
LLMonFHIR
A Demonstration using LLMs to Explain Health Records
Stars: 148
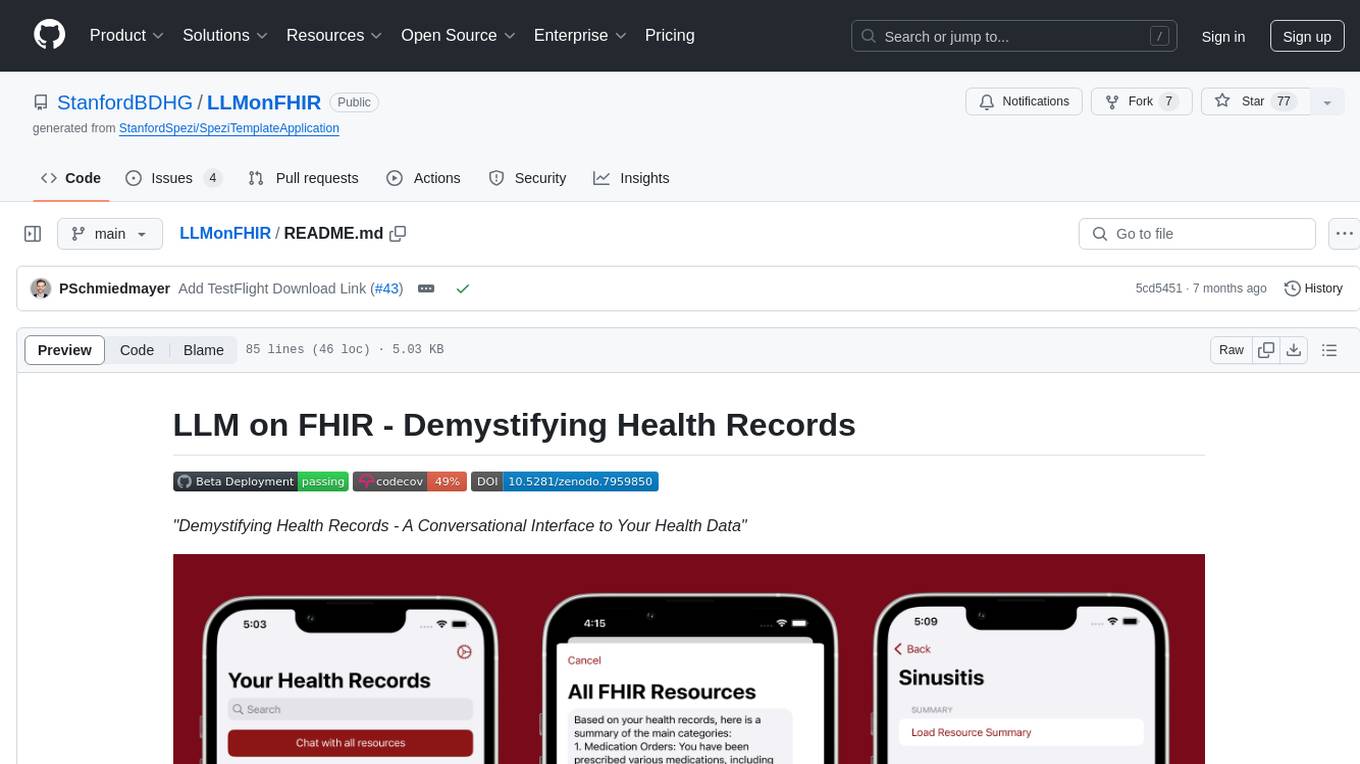
LLMonFHIR is an iOS application that utilizes large language models (LLMs) to interpret and provide context around patient data in the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) format. It connects to the OpenAI GPT API to analyze FHIR resources, supports multiple languages, and allows users to interact with their health data stored in the Apple Health app. The app aims to simplify complex health records, provide insights, and facilitate deeper understanding through a conversational interface. However, it is an experimental app for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. Users are advised to verify information provided by AI models and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
README:

|

|

|
| Select Multiple Studies | Study-specific Content | Task-driven Chat Flows |
This repository demonstrates how large language models can interpret and provide context around patient data in FHIR format. The LLM on FHIR application is designed as a research study to evaluate the effectiveness of conversational AI in helping users understand their health records.
The study leverages the Spezi framework and connects to the OpenAI GPT API to interpret FHIR resources. Participants can engage with their health data through a conversational interface, ask follow-up questions, and receive AI-generated summaries and explanations tailored to their system language.
[!NOTE] Interested in participating? Download LLM on FHIR on your iOS device via TestFlight!
LLM on FHIR is an experimental iOS app. It is designed for general informational purposes, providing users a platform to interact with health records stored in Apple Health using OpenAI models.
-
Not a Substitute for Professional Advice: LLM on FHIR is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
-
Limitations of AI Models: Remember, AI models can sometimes make mistakes or generate misleading information. Always cross-check and verify the information provided.
-
Use at Your Own Risk: Any use of LLM on FHIR is at the user's own risk. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for personalized advice regarding your health and well-being.
-
Demonstration Only: This app is intended for demonstration only and should not be used to process any personal health information.
Remember that your health data will be sent to OpenAI for processing. Please inspect and carefully read the OpenAI API data usage policies and settings accordingly.
LLM on FHIR requires access to the FHIR health records stored in the Apple Health app. You have the control to select the different types of health records you wish to inspect in LLM on FHIR.
In case no health records are available, please follow the instructions to connect and retrieve your health records from your provider. If your health records are visible in the Apple Health app, please ensure that LLM on FHIR has access to your health records in the Apple Health App. You can find these settings in the privacy section of your profile in Apple Health.
[!TIP] You can also use a set of Synthea-based patients loaded from SpeziFHIR (SpeziFHIRMockPatients) to test out the application without the need to connect it to HealthKit. You can select the synthetic patients in the account settings view of the application.
The Spezi Template Application uses a modularized structure using the Spezi modules enabled by the Swift Package Manager.
The application uses the FHIR standard to provide a shared repository for data exchanged between different modules. You can learn more about the Spezi standards-based software architecture in the Spezi documentation.
You can build and run the application using Xcode by opening up the LLMonFHIR.xcodeproj.
When running LLMonFHIR via Xcode, you can use the --mode CLI flag to control the behaviour of the app (configurable via the Run scheme):
-
--mode standaloneperforms a regular launch, where LLMonFHIR can be used with a custom OpenAI API key to use the chat mode; -
--mode study:<study-id>launches LLMonFHIR into its study mode, loads the study with the specified id from the UserStudyConfig.plist file, and automatically opens it; -
--mode studylaunches LLMonFHIR into its study mode, showing a "Scan QR Code" button to select and open a study.
LLMonFHIR contains a UserStudyConfig.plist file, which is loaded on launch, and used to configure the app and populate it with studies. The UserStudyConfig.plist file contains the following:
- Firebase configuration: used, if present, to connect the app to a Firebase environment, which is used to upload study reports
- app launch mode: used to control how the app should behave upon launch (e.g., whether the study-only mode should be enabled, and optionally to also directly launch a study)
- list of available studies (see the
Studytype within the iOS codebase for more details)
The UserStudyConfig.plist file bundled with the repo is missing some data (the OpenAI key, the Firebase credentials, and the study report encryption key).
You can use the export-config tool in the LLMonFHIRShared folder to generate a complete config file:
swift run LLMonFHIRCLI export-config \
-f ~/GoogleService-Info.plist \
-o edu.stanford.LLMonFHIR.study1:sk-123 \
-o edu.stanford.LLMonFHIR.study2:sk-456 \
-k edu.stanford.LLMonFHIR.study1:./public_key1.pem \
-k edu.stanford.LLMonFHIR.study2:./public_key2.pem \
../LLMonFHIR/Supporting\ Files/UserStudyConfig.plist
Some of the flags use a -x <studyId>:<value> format and can be specified multiple times, to specify each study's value.
You can also add one entry that uses * as the study id, in order to define a default value for all studies not explicitly listed.
(E.g., -o '*':$OPENAI_KEY would define the OpenAI key used by all studies that don't have a -o entry of their own.)
The report files generated form the usability study are optionally encrypted, using the public key stored in UserStudyConfig.plist.
You can generate a public/private key pair using the following commands:
# generate private key
openssl genpkey -algorithm X25519 -out private_key.pem
# extract public key
openssl pkey -in private_key.pem -pubout -out public_key.pem
Use the export-config tool showcased above to place your public key in the user study config file:.
In order to decrypt a report file created by the app, you can use the decrypt-study-report tool in the LLMonFHIRShared folder:
swift run LLMonFHIRCLI decrypt-study-report -k private_key.pem studyReport report.json
LLMonFHIR can run LLM inference for resource summarization and interpretation on nearby machines in your local network, called fog nodes, instead of only on-device or in the cloud. The app discovers a fog node via mDNS, connects to it, and streams model responses back while dispatching inference tasks. This setup provides low latency, strong performance, and improved privacy, since models run on your own hardware inside your own network.
For instructions on running a minimal Docker-based fog node on Linux or macOS, see FogNode/README.md.
The LLMonFHIRShared sub-package contains a tool that allows simulating user chat sessions.
During a simulated chat session, the LLM is provided the same context and data it would be during normal usage of the app, except that the inputs (both the patient's health records, as well as the questions being asked by the user) are pre-defined. This allows evaluating how different models (or even the same model, across multiple conversations) will handle various scenarios and situations.
For each simulated session, a report file is generated, with the same structure as the report files generated for regular usage sessions in the app.
Session simulation is controled via a JSON config file, which defines the parameters of each session, i.e.:
- the FHIR bundle containing a synthetic patient
- this can be either the name of a patient in one of the bundles embedded in the LLMonFHIRShared/Resources folder, or a filepath, which will be resolved relative to the location of the config JSON file
- the session's OpenAI model and temperature
- the session's API key
- the study, in whose context the session should take place
- the specific questions the simulated patient should ask the LLM.
The example config below performs 6 simulated runs of the edu.stanford.LLMonFHIR.gynStudy study, 3 each using GPT-4o and GPT-5.2, with each session providing the LLM the exact same data and asking the exact same questions.
[{
"numberOfRuns": 3,
"studyId": "edu.stanford.LLMonFHIR.gynStudy",
"bundleName": "Elena Kim",
"model": "gpt-4o",
"temperature": 1,
"openAIKey": "sk-proj-...",
"userQuestions": [
"Tell me about my recent diagnoses and how they affect my fertility.",
"How are my hormonal levels?",
"So long and thanls for all the fish!!"
]
}, {
"numberOfRuns": 3,
"studyId": "edu.stanford.LLMonFHIR.gynStudy",
"bundleName": "Elena Kim",
"model": "gpt-5.2",
"temperature": 1,
"openAIKey": "sk-proj-...",
"userQuestions": [
"Tell me about my recent diagnoses and how they affect my fertility.",
"How are my hormonal levels?",
"So long and thanls for all the fish!!"
]
}]
This project is based on Spezi framework and builds on top of the Stanford Spezi Template Application provided using the MIT license.
You can find a list of contributors in the CONTRIBUTORS.md file.
The LLM on FHIR project, Spezi Template Application, and the Spezi framework are licensed under the MIT license.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLMonFHIR
Similar Open Source Tools

LLMonFHIR
LLMonFHIR is an iOS application that utilizes large language models (LLMs) to interpret and provide context around patient data in the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) format. It connects to the OpenAI GPT API to analyze FHIR resources, supports multiple languages, and allows users to interact with their health data stored in the Apple Health app. The app aims to simplify complex health records, provide insights, and facilitate deeper understanding through a conversational interface. However, it is an experimental app for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. Users are advised to verify information provided by AI models and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.

eureka-ml-insights
The Eureka ML Insights Framework is a repository containing code designed to help researchers and practitioners run reproducible evaluations of generative models efficiently. Users can define custom pipelines for data processing, inference, and evaluation, as well as utilize pre-defined evaluation pipelines for key benchmarks. The framework provides a structured approach to conducting experiments and analyzing model performance across various tasks and modalities.
AIlice
AIlice is a fully autonomous, general-purpose AI agent that aims to create a standalone artificial intelligence assistant, similar to JARVIS, based on the open-source LLM. AIlice achieves this goal by building a "text computer" that uses a Large Language Model (LLM) as its core processor. Currently, AIlice demonstrates proficiency in a range of tasks, including thematic research, coding, system management, literature reviews, and complex hybrid tasks that go beyond these basic capabilities. AIlice has reached near-perfect performance in everyday tasks using GPT-4 and is making strides towards practical application with the latest open-source models. We will ultimately achieve self-evolution of AI agents. That is, AI agents will autonomously build their own feature expansions and new types of agents, unleashing LLM's knowledge and reasoning capabilities into the real world seamlessly.

rag-experiment-accelerator
The RAG Experiment Accelerator is a versatile tool that helps you conduct experiments and evaluations using Azure AI Search and RAG pattern. It offers a rich set of features, including experiment setup, integration with Azure AI Search, Azure Machine Learning, MLFlow, and Azure OpenAI, multiple document chunking strategies, query generation, multiple search types, sub-querying, re-ranking, metrics and evaluation, report generation, and multi-lingual support. The tool is designed to make it easier and faster to run experiments and evaluations of search queries and quality of response from OpenAI, and is useful for researchers, data scientists, and developers who want to test the performance of different search and OpenAI related hyperparameters, compare the effectiveness of various search strategies, fine-tune and optimize parameters, find the best combination of hyperparameters, and generate detailed reports and visualizations from experiment results.
quick-start-connectors
Cohere's Build-Your-Own-Connector framework allows integration of Cohere's Command LLM via the Chat API endpoint to any datastore/software holding text information with a search endpoint. Enables user queries grounded in proprietary information. Use-cases include question/answering, knowledge working, comms summary, and research. Repository provides code for popular datastores and a template connector. Requires Python 3.11+ and Poetry. Connectors can be built and deployed using Docker. Environment variables set authorization values. Pre-commits for linting. Connectors tailored to integrate with Cohere's Chat API for creating chatbots. Connectors return documents as JSON objects for Cohere's API to generate answers with citations.
ai-rag-chat-evaluator
This repository contains scripts and tools for evaluating a chat app that uses the RAG architecture. It provides parameters to assess the quality and style of answers generated by the chat app, including system prompt, search parameters, and GPT model parameters. The tools facilitate running evaluations, with examples of evaluations on a sample chat app. The repo also offers guidance on cost estimation, setting up the project, deploying a GPT-4 model, generating ground truth data, running evaluations, and measuring the app's ability to say 'I don't know'. Users can customize evaluations, view results, and compare runs using provided tools.
PromptAgent
PromptAgent is a repository for a novel automatic prompt optimization method that crafts expert-level prompts using language models. It provides a principled framework for prompt optimization by unifying prompt sampling and rewarding using MCTS algorithm. The tool supports different models like openai, palm, and huggingface models. Users can run PromptAgent to optimize prompts for specific tasks by strategically sampling model errors, generating error feedbacks, simulating future rewards, and searching for high-reward paths leading to expert prompts.
chronon
Chronon is a platform that simplifies and improves ML workflows by providing a central place to define features, ensuring point-in-time correctness for backfills, simplifying orchestration for batch and streaming pipelines, offering easy endpoints for feature fetching, and guaranteeing and measuring consistency. It offers benefits over other approaches by enabling the use of a broad set of data for training, handling large aggregations and other computationally intensive transformations, and abstracting away the infrastructure complexity of data plumbing.

airbroke
Airbroke is an open-source error catcher tool designed for modern web applications. It provides a PostgreSQL-based backend with an Airbrake-compatible HTTP collector endpoint and a React-based frontend for error management. The tool focuses on simplicity, maintaining a small database footprint even under heavy data ingestion. Users can ask AI about issues, replay HTTP exceptions, and save/manage bookmarks for important occurrences. Airbroke supports multiple OAuth providers for secure user authentication and offers occurrence charts for better insights into error occurrences. The tool can be deployed in various ways, including building from source, using Docker images, deploying on Vercel, Render.com, Kubernetes with Helm, or Docker Compose. It requires Node.js, PostgreSQL, and specific system resources for deployment.
HuggingFists
HuggingFists is a low-code data flow tool that enables convenient use of LLM and HuggingFace models. It provides functionalities similar to Langchain, allowing users to design, debug, and manage data processing workflows, create and schedule workflow jobs, manage resources environment, and handle various data artifact resources. The tool also offers account management for users, allowing centralized management of data source accounts and API accounts. Users can access Hugging Face models through the Inference API or locally deployed models, as well as datasets on Hugging Face. HuggingFists supports breakpoint debugging, branch selection, function calls, workflow variables, and more to assist users in developing complex data processing workflows.
roam-extension-live-ai-assistant
Live AI is an AI Assistant tailor-made for Roam, providing access to the latest LLMs directly in Roam blocks. Users can interact with AI to extend their thinking, explore their graph, and chat with structured responses. The tool leverages Roam's features to write prompts, query graph parts, and chat with content. Users can dictate, translate, transform, and enrich content easily. Live AI supports various tasks like audio and video analysis, PDF reading, image generation, and web search. The tool offers features like Chat panel, Live AI context menu, and Ask Your Graph agent for versatile usage. Users can control privacy levels, compare AI models, create custom prompts, and apply styles for response formatting. Security concerns are addressed by allowing users to control data sent to LLMs.
ezkl
EZKL is a library and command-line tool for doing inference for deep learning models and other computational graphs in a zk-snark (ZKML). It enables the following workflow: 1. Define a computational graph, for instance a neural network (but really any arbitrary set of operations), as you would normally in pytorch or tensorflow. 2. Export the final graph of operations as an .onnx file and some sample inputs to a .json file. 3. Point ezkl to the .onnx and .json files to generate a ZK-SNARK circuit with which you can prove statements such as: > "I ran this publicly available neural network on some private data and it produced this output" > "I ran my private neural network on some public data and it produced this output" > "I correctly ran this publicly available neural network on some public data and it produced this output" In the backend we use the collaboratively-developed Halo2 as a proof system. The generated proofs can then be verified with much less computational resources, including on-chain (with the Ethereum Virtual Machine), in a browser, or on a device.
pgai
pgai simplifies the process of building search and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) AI applications with PostgreSQL. It brings embedding and generation AI models closer to the database, allowing users to create embeddings, retrieve LLM chat completions, reason over data for classification, summarization, and data enrichment directly from within PostgreSQL in a SQL query. The tool requires an OpenAI API key and a PostgreSQL client to enable AI functionality in the database. Users can install pgai from source, run it in a pre-built Docker container, or enable it in a Timescale Cloud service. The tool provides functions to handle API keys using psql or Python, and offers various AI functionalities like tokenizing, detokenizing, embedding, chat completion, and content moderation.
reverse-engineering-assistant
ReVA (Reverse Engineering Assistant) is a project aimed at building a disassembler agnostic AI assistant for reverse engineering tasks. It utilizes a tool-driven approach, providing small tools to the user to empower them in completing complex tasks. The assistant is designed to accept various inputs, guide the user in correcting mistakes, and provide additional context to encourage exploration. Users can ask questions, perform tasks like decompilation, class diagram generation, variable renaming, and more. ReVA supports different language models for online and local inference, with easy configuration options. The workflow involves opening the RE tool and program, then starting a chat session to interact with the assistant. Installation includes setting up the Python component, running the chat tool, and configuring the Ghidra extension for seamless integration. ReVA aims to enhance the reverse engineering process by breaking down actions into small parts, including the user's thoughts in the output, and providing support for monitoring and adjusting prompts.
aisuite
Aisuite is a simple, unified interface to multiple Generative AI providers. It allows developers to easily interact with various Language Model (LLM) providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure, Google, AWS, and more through a standardized interface. The library focuses on chat completions and provides a thin wrapper around python client libraries, enabling creators to test responses from different LLM providers without changing their code. Aisuite maximizes stability by using HTTP endpoints or SDKs for making calls to the providers. Users can install the base package or specific provider packages, set up API keys, and utilize the library to generate chat completion responses from different models.

project_alice
Alice is an agentic workflow framework that integrates task execution and intelligent chat capabilities. It provides a flexible environment for creating, managing, and deploying AI agents for various purposes, leveraging a microservices architecture with MongoDB for data persistence. The framework consists of components like APIs, agents, tasks, and chats that interact to produce outputs through files, messages, task results, and URL references. Users can create, test, and deploy agentic solutions in a human-language framework, making it easy to engage with by both users and agents. The tool offers an open-source option, user management, flexible model deployment, and programmatic access to tasks and chats.
For similar tasks

LLMonFHIR
LLMonFHIR is an iOS application that utilizes large language models (LLMs) to interpret and provide context around patient data in the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) format. It connects to the OpenAI GPT API to analyze FHIR resources, supports multiple languages, and allows users to interact with their health data stored in the Apple Health app. The app aims to simplify complex health records, provide insights, and facilitate deeper understanding through a conversational interface. However, it is an experimental app for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. Users are advised to verify information provided by AI models and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
For similar jobs
ludwig
Ludwig is a declarative deep learning framework designed for scale and efficiency. It is a low-code framework that allows users to build custom AI models like LLMs and other deep neural networks with ease. Ludwig offers features such as optimized scale and efficiency, expert level control, modularity, and extensibility. It is engineered for production with prebuilt Docker containers, support for running with Ray on Kubernetes, and the ability to export models to Torchscript and Triton. Ludwig is hosted by the Linux Foundation AI & Data.
wenda
Wenda is a platform for large-scale language model invocation designed to efficiently generate content for specific environments, considering the limitations of personal and small business computing resources, as well as knowledge security and privacy issues. The platform integrates capabilities such as knowledge base integration, multiple large language models for offline deployment, auto scripts for additional functionality, and other practical capabilities like conversation history management and multi-user simultaneous usage.

LLMonFHIR
LLMonFHIR is an iOS application that utilizes large language models (LLMs) to interpret and provide context around patient data in the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) format. It connects to the OpenAI GPT API to analyze FHIR resources, supports multiple languages, and allows users to interact with their health data stored in the Apple Health app. The app aims to simplify complex health records, provide insights, and facilitate deeper understanding through a conversational interface. However, it is an experimental app for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. Users are advised to verify information provided by AI models and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.

Chinese-Mixtral-8x7B
Chinese-Mixtral-8x7B is an open-source project based on Mistral's Mixtral-8x7B model for incremental pre-training of Chinese vocabulary, aiming to advance research on MoE models in the Chinese natural language processing community. The expanded vocabulary significantly improves the model's encoding and decoding efficiency for Chinese, and the model is pre-trained incrementally on a large-scale open-source corpus, enabling it with powerful Chinese generation and comprehension capabilities. The project includes a large model with expanded Chinese vocabulary and incremental pre-training code.
AI-Horde-Worker
AI-Horde-Worker is a repository containing the original reference implementation for a worker that turns your graphics card(s) into a worker for the AI Horde. It allows users to generate or alchemize images for others. The repository provides instructions for setting up the worker on Windows and Linux, updating the worker code, running with multiple GPUs, and stopping the worker. Users can configure the worker using a WebUI to connect to the horde with their username and API key. The repository also includes information on model usage and running the Docker container with specified environment variables.
openshield
OpenShield is a firewall designed for AI models to protect against various attacks such as prompt injection, insecure output handling, training data poisoning, model denial of service, supply chain vulnerabilities, sensitive information disclosure, insecure plugin design, excessive agency granting, overreliance, and model theft. It provides rate limiting, content filtering, and keyword filtering for AI models. The tool acts as a transparent proxy between AI models and clients, allowing users to set custom rate limits for OpenAI endpoints and perform tokenizer calculations for OpenAI models. OpenShield also supports Python and LLM based rules, with upcoming features including rate limiting per user and model, prompts manager, content filtering, keyword filtering based on LLM/Vector models, OpenMeter integration, and VectorDB integration. The tool requires an OpenAI API key, Postgres, and Redis for operation.
VoAPI
VoAPI is a new high-value/high-performance AI model interface management and distribution system. It is a closed-source tool for personal learning use only, not for commercial purposes. Users must comply with upstream AI model service providers and legal regulations. The system offers a visually appealing interface, independent development documentation page support, service monitoring page configuration support, and third-party login support. It also optimizes interface elements, user registration time support, data operation button positioning, and more.
VoAPI
VoAPI is a new high-value/high-performance AI model interface management and distribution system. It is a closed-source tool for personal learning use only, not for commercial purposes. Users must comply with upstream AI model service providers and legal regulations. The system offers a visually appealing interface with features such as independent development documentation page support, service monitoring page configuration support, and third-party login support. Users can manage user registration time, optimize interface elements, and support features like online recharge, model pricing display, and sensitive word filtering. VoAPI also provides support for various AI models and platforms, with the ability to configure homepage templates, model information, and manufacturer information.