ludwig
Low-code framework for building custom LLMs, neural networks, and other AI models
Stars: 11034
Ludwig is a declarative deep learning framework designed for scale and efficiency. It is a low-code framework that allows users to build custom AI models like LLMs and other deep neural networks with ease. Ludwig offers features such as optimized scale and efficiency, expert level control, modularity, and extensibility. It is engineered for production with prebuilt Docker containers, support for running with Ray on Kubernetes, and the ability to export models to Torchscript and Triton. Ludwig is hosted by the Linux Foundation AI & Data.
README:
[!IMPORTANT] Our community has moved to Discord -- please join us there!
Ludwig is a low-code framework for building custom AI models like LLMs and other deep neural networks.
Key features:
- 🛠 Build custom models with ease: a declarative YAML configuration file is all you need to train a state-of-the-art LLM on your data. Support for multi-task and multi-modality learning. Comprehensive config validation detects invalid parameter combinations and prevents runtime failures.
- ⚡ Optimized for scale and efficiency: automatic batch size selection, distributed training (DDP, DeepSpeed), parameter efficient fine-tuning (PEFT), 4-bit quantization (QLoRA), paged and 8-bit optimizers, and larger-than-memory datasets.
- 📐 Expert level control: retain full control of your models down to the activation functions. Support for hyperparameter optimization, explainability, and rich metric visualizations.
- 🧱 Modular and extensible: experiment with different model architectures, tasks, features, and modalities with just a few parameter changes in the config. Think building blocks for deep learning.
- 🚢 Engineered for production: prebuilt Docker containers, native support for running with Ray on Kubernetes, export models to Torchscript and Triton, upload to HuggingFace with one command.
Ludwig is hosted by the Linux Foundation AI & Data.
Install from PyPi. Be aware that Ludwig requires Python 3.8+.
pip install ludwigOr install with all optional dependencies:
pip install ludwig[full]Please see contributing for more detailed installation instructions.
Want to take a quick peak at some of the Ludwig 0.8 features? Check out this Colab Notebook 🚀
Looking to fine-tune Llama-2 or Mistral? Check out these notebooks:
For a full tutorial, check out the official getting started guide, or take a look at end-to-end Examples.
Let's fine-tune a pretrained LLaMA-2-7b large language model to follow instructions like a chatbot ("instruction tuning").
- HuggingFace API Token
- Access approval to Llama2-7b-hf
- GPU with at least 12 GiB of VRAM (in our tests, we used an Nvidia T4)
We'll use the Stanford Alpaca dataset, which will be formatted as a table-like file that looks like this:
| instruction | input | output |
|---|---|---|
| Give three tips for staying healthy. | 1.Eat a balanced diet and make sure to include... | |
| Arrange the items given below in the order to ... | cake, me, eating | I eating cake. |
| Write an introductory paragraph about a famous... | Michelle Obama | Michelle Obama is an inspirational woman who r... |
| ... | ... | ... |
Create a YAML config file named model.yaml with the following:
model_type: llm
base_model: meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf
quantization:
bits: 4
adapter:
type: lora
prompt:
template: |
Below is an instruction that describes a task, paired with an input that may provide further context.
Write a response that appropriately completes the request.
### Instruction:
{instruction}
### Input:
{input}
### Response:
input_features:
- name: prompt
type: text
output_features:
- name: output
type: text
trainer:
type: finetune
learning_rate: 0.0001
batch_size: 1
gradient_accumulation_steps: 16
epochs: 3
learning_rate_scheduler:
decay: cosine
warmup_fraction: 0.01
preprocessing:
sample_ratio: 0.1
backend:
type: localAnd now let's train the model:
export HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN = "<api_token>"
ludwig train --config model.yaml --dataset "ludwig://alpaca"Let's build a neural network that predicts whether a given movie critic's review on Rotten Tomatoes was positive or negative.
Our dataset will be a CSV file that looks like this:
| movie_title | content_rating | genres | runtime | top_critic | review_content | recommended |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deliver Us from Evil | R | Action & Adventure, Horror | 117.0 | TRUE | Director Scott Derrickson and his co-writer, Paul Harris Boardman, deliver a routine procedural with unremarkable frights. | 0 |
| Barbara | PG-13 | Art House & International, Drama | 105.0 | FALSE | Somehow, in this stirring narrative, Barbara manages to keep hold of her principles, and her humanity and courage, and battles to save a dissident teenage girl whose life the Communists are trying to destroy. | 1 |
| Horrible Bosses | R | Comedy | 98.0 | FALSE | These bosses cannot justify either murder or lasting comic memories, fatally compromising a farce that could have been great but ends up merely mediocre. | 0 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Download a sample of the dataset from here.
wget https://ludwig.ai/latest/data/rotten_tomatoes.csvNext create a YAML config file named model.yaml with the following:
input_features:
- name: genres
type: set
preprocessing:
tokenizer: comma
- name: content_rating
type: category
- name: top_critic
type: binary
- name: runtime
type: number
- name: review_content
type: text
encoder:
type: embed
output_features:
- name: recommended
type: binaryThat's it! Now let's train the model:
ludwig train --config model.yaml --dataset rotten_tomatoes.csvHappy modeling
Try applying Ludwig to your data. Reach out on Discord if you have any questions.
-
Minimal machine learning boilerplate
Ludwig takes care of the engineering complexity of machine learning out of the box, enabling research scientists to focus on building models at the highest level of abstraction. Data preprocessing, hyperparameter optimization, device management, and distributed training for
torch.nn.Modulemodels come completely free. -
Easily build your benchmarks
Creating a state-of-the-art baseline and comparing it with a new model is a simple config change.
-
Easily apply new architectures to multiple problems and datasets
Apply new models across the extensive set of tasks and datasets that Ludwig supports. Ludwig includes a full benchmarking toolkit accessible to any user, for running experiments with multiple models across multiple datasets with just a simple configuration.
-
Highly configurable data preprocessing, modeling, and metrics
Any and all aspects of the model architecture, training loop, hyperparameter search, and backend infrastructure can be modified as additional fields in the declarative configuration to customize the pipeline to meet your requirements. For details on what can be configured, check out Ludwig Configuration docs.
-
Multi-modal, multi-task learning out-of-the-box
Mix and match tabular data, text, images, and even audio into complex model configurations without writing code.
-
Rich model exporting and tracking
Automatically track all trials and metrics with tools like Tensorboard, Comet ML, Weights & Biases, MLFlow, and Aim Stack.
-
Automatically scale training to multi-GPU, multi-node clusters
Go from training on your local machine to the cloud without code changes.
-
Low-code interface for state-of-the-art models, including pre-trained Huggingface Transformers
Ludwig also natively integrates with pre-trained models, such as the ones available in Huggingface Transformers. Users can choose from a vast collection of state-of-the-art pre-trained PyTorch models to use without needing to write any code at all. For example, training a BERT-based sentiment analysis model with Ludwig is as simple as:
ludwig train --dataset sst5 --config_str "{input_features: [{name: sentence, type: text, encoder: bert}], output_features: [{name: label, type: category}]}" -
Low-code interface for AutoML
Ludwig AutoML allows users to obtain trained models by providing just a dataset, the target column, and a time budget.
auto_train_results = ludwig.automl.auto_train(dataset=my_dataset_df, target=target_column_name, time_limit_s=7200)
-
Easy productionisation
Ludwig makes it easy to serve deep learning models, including on GPUs. Launch a REST API for your trained Ludwig model.
ludwig serve --model_path=/path/to/model
Ludwig supports exporting models to efficient Torchscript bundles.
ludwig export_torchscript -–model_path=/path/to/model
- Named Entity Recognition Tagging
- Natural Language Understanding
- Machine Translation
- Chit-Chat Dialogue Modeling through seq2seq
- Sentiment Analysis
- One-shot Learning with Siamese Networks
- Visual Question Answering
- Spoken Digit Speech Recognition
- Speaker Verification
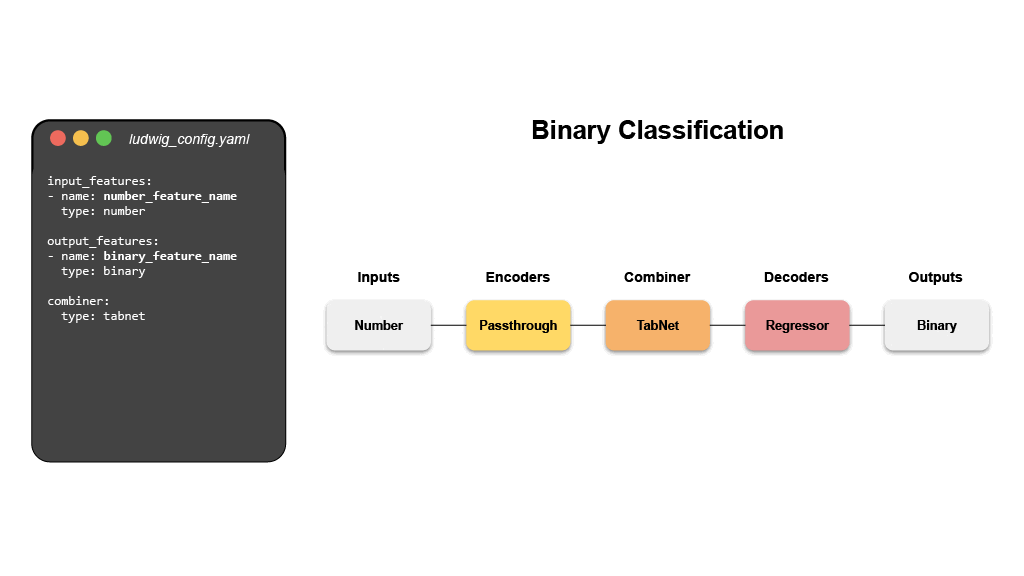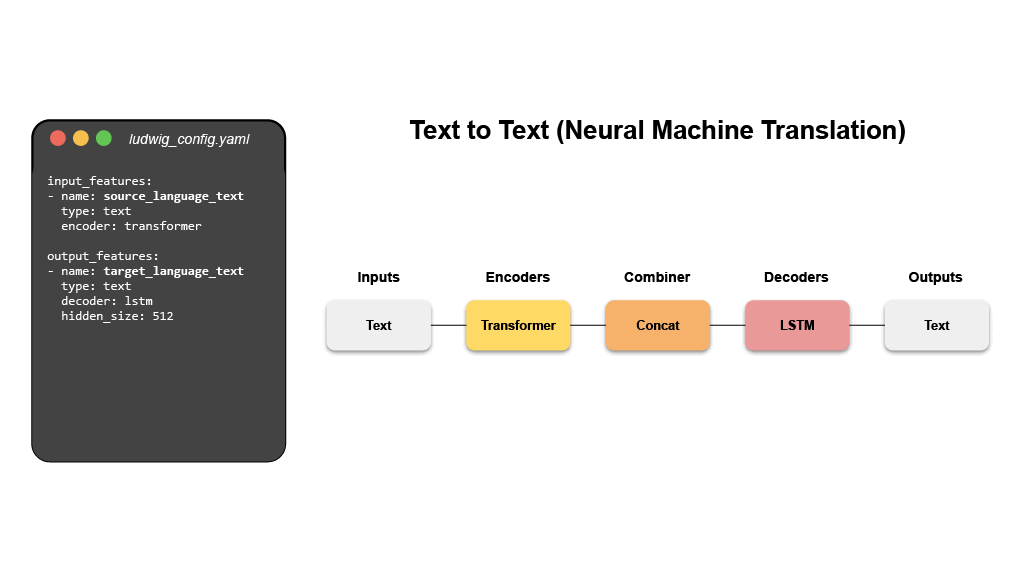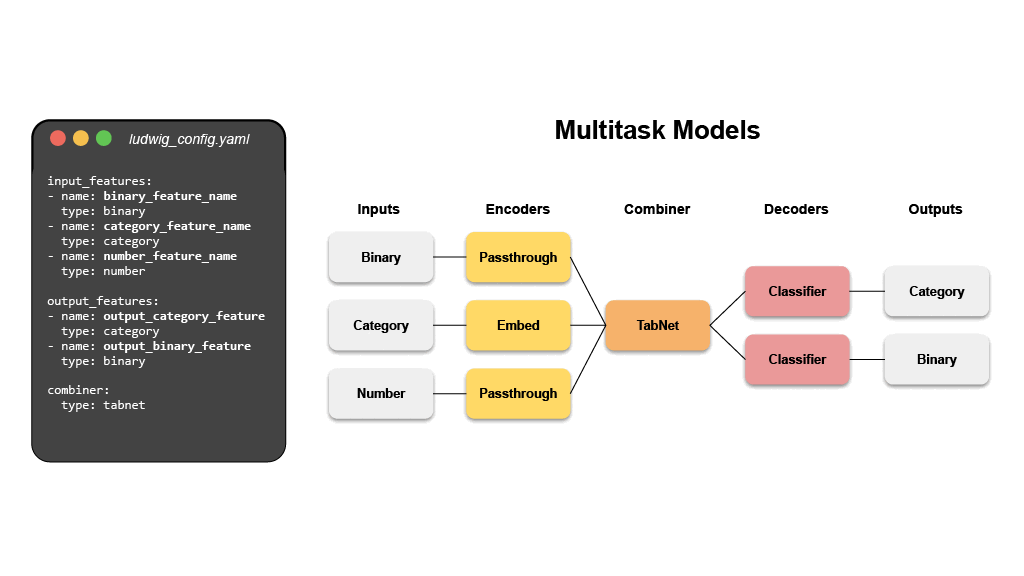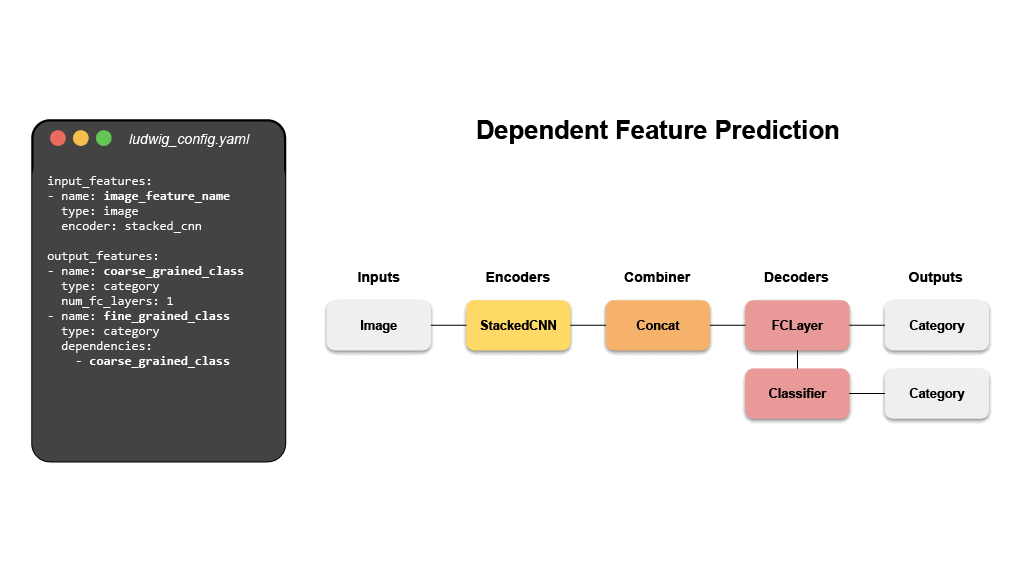
- Binary Classification (Titanic)
- Timeseries forecasting
- Timeseries forecasting (Weather)
- Movie rating prediction
- Multi-label classification
- Multi-Task Learning
- Simple Regression: Fuel Efficiency Prediction
- Fraud Detection
Read our publications on Ludwig, declarative ML, and Ludwig’s SoTA benchmarks.
Learn more about how Ludwig works, how to get started, and work through more examples.
If you are interested in contributing, have questions, comments, or thoughts to share, or if you just want to be in the know, please consider joining our Community Discord and follow us on X!
Ludwig is an actively managed open-source project that relies on contributions from folks just like you. Consider joining the active group of Ludwig contributors to make Ludwig an even more accessible and feature rich framework for everyone to use!
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ludwig
Similar Open Source Tools

ludwig
Ludwig is a declarative deep learning framework designed for scale and efficiency. It is a low-code framework that allows users to build custom AI models like LLMs and other deep neural networks with ease. Ludwig offers features such as optimized scale and efficiency, expert level control, modularity, and extensibility. It is engineered for production with prebuilt Docker containers, support for running with Ray on Kubernetes, and the ability to export models to Torchscript and Triton. Ludwig is hosted by the Linux Foundation AI & Data.
model2vec
Model2Vec is a technique to turn any sentence transformer into a really small static model, reducing model size by 15x and making the models up to 500x faster, with a small drop in performance. It outperforms other static embedding models like GLoVe and BPEmb, is lightweight with only `numpy` as a major dependency, offers fast inference, dataset-free distillation, and is integrated into Sentence Transformers, txtai, and Chonkie. Model2Vec creates powerful models by passing a vocabulary through a sentence transformer model, reducing dimensionality using PCA, and weighting embeddings using zipf weighting. Users can distill their own models or use pre-trained models from the HuggingFace hub. Evaluation can be done using the provided evaluation package. Model2Vec is licensed under MIT.
basiclingua-LLM-Based-NLP
BasicLingua is a Python library that provides functionalities for linguistic tasks such as tokenization, stemming, lemmatization, and many others. It is based on the Gemini Language Model, which has demonstrated promising results in dealing with text data. BasicLingua can be used as an API or through a web demo. It is available under the MIT license and can be used in various projects.
LLM-Pruner
LLM-Pruner is a tool for structural pruning of large language models, allowing task-agnostic compression while retaining multi-task solving ability. It supports automatic structural pruning of various LLMs with minimal human effort. The tool is efficient, requiring only 3 minutes for pruning and 3 hours for post-training. Supported LLMs include Llama-3.1, Llama-3, Llama-2, LLaMA, BLOOM, Vicuna, and Baichuan. Updates include support for new LLMs like GQA and BLOOM, as well as fine-tuning results achieving high accuracy. The tool provides step-by-step instructions for pruning, post-training, and evaluation, along with a Gradio interface for text generation. Limitations include issues with generating repetitive or nonsensical tokens in compressed models and manual operations for certain models.
mflux
MFLUX is a line-by-line port of the FLUX implementation in the Huggingface Diffusers library to Apple MLX. It aims to run powerful FLUX models from Black Forest Labs locally on Mac machines. The codebase is minimal and explicit, prioritizing readability over generality and performance. Models are implemented from scratch in MLX, with tokenizers from the Huggingface Transformers library. Dependencies include Numpy and Pillow for image post-processing. Installation can be done using `uv tool` or classic virtual environment setup. Command-line arguments allow for image generation with specified models, prompts, and optional parameters. Quantization options for speed and memory reduction are available. LoRA adapters can be loaded for fine-tuning image generation. Controlnet support provides more control over image generation with reference images. Current limitations include generating images one by one, lack of support for negative prompts, and some LoRA adapters not working.

CogVideo
CogVideo is an open-source repository that provides pretrained text-to-video models for generating videos based on input text. It includes models like CogVideoX-2B and CogVideo, offering powerful video generation capabilities. The repository offers tools for inference, fine-tuning, and model conversion, along with demos showcasing the model's capabilities through CLI, web UI, and online experiences. CogVideo aims to facilitate the creation of high-quality videos from textual descriptions, catering to a wide range of applications.
qlib
Qlib is an open-source, AI-oriented quantitative investment platform that supports diverse machine learning modeling paradigms, including supervised learning, market dynamics modeling, and reinforcement learning. It covers the entire chain of quantitative investment, from alpha seeking to order execution. The platform empowers researchers to explore ideas and implement productions using AI technologies in quantitative investment. Qlib collaboratively solves key challenges in quantitative investment by releasing state-of-the-art research works in various paradigms. It provides a full ML pipeline for data processing, model training, and back-testing, enabling users to perform tasks such as forecasting market patterns, adapting to market dynamics, and modeling continuous investment decisions.
TokenFormer
TokenFormer is a fully attention-based neural network architecture that leverages tokenized model parameters to enhance architectural flexibility. It aims to maximize the flexibility of neural networks by unifying token-token and token-parameter interactions through the attention mechanism. The architecture allows for incremental model scaling and has shown promising results in language modeling and visual modeling tasks. The codebase is clean, concise, easily readable, state-of-the-art, and relies on minimal dependencies.
PowerInfer
PowerInfer is a high-speed Large Language Model (LLM) inference engine designed for local deployment on consumer-grade hardware, leveraging activation locality to optimize efficiency. It features a locality-centric design, hybrid CPU/GPU utilization, easy integration with popular ReLU-sparse models, and support for various platforms. PowerInfer achieves high speed with lower resource demands and is flexible for easy deployment and compatibility with existing models like Falcon-40B, Llama2 family, ProSparse Llama2 family, and Bamboo-7B.
FuzzyAI
The FuzzyAI Fuzzer is a powerful tool for automated LLM fuzzing, designed to help developers and security researchers identify jailbreaks and mitigate potential security vulnerabilities in their LLM APIs. It supports various fuzzing techniques, provides input generation capabilities, can be easily integrated into existing workflows, and offers an extensible architecture for customization and extension. The tool includes attacks like ArtPrompt, Taxonomy-based paraphrasing, Many-shot jailbreaking, Genetic algorithm, Hallucinations, DAN (Do Anything Now), WordGame, Crescendo, ActorAttack, Back To The Past, Please, Thought Experiment, and Default. It supports models from providers like Anthropic, OpenAI, Gemini, Azure, Bedrock, AI21, and Ollama, with the ability to add support for newer models. The tool also supports various cloud APIs and datasets for testing and experimentation.
exllamav2
ExLlamaV2 is an inference library for running local LLMs on modern consumer GPUs. It is a faster, better, and more versatile codebase than its predecessor, ExLlamaV1, with support for a new quant format called EXL2. EXL2 is based on the same optimization method as GPTQ and supports 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8-bit quantization. It allows for mixing quantization levels within a model to achieve any average bitrate between 2 and 8 bits per weight. ExLlamaV2 can be installed from source, from a release with prebuilt extension, or from PyPI. It supports integration with TabbyAPI, ExUI, text-generation-webui, and lollms-webui. Key features of ExLlamaV2 include: - Faster and better kernels - Cleaner and more versatile codebase - Support for EXL2 quantization format - Integration with various web UIs and APIs - Community support on Discord
opencompass
OpenCompass is a one-stop platform for large model evaluation, aiming to provide a fair, open, and reproducible benchmark for large model evaluation. Its main features include: * Comprehensive support for models and datasets: Pre-support for 20+ HuggingFace and API models, a model evaluation scheme of 70+ datasets with about 400,000 questions, comprehensively evaluating the capabilities of the models in five dimensions. * Efficient distributed evaluation: One line command to implement task division and distributed evaluation, completing the full evaluation of billion-scale models in just a few hours. * Diversified evaluation paradigms: Support for zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought evaluations, combined with standard or dialogue-type prompt templates, to easily stimulate the maximum performance of various models. * Modular design with high extensibility: Want to add new models or datasets, customize an advanced task division strategy, or even support a new cluster management system? Everything about OpenCompass can be easily expanded! * Experiment management and reporting mechanism: Use config files to fully record each experiment, and support real-time reporting of results.
repromodel
ReproModel is an open-source toolbox designed to boost AI research efficiency by enabling researchers to reproduce, compare, train, and test AI models faster. It provides standardized models, dataloaders, and processing procedures, allowing researchers to focus on new datasets and model development. With a no-code solution, users can access benchmark and SOTA models and datasets, utilize training visualizations, extract code for publication, and leverage an LLM-powered automated methodology description writer. The toolbox helps researchers modularize development, compare pipeline performance reproducibly, and reduce time for model development, computation, and writing. Future versions aim to facilitate building upon state-of-the-art research by loading previously published study IDs with verified code, experiments, and results stored in the system.
exllamav2
ExLlamaV2 is an inference library designed for running local LLMs on modern consumer GPUs. The library supports paged attention via Flash Attention 2.5.7+, offers a new dynamic generator with features like dynamic batching, smart prompt caching, and K/V cache deduplication. It also provides an API for local or remote inference using TabbyAPI, with extended features like HF model downloading and support for HF Jinja2 chat templates. ExLlamaV2 aims to optimize performance and speed across different GPU models, with potential future optimizations and variations in speeds. The tool can be integrated with TabbyAPI for OpenAI-style web API compatibility and supports a standalone web UI called ExUI for single-user interaction with chat and notebook modes. ExLlamaV2 also offers support for text-generation-webui and lollms-webui through specific loaders and bindings.
AgentLab
AgentLab is an open, easy-to-use, and extensible framework designed to accelerate web agent research. It provides features for developing and evaluating agents on various benchmarks supported by BrowserGym. The framework allows for large-scale parallel agent experiments using ray, building blocks for creating agents over BrowserGym, and a unified LLM API for OpenRouter, OpenAI, Azure, or self-hosted using TGI. AgentLab also offers reproducibility features, a unified LeaderBoard, and supports multiple benchmarks like WebArena, WorkArena, WebLinx, VisualWebArena, AssistantBench, GAIA, Mind2Web-live, and MiniWoB.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.
For similar tasks

ludwig
Ludwig is a declarative deep learning framework designed for scale and efficiency. It is a low-code framework that allows users to build custom AI models like LLMs and other deep neural networks with ease. Ludwig offers features such as optimized scale and efficiency, expert level control, modularity, and extensibility. It is engineered for production with prebuilt Docker containers, support for running with Ray on Kubernetes, and the ability to export models to Torchscript and Triton. Ludwig is hosted by the Linux Foundation AI & Data.
fairseq
Fairseq is a sequence modeling toolkit that enables researchers and developers to train custom models for translation, summarization, language modeling, and other text generation tasks. It provides reference implementations of various sequence modeling papers covering CNN, LSTM networks, Transformer networks, LightConv, DynamicConv models, Non-autoregressive Transformers, Finetuning, and more. The toolkit supports multi-GPU training, fast generation on CPU and GPU, mixed precision training, extensibility, flexible configuration based on Hydra, and full parameter and optimizer state sharding. Pre-trained models are available for translation and language modeling with a torch.hub interface. Fairseq also offers pre-trained models and examples for tasks like XLS-R, cross-lingual retrieval, wav2vec 2.0, unsupervised quality estimation, and more.
MemoryLLM
MemoryLLM is a large language model designed for self-updating capabilities. It offers pretrained models with different memory capacities and features, such as chat models. The repository provides training code, evaluation scripts, and datasets for custom experiments. MemoryLLM aims to enhance knowledge retention and performance on various natural language processing tasks.
aibolit
Aibolit is a machine learning-based static analyzer for Java that helps identify patterns contributing to Cyclomatic Complexity in Java source code. It provides recommendations for fixing identified issues and allows users to suppress certain patterns. Aibolit can analyze individual Java files or entire folders of Java source code. Users can customize the output format and exclude specific files from analysis. The tool also supports training custom models for analyzing Java code. Aibolit is designed to help developers improve code quality and maintainability by identifying and addressing potential issues in Java code.
For similar jobs

ludwig
Ludwig is a declarative deep learning framework designed for scale and efficiency. It is a low-code framework that allows users to build custom AI models like LLMs and other deep neural networks with ease. Ludwig offers features such as optimized scale and efficiency, expert level control, modularity, and extensibility. It is engineered for production with prebuilt Docker containers, support for running with Ray on Kubernetes, and the ability to export models to Torchscript and Triton. Ludwig is hosted by the Linux Foundation AI & Data.
wenda
Wenda is a platform for large-scale language model invocation designed to efficiently generate content for specific environments, considering the limitations of personal and small business computing resources, as well as knowledge security and privacy issues. The platform integrates capabilities such as knowledge base integration, multiple large language models for offline deployment, auto scripts for additional functionality, and other practical capabilities like conversation history management and multi-user simultaneous usage.
LLMonFHIR
LLMonFHIR is an iOS application that utilizes large language models (LLMs) to interpret and provide context around patient data in the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) format. It connects to the OpenAI GPT API to analyze FHIR resources, supports multiple languages, and allows users to interact with their health data stored in the Apple Health app. The app aims to simplify complex health records, provide insights, and facilitate deeper understanding through a conversational interface. However, it is an experimental app for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. Users are advised to verify information provided by AI models and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.

Chinese-Mixtral-8x7B
Chinese-Mixtral-8x7B is an open-source project based on Mistral's Mixtral-8x7B model for incremental pre-training of Chinese vocabulary, aiming to advance research on MoE models in the Chinese natural language processing community. The expanded vocabulary significantly improves the model's encoding and decoding efficiency for Chinese, and the model is pre-trained incrementally on a large-scale open-source corpus, enabling it with powerful Chinese generation and comprehension capabilities. The project includes a large model with expanded Chinese vocabulary and incremental pre-training code.
AI-Horde-Worker
AI-Horde-Worker is a repository containing the original reference implementation for a worker that turns your graphics card(s) into a worker for the AI Horde. It allows users to generate or alchemize images for others. The repository provides instructions for setting up the worker on Windows and Linux, updating the worker code, running with multiple GPUs, and stopping the worker. Users can configure the worker using a WebUI to connect to the horde with their username and API key. The repository also includes information on model usage and running the Docker container with specified environment variables.
openshield
OpenShield is a firewall designed for AI models to protect against various attacks such as prompt injection, insecure output handling, training data poisoning, model denial of service, supply chain vulnerabilities, sensitive information disclosure, insecure plugin design, excessive agency granting, overreliance, and model theft. It provides rate limiting, content filtering, and keyword filtering for AI models. The tool acts as a transparent proxy between AI models and clients, allowing users to set custom rate limits for OpenAI endpoints and perform tokenizer calculations for OpenAI models. OpenShield also supports Python and LLM based rules, with upcoming features including rate limiting per user and model, prompts manager, content filtering, keyword filtering based on LLM/Vector models, OpenMeter integration, and VectorDB integration. The tool requires an OpenAI API key, Postgres, and Redis for operation.
VoAPI
VoAPI is a new high-value/high-performance AI model interface management and distribution system. It is a closed-source tool for personal learning use only, not for commercial purposes. Users must comply with upstream AI model service providers and legal regulations. The system offers a visually appealing interface, independent development documentation page support, service monitoring page configuration support, and third-party login support. It also optimizes interface elements, user registration time support, data operation button positioning, and more.
VoAPI
VoAPI is a new high-value/high-performance AI model interface management and distribution system. It is a closed-source tool for personal learning use only, not for commercial purposes. Users must comply with upstream AI model service providers and legal regulations. The system offers a visually appealing interface with features such as independent development documentation page support, service monitoring page configuration support, and third-party login support. Users can manage user registration time, optimize interface elements, and support features like online recharge, model pricing display, and sensitive word filtering. VoAPI also provides support for various AI models and platforms, with the ability to configure homepage templates, model information, and manufacturer information.