Awesome-Efficient-LLM
A curated list for Efficient Large Language Models
Stars: 1589
Awesome-Efficient-LLM is a curated list focusing on efficient large language models. It includes topics such as knowledge distillation, network pruning, quantization, inference acceleration, efficient MOE, efficient architecture of LLM, KV cache compression, text compression, low-rank decomposition, hardware/system, tuning, and survey. The repository provides a collection of papers and projects related to improving the efficiency of large language models through various techniques like sparsity, quantization, and compression.
README:
A curated list for Efficient Large Language Models
- Network Pruning / Sparsity
- Knowledge Distillation
- Quantization
- Inference Acceleration
- Efficient MOE
- Efficient Architecture of LLM
- KV Cache Compression
- Text Compression
- Low-Rank Decomposition
- Hardware / System / Serving
- Efficient Fine-tuning
- Efficient Training
- Survey or Benchmark
Please check out all the papers by selecting the sub-area you're interested in. On this main page, only papers released in the past 90 days are shown.
- May 29, 2024: We've had this awesome list for a year now 🥰!
- Sep 6, 2023: Add a new subdirectory project/ to organize efficient LLM projects.
- July 11, 2023: A new subdirectory efficient_plm/ is created to house papers that are applicable to PLMs.
If you'd like to include your paper, or need to update any details such as conference information or code URLs, please feel free to submit a pull request. You can generate the required markdown format for each paper by filling in the information in generate_item.py and execute python generate_item.py. We warmly appreciate your contributions to this list. Alternatively, you can email me with the links to your paper and code, and I would add your paper to the list at my earliest convenience.
For each topic, we have curated a list of recommended papers that have garnered a lot of GitHub stars or citations.
Paper from Sep 30, 2024 - Now (see Full List from May 22, 2023 here)
- Network Pruning / Sparsity
- Knowledge Distillation
- Quantization
- Inference Acceleration
- Efficient MOE
- Efficient Architecture of LLM
- KV Cache Compression
- Text Compression
- Low-Rank Decomposition
- Hardware / System / Serving
- Efficient Fine-tuning
- Efficient Training
- Survey
| Title & Authors | Introduction | Links |
|---|---|---|
 ⭐ Fast Inference of Mixture-of-Experts Language Models with Offloading Artyom Eliseev, Denis Mazur |
 |
Github Paper |
 Condense, Don't Just Prune: Enhancing Efficiency and Performance in MoE Layer Pruning Mingyu Cao, Gen Li, Jie Ji, Jiaqi Zhang, Xiaolong Ma, Shiwei Liu, Lu Yin |
 |
Github Paper |
|
Mixture of Cache-Conditional Experts for Efficient Mobile Device Inference Andrii Skliar, Ties van Rozendaal, Romain Lepert, Todor Boinovski, Mart van Baalen, Markus Nagel, Paul Whatmough, Babak Ehteshami Bejnordi |
 |
Paper |
 MoNTA: Accelerating Mixture-of-Experts Training with Network-Traffc-Aware Parallel Optimization Jingming Guo, Yan Liu, Yu Meng, Zhiwei Tao, Banglan Liu, Gang Chen, Xiang Li |
 |
Github Paper |
 MoE-I2: Compressing Mixture of Experts Models through Inter-Expert Pruning and Intra-Expert Low-Rank Decomposition Cheng Yang, Yang Sui, Jinqi Xiao, Lingyi Huang, Yu Gong, Yuanlin Duan, Wenqi Jia, Miao Yin, Yu Cheng, Bo Yuan |
 |
Github Paper |
|
HOBBIT: A Mixed Precision Expert Offloading System for Fast MoE Inference Peng Tang, Jiacheng Liu, Xiaofeng Hou, Yifei Pu, Jing Wang, Pheng-Ann Heng, Chao Li, Minyi Guo |
 |
Paper |
|
ProMoE: Fast MoE-based LLM Serving using Proactive Caching Xiaoniu Song, Zihang Zhong, Rong Chen |
 |
Paper |
|
ExpertFlow: Optimized Expert Activation and Token Allocation for Efficient Mixture-of-Experts Inference Xin He, Shunkang Zhang, Yuxin Wang, Haiyan Yin, Zihao Zeng, Shaohuai Shi, Zhenheng Tang, Xiaowen Chu, Ivor Tsang, Ong Yew Soon |
 |
Paper |
|
EPS-MoE: Expert Pipeline Scheduler for Cost-Efficient MoE Inference Yulei Qian, Fengcun Li, Xiangyang Ji, Xiaoyu Zhao, Jianchao Tan, Kefeng Zhang, Xunliang Cai |
Paper | |
 MC-MoE: Mixture Compressor for Mixture-of-Experts LLMs Gains More Wei Huang, Yue Liao, Jianhui Liu, Ruifei He, Haoru Tan, Shiming Zhang, Hongsheng Li, Si Liu, Xiaojuan Qi |
 |
Github Paper |
| Title & Authors | Introduction | Links |
|---|---|---|
  Hymba: A Hybrid-head Architecture for Small Language Models Xin Dong, Yonggan Fu, Shizhe Diao, Wonmin Byeon, Zijia Chen, Ameya Sunil Mahabaleshwarkar, Shih-Yang Liu, Matthijs Van Keirsbilck, Min-Hung Chen, Yoshi Suhara, Yingyan Lin, Jan Kautz, Pavlo Molchanov |
 |
Paper |
 ⭐ MobiLlama: Towards Accurate and Lightweight Fully Transparent GPT Omkar Thawakar, Ashmal Vayani, Salman Khan, Hisham Cholakal, Rao M. Anwer, Michael Felsberg, Tim Baldwin, Eric P. Xing, Fahad Shahbaz Khan |
 |
Github Paper Model |
 ⭐ Megalodon: Efficient LLM Pretraining and Inference with Unlimited Context Length Xuezhe Ma, Xiaomeng Yang, Wenhan Xiong, Beidi Chen, Lili Yu, Hao Zhang, Jonathan May, Luke Zettlemoyer, Omer Levy, Chunting Zhou |
 |
Github Paper |
|
Taipan: Efficient and Expressive State Space Language Models with Selective Attention Chien Van Nguyen, Huy Huu Nguyen, Thang M. Pham, Ruiyi Zhang, Hanieh Deilamsalehy, Puneet Mathur, Ryan A. Rossi, Trung Bui, Viet Dac Lai, Franck Dernoncourt, Thien Huu Nguyen |
 |
Paper |
 SeerAttention: Learning Intrinsic Sparse Attention in Your LLMs Yizhao Gao, Zhichen Zeng, Dayou Du, Shijie Cao, Hayden Kwok-Hay So, Ting Cao, Fan Yang, Mao Yang |
 |
Github Paper |
 Basis Sharing: Cross-Layer Parameter Sharing for Large Language Model Compression Jingcun Wang, Yu-Guang Chen, Ing-Chao Lin, Bing Li, Grace Li Zhang |
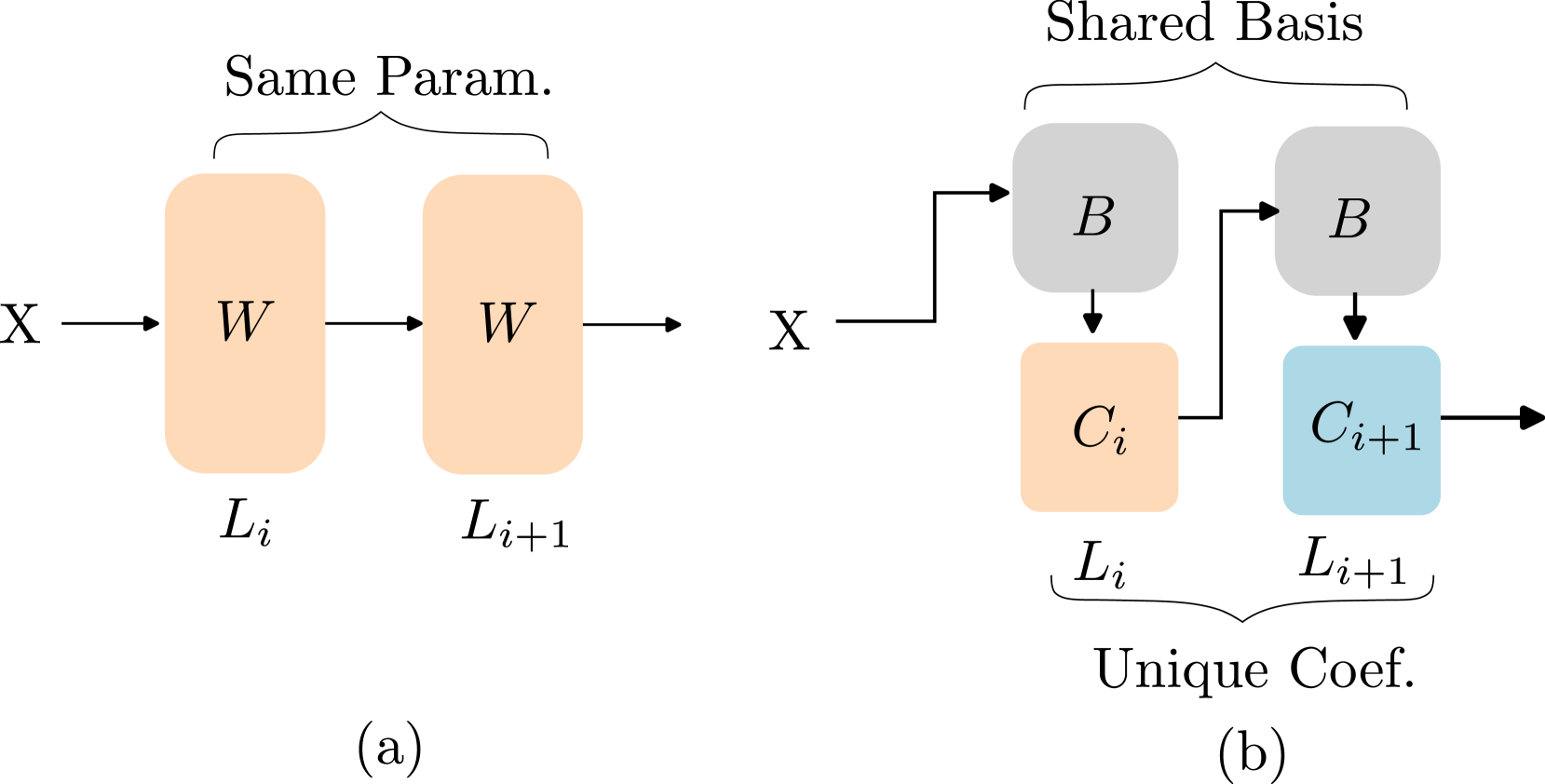 |
Github Paper |
|
Rodimus*: Breaking the Accuracy-Efficiency Trade-Off with Efficient Attentions Zhihao He, Hang Yu, Zi Gong, Shizhan Liu, Jianguo Li, Weiyao Lin |
 |
Paper |
| Title & Authors | Introduction | Links |
|---|---|---|
 ESPACE: Dimensionality Reduction of Activations for Model Compression Charbel Sakr, Brucek Khailany |
 |
Paper |
 Natural GaLore: Accelerating GaLore for memory-efficient LLM Training and Fine-tuning Arijit Das |
Github Paper |
|
|
CompAct: Compressed Activations for Memory-Efficient LLM Training Yara Shamshoum, Nitzan Hodos, Yuval Sieradzki, Assaf Schuster |
 |
Paper |
| Title & Authors | Introduction | Links |
|---|---|---|
|
Closer Look at Efficient Inference Methods: A Survey of Speculative Decoding Hyun Ryu, Eric Kim |
 |
Paper |
 LLM-Inference-Bench: Inference Benchmarking of Large Language Models on AI Accelerators Krishna Teja Chitty-Venkata, Siddhisanket Raskar, Bharat Kale, Farah Ferdaus et al |
Github Paper |
|
 Prompt Compression for Large Language Models: A Survey Zongqian Li, Yinhong Liu, Yixuan Su, Nigel Collier |
 |
Github Paper |
|
Large Language Model Inference Acceleration: A Comprehensive Hardware Perspective Jinhao Li, Jiaming Xu, Shan Huang, Yonghua Chen, Wen Li, Jun Liu, Yaoxiu Lian, Jiayi Pan, Li Ding, Hao Zhou, Guohao Dai |
 |
Paper |
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Awesome-Efficient-LLM
Similar Open Source Tools

Awesome-Efficient-LLM
Awesome-Efficient-LLM is a curated list focusing on efficient large language models. It includes topics such as knowledge distillation, network pruning, quantization, inference acceleration, efficient MOE, efficient architecture of LLM, KV cache compression, text compression, low-rank decomposition, hardware/system, tuning, and survey. The repository provides a collection of papers and projects related to improving the efficiency of large language models through various techniques like sparsity, quantization, and compression.
SLMs-Survey
SLMs-Survey is a comprehensive repository that includes papers and surveys on small language models. It covers topics such as technology, on-device applications, efficiency, enhancements for LLMs, and trustworthiness. The repository provides a detailed overview of existing SLMs, their architecture, enhancements, and specific applications in various domains. It also includes information on SLM deployment optimization techniques and the synergy between SLMs and LLMs.
awesome-llm-unlearning
This repository tracks the latest research on machine unlearning in large language models (LLMs). It offers a comprehensive list of papers, datasets, and resources relevant to the topic.
Awesome-LLM-RAG
This repository, Awesome-LLM-RAG, aims to record advanced papers on Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) in Large Language Models (LLMs). It serves as a resource hub for researchers interested in promoting their work related to LLM RAG by updating paper information through pull requests. The repository covers various topics such as workshops, tutorials, papers, surveys, benchmarks, retrieval-enhanced LLMs, RAG instruction tuning, RAG in-context learning, RAG embeddings, RAG simulators, RAG search, RAG long-text and memory, RAG evaluation, RAG optimization, and RAG applications.
Awesome-Latent-CoT
This repository contains a regularly updated paper list for Large Language Models (LLMs) reasoning in latent space. Reasoning in latent space allows for more flexible and efficient thought representation beyond language tokens, bringing AI closer to human-like cognition. The repository covers various aspects of LLMs, including pre-training, supervised finetuning, analysis, interpretability, multimodal reasoning, and applications. It aims to showcase the advancements in reasoning with latent thoughts and continuous concepts in AI models.
Awesome-Segment-Anything
Awesome-Segment-Anything is a powerful tool for segmenting and extracting information from various types of data. It provides a user-friendly interface to easily define segmentation rules and apply them to text, images, and other data formats. The tool supports both supervised and unsupervised segmentation methods, allowing users to customize the segmentation process based on their specific needs. With its versatile functionality and intuitive design, Awesome-Segment-Anything is ideal for data analysts, researchers, content creators, and anyone looking to efficiently extract valuable insights from complex datasets.
Awesome-Audio-LLM
Awesome-Audio-LLM is a repository dedicated to various models and methods related to audio and language processing. It includes a wide range of research papers and models developed by different institutions and authors. The repository covers topics such as bridging audio and language, speech emotion recognition, voice assistants, and more. It serves as a comprehensive resource for those interested in the intersection of audio and language processing.
AI-Notes
AI-Notes is a repository dedicated to practical applications of artificial intelligence and deep learning. It covers concepts such as data mining, machine learning, natural language processing, and AI. The repository contains Jupyter Notebook examples for hands-on learning and experimentation. It explores the development stages of AI, from narrow artificial intelligence to general artificial intelligence and superintelligence. The content delves into machine learning algorithms, deep learning techniques, and the impact of AI on various industries like autonomous driving and healthcare. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of AI technologies and their real-world applications.
Awesome-LLM-Reasoning-Openai-o1-Survey
The repository 'Awesome LLM Reasoning Openai-o1 Survey' provides a collection of survey papers and related works on OpenAI o1, focusing on topics such as LLM reasoning, self-play reinforcement learning, complex logic reasoning, and scaling law. It includes papers from various institutions and researchers, showcasing advancements in reasoning bootstrapping, reasoning scaling law, self-play learning, step-wise and process-based optimization, and applications beyond math. The repository serves as a valuable resource for researchers interested in exploring the intersection of language models and reasoning techniques.
ai_igu
AI-IGU is a GitHub repository focused on Artificial Intelligence (AI) concepts, technology, software development, and algorithm improvement for all ages and professions. It emphasizes the importance of future software for future scientists and the increasing need for software developers in the industry. The repository covers various topics related to AI, including machine learning, deep learning, data mining, data science, big data, and more. It provides educational materials, practical examples, and hands-on projects to enhance software development skills and create awareness in the field of AI.

VideoRefer
VideoRefer Suite is a tool designed to enhance the fine-grained spatial-temporal understanding capabilities of Video Large Language Models (Video LLMs). It consists of three primary components: Model (VideoRefer) for perceiving, reasoning, and retrieval for user-defined regions at any specified timestamps, Dataset (VideoRefer-700K) for high-quality object-level video instruction data, and Benchmark (VideoRefer-Bench) to evaluate object-level video understanding capabilities. The tool can understand any object within a video.
LLM-SFT
LLM-SFT is a Chinese large model fine-tuning tool that supports models such as ChatGLM, LlaMA, Bloom, Baichuan-7B, and frameworks like LoRA, QLoRA, DeepSpeed, UI, and TensorboardX. It facilitates tasks like fine-tuning, inference, evaluation, and API integration. The tool provides pre-trained weights for various models and datasets for Chinese language processing. It requires specific versions of libraries like transformers and torch for different functionalities.

awesome-generative-information-retrieval
This repository contains a curated list of resources on generative information retrieval, including research papers, datasets, tools, and applications. Generative information retrieval is a subfield of information retrieval that uses generative models to generate new documents or passages of text that are relevant to a given query. This can be useful for a variety of tasks, such as question answering, summarization, and document generation. The resources in this repository are intended to help researchers and practitioners stay up-to-date on the latest advances in generative information retrieval.
For similar tasks
AutoGPTQ
AutoGPTQ is an easy-to-use LLM quantization package with user-friendly APIs, based on GPTQ algorithm (weight-only quantization). It provides a simple and efficient way to quantize large language models (LLMs) to reduce their size and computational cost while maintaining their performance. AutoGPTQ supports a wide range of LLM models, including GPT-2, GPT-J, OPT, and BLOOM. It also supports various evaluation tasks, such as language modeling, sequence classification, and text summarization. With AutoGPTQ, users can easily quantize their LLM models and deploy them on resource-constrained devices, such as mobile phones and embedded systems.
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM is a project developed for the NVIDIA TensorRT Hackathon 2023, focusing on accelerating inference for the Qwen-7B-Chat model using TRT-LLM. The project offers various functionalities such as FP16/BF16 support, INT8 and INT4 quantization options, Tensor Parallel for multi-GPU parallelism, web demo setup with gradio, Triton API deployment for maximum throughput/concurrency, fastapi integration for openai requests, CLI interaction, and langchain support. It supports models like qwen2, qwen, and qwen-vl for both base and chat models. The project also provides tutorials on Bilibili and blogs for adapting Qwen models in NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, along with hardware requirements and quick start guides for different model types and quantization methods.
stable-diffusion.cpp
The stable-diffusion.cpp repository provides an implementation for inferring stable diffusion in pure C/C++. It offers features such as support for different versions of stable diffusion, lightweight and dependency-free implementation, various quantization support, memory-efficient CPU inference, GPU acceleration, and more. Users can download the built executable program or build it manually. The repository also includes instructions for downloading weights, building from scratch, using different acceleration methods, running the tool, converting weights, and utilizing various features like Flash Attention, ESRGAN upscaling, PhotoMaker support, and more. Additionally, it mentions future TODOs and provides information on memory requirements, bindings, UIs, contributors, and references.

LMOps
LMOps is a research initiative focusing on fundamental research and technology for building AI products with foundation models, particularly enabling AI capabilities with Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI models. The project explores various aspects such as prompt optimization, longer context handling, LLM alignment, acceleration of LLMs, LLM customization, and understanding in-context learning. It also includes tools like Promptist for automatic prompt optimization, Structured Prompting for efficient long-sequence prompts consumption, and X-Prompt for extensible prompts beyond natural language. Additionally, LLMA accelerators are developed to speed up LLM inference by referencing and copying text spans from documents. The project aims to advance technologies that facilitate prompting language models and enhance the performance of LLMs in various scenarios.

Awesome-Efficient-LLM
Awesome-Efficient-LLM is a curated list focusing on efficient large language models. It includes topics such as knowledge distillation, network pruning, quantization, inference acceleration, efficient MOE, efficient architecture of LLM, KV cache compression, text compression, low-rank decomposition, hardware/system, tuning, and survey. The repository provides a collection of papers and projects related to improving the efficiency of large language models through various techniques like sparsity, quantization, and compression.
TensorRT-Model-Optimizer
The NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer is a library designed to quantize and compress deep learning models for optimized inference on GPUs. It offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques including quantization and sparsity to reduce inference costs for generative AI models. Users can easily stack different optimization techniques to produce quantized checkpoints from torch or ONNX models. The quantized checkpoints are ready for deployment in inference frameworks like TensorRT-LLM or TensorRT, with planned integrations for NVIDIA NeMo and Megatron-LM. The tool also supports 8-bit quantization with Stable Diffusion for enterprise users on NVIDIA NIM. Model Optimizer is available for free on NVIDIA PyPI, and this repository serves as a platform for sharing examples, GPU-optimized recipes, and collecting community feedback.
lightning-bolts
Bolts package provides a variety of components to extend PyTorch Lightning, such as callbacks & datasets, for applied research and production. Users can accelerate Lightning training with the Torch ORT Callback to optimize ONNX graph for faster training & inference. Additionally, users can introduce sparsity with the SparseMLCallback to accelerate inference by leveraging the DeepSparse engine. Specific research implementations are encouraged, with contributions that help train SSL models and integrate with Lightning Flash for state-of-the-art models in applied research.
ms-swift
ms-swift is an official framework provided by the ModelScope community for fine-tuning and deploying large language models and multi-modal large models. It supports training, inference, evaluation, quantization, and deployment of over 400 large models and 100+ multi-modal large models. The framework includes various training technologies and accelerates inference, evaluation, and deployment modules. It offers a Gradio-based Web-UI interface and best practices for easy application of large models. ms-swift supports a wide range of model types, dataset types, hardware support, lightweight training methods, distributed training techniques, quantization training, RLHF training, multi-modal training, interface training, plugin and extension support, inference acceleration engines, model evaluation, and model quantization.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.