LLMs-from-scratch
Implement a ChatGPT-like LLM in PyTorch from scratch, step by step
Stars: 72995
This repository contains the code for coding, pretraining, and finetuning a GPT-like LLM and is the official code repository for the book Build a Large Language Model (From Scratch). In _Build a Large Language Model (From Scratch)_, you'll discover how LLMs work from the inside out. In this book, I'll guide you step by step through creating your own LLM, explaining each stage with clear text, diagrams, and examples. The method described in this book for training and developing your own small-but-functional model for educational purposes mirrors the approach used in creating large-scale foundational models such as those behind ChatGPT.
README:
This repository contains the code for developing, pretraining, and finetuning a GPT-like LLM and is the official code repository for the book Build a Large Language Model (From Scratch).
In Build a Large Language Model (From Scratch), you'll learn and understand how large language models (LLMs) work from the inside out by coding them from the ground up, step by step. In this book, I'll guide you through creating your own LLM, explaining each stage with clear text, diagrams, and examples.
The method described in this book for training and developing your own small-but-functional model for educational purposes mirrors the approach used in creating large-scale foundational models such as those behind ChatGPT. In addition, this book includes code for loading the weights of larger pretrained models for finetuning.
- Link to the official source code repository
- Link to the book at Manning (the publisher's website)
- Link to the book page on Amazon.com
- ISBN 9781633437166
To download a copy of this repository, click on the Download ZIP button or execute the following command in your terminal:
git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch.git(If you downloaded the code bundle from the Manning website, please consider visiting the official code repository on GitHub at https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch for the latest updates.)
Please note that this README.md file is a Markdown (.md) file. If you have downloaded this code bundle from the Manning website and are viewing it on your local computer, I recommend using a Markdown editor or previewer for proper viewing. If you haven't installed a Markdown editor yet, Ghostwriter is a good free option.
You can alternatively view this and other files on GitHub at https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch in your browser, which renders Markdown automatically.
Tip: If you're seeking guidance on installing Python and Python packages and setting up your code environment, I suggest reading the README.md file located in the setup directory.
| Chapter Title | Main Code (for Quick Access) | All Code + Supplementary |
|---|---|---|
| Setup recommendations | - | - |
| Ch 1: Understanding Large Language Models | No code | - |
| Ch 2: Working with Text Data | - ch02.ipynb - dataloader.ipynb (summary) - exercise-solutions.ipynb |
./ch02 |
| Ch 3: Coding Attention Mechanisms | - ch03.ipynb - multihead-attention.ipynb (summary) - exercise-solutions.ipynb |
./ch03 |
| Ch 4: Implementing a GPT Model from Scratch | - ch04.ipynb - gpt.py (summary) - exercise-solutions.ipynb |
./ch04 |
| Ch 5: Pretraining on Unlabeled Data | - ch05.ipynb - gpt_train.py (summary) - gpt_generate.py (summary) - exercise-solutions.ipynb |
./ch05 |
| Ch 6: Finetuning for Text Classification | - ch06.ipynb - gpt_class_finetune.py - exercise-solutions.ipynb |
./ch06 |
| Ch 7: Finetuning to Follow Instructions | - ch07.ipynb - gpt_instruction_finetuning.py (summary) - ollama_evaluate.py (summary) - exercise-solutions.ipynb |
./ch07 |
| Appendix A: Introduction to PyTorch | - code-part1.ipynb - code-part2.ipynb - DDP-script.py - exercise-solutions.ipynb |
./appendix-A |
| Appendix B: References and Further Reading | No code | - |
| Appendix C: Exercise Solutions | No code | - |
| Appendix D: Adding Bells and Whistles to the Training Loop | - appendix-D.ipynb | ./appendix-D |
| Appendix E: Parameter-efficient Finetuning with LoRA | - appendix-E.ipynb | ./appendix-E |
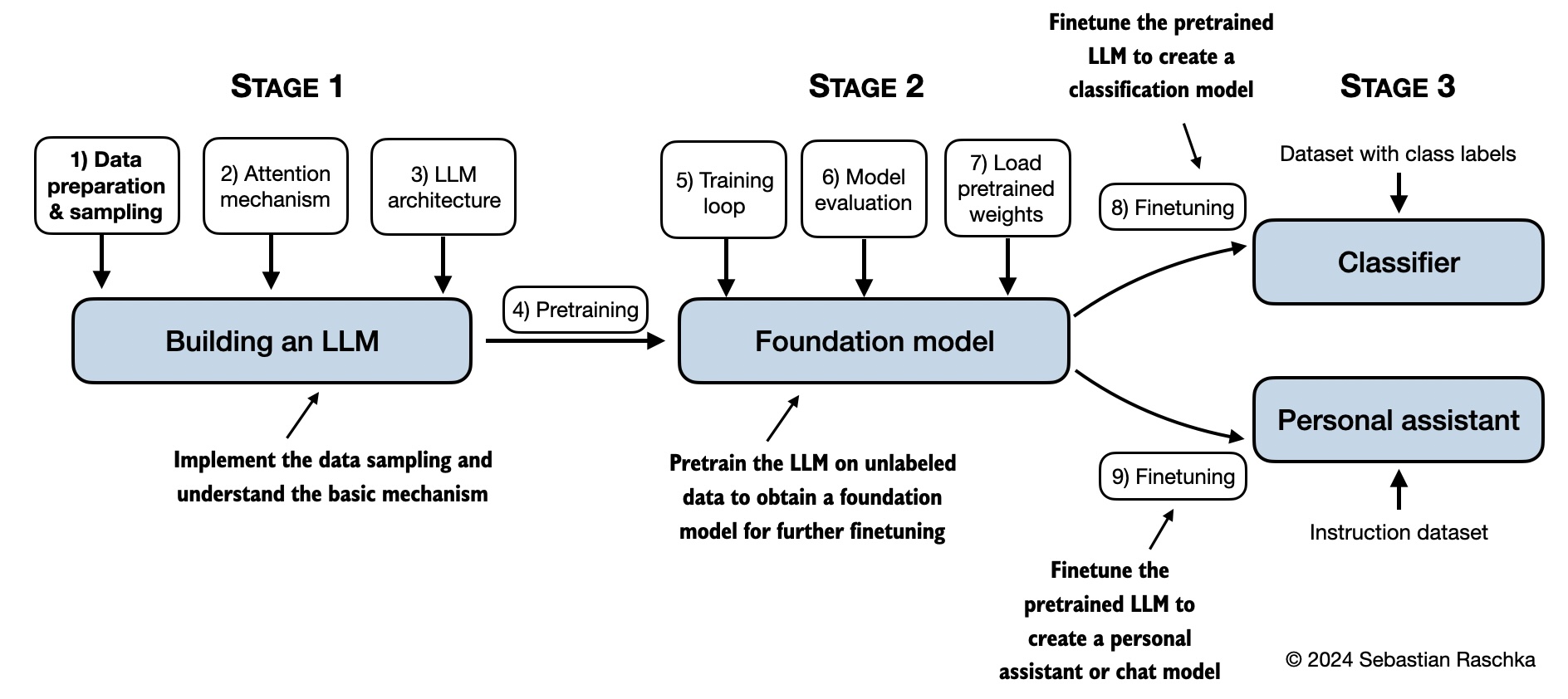
The mental model below summarizes the contents covered in this book.
The most important prerequisite is a strong foundation in Python programming. With this knowledge, you will be well prepared to explore the fascinating world of LLMs and understand the concepts and code examples presented in this book.
If you have some experience with deep neural networks, you may find certain concepts more familiar, as LLMs are built upon these architectures.
This book uses PyTorch to implement the code from scratch without using any external LLM libraries. While proficiency in PyTorch is not a prerequisite, familiarity with PyTorch basics is certainly useful. If you are new to PyTorch, Appendix A provides a concise introduction to PyTorch. Alternatively, you may find my book, PyTorch in One Hour: From Tensors to Training Neural Networks on Multiple GPUs, helpful for learning about the essentials.
The code in the main chapters of this book is designed to run on conventional laptops within a reasonable timeframe and does not require specialized hardware. This approach ensures that a wide audience can engage with the material. Additionally, the code automatically utilizes GPUs if they are available. (Please see the setup doc for additional recommendations.)
A 17-hour and 15-minute companion video course where I code through each chapter of the book. The course is organized into chapters and sections that mirror the book's structure so that it can be used as a standalone alternative to the book or complementary code-along resource.
Build A Reasoning Model (From Scratch), while a standalone book, can be considered as a sequel to Build A Large Language Model (From Scratch).
It starts with a pretrained model and implements different reasoning approaches, including inference-time scaling, reinforcement learning, and distillation, to improve the model's reasoning capabilities.
Similar to Build A Large Language Model (From Scratch), Build A Reasoning Model (From Scratch) takes a hands-on approach implementing these methods from scratch.
- Amazon link (TBD)
- Manning link
- GitHub repository
Each chapter of the book includes several exercises. The solutions are summarized in Appendix C, and the corresponding code notebooks are available in the main chapter folders of this repository (for example, ./ch02/01_main-chapter-code/exercise-solutions.ipynb.
In addition to the code exercises, you can download a free 170-page PDF titled Test Yourself On Build a Large Language Model (From Scratch) from the Manning website. It contains approximately 30 quiz questions and solutions per chapter to help you test your understanding.
Several folders contain optional materials as a bonus for interested readers:
- Setup
- Chapter 2: Working with text data
- Chapter 3: Coding attention mechanisms
- Chapter 4: Implementing a GPT model from scratch
-
Chapter 5: Pretraining on unlabeled data:
- Alternative Weight Loading Methods
- Pretraining GPT on the Project Gutenberg Dataset
- Adding Bells and Whistles to the Training Loop
- Optimizing Hyperparameters for Pretraining
- Building a User Interface to Interact With the Pretrained LLM
- Converting GPT to Llama
- Llama 3.2 From Scratch
- Qwen3 Dense and Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) From Scratch
- Gemma 3 From Scratch
- Memory-efficient Model Weight Loading
- Extending the Tiktoken BPE Tokenizer with New Tokens
- PyTorch Performance Tips for Faster LLM Training
- Chapter 6: Finetuning for classification
-
Chapter 7: Finetuning to follow instructions
- Dataset Utilities for Finding Near Duplicates and Creating Passive Voice Entries
- Evaluating Instruction Responses Using the OpenAI API and Ollama
- Generating a Dataset for Instruction Finetuning
- Improving a Dataset for Instruction Finetuning
- Generating a Preference Dataset with Llama 3.1 70B and Ollama
- Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) for LLM Alignment
- Building a User Interface to Interact With the Instruction Finetuned GPT Model
I welcome all sorts of feedback, best shared via the Manning Forum or GitHub Discussions. Likewise, if you have any questions or just want to bounce ideas off others, please don't hesitate to post these in the forum as well.
Please note that since this repository contains the code corresponding to a print book, I currently cannot accept contributions that would extend the contents of the main chapter code, as it would introduce deviations from the physical book. Keeping it consistent helps ensure a smooth experience for everyone.
If you find this book or code useful for your research, please consider citing it.
Chicago-style citation:
Raschka, Sebastian. Build A Large Language Model (From Scratch). Manning, 2024. ISBN: 978-1633437166.
BibTeX entry:
@book{build-llms-from-scratch-book,
author = {Sebastian Raschka},
title = {Build A Large Language Model (From Scratch)},
publisher = {Manning},
year = {2024},
isbn = {978-1633437166},
url = {https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch},
github = {https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLMs-from-scratch
Similar Open Source Tools

LLMs-from-scratch
This repository contains the code for coding, pretraining, and finetuning a GPT-like LLM and is the official code repository for the book Build a Large Language Model (From Scratch). In _Build a Large Language Model (From Scratch)_, you'll discover how LLMs work from the inside out. In this book, I'll guide you step by step through creating your own LLM, explaining each stage with clear text, diagrams, and examples. The method described in this book for training and developing your own small-but-functional model for educational purposes mirrors the approach used in creating large-scale foundational models such as those behind ChatGPT.
reasoning-from-scratch
This repository contains the code for developing a large language model (LLM) reasoning model. The book 'Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)' provides a hands-on approach to understanding and implementing reasoning capabilities in LLMs. It guides users through creating a small but functional reasoning model, mirroring approaches used in large-scale models like DeepSeek R1 and GPT-5 Thinking. The code includes methods for loading weights of pretrained models.
NineRec
NineRec is a benchmark dataset suite for evaluating transferable recommendation models. It provides datasets for pre-training and transfer learning in recommender systems, focusing on multimodal and foundation model tasks. The dataset includes user-item interactions, item texts in multiple languages, item URLs, and raw images. Researchers can use NineRec to develop more effective and efficient methods for pre-training recommendation models beyond end-to-end training. The dataset is accompanied by code for dataset preparation, training, and testing in PyTorch environment.
babilong
BABILong is a generative benchmark designed to evaluate the performance of NLP models in processing long documents with distributed facts. It consists of 20 tasks that simulate interactions between characters and objects in various locations, requiring models to distinguish important information from irrelevant details. The tasks vary in complexity and reasoning aspects, with test samples potentially containing millions of tokens. The benchmark aims to challenge and assess the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in handling complex, long-context information.

magpie
This is the official repository for 'Alignment Data Synthesis from Scratch by Prompting Aligned LLMs with Nothing'. Magpie is a tool designed to synthesize high-quality instruction data at scale by extracting it directly from an aligned Large Language Models (LLMs). It aims to democratize AI by generating large-scale alignment data and enhancing the transparency of model alignment processes. Magpie has been tested on various model families and can be used to fine-tune models for improved performance on alignment benchmarks such as AlpacaEval, ArenaHard, and WildBench.
Controllable-RAG-Agent
This repository contains a sophisticated deterministic graph-based solution for answering complex questions using a controllable autonomous agent. The solution is designed to ensure that answers are solely based on the provided data, avoiding hallucinations. It involves various steps such as PDF loading, text preprocessing, summarization, database creation, encoding, and utilizing large language models. The algorithm follows a detailed workflow involving planning, retrieval, answering, replanning, content distillation, and performance evaluation. Heuristics and techniques implemented focus on content encoding, anonymizing questions, task breakdown, content distillation, chain of thought answering, verification, and model performance evaluation.
PocketFlow
Pocket Flow is a 100-line minimalist LLM framework designed for (Multi-)Agents, Task Decomposition, RAG, etc. It aims to be the framework used by LLMs, focusing on stripping away low-level implementation details and emphasizing high-level programming paradigms. Pocket Flow serves as a learning resource and provides a core abstraction of a nested directed graph for breaking down tasks into multiple steps.
hi-ml
The Microsoft Health Intelligence Machine Learning Toolbox is a repository that provides low-level and high-level building blocks for Machine Learning / AI researchers and practitioners. It simplifies and streamlines work on deep learning models for healthcare and life sciences by offering tested components such as data loaders, pre-processing tools, deep learning models, and cloud integration utilities. The repository includes two Python packages, 'hi-ml-azure' for helper functions in AzureML, 'hi-ml' for ML components, and 'hi-ml-cpath' for models and workflows related to histopathology images.
MARS5-TTS
MARS5 is a novel English speech model (TTS) developed by CAMB.AI, featuring a two-stage AR-NAR pipeline with a unique NAR component. The model can generate speech for various scenarios like sports commentary and anime with just 5 seconds of audio and a text snippet. It allows steering prosody using punctuation and capitalization in the transcript. Speaker identity is specified using an audio reference file, enabling 'deep clone' for improved quality. The model can be used via torch.hub or HuggingFace, supporting both shallow and deep cloning for inference. Checkpoints are provided for AR and NAR models, with hardware requirements of 750M+450M params on GPU. Contributions to improve model stability, performance, and reference audio selection are welcome.
qlib
Qlib is an open-source, AI-oriented quantitative investment platform that supports diverse machine learning modeling paradigms, including supervised learning, market dynamics modeling, and reinforcement learning. It covers the entire chain of quantitative investment, from alpha seeking to order execution. The platform empowers researchers to explore ideas and implement productions using AI technologies in quantitative investment. Qlib collaboratively solves key challenges in quantitative investment by releasing state-of-the-art research works in various paradigms. It provides a full ML pipeline for data processing, model training, and back-testing, enabling users to perform tasks such as forecasting market patterns, adapting to market dynamics, and modeling continuous investment decisions.
gepa
GEPA (Genetic-Pareto) is a framework for optimizing arbitrary systems composed of text components like AI prompts, code snippets, or textual specs against any evaluation metric. It employs LLMs to reflect on system behavior, using feedback from execution and evaluation traces to drive targeted improvements. Through iterative mutation, reflection, and Pareto-aware candidate selection, GEPA evolves robust, high-performing variants with minimal evaluations, co-evolving multiple components in modular systems for domain-specific gains. The repository provides the official implementation of the GEPA algorithm as proposed in the paper titled 'GEPA: Reflective Prompt Evolution Can Outperform Reinforcement Learning'.
AI-Scientist
The AI Scientist is a comprehensive system for fully automatic scientific discovery, enabling Foundation Models to perform research independently. It aims to tackle the grand challenge of developing agents capable of conducting scientific research and discovering new knowledge. The tool generates papers on various topics using Large Language Models (LLMs) and provides a platform for exploring new research ideas. Users can create their own templates for specific areas of study and run experiments to generate papers. However, caution is advised as the codebase executes LLM-written code, which may pose risks such as the use of potentially dangerous packages and web access.
Woodpecker
Woodpecker is a tool designed to correct hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by introducing a training-free method that picks out and corrects inconsistencies between generated text and image content. It consists of five stages: key concept extraction, question formulation, visual knowledge validation, visual claim generation, and hallucination correction. Woodpecker can be easily integrated with different MLLMs and provides interpretable results by accessing intermediate outputs of the stages. The tool has shown significant improvements in accuracy over baseline models like MiniGPT-4 and mPLUG-Owl.
R1-Searcher
R1-searcher is a tool designed to incentivize the search capability in large reasoning models (LRMs) via reinforcement learning. It enables LRMs to invoke web search and obtain external information during the reasoning process by utilizing a two-stage outcome-supervision reinforcement learning approach. The tool does not require instruction fine-tuning for cold start and is compatible with existing Base LLMs or Chat LLMs. It includes training code, inference code, model checkpoints, and a detailed technical report.
SwiftSage
SwiftSage is a tool designed for conducting experiments in the field of machine learning and artificial intelligence. It provides a platform for researchers and developers to implement and test various algorithms and models. The tool is particularly useful for exploring new ideas and conducting experiments in a controlled environment. SwiftSage aims to streamline the process of developing and testing machine learning models, making it easier for users to iterate on their ideas and achieve better results. With its user-friendly interface and powerful features, SwiftSage is a valuable tool for anyone working in the field of AI and ML.
graphrag-local-ollama
GraphRAG Local Ollama is a repository that offers an adaptation of Microsoft's GraphRAG, customized to support local models downloaded using Ollama. It enables users to leverage local models with Ollama for large language models (LLMs) and embeddings, eliminating the need for costly OpenAPI models. The repository provides a simple setup process and allows users to perform question answering over private text corpora by building a graph-based text index and generating community summaries for closely-related entities. GraphRAG Local Ollama aims to improve the comprehensiveness and diversity of generated answers for global sensemaking questions over datasets.
For similar tasks
awesome-transformer-nlp
This repository contains a hand-curated list of great machine (deep) learning resources for Natural Language Processing (NLP) with a focus on Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), attention mechanism, Transformer architectures/networks, Chatbot, and transfer learning in NLP.

LLMs-from-scratch
This repository contains the code for coding, pretraining, and finetuning a GPT-like LLM and is the official code repository for the book Build a Large Language Model (From Scratch). In _Build a Large Language Model (From Scratch)_, you'll discover how LLMs work from the inside out. In this book, I'll guide you step by step through creating your own LLM, explaining each stage with clear text, diagrams, and examples. The method described in this book for training and developing your own small-but-functional model for educational purposes mirrors the approach used in creating large-scale foundational models such as those behind ChatGPT.
PaddleNLP
PaddleNLP is an easy-to-use and high-performance NLP library. It aggregates high-quality pre-trained models in the industry and provides out-of-the-box development experience, covering a model library for multiple NLP scenarios with industry practice examples to meet developers' flexible customization needs.
Tutorial
The Bookworm·Puyu large model training camp aims to promote the implementation of large models in more industries and provide developers with a more efficient platform for learning the development and application of large models. Within two weeks, you will learn the entire process of fine-tuning, deploying, and evaluating large models.
llms-from-scratch-cn
This repository provides a detailed tutorial on how to build your own large language model (LLM) from scratch. It includes all the code necessary to create a GPT-like LLM, covering the encoding, pre-training, and fine-tuning processes. The tutorial is written in a clear and concise style, with plenty of examples and illustrations to help you understand the concepts involved. It is suitable for developers and researchers with some programming experience who are interested in learning more about LLMs and how to build them.
LLMBook-zh.github.io
This book aims to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of large language model technology, including its basic principles, key technologies, and application prospects. Through in-depth research and practice, we can continuously explore and improve large language model technology, and contribute to the development of the field of artificial intelligence.
LLM-Blender
LLM-Blender is a framework for ensembling large language models (LLMs) to achieve superior performance. It consists of two modules: PairRanker and GenFuser. PairRanker uses pairwise comparisons to distinguish between candidate outputs, while GenFuser merges the top-ranked candidates to create an improved output. LLM-Blender has been shown to significantly surpass the best LLMs and baseline ensembling methods across various metrics on the MixInstruct benchmark dataset.
SeaLLMs
SeaLLMs are a family of language models optimized for Southeast Asian (SEA) languages. They were pre-trained from Llama-2, on a tailored publicly-available dataset, which comprises texts in Vietnamese 🇻🇳, Indonesian 🇮🇩, Thai 🇹🇭, Malay 🇲🇾, Khmer🇰🇭, Lao🇱🇦, Tagalog🇵🇭 and Burmese🇲🇲. The SeaLLM-chat underwent supervised finetuning (SFT) and specialized self-preferencing DPO using a mix of public instruction data and a small number of queries used by SEA language native speakers in natural settings, which **adapt to the local cultural norms, customs, styles and laws in these areas**. SeaLLM-13b models exhibit superior performance across a wide spectrum of linguistic tasks and assistant-style instruction-following capabilities relative to comparable open-source models. Moreover, they outperform **ChatGPT-3.5** in non-Latin languages, such as Thai, Khmer, Lao, and Burmese.
For similar jobs
LLM-FineTuning-Large-Language-Models
This repository contains projects and notes on common practical techniques for fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs). It includes fine-tuning LLM notebooks, Colab links, LLM techniques and utils, and other smaller language models. The repository also provides links to YouTube videos explaining the concepts and techniques discussed in the notebooks.
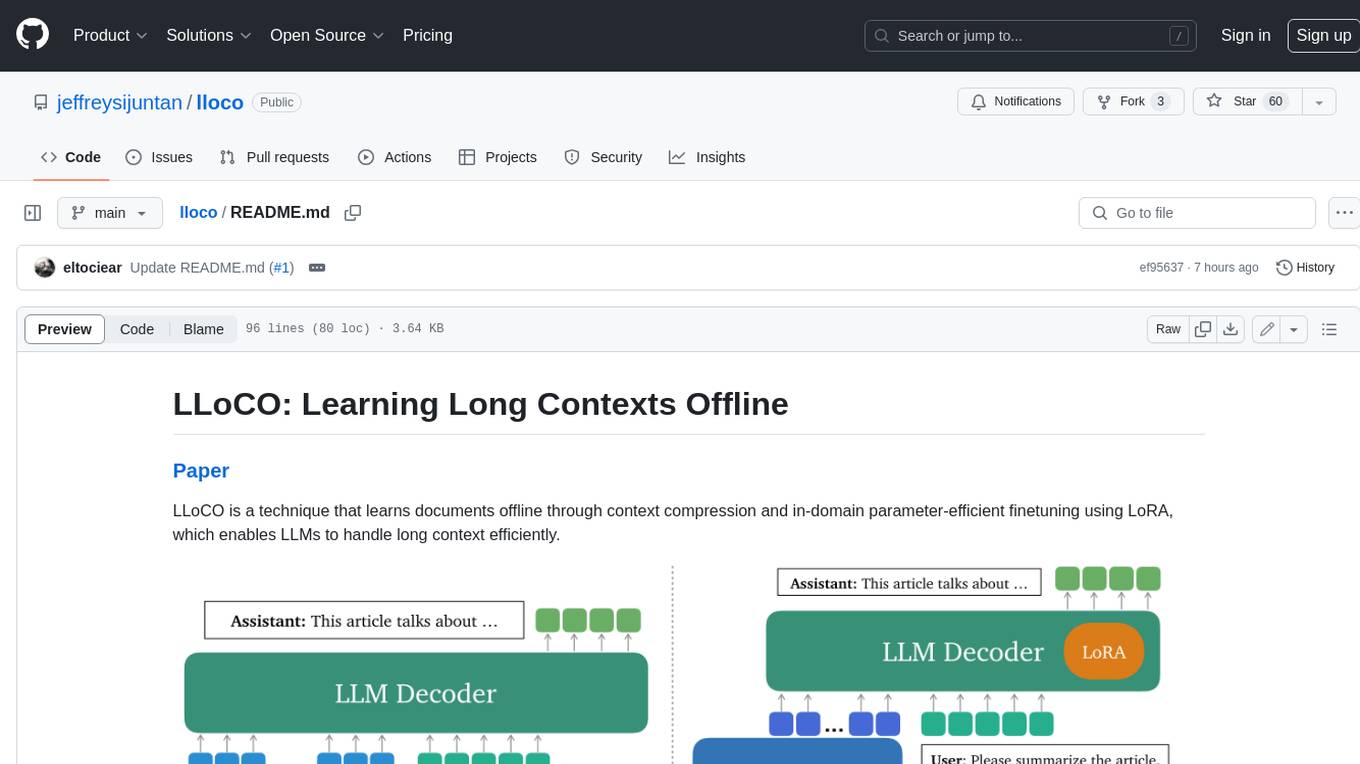
lloco
LLoCO is a technique that learns documents offline through context compression and in-domain parameter-efficient finetuning using LoRA, which enables LLMs to handle long context efficiently.
camel
CAMEL is an open-source library designed for the study of autonomous and communicative agents. We believe that studying these agents on a large scale offers valuable insights into their behaviors, capabilities, and potential risks. To facilitate research in this field, we implement and support various types of agents, tasks, prompts, models, and simulated environments.
llm-baselines
LLM-baselines is a modular codebase to experiment with transformers, inspired from NanoGPT. It provides a quick and easy way to train and evaluate transformer models on a variety of datasets. The codebase is well-documented and easy to use, making it a great resource for researchers and practitioners alike.
python-tutorial-notebooks
This repository contains Jupyter-based tutorials for NLP, ML, AI in Python for classes in Computational Linguistics, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Machine Learning (ML), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) at Indiana University.
EvalAI
EvalAI is an open-source platform for evaluating and comparing machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms at scale. It provides a central leaderboard and submission interface, making it easier for researchers to reproduce results mentioned in papers and perform reliable & accurate quantitative analysis. EvalAI also offers features such as custom evaluation protocols and phases, remote evaluation, evaluation inside environments, CLI support, portability, and faster evaluation.
Weekly-Top-LLM-Papers
This repository provides a curated list of weekly published Large Language Model (LLM) papers. It includes top important LLM papers for each week, organized by month and year. The papers are categorized into different time periods, making it easy to find the most recent and relevant research in the field of LLM.
self-llm
This project is a Chinese tutorial for domestic beginners based on the AutoDL platform, providing full-process guidance for various open-source large models, including environment configuration, local deployment, and efficient fine-tuning. It simplifies the deployment, use, and application process of open-source large models, enabling more ordinary students and researchers to better use open-source large models and helping open and free large models integrate into the lives of ordinary learners faster.