LMOps
General technology for enabling AI capabilities w/ LLMs and MLLMs
Stars: 3591

LMOps is a research initiative focusing on fundamental research and technology for building AI products with foundation models, particularly enabling AI capabilities with Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI models. The project explores various aspects such as prompt optimization, longer context handling, LLM alignment, acceleration of LLMs, LLM customization, and understanding in-context learning. It also includes tools like Promptist for automatic prompt optimization, Structured Prompting for efficient long-sequence prompts consumption, and X-Prompt for extensible prompts beyond natural language. Additionally, LLMA accelerators are developed to speed up LLM inference by referencing and copying text spans from documents. The project aims to advance technologies that facilitate prompting language models and enhance the performance of LLMs in various scenarios.
README:
LMOps is a research initiative on fundamental research and technology for building AI products w/ foundation models, especially on the general technology for enabling AI capabilities w/ LLMs and Generative AI models.
- Better Prompts: Automatic Prompt Optimization, Promptist, Extensible prompts, Universal prompt retrieval, LLM Retriever, In-Context Demonstration Selection
- Longer Context: Structured prompting, Length-Extrapolatable Transformers
- LLM Alignment: Alignment via LLM feedback
- LLM Accelerator (Faster Inference): Lossless Acceleration of LLMs
- LLM Customization: Adapt LLM to domains
- Fundamentals: Understanding In-Context Learning
- microsoft/unilm: Large-scale Self-supervised Pre-training Across Tasks, Languages, and Modalities
- microsoft/torchscale: Transformers at (any) Scale
- [Paper Release] Nov, 2023: In-Context Demonstration Selection with Cross Entropy Difference (EMNLP 2023)
- [Paper Release] Oct, 2023: Tuna: Instruction Tuning using Feedback from Large Language Models (EMNLP 2023)
- [Paper Release] Oct, 2023: Automatic Prompt Optimization with "Gradient Descent" and Beam Search (EMNLP 2023)
- [Paper Release] Oct, 2023: UPRISE: Universal Prompt Retrieval for Improving Zero-Shot Evaluation (EMNLP 2023)
- [Paper Release] July, 2023: Learning to Retrieve In-Context Examples for Large Language Models
- [Paper Release] April, 2023: Inference with Reference: Lossless Acceleration of Large Language Models
- [Paper Release] Dec, 2022: Why Can GPT Learn In-Context? Language Models Secretly Perform Finetuning as Meta Optimizers
- [Paper & Model & Demo Release] Dec, 2022: Optimizing Prompts for Text-to-Image Generation
- [Paper & Code Release] Dec, 2022: Structured Prompting: Scaling In-Context Learning to 1,000 Examples
- [Paper Release] Nov, 2022: Extensible Prompts for Language Models
Advanced technologies facilitating prompting language models.
[Paper] Optimizing Prompts for Text-to-Image Generation
- Language models serve as a prompt interface that optimizes user input into model-preferred prompts.
- Learn a language model for automatic prompt optimization via reinforcement learning.
[Paper] Structured Prompting: Scaling In-Context Learning to 1,000 Examples
- Example use cases:
- Prepend (many) retrieved (long) documents as context in GPT.
- Scale in-context learning to many demonstration examples.
[Paper] Extensible Prompts for Language Models
- Extensible interface allowing prompting LLMs beyond natural language for fine-grain specifications
- Context-guided imaginary word learning for general usability
[Paper] Inference with Reference: Lossless Acceleration of Large Language Models
- Outputs of LLMs often have significant overlaps with some references (e.g., retrieved documents).
- LLMA losslessly accelerate the inference of LLMs by copying and verifying text spans from references into the LLM inputs.
- Applicable to important LLM scenarios such as retrieval-augmented generation and multi-turn conversations.
- Achieves 2~3 times speed-up without additional models.
[Paper] Why Can GPT Learn In-Context? Language Models Secretly Perform Finetuning as Meta Optimizers
- According to the demonstration examples, GPT produces meta gradients for In-Context Learning (ICL) through forward computation. ICL works by applying these meta gradients to the model through attention.
- The meta optimization process of ICL shares a dual view with finetuning that explicitly updates the model parameters with back-propagated gradients.
- We can translate optimization algorithms (such as SGD with Momentum) to their corresponding Transformer architectures.
Hiring: aka.ms/GeneralAI
We are hiring at all levels (including FTE researchers and interns)! If you are interested in working with us on Foundation Models (aka large-scale pre-trained models) and AGI, NLP, MT, Speech, Document AI and Multimodal AI, please send your resume to [email protected].
This project is licensed under the license found in the LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree.
Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct
For help or issues using the pre-trained models, please submit a GitHub issue.
For other communications, please contact Furu Wei ([email protected]).
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LMOps
Similar Open Source Tools

LMOps
LMOps is a research initiative focusing on fundamental research and technology for building AI products with foundation models, particularly enabling AI capabilities with Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI models. The project explores various aspects such as prompt optimization, longer context handling, LLM alignment, acceleration of LLMs, LLM customization, and understanding in-context learning. It also includes tools like Promptist for automatic prompt optimization, Structured Prompting for efficient long-sequence prompts consumption, and X-Prompt for extensible prompts beyond natural language. Additionally, LLMA accelerators are developed to speed up LLM inference by referencing and copying text spans from documents. The project aims to advance technologies that facilitate prompting language models and enhance the performance of LLMs in various scenarios.
long-llms-learning
A repository sharing the panorama of the methodology literature on Transformer architecture upgrades in Large Language Models for handling extensive context windows, with real-time updating the newest published works. It includes a survey on advancing Transformer architecture in long-context large language models, flash-ReRoPE implementation, latest news on data engineering, lightning attention, Kimi AI assistant, chatglm-6b-128k, gpt-4-turbo-preview, benchmarks like InfiniteBench and LongBench, long-LLMs-evals for evaluating methods for enhancing long-context capabilities, and LLMs-learning for learning technologies and applicated tasks about Large Language Models.
Macaw-LLM
Macaw-LLM is a pioneering multi-modal language modeling tool that seamlessly integrates image, audio, video, and text data. It builds upon CLIP, Whisper, and LLaMA models to process and analyze multi-modal information effectively. The tool boasts features like simple and fast alignment, one-stage instruction fine-tuning, and a new multi-modal instruction dataset. It enables users to align multi-modal features efficiently, encode instructions, and generate responses across different data types.
llm-course
The LLM course is divided into three parts: 1. 🧩 **LLM Fundamentals** covers essential knowledge about mathematics, Python, and neural networks. 2. 🧑🔬 **The LLM Scientist** focuses on building the best possible LLMs using the latest techniques. 3. 👷 **The LLM Engineer** focuses on creating LLM-based applications and deploying them. For an interactive version of this course, I created two **LLM assistants** that will answer questions and test your knowledge in a personalized way: * 🤗 **HuggingChat Assistant**: Free version using Mixtral-8x7B. * 🤖 **ChatGPT Assistant**: Requires a premium account. ## 📝 Notebooks A list of notebooks and articles related to large language models. ### Tools | Notebook | Description | Notebook | |----------|-------------|----------| | 🧐 LLM AutoEval | Automatically evaluate your LLMs using RunPod |  | | 🥱 LazyMergekit | Easily merge models using MergeKit in one click. |  | | 🦎 LazyAxolotl | Fine-tune models in the cloud using Axolotl in one click. |  | | ⚡ AutoQuant | Quantize LLMs in GGUF, GPTQ, EXL2, AWQ, and HQQ formats in one click. |  | | 🌳 Model Family Tree | Visualize the family tree of merged models. |  | | 🚀 ZeroSpace | Automatically create a Gradio chat interface using a free ZeroGPU. |  |
LazyLLM
LazyLLM is a low-code development tool for building complex AI applications with multiple agents. It assists developers in building AI applications at a low cost and continuously optimizing their performance. The tool provides a convenient workflow for application development and offers standard processes and tools for various stages of application development. Users can quickly prototype applications with LazyLLM, analyze bad cases with scenario task data, and iteratively optimize key components to enhance the overall application performance. LazyLLM aims to simplify the AI application development process and provide flexibility for both beginners and experts to create high-quality applications.
HuixiangDou2
HuixiangDou2 is a robustly optimized GraphRAG approach that integrates multiple open-source projects to improve performance in graph-based augmented generation. It conducts comparative experiments and achieves a significant score increase, leading to a GraphRAG implementation with recognized performance. The repository provides code improvements, dense retrieval for querying entities and relationships, real domain knowledge testing, and impact analysis on accuracy.

fenic
fenic is an opinionated DataFrame framework from typedef.ai for building AI and agentic applications. It transforms unstructured and structured data into insights using familiar DataFrame operations enhanced with semantic intelligence. With support for markdown, transcripts, and semantic operators, plus efficient batch inference across various model providers. fenic is purpose-built for LLM inference, providing a query engine designed for AI workloads, semantic operators as first-class citizens, native unstructured data support, production-ready infrastructure, and a familiar DataFrame API.
GOLEM
GOLEM is an open-source AI framework focused on optimization and learning of structured graph-based models using meta-heuristic methods. It emphasizes the potential of meta-heuristics in complex problem spaces where gradient-based methods are not suitable, and the importance of structured models in various problem domains. The framework offers features like structured model optimization, metaheuristic methods, multi-objective optimization, constrained optimization, extensibility, interpretability, and reproducibility. It can be applied to optimization problems represented as directed graphs with defined fitness functions. GOLEM has applications in areas like AutoML, Bayesian network structure search, differential equation discovery, geometric design, and neural architecture search. The project structure includes packages for core functionalities, adapters, graph representation, optimizers, genetic algorithms, utilities, serialization, visualization, examples, and testing. Contributions are welcome, and the project is supported by ITMO University's Research Center Strong Artificial Intelligence in Industry.
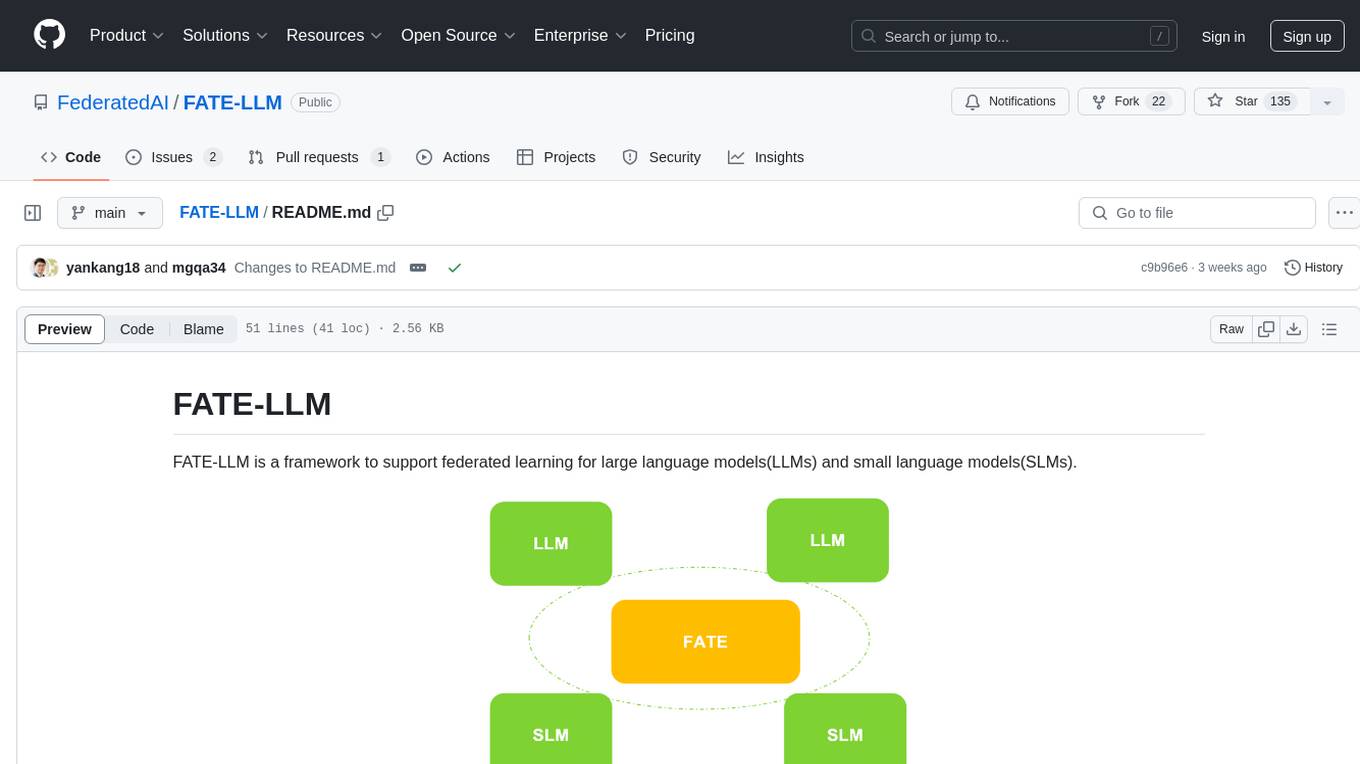
FATE-LLM
FATE-LLM is a framework supporting federated learning for large and small language models. It promotes training efficiency of federated LLMs using Parameter-Efficient methods, protects the IP of LLMs using FedIPR, and ensures data privacy during training and inference through privacy-preserving mechanisms.

raga-llm-hub
Raga LLM Hub is a comprehensive evaluation toolkit for Language and Learning Models (LLMs) with over 100 meticulously designed metrics. It allows developers and organizations to evaluate and compare LLMs effectively, establishing guardrails for LLMs and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) applications. The platform assesses aspects like Relevance & Understanding, Content Quality, Hallucination, Safety & Bias, Context Relevance, Guardrails, and Vulnerability scanning, along with Metric-Based Tests for quantitative analysis. It helps teams identify and fix issues throughout the LLM lifecycle, revolutionizing reliability and trustworthiness.
rlhf_thinking_model
This repository is a collection of research notes and resources focusing on training large language models (LLMs) and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). It includes methodologies, techniques, and state-of-the-art approaches for optimizing preferences and model alignment in LLM training. The purpose is to serve as a reference for researchers and engineers interested in reinforcement learning, large language models, model alignment, and alternative RL-based methods.

KAG
KAG is a logical reasoning and Q&A framework based on the OpenSPG engine and large language models. It is used to build logical reasoning and Q&A solutions for vertical domain knowledge bases. KAG supports logical reasoning, multi-hop fact Q&A, and integrates knowledge and chunk mutual indexing structure, conceptual semantic reasoning, schema-constrained knowledge construction, and logical form-guided hybrid reasoning and retrieval. The framework includes kg-builder for knowledge representation and kg-solver for logical symbol-guided hybrid solving and reasoning engine. KAG aims to enhance LLM service framework in professional domains by integrating logical and factual characteristics of KGs.
Open-Reasoning-Tasks
The Open-Reasoning-Tasks repository is a collaborative project aimed at creating a comprehensive list of reasoning tasks for training large language models (LLMs). Contributors can submit tasks with descriptions, examples, and optional diagrams to enhance LLMs' reasoning capabilities.
ianvs
Ianvs is a distributed synergy AI benchmarking project incubated in KubeEdge SIG AI. It aims to test the performance of distributed synergy AI solutions following recognized standards, providing end-to-end benchmark toolkits, test environment management tools, test case control tools, and benchmark presentation tools. It also collaborates with other organizations to establish comprehensive benchmarks and related applications. The architecture includes critical components like Test Environment Manager, Test Case Controller, Generation Assistant, Simulation Controller, and Story Manager. Ianvs documentation covers quick start, guides, dataset descriptions, algorithms, user interfaces, stories, and roadmap.
For similar tasks
AutoGPTQ
AutoGPTQ is an easy-to-use LLM quantization package with user-friendly APIs, based on GPTQ algorithm (weight-only quantization). It provides a simple and efficient way to quantize large language models (LLMs) to reduce their size and computational cost while maintaining their performance. AutoGPTQ supports a wide range of LLM models, including GPT-2, GPT-J, OPT, and BLOOM. It also supports various evaluation tasks, such as language modeling, sequence classification, and text summarization. With AutoGPTQ, users can easily quantize their LLM models and deploy them on resource-constrained devices, such as mobile phones and embedded systems.
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM is a project developed for the NVIDIA TensorRT Hackathon 2023, focusing on accelerating inference for the Qwen-7B-Chat model using TRT-LLM. The project offers various functionalities such as FP16/BF16 support, INT8 and INT4 quantization options, Tensor Parallel for multi-GPU parallelism, web demo setup with gradio, Triton API deployment for maximum throughput/concurrency, fastapi integration for openai requests, CLI interaction, and langchain support. It supports models like qwen2, qwen, and qwen-vl for both base and chat models. The project also provides tutorials on Bilibili and blogs for adapting Qwen models in NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, along with hardware requirements and quick start guides for different model types and quantization methods.
stable-diffusion.cpp
The stable-diffusion.cpp repository provides an implementation for inferring stable diffusion in pure C/C++. It offers features such as support for different versions of stable diffusion, lightweight and dependency-free implementation, various quantization support, memory-efficient CPU inference, GPU acceleration, and more. Users can download the built executable program or build it manually. The repository also includes instructions for downloading weights, building from scratch, using different acceleration methods, running the tool, converting weights, and utilizing various features like Flash Attention, ESRGAN upscaling, PhotoMaker support, and more. Additionally, it mentions future TODOs and provides information on memory requirements, bindings, UIs, contributors, and references.

LMOps
LMOps is a research initiative focusing on fundamental research and technology for building AI products with foundation models, particularly enabling AI capabilities with Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI models. The project explores various aspects such as prompt optimization, longer context handling, LLM alignment, acceleration of LLMs, LLM customization, and understanding in-context learning. It also includes tools like Promptist for automatic prompt optimization, Structured Prompting for efficient long-sequence prompts consumption, and X-Prompt for extensible prompts beyond natural language. Additionally, LLMA accelerators are developed to speed up LLM inference by referencing and copying text spans from documents. The project aims to advance technologies that facilitate prompting language models and enhance the performance of LLMs in various scenarios.
Awesome-Efficient-LLM
Awesome-Efficient-LLM is a curated list focusing on efficient large language models. It includes topics such as knowledge distillation, network pruning, quantization, inference acceleration, efficient MOE, efficient architecture of LLM, KV cache compression, text compression, low-rank decomposition, hardware/system, tuning, and survey. The repository provides a collection of papers and projects related to improving the efficiency of large language models through various techniques like sparsity, quantization, and compression.
TensorRT-Model-Optimizer
The NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer is a library designed to quantize and compress deep learning models for optimized inference on GPUs. It offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques including quantization and sparsity to reduce inference costs for generative AI models. Users can easily stack different optimization techniques to produce quantized checkpoints from torch or ONNX models. The quantized checkpoints are ready for deployment in inference frameworks like TensorRT-LLM or TensorRT, with planned integrations for NVIDIA NeMo and Megatron-LM. The tool also supports 8-bit quantization with Stable Diffusion for enterprise users on NVIDIA NIM. Model Optimizer is available for free on NVIDIA PyPI, and this repository serves as a platform for sharing examples, GPU-optimized recipes, and collecting community feedback.
lightning-bolts
Bolts package provides a variety of components to extend PyTorch Lightning, such as callbacks & datasets, for applied research and production. Users can accelerate Lightning training with the Torch ORT Callback to optimize ONNX graph for faster training & inference. Additionally, users can introduce sparsity with the SparseMLCallback to accelerate inference by leveraging the DeepSparse engine. Specific research implementations are encouraged, with contributions that help train SSL models and integrate with Lightning Flash for state-of-the-art models in applied research.
ms-swift
ms-swift is an official framework provided by the ModelScope community for fine-tuning and deploying large language models and multi-modal large models. It supports training, inference, evaluation, quantization, and deployment of over 400 large models and 100+ multi-modal large models. The framework includes various training technologies and accelerates inference, evaluation, and deployment modules. It offers a Gradio-based Web-UI interface and best practices for easy application of large models. ms-swift supports a wide range of model types, dataset types, hardware support, lightweight training methods, distributed training techniques, quantization training, RLHF training, multi-modal training, interface training, plugin and extension support, inference acceleration engines, model evaluation, and model quantization.
For similar jobs
responsible-ai-toolbox
Responsible AI Toolbox is a suite of tools providing model and data exploration and assessment interfaces and libraries for understanding AI systems. It empowers developers and stakeholders to develop and monitor AI responsibly, enabling better data-driven actions. The toolbox includes visualization widgets for model assessment, error analysis, interpretability, fairness assessment, and mitigations library. It also offers a JupyterLab extension for managing machine learning experiments and a library for measuring gender bias in NLP datasets.
LLMLingua
LLMLingua is a tool that utilizes a compact, well-trained language model to identify and remove non-essential tokens in prompts. This approach enables efficient inference with large language models, achieving up to 20x compression with minimal performance loss. The tool includes LLMLingua, LongLLMLingua, and LLMLingua-2, each offering different levels of prompt compression and performance improvements for tasks involving large language models.
llm-examples
Starter examples for building LLM apps with Streamlit. This repository showcases a growing collection of LLM minimum working examples, including a Chatbot, File Q&A, Chat with Internet search, LangChain Quickstart, LangChain PromptTemplate, and Chat with user feedback. Users can easily get their own OpenAI API key and set it as an environment variable in Streamlit apps to run the examples locally.

LMOps
LMOps is a research initiative focusing on fundamental research and technology for building AI products with foundation models, particularly enabling AI capabilities with Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI models. The project explores various aspects such as prompt optimization, longer context handling, LLM alignment, acceleration of LLMs, LLM customization, and understanding in-context learning. It also includes tools like Promptist for automatic prompt optimization, Structured Prompting for efficient long-sequence prompts consumption, and X-Prompt for extensible prompts beyond natural language. Additionally, LLMA accelerators are developed to speed up LLM inference by referencing and copying text spans from documents. The project aims to advance technologies that facilitate prompting language models and enhance the performance of LLMs in various scenarios.
awesome-tool-llm
This repository focuses on exploring tools that enhance the performance of language models for various tasks. It provides a structured list of literature relevant to tool-augmented language models, covering topics such as tool basics, tool use paradigm, scenarios, advanced methods, and evaluation. The repository includes papers, preprints, and books that discuss the use of tools in conjunction with language models for tasks like reasoning, question answering, mathematical calculations, accessing knowledge, interacting with the world, and handling non-textual modalities.
gaianet-node
GaiaNet-node is a tool that allows users to run their own GaiaNet node, enabling them to interact with an AI agent. The tool provides functionalities to install the default node software stack, initialize the node with model files and vector database files, start the node, stop the node, and update configurations. Users can use pre-set configurations or pass a custom URL for initialization. The tool is designed to facilitate communication with the AI agent and access node information via a browser. GaiaNet-node requires sudo privilege for installation but can also be installed without sudo privileges with specific commands.
llmops-duke-aipi
LLMOps Duke AIPI is a course focused on operationalizing Large Language Models, teaching methodologies for developing applications using software development best practices with large language models. The course covers various topics such as generative AI concepts, setting up development environments, interacting with large language models, using local large language models, applied solutions with LLMs, extensibility using plugins and functions, retrieval augmented generation, introduction to Python web frameworks for APIs, DevOps principles, deploying machine learning APIs, LLM platforms, and final presentations. Students will learn to build, share, and present portfolios using Github, YouTube, and Linkedin, as well as develop non-linear life-long learning skills. Prerequisites include basic Linux and programming skills, with coursework available in Python or Rust. Additional resources and references are provided for further learning and exploration.
Awesome-AISourceHub
Awesome-AISourceHub is a repository that collects high-quality information sources in the field of AI technology. It serves as a synchronized source of information to avoid information gaps and information silos. The repository aims to provide valuable resources for individuals such as AI book authors, enterprise decision-makers, and tool developers who frequently use Twitter to share insights and updates related to AI advancements. The platform emphasizes the importance of accessing information closer to the source for better quality content. Users can contribute their own high-quality information sources to the repository by following specific steps outlined in the contribution guidelines. The repository covers various platforms such as Twitter, public accounts, knowledge planets, podcasts, blogs, websites, YouTube channels, and more, offering a comprehensive collection of AI-related resources for individuals interested in staying updated with the latest trends and developments in the AI field.