
SWE-agent
SWE-agent takes a GitHub issue and tries to automatically fix it, using GPT-4, or your LM of choice. It can also be employed for offensive cybersecurity or competitive coding challenges. [NeurIPS 2024]
Stars: 13448
SWE-agent is a tool that turns language models (e.g. GPT-4) into software engineering agents capable of fixing bugs and issues in real GitHub repositories. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on the full test set by resolving 12.29% of issues. The tool is built and maintained by researchers from Princeton University. SWE-agent provides a command line tool and a graphical web interface for developers to interact with. It introduces an Agent-Computer Interface (ACI) to facilitate browsing, viewing, editing, and executing code files within repositories. The tool includes features such as a linter for syntax checking, a specialized file viewer, and a full-directory string searching command to enhance the agent's capabilities. SWE-agent aims to improve prompt engineering and ACI design to enhance the performance of language models in software engineering tasks.
README:
Documentation | Discord | Preprint | EnIGMA preprint
SWE-agent turns LMs (e.g. GPT-4) into software engineering agents that can resolve issues in real GitHub repositories and more.
On SWE-bench, SWE-agent resolves 12.47% of issues of the full test set and 23% of issues of SWE-bench lite. SWE-agent EnIGMA solves more than 3x more challenges of the offensive cybersecurity NYU CTF benchmark than the previous SOTA agent.
We accomplish our results by designing simple LM-centric commands and feedback formats to make it easier for the LM to browse the repository, view, edit and execute code files. We call this an Agent-Computer Interface (ACI). Read more about it in our paper!
SWE-agent is built and maintained by researchers from Princeton University.
👉 Try SWE-agent in your browser: 
Read our documentation to learn more:
- Installation
- Command line usage
- Using the web UI
- Benchmarking on SWE-bench
- Frequently Asked Questions
Our most recent lecture touches on the project's motivation, showcases our research findings and provides a hands-on tutorial on how to install, use, and configure SWE-agent:
SWE-agent: EnIGMA is a mode for solving offensive cybersecurity (capture the flag) challenges. EnIGMA achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple cybersecurity benchmarks (see leaderboard). The EnIGMA project introduced multiple features that are available in all modes of SWE-agent, such as the debugger and server connection tools and a summarizer to handle long outputs.
- If you'd like to ask questions, learn about upcoming features, and participate in future development, join our Discord community!
- If you'd like to contribute to the codebase, we welcome issues and pull requests!
Contact person: John Yang and Carlos E. Jimenez (Email: [email protected], [email protected]).
If you found this work helpful, please consider citing it using the following:
@misc{yang2024sweagent,
title={SWE-agent: Agent-Computer Interfaces Enable Automated Software Engineering},
author={John Yang and Carlos E. Jimenez and Alexander Wettig and Kilian Lieret and Shunyu Yao and Karthik Narasimhan and Ofir Press},
year={2024},
eprint={2405.15793},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.SE}
}If you used the summarizer, interactive commands or the offensive cybersecurity capabilities in SWE-agent, please also consider citing:
@misc{abramovich2024enigmaenhancedinteractivegenerative,
title={EnIGMA: Enhanced Interactive Generative Model Agent for CTF Challenges},
author={Talor Abramovich and Meet Udeshi and Minghao Shao and Kilian Lieret and Haoran Xi and Kimberly Milner and Sofija Jancheska and John Yang and Carlos E. Jimenez and Farshad Khorrami and Prashanth Krishnamurthy and Brendan Dolan-Gavitt and Muhammad Shafique and Karthik Narasimhan and Ramesh Karri and Ofir Press},
year={2024},
eprint={2409.16165},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.16165},
}MIT. Check LICENSE.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for SWE-agent
Similar Open Source Tools

SWE-agent
SWE-agent is a tool that turns language models (e.g. GPT-4) into software engineering agents capable of fixing bugs and issues in real GitHub repositories. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on the full test set by resolving 12.29% of issues. The tool is built and maintained by researchers from Princeton University. SWE-agent provides a command line tool and a graphical web interface for developers to interact with. It introduces an Agent-Computer Interface (ACI) to facilitate browsing, viewing, editing, and executing code files within repositories. The tool includes features such as a linter for syntax checking, a specialized file viewer, and a full-directory string searching command to enhance the agent's capabilities. SWE-agent aims to improve prompt engineering and ACI design to enhance the performance of language models in software engineering tasks.
RD-Agent
RD-Agent is a tool designed to automate critical aspects of industrial R&D processes, focusing on data-driven scenarios to streamline model and data development. It aims to propose new ideas ('R') and implement them ('D') automatically, leading to solutions of significant industrial value. The tool supports scenarios like Automated Quantitative Trading, Data Mining Agent, Research Copilot, and more, with a framework to push the boundaries of research in data science. Users can create a Conda environment, install the RDAgent package from PyPI, configure GPT model, and run various applications for tasks like quantitative trading, model evolution, medical prediction, and more. The tool is intended to enhance R&D processes and boost productivity in industrial settings.
MaxKB
MaxKB is a knowledge base Q&A system based on the LLM large language model. MaxKB = Max Knowledge Base, which aims to become the most powerful brain of the enterprise.
agents-towards-production
Agents Towards Production is an open-source playbook for building production-ready GenAI agents that scale from prototype to enterprise. Tutorials cover stateful workflows, vector memory, real-time web search APIs, Docker deployment, FastAPI endpoints, security guardrails, GPU scaling, browser automation, fine-tuning, multi-agent coordination, observability, evaluation, and UI development.
modelscope-agent
ModelScope-Agent is a customizable and scalable Agent framework. A single agent has abilities such as role-playing, LLM calling, tool usage, planning, and memory. It mainly has the following characteristics: - **Simple Agent Implementation Process**: Simply specify the role instruction, LLM name, and tool name list to implement an Agent application. The framework automatically arranges workflows for tool usage, planning, and memory. - **Rich models and tools**: The framework is equipped with rich LLM interfaces, such as Dashscope and Modelscope model interfaces, OpenAI model interfaces, etc. Built in rich tools, such as **code interpreter**, **weather query**, **text to image**, **web browsing**, etc., make it easy to customize exclusive agents. - **Unified interface and high scalability**: The framework has clear tools and LLM registration mechanism, making it convenient for users to expand more diverse Agent applications. - **Low coupling**: Developers can easily use built-in tools, LLM, memory, and other components without the need to bind higher-level agents.

xpander.ai
xpander.ai is a Backend-as-a-Service for autonomous agents that abstracts the ops layer, allowing AI engineers to focus on behavior and outcomes. It provides managed agent hosting with version control and CI/CD, a fully managed PostgreSQL memory layer, and a library of 2,000+ functions. The platform features an AI native triggering system that processes inputs from various sources and delivers unified messages to agents. With support for any agent framework or SDK, including Agno and OpenAI, xpander.ai enables users to build intelligent, production-ready AI agents without dealing with infrastructure complexity.

openrl
OpenRL is an open-source general reinforcement learning research framework that supports training for various tasks such as single-agent, multi-agent, offline RL, self-play, and natural language. Developed based on PyTorch, the goal of OpenRL is to provide a simple-to-use, flexible, efficient and sustainable platform for the reinforcement learning research community. It supports a universal interface for all tasks/environments, single-agent and multi-agent tasks, offline RL training with expert dataset, self-play training, reinforcement learning training for natural language tasks, DeepSpeed, Arena for evaluation, importing models and datasets from Hugging Face, user-defined environments, models, and datasets, gymnasium environments, callbacks, visualization tools, unit testing, and code coverage testing. It also supports various algorithms like PPO, DQN, SAC, and environments like Gymnasium, MuJoCo, Atari, and more.
software-agent-sdk
The OpenHands Software Agent SDK is a set of Python and REST APIs for building agents that work with code. It allows users to perform one-off tasks, routine maintenance tasks, and major tasks involving multiple agents. Agents can use the local machine or run in ephemeral workspaces like Docker or Kubernetes. The SDK can also be used to create new developer experiences, powering tools like the OpenHands CLI and OpenHands Cloud.
biochatter
Generative AI models have shown tremendous usefulness in increasing accessibility and automation of a wide range of tasks. This repository contains the `biochatter` Python package, a generic backend library for the connection of biomedical applications to conversational AI. It aims to provide a common framework for deploying, testing, and evaluating diverse models and auxiliary technologies in the biomedical domain. BioChatter is part of the BioCypher ecosystem, connecting natively to BioCypher knowledge graphs.

sealos
Sealos is a cloud operating system distribution based on the Kubernetes kernel, designed for a seamless development lifecycle. It allows users to spin up full-stack environments in seconds, effortlessly push releases, and scale production seamlessly. With core features like easy application management, quick database creation, and cloud universality, Sealos offers efficient and economical cloud management with high universality and ease of use. The platform also emphasizes agility and security through its multi-tenancy sharing model. Sealos is supported by a community offering full documentation, Discord support, and active development roadmap.

lerobot
LeRobot is a state-of-the-art AI library for real-world robotics in PyTorch. It aims to provide models, datasets, and tools to lower the barrier to entry to robotics, focusing on imitation learning and reinforcement learning. LeRobot offers pretrained models, datasets with human-collected demonstrations, and simulation environments. It plans to support real-world robotics on affordable and capable robots. The library hosts pretrained models and datasets on the Hugging Face community page.
archestra
Archestra is an enterprise-grade platform that enables non-technical users to safely leverage AI agents and MCP servers. It provides a secure runtime environment for AI interactions with sandboxing, resource controls, and prompt injection prevention. The platform supports MCP Protocol and is designed with a local-first architecture, enterprise-level security, and extensible tool system.
LMCache
LMCache is a serving engine extension designed to reduce time to first token (TTFT) and increase throughput, particularly in long-context scenarios. It stores key-value caches of reusable texts across different locations like GPU, CPU DRAM, and Local Disk, allowing the reuse of any text in any serving engine instance. By combining LMCache with vLLM, significant delay savings and GPU cycle reduction are achieved in various large language model (LLM) use cases, such as multi-round question answering and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). LMCache provides integration with the latest vLLM version, offering both online serving and offline inference capabilities. It supports sharing key-value caches across multiple vLLM instances and aims to provide stable support for non-prefix key-value caches along with user and developer documentation.
cognee
Cognee is an open-source framework designed for creating self-improving deterministic outputs for Large Language Models (LLMs) using graphs, LLMs, and vector retrieval. It provides a platform for AI engineers to enhance their models and generate more accurate results. Users can leverage Cognee to add new information, utilize LLMs for knowledge creation, and query the system for relevant knowledge. The tool supports various LLM providers and offers flexibility in adding different data types, such as text files or directories. Cognee aims to streamline the process of working with LLMs and improving AI models for better performance and efficiency.

LightLLM
LightLLM is a lightweight library for linear and logistic regression models. It provides a simple and efficient way to train and deploy machine learning models for regression tasks. The library is designed to be easy to use and integrate into existing projects, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced data scientists. With LightLLM, users can quickly build and evaluate regression models using a variety of algorithms and hyperparameters. The library also supports feature engineering and model interpretation, allowing users to gain insights from their data and make informed decisions based on the model predictions.
xpert
Xpert is a powerful tool for data analysis and visualization. It provides a user-friendly interface to explore and manipulate datasets, perform statistical analysis, and create insightful visualizations. With Xpert, users can easily import data from various sources, clean and preprocess data, analyze trends and patterns, and generate interactive charts and graphs. Whether you are a data scientist, analyst, researcher, or student, Xpert simplifies the process of data analysis and visualization, making it accessible to users with varying levels of expertise.
For similar tasks

SWE-agent
SWE-agent is a tool that turns language models (e.g. GPT-4) into software engineering agents capable of fixing bugs and issues in real GitHub repositories. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on the full test set by resolving 12.29% of issues. The tool is built and maintained by researchers from Princeton University. SWE-agent provides a command line tool and a graphical web interface for developers to interact with. It introduces an Agent-Computer Interface (ACI) to facilitate browsing, viewing, editing, and executing code files within repositories. The tool includes features such as a linter for syntax checking, a specialized file viewer, and a full-directory string searching command to enhance the agent's capabilities. SWE-agent aims to improve prompt engineering and ACI design to enhance the performance of language models in software engineering tasks.
agentscope
AgentScope is a multi-agent platform designed to empower developers to build multi-agent applications with large-scale models. It features three high-level capabilities: Easy-to-Use, High Robustness, and Actor-Based Distribution. AgentScope provides a list of `ModelWrapper` to support both local model services and third-party model APIs, including OpenAI API, DashScope API, Gemini API, and ollama. It also enables developers to rapidly deploy local model services using libraries such as ollama (CPU inference), Flask + Transformers, Flask + ModelScope, FastChat, and vllm. AgentScope supports various services, including Web Search, Data Query, Retrieval, Code Execution, File Operation, and Text Processing. Example applications include Conversation, Game, and Distribution. AgentScope is released under Apache License 2.0 and welcomes contributions.
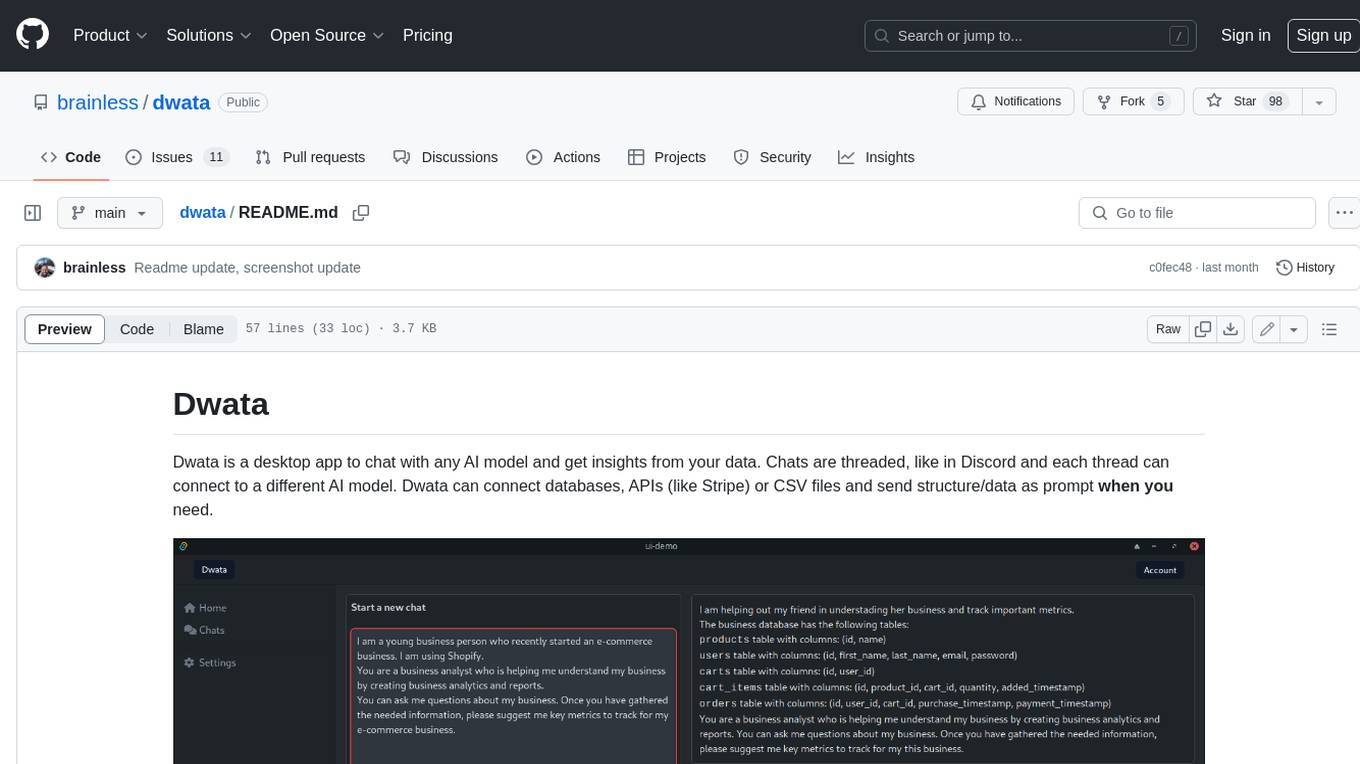
dwata
Dwata is a desktop application that allows users to chat with any AI model and gain insights from their data. Chats are organized into threads, similar to Discord, with each thread connecting to a different AI model. Dwata can connect to databases, APIs (such as Stripe), or CSV files and send structured data as prompts when needed. The AI's response will often include SQL or Python code, which can be used to extract the desired insights. Dwata can validate AI-generated SQL to ensure that the tables and columns referenced are correct and can execute queries against the database from within the application. Python code (typically using Pandas) can also be executed from within Dwata, although this feature is still in development. Dwata supports a range of AI models, including OpenAI's GPT-4, GPT-4 Turbo, and GPT-3.5 Turbo; Groq's LLaMA2-70b and Mixtral-8x7b; Phind's Phind-34B and Phind-70B; Anthropic's Claude; and Ollama's Llama 2, Mistral, and Phi-2 Gemma. Dwata can compare chats from different models, allowing users to see the responses of multiple models to the same prompts. Dwata can connect to various data sources, including databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB), SaaS products (Stripe, Shopify), CSV files/folders, and email (IMAP). The desktop application does not collect any private or business data without the user's explicit consent.
Tiger
Tiger is a community-driven project developing a reusable and integrated tool ecosystem for LLM Agent Revolution. It utilizes Upsonic for isolated tool storage, profiling, and automatic document generation. With Tiger, you can create a customized environment for your agents or leverage the robust and publicly maintained Tiger curated by the community itself.
NeoGPT
NeoGPT is an AI assistant that transforms your local workspace into a powerhouse of productivity from your CLI. With features like code interpretation, multi-RAG support, vision models, and LLM integration, NeoGPT redefines how you work and create. It supports executing code seamlessly, multiple RAG techniques, vision models, and interacting with various language models. Users can run the CLI to start using NeoGPT and access features like Code Interpreter, building vector database, running Streamlit UI, and changing LLM models. The tool also offers magic commands for chat sessions, such as resetting chat history, saving conversations, exporting settings, and more. Join the NeoGPT community to experience a new era of efficiency and contribute to its evolution.
Phi-3-Vision-MLX
Phi-3-MLX is a versatile AI framework that leverages both the Phi-3-Vision multimodal model and the Phi-3-Mini-128K language model optimized for Apple Silicon using the MLX framework. It provides an easy-to-use interface for a wide range of AI tasks, from advanced text generation to visual question answering and code execution. The project features support for batched generation, flexible agent system, custom toolchains, model quantization, LoRA fine-tuning capabilities, and API integration for extended functionality.
llm-sandbox
LLM Sandbox is a lightweight and portable sandbox environment designed to securely execute large language model (LLM) generated code in a safe and isolated manner using Docker containers. It provides an easy-to-use interface for setting up, managing, and executing code in a controlled Docker environment, simplifying the process of running code generated by LLMs. The tool supports multiple programming languages, offers flexibility with predefined Docker images or custom Dockerfiles, and allows scalability with support for Kubernetes and remote Docker hosts.
lovelaice
Lovelaice is an AI-powered assistant for your terminal and editor. It can run bash commands, search the Internet, answer general and technical questions, complete text files, chat casually, execute code in various languages, and more. Lovelaice is configurable with API keys and LLM models, and can be used for a wide range of tasks requiring bash commands or coding assistance. It is designed to be versatile, interactive, and helpful for daily tasks and projects.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

