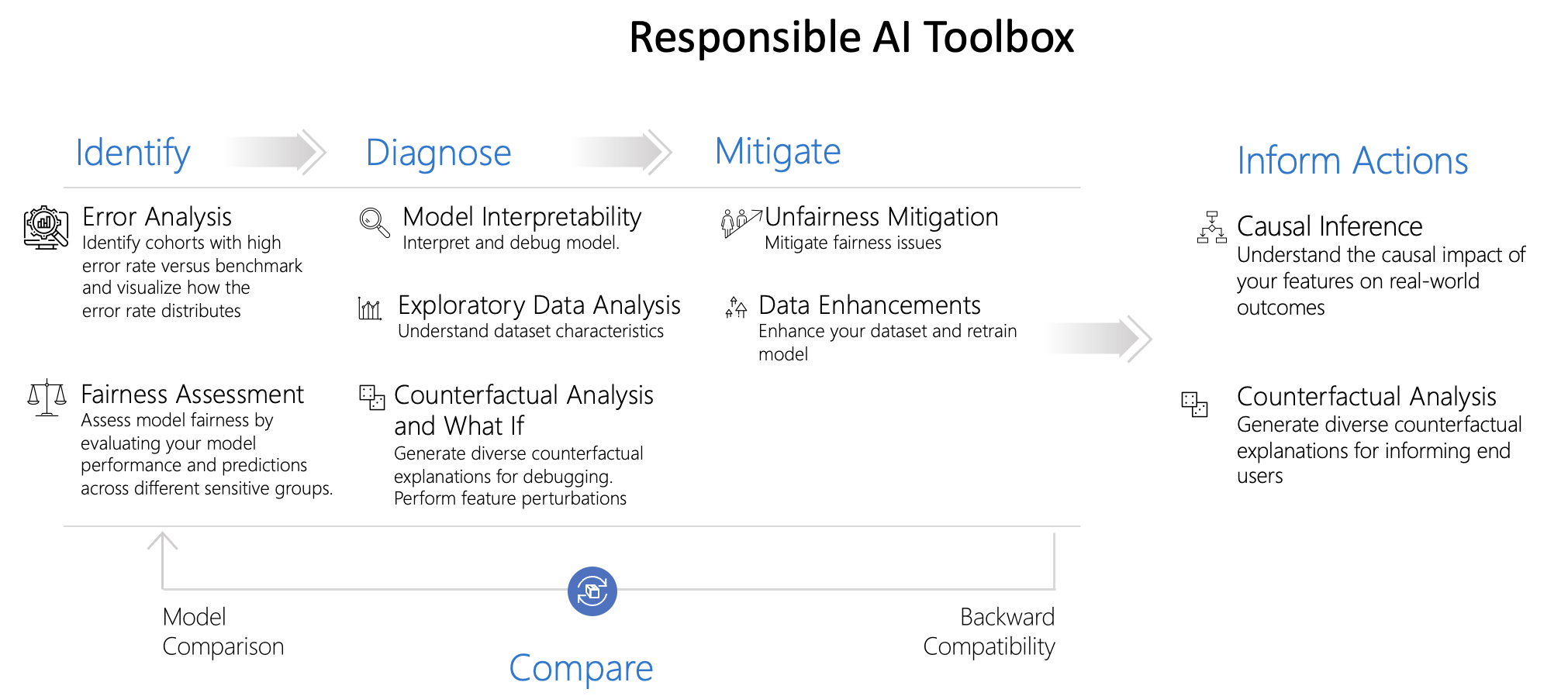
Responsible AI dashboard is a single pane of glass, enabling you to easily flow through different stages of model debugging and decision-making. This customizable experience can be taken in a multitude of directions, from analyzing the model or data holistically, to conducting a deep dive or comparison on cohorts of interest, to explaining and perturbing model predictions for individual instances, and to informing users on business decisions and actions.
In order to achieve these capabilities, the dashboard integrates together ideas and technologies from several open-source toolkits in the areas of
-
Error Analysis powered by Error Analysis, which identifies cohorts of data with higher error rate than the overall benchmark. These discrepancies might occur when the system or model underperforms for specific demographic groups or infrequently observed input conditions in the training data.
-
Fairness Assessment powered by Fairlearn, which identifies which groups of people may be disproportionately negatively impacted by an AI system and in what ways.
-
Model Interpretability powered by InterpretML, which explains blackbox models, helping users understand their model's global behavior, or the reasons behind individual predictions.
-
Counterfactual Analysis powered by DiCE, which shows feature-perturbed versions of the same datapoint who would have received a different prediction outcome, e.g., Taylor's loan has been rejected by the model. But they would have received the loan if their income was higher by $10,000.
-
Causal Analysis powered by EconML, which focuses on answering What If-style questions to apply data-driven decision-making – how would revenue be affected if a corporation pursues a new pricing strategy? Would a new medication improve a patient’s condition, all else equal?
-
Data Balance powered by Responsible AI, which helps users gain an overall understanding of their data, identify features receiving the positive outcome more than others, and visualize feature distributions.
Responsible AI dashboard is designed to achieve the following goals:
- To help further accelerate engineering processes in machine learning by enabling practitioners to design customizable workflows and tailor Responsible AI dashboards that best fit with their model assessment and data-driven decision making scenarios.
- To help model developers create end to end and fluid debugging experiences and navigate seamlessly through error identification and diagnosis by using interactive visualizations that identify errors, inspect the data, generate global and local explanations models, and potentially inspect problematic examples.
- To help business stakeholders explore causal relationships in the data and take informed decisions in the real world.
This repository contains the Jupyter notebooks with examples to showcase how to use this widget. Get started here.
Use the following pip command to install the Responsible AI Toolbox.
If running in jupyter, please make sure to restart the jupyter kernel after installing.
pip install raiwidgets
The Responsible AI Toolbox’s strength lies in its customizability. It empowers users to design tailored, end-to-end model debugging and decision-making workflows that address their particular needs. Need some inspiration? Here are some examples of how Toolbox components can be put together to analyze scenarios in different ways:
Please note that model overview (including fairness analysis) and data explorer components are activated by default!
| Responsible AI Dashboard Flow | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Model Overview -> Error Analysis -> Data Explorer | To identify model errors and diagnose them by understanding the underlying data distribution |
| Model Overview -> Fairness Assessment -> Data Explorer | To identify model fairness issues and diagnose them by understanding the underlying data distribution |
| Model Overview -> Error Analysis -> Counterfactuals Analysis and What-If | To diagnose errors in individual instances with counterfactual analysis (minimum change to lead to a different model prediction) |
| Model Overview -> Data Explorer -> Data Balance | To understand the root cause of errors and fairness issues introduced via data imbalances or lack of representation of a particular data cohort |
| Model Overview -> Interpretability | To diagnose model errors through understanding how the model has made its predictions |
| Data Explorer -> Causal Inference | To distinguish between correlations and causations in the data or decide the best treatments to apply to see a positive outcome |
| Interpretability -> Causal Inference | To learn whether the factors that model has used for decision making has any causal effect on the real-world outcome. |
| Data Explorer -> Counterfactuals Analysis and What-If | To address customer questions about what they can do next time to get a different outcome from an AI. |
| Data Explorer -> Data Balance | To gain an overall understanding of the data, identify features receiving the positive outcome more than others, and visualize feature distributions |
Tabular Examples:
- Try the tool: make decisions for house improvements (decision making)
- Try the tool: provide recommendations to patients using diabetes data (decision making)
- Try the tool: model debugging of a census income prediction model (classification)
- Try the tool: model debugging of a housing price prediction model (classification)
- Try the tool: model debugging of a diabetes progression prediction model (regression)
Text Examples:
- Try the tool: model debugging of an OpenAI Question Answering model on SQuAD
- Try the tool: model debugging of a HuggingFace Question Answering model on SQuAD
- Try the tool: model debugging of a DBPedia text classification model
- Try the tool: model debugging of a binary text classification model
- Try the tool: model debugging of a COVID-19 multilabel text classification model
Vision Examples:
- Try the tool: model debugging of a fridge image classification model
- Try the tool: model debugging of a fridge multilabel image classification model
- Try the tool: model debugging of a fridge object detection model
This Responsible AI Toolbox API supports models that are trained on datasets in Python numpy.ndarray, pandas.DataFrame, iml.datatypes.DenseData, or scipy.sparse.csr_matrix format.
The explanation functions of Interpret-Community accept both models and pipelines as input as long as the model or pipeline implements a predict or predict_proba function that conforms to the Scikit convention. If not compatible, you can wrap your model's prediction function into a wrapper function that transforms the output into the format that is supported (predict or predict_proba of Scikit), and pass that wrapper function to your selected interpretability techniques.
If a pipeline script is provided, the explanation function assumes that the running pipeline script returns a prediction. The repository also supports models trained via PyTorch, TensorFlow, and Keras deep learning frameworks.
Tools within the Responsible AI Toolbox can also be used with AI models offered as APIs by providers such as Azure Cognitive Services. To see example use cases, see the folders below:
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for responsible-ai-toolbox
Similar Open Source Tools

responsible-ai-toolbox
Responsible AI Toolbox is a suite of tools providing model and data exploration and assessment interfaces and libraries for understanding AI systems. It empowers developers and stakeholders to develop and monitor AI responsibly, enabling better data-driven actions. The toolbox includes visualization widgets for model assessment, error analysis, interpretability, fairness assessment, and mitigations library. It also offers a JupyterLab extension for managing machine learning experiments and a library for measuring gender bias in NLP datasets.
incubator-hugegraph-ai
hugegraph-ai aims to explore the integration of HugeGraph with artificial intelligence (AI) and provide comprehensive support for developers to leverage HugeGraph's AI capabilities in their projects. It includes modules for large language models, graph machine learning, and a Python client for HugeGraph. The project aims to address challenges like timeliness, hallucination, and cost-related issues by integrating graph systems with AI technologies.

xaitk-saliency
The `xaitk-saliency` package is an open source Explainable AI (XAI) framework for visual saliency algorithm interfaces and implementations, designed for analytics and autonomy applications. It provides saliency algorithms for various image understanding tasks such as image classification, image similarity, object detection, and reinforcement learning. The toolkit targets data scientists and developers who aim to incorporate visual saliency explanations into their workflow or product, offering both direct accessibility for experimentation and modular integration into systems and applications through Strategy and Adapter patterns. The package includes documentation, examples, and a demonstration tool for visual saliency generation in a user-interface.

asreview
The ASReview project implements active learning for systematic reviews, utilizing AI-aided pipelines to assist in finding relevant texts for search tasks. It accelerates the screening of textual data with minimal human input, saving time and increasing output quality. The software offers three modes: Oracle for interactive screening, Exploration for teaching purposes, and Simulation for evaluating active learning models. ASReview LAB is designed to support decision-making in any discipline or industry by improving efficiency and transparency in screening large amounts of textual data.
langchain-benchmarks
A package to help benchmark various LLM related tasks. The benchmarks are organized by end-to-end use cases, and utilize LangSmith heavily. We have several goals in open sourcing this: * Showing how we collect our benchmark datasets for each task * Showing what the benchmark datasets we use for each task is * Showing how we evaluate each task * Encouraging others to benchmark their solutions on these tasks (we are always looking for better ways of doing things!)
LazyLLM
LazyLLM is a low-code development tool for building complex AI applications with multiple agents. It assists developers in building AI applications at a low cost and continuously optimizing their performance. The tool provides a convenient workflow for application development and offers standard processes and tools for various stages of application development. Users can quickly prototype applications with LazyLLM, analyze bad cases with scenario task data, and iteratively optimize key components to enhance the overall application performance. LazyLLM aims to simplify the AI application development process and provide flexibility for both beginners and experts to create high-quality applications.

fenic
fenic is an opinionated DataFrame framework from typedef.ai for building AI and agentic applications. It transforms unstructured and structured data into insights using familiar DataFrame operations enhanced with semantic intelligence. With support for markdown, transcripts, and semantic operators, plus efficient batch inference across various model providers. fenic is purpose-built for LLM inference, providing a query engine designed for AI workloads, semantic operators as first-class citizens, native unstructured data support, production-ready infrastructure, and a familiar DataFrame API.
parallax
Parallax is a fully decentralized inference engine developed by Gradient. It allows users to build their own AI cluster for model inference across distributed nodes with varying configurations and physical locations. Core features include hosting local LLM on personal devices, cross-platform support, pipeline parallel model sharding, paged KV cache management, continuous batching for Mac, dynamic request scheduling, and routing for high performance. The backend architecture includes P2P communication powered by Lattica, GPU backend powered by SGLang and vLLM, and MAC backend powered by MLX LM.

raga-llm-hub
Raga LLM Hub is a comprehensive evaluation toolkit for Language and Learning Models (LLMs) with over 100 meticulously designed metrics. It allows developers and organizations to evaluate and compare LLMs effectively, establishing guardrails for LLMs and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) applications. The platform assesses aspects like Relevance & Understanding, Content Quality, Hallucination, Safety & Bias, Context Relevance, Guardrails, and Vulnerability scanning, along with Metric-Based Tests for quantitative analysis. It helps teams identify and fix issues throughout the LLM lifecycle, revolutionizing reliability and trustworthiness.

LightLLM
LightLLM is a lightweight library for linear and logistic regression models. It provides a simple and efficient way to train and deploy machine learning models for regression tasks. The library is designed to be easy to use and integrate into existing projects, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced data scientists. With LightLLM, users can quickly build and evaluate regression models using a variety of algorithms and hyperparameters. The library also supports feature engineering and model interpretation, allowing users to gain insights from their data and make informed decisions based on the model predictions.
open-model-database
OpenModelDB is a community-driven database of AI upscaling models, providing a centralized platform for users to access and compare various models. The repository contains a collection of models and model metadata, facilitating easy exploration and evaluation of different AI upscaling solutions. With a focus on enhancing the accessibility and usability of AI models, OpenModelDB aims to streamline the process of finding and selecting the most suitable models for specific tasks or projects.
Docs2KG
Docs2KG is a tool designed for constructing a unified knowledge graph from heterogeneous documents. It addresses the challenges of digitizing diverse unstructured documents and constructing a high-quality knowledge graph with less effort. The tool combines bottom-up and top-down approaches, utilizing a human-LLM collaborative interface to enhance the generated knowledge graph. It organizes the knowledge graph into MetaKG, LayoutKG, and SemanticKG, providing a comprehensive view of document content. Docs2KG aims to streamline the process of knowledge graph construction and offers metrics for evaluating the quality of automatic construction.
nixtla
Nixtla is a production-ready generative pretrained transformer for time series forecasting and anomaly detection. It can accurately predict various domains such as retail, electricity, finance, and IoT with just a few lines of code. TimeGPT introduces a paradigm shift with its standout performance, efficiency, and simplicity, making it accessible even to users with minimal coding experience. The model is based on self-attention and is independently trained on a vast time series dataset to minimize forecasting error. It offers features like zero-shot inference, fine-tuning, API access, adding exogenous variables, multiple series forecasting, custom loss function, cross-validation, prediction intervals, and handling irregular timestamps.
NeMo
NVIDIA NeMo Framework is a scalable and cloud-native generative AI framework built for researchers and PyTorch developers working on Large Language Models (LLMs), Multimodal Models (MMs), Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Text to Speech (TTS), and Computer Vision (CV) domains. It is designed to help you efficiently create, customize, and deploy new generative AI models by leveraging existing code and pre-trained model checkpoints.

koordinator
Koordinator is a QoS based scheduling system for hybrid orchestration workloads on Kubernetes. It aims to improve runtime efficiency and reliability of latency sensitive workloads and batch jobs, simplify resource-related configuration tuning, and increase pod deployment density. It enhances Kubernetes user experience by optimizing resource utilization, improving performance, providing flexible scheduling policies, and easy integration into existing clusters.
NeMo
NeMo Framework is a generative AI framework built for researchers and pytorch developers working on large language models (LLMs), multimodal models (MM), automatic speech recognition (ASR), and text-to-speech synthesis (TTS). The primary objective of NeMo is to provide a scalable framework for researchers and developers from industry and academia to more easily implement and design new generative AI models by being able to leverage existing code and pretrained models.
For similar tasks

responsible-ai-toolbox
Responsible AI Toolbox is a suite of tools providing model and data exploration and assessment interfaces and libraries for understanding AI systems. It empowers developers and stakeholders to develop and monitor AI responsibly, enabling better data-driven actions. The toolbox includes visualization widgets for model assessment, error analysis, interpretability, fairness assessment, and mitigations library. It also offers a JupyterLab extension for managing machine learning experiments and a library for measuring gender bias in NLP datasets.
For similar jobs

responsible-ai-toolbox
Responsible AI Toolbox is a suite of tools providing model and data exploration and assessment interfaces and libraries for understanding AI systems. It empowers developers and stakeholders to develop and monitor AI responsibly, enabling better data-driven actions. The toolbox includes visualization widgets for model assessment, error analysis, interpretability, fairness assessment, and mitigations library. It also offers a JupyterLab extension for managing machine learning experiments and a library for measuring gender bias in NLP datasets.
fairlearn
Fairlearn is a Python package designed to help developers assess and mitigate fairness issues in artificial intelligence (AI) systems. It provides mitigation algorithms and metrics for model assessment. Fairlearn focuses on two types of harms: allocation harms and quality-of-service harms. The package follows the group fairness approach, aiming to identify groups at risk of experiencing harms and ensuring comparable behavior across these groups. Fairlearn consists of metrics for assessing model impacts and algorithms for mitigating unfairness in various AI tasks under different fairness definitions.
Open-Prompt-Injection
OpenPromptInjection is an open-source toolkit for attacks and defenses in LLM-integrated applications, enabling easy implementation, evaluation, and extension of attacks, defenses, and LLMs. It supports various attack and defense strategies, including prompt injection, paraphrasing, retokenization, data prompt isolation, instructional prevention, sandwich prevention, perplexity-based detection, LLM-based detection, response-based detection, and know-answer detection. Users can create models, tasks, and apps to evaluate different scenarios. The toolkit currently supports PaLM2 and provides a demo for querying models with prompts. Users can also evaluate ASV for different scenarios by injecting tasks and querying models with attacked data prompts.
aws-machine-learning-university-responsible-ai
This repository contains slides, notebooks, and data for the Machine Learning University (MLU) Responsible AI class. The mission is to make Machine Learning accessible to everyone, covering widely used ML techniques and applying them to real-world problems. The class includes lectures, final projects, and interactive visuals to help users learn about Responsible AI and core ML concepts.
AIF360
The AI Fairness 360 toolkit is an open-source library designed to detect and mitigate bias in machine learning models. It provides a comprehensive set of metrics, explanations, and algorithms for bias mitigation in various domains such as finance, healthcare, and education. The toolkit supports multiple bias mitigation algorithms and fairness metrics, and is available in both Python and R. Users can leverage the toolkit to ensure fairness in AI applications and contribute to its development for extensibility.
Awesome-Interpretability-in-Large-Language-Models
This repository is a collection of resources focused on interpretability in large language models (LLMs). It aims to help beginners get started in the area and keep researchers updated on the latest progress. It includes libraries, blogs, tutorials, forums, tools, programs, papers, and more related to interpretability in LLMs.
hallucination-index
LLM Hallucination Index - RAG Special is a comprehensive evaluation of large language models (LLMs) focusing on context length and open vs. closed-source attributes. The index explores the impact of context length on model performance and tests the assumption that closed-source LLMs outperform open-source ones. It also investigates the effectiveness of prompting techniques like Chain-of-Note across different context lengths. The evaluation includes 22 models from various brands, analyzing major trends and declaring overall winners based on short, medium, and long context insights. Methodologies involve rigorous testing with different context lengths and prompting techniques to assess models' abilities in handling extensive texts and detecting hallucinations.
llm-misinformation-survey
The 'llm-misinformation-survey' repository is dedicated to the survey on combating misinformation in the age of Large Language Models (LLMs). It explores the opportunities and challenges of utilizing LLMs to combat misinformation, providing insights into the history of combating misinformation, current efforts, and future outlook. The repository serves as a resource hub for the initiative 'LLMs Meet Misinformation' and welcomes contributions of relevant research papers and resources. The goal is to facilitate interdisciplinary efforts in combating LLM-generated misinformation and promoting the responsible use of LLMs in fighting misinformation.